A Behavioral Study of the Impact of Emotion Valence on Movement Speed
-
摘要:目的 探讨情绪效价对动作速度的影响特征以及情绪效价对动作速度影响的延时特征。方法 将情绪诱发与提示目标任务范式相结合,选取53名普通大学生作为被试,要求其观看情绪图片,之后在目标刺激的提示下快速完成6次按键动作任务。结果 ① 伪随机呈现情绪图片时,诱发的负性情绪和正性情绪较中性情绪均有加快动作速度的趋势,但未达到显著性差异水平(P=0.237);②分组呈现图片时,诱发的负性情绪下的动作速度显著慢于中性情绪(P=0.041)。结论 ① 相较于正性情绪,负性情绪对动作速度的影响更大。②负性情绪对动作速度的影响随着负性情绪强度的变化出现了分离;负性情绪强度小时,呈现加快动作速度的趋势;负性情绪强度大时,则会显著减慢动作速度。③负性情绪越强,对动作速度影响的持续时间越长。Abstract:Objective To investigate how emotion valence affects the movement speed.Method Emotion-induction and prompt-target task paradigms were combined in the study.Subjects were asked to view emotional pictures first, then continuously performed a movement task six times at the prompt of the target stimulus.Result 1) In Experiment 1, negative and positive conditions tend to increase the movement speed compared to neutral conditions, but did not reach the significant differences level; 2) In Experiment 2, the movement speed under negative conditions was significantly slower than that of neutral conditions.Conclusion 1) Compared with positive emotions, negative emotions have a greater impact on the movement speed; 2) Negative emotions will significantly slow down the movement speed, and the more negative emotions, the longer the duration of the impact on the movement speed.
-
Keywords:
- emotion valance /
- movement speed /
- behavior study /
- positive emotion /
- negative emotion
-
在竞技运动中,动作速度可能是影响运动员获胜的重要原因;而制约动作速度的因素很多,其中情绪是最常见的因素之一。已有研究表明,情绪在外界刺激的作用下,会直接影响动作表现,尤其是动作速度[1]。因此,如何在情绪的影响下调节和控制动作速度,对于运动员获胜尤为重要。竞技比赛是一个动态的发展过程,往往伴随着多种情绪的变化。在积极的情绪状态下,运动员一定会发挥得更好吗?在消极的情绪状态下,运动员一定会发挥失常吗?对这一问题,目前仍然无统一的结论。值得肯定的是,不同的情绪效价对动作速度的影响是不同的。因此,探讨情绪效价对动作速度的影响特征,有助于指导运动员在赛场上因时制宜地调节自身情绪状态,进而有效调控自身的动作速度。
情绪与动作行为之间的关系可通过情绪动机模型解释。情绪动机模型显示,情绪的产生来源于不同的动机驱动系统。遇到危险的情景时,防御动机系统就会被激活,产生负性情绪,做出逃跑或攻击等行为应对这一情景;正性情绪则由趋近动机驱动,这种情绪往往产生于生存的环境[2]。刺激的情绪信息可指导人们快速地做出相应的趋近或回避反应,进而对人们的动作速度产生影响。在此类研究中,情绪刺激与动作执行任务的靶刺激通常为同一个情绪刺激物,以该刺激物的情绪属性指导行为,当行为与“趋利避害”一致时,会加快动作速度,不一致时则会减慢动作速度[3]。例如,Önal-Hartmann等[4]在实验中将正性或负性情绪图片作为靶刺激,分别让被试根据图片的效价推或拉杠杆,发现负性情绪刺激导致较快的“推”动作任务,而正性情绪刺激导致较快的“拉”动作任务。Rotteveel等[5]发现,正性情绪促进趋近动作,负性情绪促进回避动作的现象不是自动化的加工,而是需要意识的参与。也有研究[6]表明,相较于中性刺激,人们对危险刺激和恐怖刺激的辨别更快。Beatty等[7]则认为,无论是正性刺激还是负性刺激均会加快动作速度。
然而,在竞技比赛中,时常有高水平运动员因为情绪波动而发挥失常。由此展开的研究[8-10]认为,在正性情绪状态下,个体的注意力和认知范围更大,思维方式更加灵活,这有利于运动员对动作速度的调控,负性情绪状态则相反,会对动作速度的调控产生干扰作用。例如,Pereira等[11]发现,正性情绪会加快动作速度,而负性情绪会减慢动作速度。之后,Contreras等[12]通过线索go-nogo任务发现,情绪对动作速度的促进和干扰效应依赖于情绪刺激和目标刺激的时间间隔,而时间间隔又与被试对情绪刺激的注意时间有关,他们认为,随着人们对情绪图片的注意转移,这种干扰效应会降低。Coombes等[13]通过让被试观看不同效价的情绪图片诱发情绪后,再让被试完成画方框的任务,结果发现情绪效价只对动作的准确性有显著性影响,对动作速度则无显著性影响。
综上所述,大部分研究表明情绪效价确实会对动作速度产生影响,正性情绪更有利于对动作速度的调控,负性情绪对动作速度的影响结论不一。此外,以往大部分研究集中于情绪效价对动作速度的即时影响上,很少有研究关注情绪效价对动作速度影响的延时特征。情绪作为一种持续的状态,所产生的影响可能是持续性的,因此,探究情绪对动作速度影响的延时特征具有重要的现实意义。本文将通过2个具体的实验探讨情绪效价对动作速度的影响特征,以及情绪效价对动作速度影响的延时特征。
前人研究[11, 14]发现,观看情绪图片可以诱发一种短暂的情绪状态,即情绪状态可以通过观看情绪性图片进行调节。因此,笔者假设伪随机呈现不同效价情绪图片时,诱发的情绪强度小,情绪效价对动作速度的影响不明显;而整组呈现负性情绪图片诱发的情绪强度大,此时,负性情绪会对动作任务的完成产生显著的干扰效应,且持续时间长。
1. 实验一
初步探讨情绪效价对动作速度的影响及其延时特征,假设相较于中性情绪,正性和负性情绪均会对动作速度产生影响。
1.1 研究对象
29名上海体育学院普通大学生自愿参加本实验,14名男性,15名女性,年龄为(21.1±2.3)岁,视力或矫正视力正常,身体健康,右利手,所有参与实验的志愿者做完实验后获取适量报酬。
1.2 实验设计
采用3×6被试内实验设计,因素1为情绪效价,分为3个水平,即正性、中性、负性;因素2为时间因素,通过6次按键操纵,分为6个水平。
1.3 实验材料
选取190张情绪图片作为刺激材料,正式实验180张,正性、中性、负性图片各60张,剩余的10张图片用于练习。情绪图片的效价依次为正性7.37,中性5.03,负性2.48。所有图片均来自中国情绪图片库系统[15]和国际情绪图片库[16]。所有图片的分辨率为100像素,大小为15 cm×10 cm。
1.4 实验任务及程序
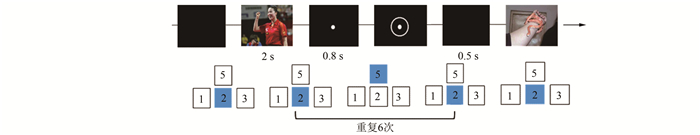
实验程序采用E-prime 2.0软件编制,具体实验流程如图 1所示。正式实验开始时,屏幕上会出现2 s的情绪图片,被试须仔细观察图片,同时,将食指按住数字键2不松手,接着出现提示刺激注视点0.8 s,之后出现目标刺激圆环,出现圆环的同时,被试须快速地完成动作任务,即松开2按5再返回2,屏幕呈现0.5 s黑屏。接着会再次出现5次注视点、圆环、黑屏,即每张图片后被试须连续完成6次动作任务。实验共分3组,每组60个试次,正中负各20次,以伪随机的方式呈现,以保证相同效价的图片最多连续呈现2次。
1.5 数据采集及分析
采用E-prime 2.0软件采集数据,主要采集指标为每次完成动作任务所需的时间(松开2按5再返回2的时间)。采用SPSS 17.0统计软件包对行为数据进行双因素重复测量方差分析。
1.6 结果
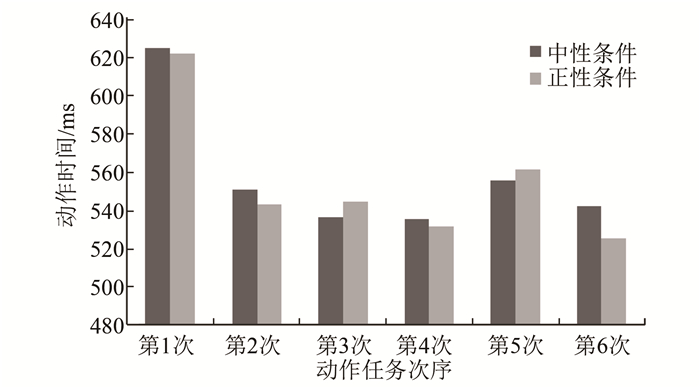
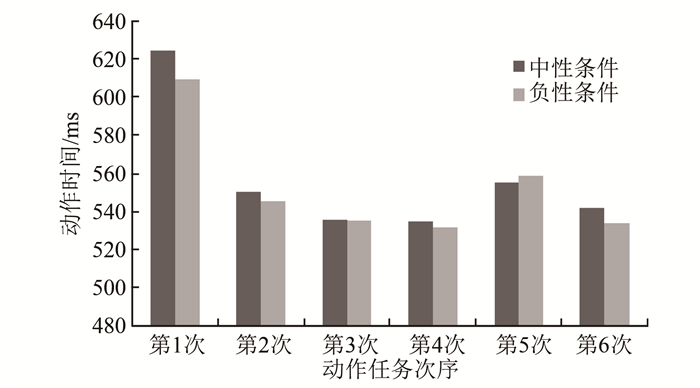
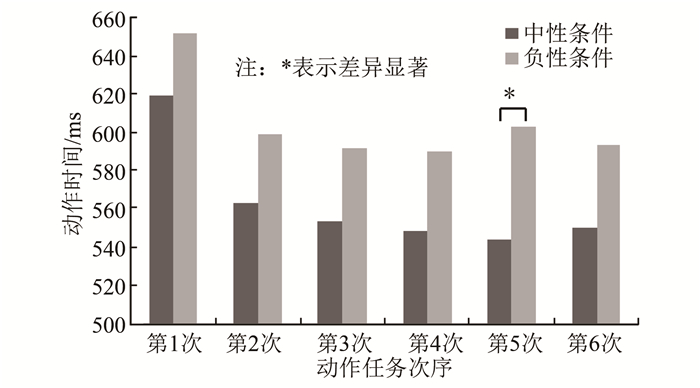
实验一以情绪效价和时间因素作为自变量,以每次完成动作任务的时间为因变量进行双因素重复测量方差分析。结果显示,情绪效价主效应不显著,F(2,28)=1.52,显著性水平P=0.237,但相较于中性条件,正性条件和负性条件下的动作时间均有缩短的趋势,正性条件下的第1、第2、第4、第6次动作时间均少于中性条件(图 2),负性条件下的第1、第2、第3、第4、第6次动作时间均少于中性条件(图 3)。可见:负性条件下的趋势更明显, 持续时间更长;时间主效应显著,F(5,28)=20.48,P<0.05;双因素交互作用不显著,F(10,28)=1.47,P=0.225。
根据以上结果分析可知,伪随机呈现情绪图片时,情绪效价对动作速度的影响并未达到显著性差异水平,不过正性情绪条件和负性情绪条件有加快动作速度的趋势,且负性情绪条件对动作速度影响的趋势更大,持续时间更长。因此,实验二主要研究负性情绪对动作速度的影响。
2. 实验二
由于情绪状态可以通过观看情绪图片来调节[14],实验一中的情绪图片是伪随机呈现的,因此不同效价的图片可能会产生相互干扰,导致诱发的情绪强度较弱。在实验二中,采用分组呈现情绪图片的方法,并将同组图片分为早、中、晚3个时期,通过比较不同时期中性条件和负性条件下每次完成动作任务的时间,探讨负性情绪对动作速度的影响及其延时特征。假设整组图片中晚期诱发的情绪强度最强,会对动作速度产生显著的干扰效应,且持续时间长。
2.1 研究对象
24名上海体育学院普通大学生自愿参加本实验,10名男性,14名女性,年龄为(21.5±2.31)岁。视力或矫正视力正常,身体健康,右利手,所有参与实验的志愿者做完实验后获取适量报酬。
2.2 实验设计
采用2×6被试内实验设计,因素1为情绪效价,分为2个水平,即中性、负性;因素2为时间因素,通过6次按键来操纵,分为6个水平。
2.3 实验材料
选取310张情绪图片作为刺激材料,正式实验图片共300张,中性图片150张,早、中、晚3个时期各50张,负性图片150张,早、中、晚3个时期各50张,剩余10张图片用于练习。情绪图片的效价依次为中性5.05,负性2.63。所有图片均来自中国情绪图片库系统[15]和国际情绪图片库[16]。所有图片的分辨率为100像素,大小为15 cm×10 cm。
2.4 实验任务及程序
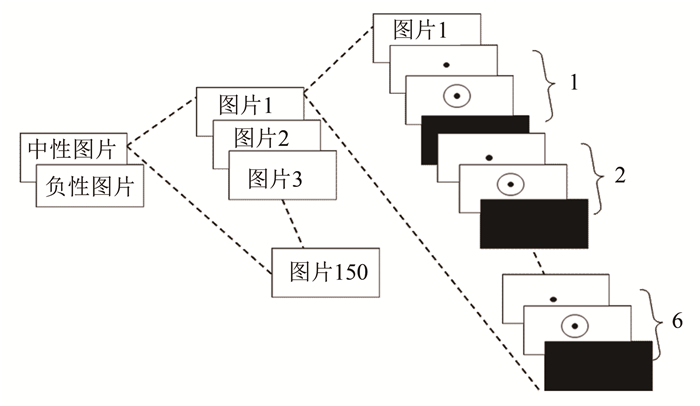
实验二的程序和实验一相似,不同之处在于实验二的情绪图片分组呈现,负性情绪组和中性情绪组各150个试次,每张情绪图片呈现后重复6次动作任务(同实验一),如图 4所示。2组图片呈现产生的顺序效应通过被试间调节平衡。
2.5 数据采集及分析
通过E-prime 2.0软件分别采集中性条件和负性条件下早、中、晚3个时期的动作时间。将数据输入Excel初步整理后,采用SPSS 17.0统计软件包分别对早、中、晚3个时期的行为数据进行双因素重复测量方差分析。
2.6 结果
2.6.1 早期中性条件和负性条件下动作速度的差异
情绪效价主效应不显著,F(1,23)=2.22,P=0.15,但负性效价下的动作时间长于中性条件;时间主效应显著,F(5,23)=20.37,P<0.05;双因素交互作用不显著,F(5,23)=1.33,P=0.293(图 5)。用配对t检验对不同效价条件下每次动作的时间差异进行比较后得出,中性条件和负性条件下的6次动作时间均未达到显著性差异水平。
2.6.2 中期中性条件和负性条件下动作速度的差异
情绪效价主效应不显著,F(1,23)=3.2,P=0.087,但负性效价下的动作时间要长于中性条件;时间主效应显著,F(5,23)=15.239,P<0.05;双因素交互作用不显著,F(5,23)=1.86,P=0.148(图 6)。用配对t检验对不同效价条件下每次动作时间的差异进行比较后得出,中性条件和负性条件下的第5次动作时间有显著性差异, P=0.044。
2.6.3 晚期中性条件和负性条件下动作速度的差异
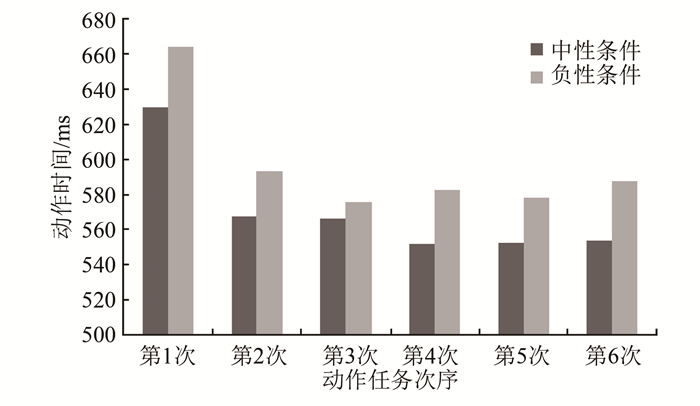
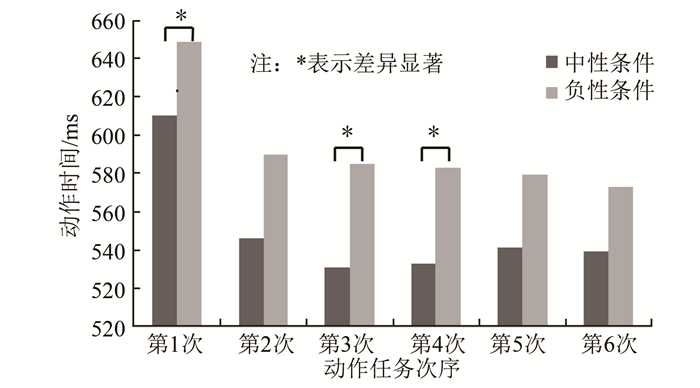
情绪效价主效应显著,F(1,23)=4.7,P=0.041,负性效价下的动作时间显著长于中性条件;时间主效应显著,F(5,23)=14.891,P<0.05;双因素交互作用不显著,F(5,23)=2.199,P=0.097(图 7)。用配对t检验对不同效价条件下每次动作时间的差异进行比较后得出,中性条件和负性条件下的第1次动作时间差异显著,P=0.033;第3次动作时间差异显著,P=0.019;第4次动作时间差异显著,P=0.030。
根据以上3个阶段的结果分析可以得出:早、中、晚3个时期,负性条件下的动作速度均慢于中性条件,且晚期达到了显著性差异水平。进一步分析得出,早期6次动作时间均无显著差异,中期仅第5次动作时间的差异显著,晚期第1、第3、第4次的动作时间均达到显著性差异水平。这表明观看负性情绪图片可诱发负性情绪,且观看的时间越长,诱发的负性情绪强度越大,对动作速度影响的持续时间越长。
3. 讨论
3.1 情绪效价对动作速度的影响特征
本文中的2个实验均表明情绪效价会对动作速度产生影响。实验一的数据结果显示,正性情绪和负性情绪均有加快动作速度的趋势,且负性情绪下的趋势更明显,但均未达到显著性水平。正性情绪扩展建设理论认为,正性情绪能扩展个体的认知和行动范围,处于积极情绪状态的个体,知觉、注意[17]、记忆范围[18]更广,思维[19]更加灵活,进而对个体的行为产生积极的影响[8]。这一观点与实验一正性情绪有加快动作速度的趋势相符。
相较于正性情绪,负性情绪加快动作速度的趋势更明显可能是由于负性情绪如愤怒、恐惧等对人类进化更具适应性意义,具体表现为个体更容易辨别恐惧或厌恶情绪刺激[20]。因此,个体对负性刺激存在负性偏向[21],负性刺激通常会带来更强烈的行为结果。例如,在危险的情景下,人们的回避系统会选择快速逃跑来应对[22]。这种负性偏向性具有显著的性别差异。Hillman等[23]报告称,当面对消极图片时,女性被试表现出的身体位置移动要显著强烈于男性被试。并且,负性刺激更能引起个体的注意,优先得到心理加工[24]。Anderson等[25]对注意瞬脱进行研究时发现:如果2个靶刺激接连出现,因注意被第一刺激吸引,随后的第二靶刺激将被忽视;但如果第二靶刺激的内容是负性刺激,这种忽视情况将大大改善。
另外,相关脑机制研究发现,情绪加工能够激活相关运动皮层[26]。Coombes等[27]发现,观看情绪性图片可导致运动皮层兴奋性改变。进一步研究后发现,负性情绪可以通过调节皮质内的GABAergic系统增强初级运动皮层的可塑性,而且负性情绪刺激下被试初级皮层内的抑制能力显著增强[28]。
3.2 情绪效价影响动作速度的延时特征
实验二数据结果显示,负性情绪会显著减慢动作速度,且负性情绪的强度越大,对动作速度影响的持续时间越长。这可能是由于处于负性情绪时,个体的注意力和认知范围变窄,思维往往固着于引起负性情绪的事件上[8-10],进而对个体行为产生干扰。通过研究情绪对篮球运动的影响发现,愤怒和两难的情绪会降低成功率[29]。
Pereira等[11]认为,观看随机顺序情绪图片会对之后的目标检测任务产生短暂的干扰效应,而观看整组负性情绪图片会产生持续的干扰效应。他们认为,短暂的干扰效应可能源于注意的调节。有研究表明,注意的持续时间为0.5 s或0.6~0.8 s[30],而在他们的实验中,情绪图片和目标检测任务的间隔时间为0.5~0.7 ms,负性情绪图片可能占用了注意资源,减少了用于目标检测任务的可用资源,进而导致对目标检测任务的短暂干扰效应。Contreras等[12]发现,时间间隔大于0.6 s就会促进行为反应。本文中情绪图片和动作任务的时间间隔为0.8 s,据已有研究推测被试动作任务不受注意持续性的影响,这也可能是本研究实验一的结果(负性情绪有加快动作速度的趋势)与他们的研究结果(负性情绪下反应时间较长)不符的原因。Pereira等[11]认为,持续的干扰效应不是源于注意,而是与情绪状态以及趋近和回避动机系统有关。当行为和“趋利避害”不一致时,就会对行为产生干扰作用。本文中的动作任务(松开2,按5)与趋近行为一致,因此当呈现负性刺激时,就可能对动作速度产生干扰。也有研究者认为,情绪刺激可能会预激活与反应无关的运动系统,进而导致运动速度减慢[31]。
实验二中观看整组负性和中性图片时,只有晚期情绪效价主效应显著; 对中性条件和负性条件下的6次动作时间分别做配对t检验,发现早期均无差异,中期有1次差异显著,而晚期则有3次均达到显著性差异水平。这表明晚期情绪效价对动作速度的影响更明显,持续时间更长。Pereira等[11]发现,诱发稳定的负性情绪可以对反应时间产生持续的干扰效应。Ruffalo等[14]认为,观看情绪图片可以调节情绪状态,结合笔者的实验结果可以推测,晚期负性情绪图片可以诱发较强的负性情绪,从而对动作速度的影响更明显,持续时间更长。另有研究表明,观看负性情绪图片会产生冻结效应[32],观看恐惧的肢体动作会显著抑制初级运动皮层的活性[33],这些均证明负性情绪会对动作速度产生干扰,但究竟情绪通过怎样的途径影响动作速度还有待进一步探究。
4. 结论
(1) 情绪效价会对动作速度产生影响,且相较于正性情绪,负性情绪对动作速度的影响更大。
(2) 负性情绪对动作速度的影响随着负性情绪强度的大小出现分离:负性情绪强度小时,呈现加快动作速度的趋势;负性情绪强度大时,则会显著减慢动作速度。
(3) 负性情绪强度越大,对动作速度影响的持续时间越长。
-
[1] GROSS M M, CRANE E A, FREDRICKSON B L.Effort-shape and kinematic assessment of bodily expression of emotion during gait[J].Human Movement Science, 2012, 31(1):202-221 doi: 10.1016/j.humov.2011.05.001
[2] BRADLEY M M, CODISPOTI M, CUTHBERT B N, et al.Emotion and motivation Ⅰ:Defensive and appetitive reactions in picture processing[J].Emotion, 2001, 1(3):276 doi: 10.1037/1528-3542.1.3.276
[3] 张晓雯, 禤宇明, 傅小兰.情绪效价对趋避反应的作用[J].心理科学进展, 2012, 20(7):1023-1030 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XLXD201207010.htm [4] ÖNAL-HARTMANN C, PAULI P, OCKLENBURG S, et al.The motor side of emotions:Investigating the relationship between hemispheres, motor reactions and emotional stimuli[J].Psychological Research, 2012, 76(3):311-316 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21556809 [5] ROTTEVEEL M, PHAF R H.Automatic affective evaluation does not automatically predispose for arm flexion and extension[J].Emotion, 2004, 4(2):156 doi: 10.1037/1528-3542.4.2.156
[6] ISHAI A, PESSOA L, BIKLE P C, et al.Repetition suppression of faces is modulated by emotion[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2004, 101(26):9827-9832 doi: 10.1073/pnas.0403559101
[7] BEATTY G F, FAWVER B, HANCOCK G M, et al.Regulating emotions uniquely modifies reaction time, rate of force production, and accuracy of a goal-directed motor action[J].Human Movement Science, 2014, 33:1-13 doi: 10.1016/j.humov.2013.12.001
[8] FREDRICKSON B L.The role of positive emotions in positive psychology:The-broaden-and-build theory of positive emotions[J].Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, 2001, 56(3):218-226 https://eric.ed.gov/?id=EJ627465
[9] MELCHER T, OBST K, MANN A, et al.Antagonistic modulatory influences of negative affect on cognitive control:Reduced and enhanced interference resolution capability after the induction of fear and sadness[J].Acta Psychologica, 2012, 139(3):507-514 doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2012.01.012
[10] STIGCHEL S V D, IMANTS P, RIDDERINKHOF K R.Positive affect increases cognitive control in theantisaccade task[J].Brain and Cognition, 2011, 75(2):177-181 doi: 10.1016/j.bandc.2010.11.007
[11] PEREIRA M G, VOLCHAN E, DE SOUZA G G L, et al.Sustained and transient modulation of performance induced by emotional picture viewing[J].Emotion, 2006, 6(4):622 doi: 10.1037/1528-3542.6.4.622
[12] CONTRERAS D, MEGIAS A, MALDONADO A, et al.Facilitation and interference of behavioral responses by task-irrelevant affect-laden stimuli[J].Motivation and Emotion, 2013, 37(3):496-507 doi: 10.1007/s11031-012-9327-0
[13] COOMBES S A, JANELLE C M, DULEY A R.Emotion and motor control:Movement attributes following affective picture processing[J].Journal of Motor Behavior, 2005, 37(6):425-436 doi: 10.3200/JMBR.37.6.425-436
[14] LARSON C L, RUFFALO D, NIETERT J Y, et al.Stability of emotion-modulated startle during short and long picture presentation[J].Psychophysiology, 2005, 42(5):604-610 doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.2005.00345.x/references
[15] 白露, 马慧, 黄宇霞, 等.中国情绪图片系统的编制:在46名中国大学生中的试用[J].中国心理卫生杂志, 2005, 19(11):719-722 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6729.2005.11.001 [16] LANG P J, BRADLEY M M, CUTHBERT B N. International affective picture system (IAPS): Technical manualand affective ratings[D]. Gainesville, FL: NIMH Center for the Study of Emotion and Attention, University of Florida, 1997: 1-9
[17] JOHNSON K J, WAUGH C E, FREDRICKSON B L.Smile to see the forest:Facially expressed positive emotions broaden cognition[J].Cognition and Emotion, 2010, 24(2):299-321 doi: 10.1080/02699930903384667
[18] TALARICO J M, BERNTSEN D, RUBIN D C.Positive emotions enhance recall of peripheral details[J].Cognition and Emotion, 2009, 23(2):380-398 doi: 10.1080/02699930801993999
[19] ROWE G, HIRSH J B, ANDERSON A K.Positive affect increases the breadth of attentional selection[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2007, 104(1):383-388 doi: 10.1073/pnas.0605198104
[20] ÖHMAN A, FLYKT A, ESTEVES F.Emotion drives attention:Detecting the snake in the grass[J].Journal of Experimental Psychology:General, 2001, 130(3):466 http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/11561921 [21] YUAN J, ZHANG Q, CHEN A, et al.Are we sensitive to valence differences in emotionally negative stimuli?Electrophysiological evidence from an ERP study[J].Neuropsychologia, 2007, 45(12):2764-2771 doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2007.04.018
[22] BASTOS A F, VIEIRA A S, OLIVEIRA J M, et al.Stop or move:Defensive strategies in humans[J].Behavioural Brain Research, 2016, 302:252-262 doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2016.01.043
[23] HILLMAN C H, ROSENGREN K S, SMITH D P.Emotion and motivated behavior:Postural adjustments to affective picture viewing[J].Biological Psychology, 2004, 66(1):51-62 doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2003.07.005
[24] 袁加锦. 情绪效价强度效应及神经机制研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2009: 1-95 [25] ANDERSON A K, PHELPS E A.Lesions of the human amygdala impair enhanced perception of emotionally salient events[J].Nature, 2001, 411:305-309 doi: 10.1038/35077083
[26] HAJCAK G, MOLNAR C, GEORGE M S, et al.Emotion facilitates action:A transcranial magnetic stimulation study of motor cortex excitability during picture viewing[J].Psychophysiology, 2007, 44(1):91-97 doi: 10.1111/psyp.2007.44.issue-1
[27] COOMBES S A, TANDONNET C, FUJIYAMA H, et al.Emotion and motor preparation:A transcranial magnetic stimulation study of corticospinal motor tract excitability[J].Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience, 2009, 9(4):380-388 http://cat.inist.fr/?aModele=afficheN&cpsidt=22157715
[28] KOGANEMARU S, DOMEN K, FUKUYAMA H, et al.Negative emotion can enhance human motor cortical plasticity[J].European Journal of Neuroscience, 2012, 35(10):1637-1645 doi: 10.1111/ejn.2012.35.issue-10
[29] UPHILL M, GROOM R, JONES M.The influence of in-game emotions on basketball performance[J].European Journal of Sport Science, 2014, 14(1):76-83 doi: 10.1080/17461391.2012.729088
[30] MULLER M M, TEDER-SALEJARVI W, HILLYARD S A.The time course of cortical facilitation during cued shifts of spatial attention[J].Nature Neuroscience, 1998, 1(7):631-634 doi: 10.1038/2865
[31] PEREIRA M G, VOLCHAN E, OLIVEIRA L, et al.Behavioral modulation by mutilation pictures in women[J].Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research, 2004, 37(3):353-362 doi: 10.1590/S0100-879X2004000300011
[32] AZEVEDO T M, VOLCHAN E, IMBIRIBA L A, et al.A freezing-like posture to pictures of mutilation[J].Psychophysiology, 2005, 42(3):255-260 doi: 10.1111/psyp.2005.42.issue-3
[33] BORGOMANERI S, VITALE F, GAZZOLA V, et al.Seeing fearful body language rapidly freezes the observer's motor cortex[J].Cortex, 2015, 65:232-245 doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2015.01.014
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 姚家宜,谢秋莹,王笃明. 宣传方式对受众环保意识的影响. 浙江理工大学学报(社会科学版). 2020(02): 179-186 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 李华伟,吴超. 一种考虑单步统计特征的运动员动作速度识别分析. 电子测量技术. 2019(17): 32-35 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 程韵枫,董宝林. 锻炼氛围、主观体验对大学生余暇体育锻炼的影响. 天津体育学院学报. 2018(02): 177-184 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(8)




 下载:
下载: