The Mechanism of Macrophage Chemotaxis during the Repair Process Following Contusion of Skeletal Muscle
-
摘要:目的 探究巨噬细胞在挫伤骨骼肌修复过程中的趋化机制。方法 将66只ICR雄性小鼠随机分为对照组(C组,n=11)和骨骼肌挫伤组(S组,n=55)。骨骼肌挫伤后12 h、1 d、5 d、10 d和15 d分别取双侧腓肠肌。HE染色观察骨骼肌挫伤后修复过程中的形态学变化,荧光定量PCR检测骨骼肌挫伤后巨噬细胞和趋化因子的时空表达规律。结果 ① 骨骼肌挫伤后12 h,可见肌纤维坏死、肿胀和大量炎性细胞浸润。伤后第5天,可见少量再生肌纤维,伤后第10天再生肌纤维数量大大增加,伤后第15天虽有少量再生肌纤维,但肌纤维结构完整性较好,骨骼肌损伤修复基本完成。②与对照组相比,M1巨噬细胞标志物(CD68)在骨骼肌挫伤后显著增加,随后M2巨噬细胞标志物(CD206和CD163)显著增加。③骨骼肌挫伤后MCP-1及其受体CCR2 mRNA表达均显著增加(P < 0.01)。SDF-1 mRNA在挫伤后12 h、10 d和15 d表达均显著增加(P < 0.01),其受体CXCR4表达无显著变化。④骨骼肌挫伤后,MCP-1与CD68存在强相关,亦与其受体CCR2呈强相关,而SDF-1只与其受体CXCR4相关。结论 MCP-1/CCR2轴可能参与了挫伤骨骼肌修复过程中M1巨噬细胞的趋化。Abstract:Objective The objective of this study is to explore the mechanism of macrophage chemotaxis during the repair process following contusion of skeletal muscle.Methods 66 ICR male mice were randomly divided into control group(C group, n=11) and muscle contusion group(S group, n=55).Their gastrocnemius muscles were harvested at the time points of 12 h, 1 d, 5 d, 10 d and 15 d post-injury. The changes in skeletal muscle morphology were assessed by HE staining. The gene expression of macrophage and chemokines was analyzed by real-time PCR.Results ① On 12 h post-injury, cross sections of gastrocnemius muscles showed substantial fiber damage and inflammatory infiltrate.On day 5 post-injury, a small quantity of centronucleated myofibers were observed.On day 10 post-injury, central nucleation phenomenon became more pronounced.On day 15 post-injury, central nucleation almost disappeared.② The molecule marker of M1 macrophages(CD68) increased significantly post-injury, and the molecule marker of M2 macrophages(CD206 and CD163) increased significantly later.③ MCP-1 and CCR2 mRNA increased significantly post-injury(P < 0.01).SDF-1 mRNA increased significantly at 12 h, 10 d and 15 d (P < 0.01).However, CXCR4 mRNA did not change significantly post injury.④ The results showed that there was significant correlation between MCP-1 and CD68, and CCR2.In addition, there was significant correlation between SDF-1 and CXCR4.Conclusion MCP-1/CCR2 may be involved in the chemotaxis of M1 macrophages during skeletal muscle regeneration post-injury.
-
Keywords:
- skeletal muscle /
- injury and repair /
- macrophage /
- chemotaxis
-
骨骼肌是人体最重要的器官之一, 约占体质量的40%。骨骼肌收缩牵拉骨骼绕关节转动, 为人体运动提供动力。骨骼肌具有较强的损伤后再生能力, 而这种再生能力主要依赖于肌卫星细胞[1]。肌卫星细胞是一种肌原性前体细胞, 存在于肌细胞膜和基底膜之间。当骨骼肌损伤时, 肌卫星细胞被激活, 然后增殖分化, 与受损肌纤维融合, 修复损伤骨骼肌[2]。
近年来研究表明, 巨噬细胞在骨骼肌损伤修复过程中也具有重要作用, 它不仅参与损伤后肌卫星细胞的激活, 还促进坏死肌纤维及细胞碎片的清除, 调节炎症反应[3]。骨骼肌损伤后, 巨噬细胞在多种因素刺激下游离到损伤部位, 参与损伤组织修复[4]。研究发现, 趋化因子在骨骼肌损伤后巨噬细胞的趋化中发挥了重要作用[5-6]。在骨骼肌挫伤这一特定病理状态下, 巨噬细胞如何趋化到损伤部位却鲜有研究。因此, 本文建立了骨骼肌挫伤模型, 通过HE染色观察骨骼肌挫伤后修复过程中的形态学变化, 通过RT-PCR检测骨骼肌挫伤后巨噬细胞和趋化因子的时空表达规律, 并对巨噬细胞和趋化因子表达进行相关性分析, 以探索骨骼肌挫伤后巨噬细胞趋化的具体机制。这将加深对骨骼肌挫伤修复机制的理解与认识, 为研制治疗骨骼肌挫伤的药物提供新的思路, 具有潜在的临床应用价值。
1. 材料和方法
1.1 实验动物与分组
8~10周龄健康ICR雄性小鼠66只, 购自上海杰思捷实验动物有限公司。饲养环境温度为21~25℃, 湿度为40%~50%, 12 h光照, 12 h黑暗, 自由饮食。随机选取11只作为对照组(C组), 余下进行腓肠肌挫伤处理, 分为伤后12 h、1 d、5 d、10 d和15 d组, 每组11只。
1.2 骨骼肌挫伤模型
小鼠用400 mg/kg体质量水合氯醛腹腔注射麻醉后, 膝关节伸直0°, 踝关节背伸90°位, 将质量16.8 g, 直径15.9 mm的实心不锈钢钢珠置于一透明管道顶端(高100 cm, 内径16.0 mm)释放后垂直击中一打击装置, 打击装置底端撞击小鼠双侧腓肠肌肌腹中段(打击面积28.26 mm2)。骨骼肌挫伤后, 可见腓肠肌血肿, HE染色可见肌纤维肿胀、坏死、红细胞渗出和炎性细胞浸润。此法已多次被验证可成功建模[7-9]。
1.3 动物取材
小鼠腓肠肌挫伤后在不同时间点(12 h、1 d、5 d、10 d和15 d)取材。小鼠麻醉后颈椎脱位致死, 迅速取双侧受损腓肠肌。其中3只小鼠共6条腿腓肠肌进行HE染色, 剩余8只小鼠的左腿腓肠肌用于荧光定量PCR检测。
1.4 HE染色
小鼠腓肠肌取材, 经4%多聚甲醛(国药集团化学试剂有限公司产)固定后, 用石蜡(国药集团化学试剂有限公司产)包埋, 然后于切片机(Leica-EG 1 160, 德国产)切3~4 μm的薄片。切片经脱蜡处理后, 用苏木素-伊红染色, 然后中性树胶封片。20倍物镜下观察并拍照(Labphot-2, Nikon, 美国产)。
1.5 实时荧光定量PCR
1.5.1 RNA抽提
称重骨骼肌(约50 mg), 并将组织剪碎, 然后放入2 mL离心管中, 加入1 mL Trizol(Invitrogen公司产); 机械匀浆器(IKA, 德国产)匀浆5~6次, 每次10 s, 静置5 min后, 13 400 g离心(centrifuge5 417R, 德国Eppendorf公司产)10 min, 然后取上清(约800~900 μL)放入1.5 mL离心管中; 每使用1 mL Trizol加200 μL氯仿(国药集团化学试剂有限公司产), 剧烈震荡15 s, 然后静置3 min; 4 ℃条件下, 13 400 g离心10 min后, 样品分为3层, 中间层和上层是无色水相, RNA主要在水相中(约500 μL), 将RNA转移到1.5 mL离心管中; 在得到的水相中, 加入等体积异丙醇(国药集团化学试剂有限公司产), 混匀, 室温放置20~30 min; 4 ℃条件下13 400 g离心10 min后, 弃上清, 离心后RNA沉在管底, 呈微小羽毛状; 加入1 mL 75%的乙醇(国药集团化学试剂有限公司产)洗涤2次; 在4 ℃条件下2 300 g离心5 min, 弃上清; 干燥5 min后, 加入30~100 μL DEPC水(生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司产), 分析RNA的浓度或放-20 ℃短期保存, -80 ℃长期保存。
1.5.2 cDNA合成
cDNA合成按RevertAid第一链cDNA Synthesis试剂盒说明进行, 取2 μg总RNA、1μL随机六聚体引物、4μL 5X Reaction Buffer、1μL RiboLockTM RNA酶抑制剂(20 u/μL)、2μL 10 mmol/L dNTP Mix、1μL RevertAidTM M-MuLV逆转录酶(200 u/μL)和适量无RNA酶高纯水, 总体积共20μL。于梯度PCR仪(Mastercycler EP, 德国Eppendorf公司产)进行逆转录。反应过程中的温度和时间控制是25 ℃ 5 min、42 ℃ 60 min、70 ℃ 5 min, 然后温度降低到4 ℃, cDNA合成完成。
1.5.3 荧光定量PCR
荧光定量PCR反应体系包括12.5 μL 2×Maxima SYBR Green/ROX qPCR Master mix (Thermo Scientific)、1μL cDNA、无核酸酶水和300 nmol/L的上下游引物。引物由生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司合成(表 1)。使用荧光定量PCR仪进行扩增。反应条件为:预变性95 ℃ 10 min, 然后95 ℃变性15 s, 60 ℃ 1 min共40个循环。通过2-△△CT方法计算所测样本mRNA的相对含量[10-11]。
表 1 荧光定量PCR引物序列Table 1. Primer Sequences for PCR目标基因 上游引物序列 下游引物序列 CD68 5’-CAAAGCTTCTGCTGTGGAAAT-3’ 5’-GACTGGTCACGGTTGCAAG-3’ CD163 5’- GCAAAAACTGGCAGTGGG -3’ 5’- GTCAAAATCACAGACGGAGC -3’ CD206 5’- GGATTGTGGAGCAGATGGAAG -3’ 5’- CTTGAATGGAAATGCACAGAC -3’ MCP-1 5’-GCTCAGCCAGATGCAGTTAAC-3’ 5’- CTCTCTCTTGAGCTTGGTGAC-3’ CCR2 5’- GAAAAGCCAACTCCTTCATCAG -3’ 5’- TCTAAGCACACCACTTCCTCTG -3’ SDF-1 5’- ACGGAAGAACCAAAGAGAAAGA -3’ 5’-CTCAGACAGCGAGGCACAT -3’ CXCR4 5’- CAAGGCCCTCAAGACGACAG-3’ 5’- CCCCCAAAAGGATGAAGGAG-3’ GAPDH 5’-ACTCCACTCACGGCAAATTC-3’ 5’-TCTCCATGGTGGTGAAGACA-3’ 1.6 统计学分析
实验数据采用SPSS 20.0软件处理, 结果以均数±标准差表示。One-way ANOVA和Bonferroni事后检验, 以P < 0.05为差异具有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 挫伤骨骼肌修复过程中形态学变化
骨骼肌挫伤后, 在伤后12 h~1 d组, 取材时可见腓肠肌表面有明显血肿, 特别是伤后12 h组最明显, 5 d组开始有所改善, 14 d和21 d组已观察不到此现象。HE染色结果表明, 未损伤骨骼肌形态规则, 细胞核分布于肌膜下, 无坏死肌纤维。骨骼肌挫伤后12 h~1 d, 肌纤维肿胀、结构完整性被破坏, 出现大量炎性细胞浸润。伤后第5天仍有较多炎性细胞浸润, 但出现少量再生肌纤维(中央成核肌纤维)。伤后第10天再生肌纤维数量大大增加, 伤后第15天仍见少量再生肌纤维, 但肌纤维结构较完整, 损伤后修复基本完成(图 1)。
2.2 骨骼肌挫伤后巨噬细胞标志物表达变化
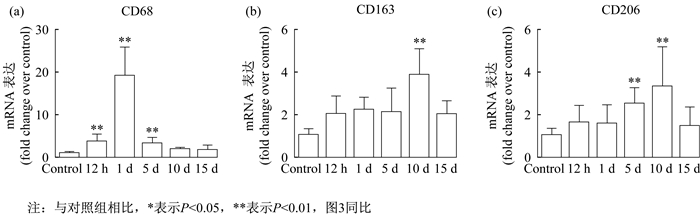
RT-PCR结果显示, 骨骼肌挫伤后CD68(M1巨噬细胞标志物)[8]mRNA表达升高, 且在挫伤后第1天达到峰值(P < 0.01), 第5天仍显著高于对照组(P < 0.01)。CD206为M2a巨噬细胞标志物[8], 与对照组相比, 在挫伤后5 d和10 d均显著增加, 且第10天达到峰值(P < 0.01)。CD163作为M2c巨噬细胞标志物[12], 与对照组相比, 在挫伤后第10天表达显著增加(P < 0.01)(图 2)。
2.3 骨骼肌挫伤后趋化因子表达变化
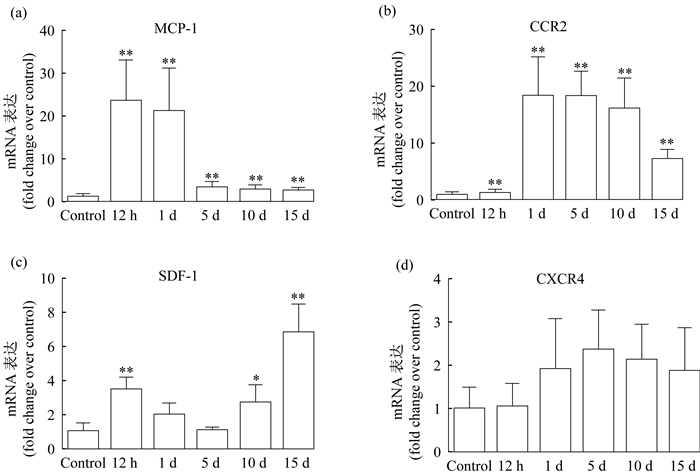
如图 3所示, 与损伤组相比, 单核细胞趋化蛋白1(MCP-1)在骨骼肌挫伤后12 h显著增加并达峰值(P < 0.01), 且在伤后1 d、5 d和15 d仍显著增加(P < 0.01)[图 3(a)]。CC趋化因子受体2(CCR2)在挫伤后1 d、5 d和15d mRNA表达均显著高于对照组(P < 0.01)[图 3(b)]。基质细胞衍生因子-1(SDF-1)mRNA在挫伤后12 h、10 d和15 d表达均显著增加[图 3(c)]。CXC趋化因子受体4(CXCR4)虽在骨骼肌挫伤后表达出现变化, 但与对照组相比并无显著差异(P>0.05)[图 3(d)]。
2.4 巨噬细胞与趋化因子的相关性分析
通过皮尔逊相关分析发现, 骨骼肌挫伤后, MCP-1与CD68存在强相关(r=0.654, P=0.001), 与其受体CCR2呈强相关(r=0.617, P=0.015), 与CD163和CD206无相关。SDF-1与其受体CXCR4呈相关(r=0.187, P=0.023), 与CD68、CD163和CD206均无相关(表 2)。
表 2 趋化因子与其受体及巨噬细胞标志物的相关性Table 2. Correlation between thechemokines and their receptors and markers of macrophages基因 MCP-1 SDF-1 r P r P CD68 0.654 0.001 * * CD163 * * * * CD206 * * * * CCR2 0.617 0.015 — — CXCR4 — — 0.187 0.023 注:*表示无相关; —表示未进行相关分析 3. 讨论
3.1 骨骼肌挫伤模型的构建
Ceafalan等[13]发现, 小鼠腓肠肌压碎性损伤后, 大量肌纤维坏死、炎性细胞浸润, 在伤后第5天首次发现中央成核肌纤维(再生肌纤维), 伤后第14天大部分再生肌纤维已成熟。本实验结果与Ceafalan等的结果相似, 骨骼肌挫伤后肌纤维坏死、肿胀、大量炎性细胞浸润, 伤后第7天有大量再生肌纤维, 伤后第14天大部分再生肌纤维已成熟。与之不同的是, 在本实验中, 骨骼肌挫伤后第3天即可见少量再生肌纤维。出现这种差异的原因可能是骨骼肌压碎伤较挫伤更为严重, 因此再生肌纤维出现得较晚。此外, Wright等[14]发现, 小鼠腓肠肌挫伤后第7天, 损伤部位出现大量再生肌纤维。Nozaki等[15]发现, 小鼠腓肠肌挫伤后第14天, 损伤骨骼肌仍有少量再生肌纤维, 大部分再生肌纤维已成熟。以上结果与本文相似, 提示骨骼肌挫伤模型建立成功[7, 16]。
3.2 骨骼肌挫伤后巨噬细胞浸润的规律
巨噬细胞在骨骼肌损伤修复过程中发挥重要作用[9, 12]。巨噬细胞通常可分为2种基本类型:M1和M2巨噬细胞。M2巨噬细胞又可进一步分为M2a、M2b和M2c 3种类型[3, 17]。M1巨噬细胞为促炎性巨噬细胞, 它可分泌多种促炎细胞因子(如IFN-γ、TNF-α和IL-6等), 清除坏死肌纤维及细胞碎片等, 促进机体炎症反应[18]。M2巨噬细胞为抗炎性巨噬细胞, 可分泌多种肌再生因子(如IGF、MGF和HGF等)及抗炎细胞因子(IL-10), 促进骨骼肌损伤修复[19]。巨噬细胞在损伤骨骼肌中的表达存在一定规律性, 如Tonkin等[20]发现, 小鼠胫骨前肌注射心脏毒素损伤后第2天M1巨噬细胞达峰值, 随后表达下降, 而M2巨噬细胞在伤后第5天达峰值。Shono等[21]发现, 小鼠腓肠肌挤压损伤后1~4 d M1型巨噬细胞表达显著增加, M2巨噬细胞在伤后7~10 d表达显著增加。与上述损伤模型相似, 本文发现, M1巨噬细胞在骨骼肌挫伤后1~5 d显著增加(P < 0.01), M2a巨噬细胞在挫伤后5~10 d显著增加, M2c巨噬细胞在挫伤后第10天显著增加。此外, 本实验结果与上述研究者略有差异的原因可能与骨骼肌损伤方式不同(心脏毒素致伤与骨骼肌挫伤; 挤压致伤与骨骼肌挫伤)及损伤肌肉类型(胫骨前肌与腓肠肌)不同有关。尽管不同研究之间略有差异, 但这些结果提示, 骨骼肌损伤后巨噬细胞浸润存在一定规律性, 在骨骼肌损伤早期M1巨噬细胞浸润占优势, 随后M1巨噬细胞转化为M2巨噬细胞, 在损伤后期M2巨噬细胞显著增多[22]。
3.3 骨骼肌挫伤后修复过程中巨噬细胞趋化的可能机制
MCP-1/CCR2轴参与了多种病理环境中巨噬细胞的迁移, 如肿瘤组织中MCP-1与CCR2结合可促进巨噬细胞趋化[23-24], 离体状态下MCP-1可促进经典激活型巨噬细胞(M1巨噬细胞)的迁移与激活[25]。骨骼肌挫伤后, MCP-1/CCR2轴是否参与了巨噬细胞的募集则不得而知。本文通过RT-PCR检测挫伤骨骼肌修复过程中巨噬细胞和趋化因子的表达, 采用相关性分析探讨骨骼肌损伤修复过程中巨噬细胞趋化的可能机制。结果显示, 骨骼肌挫伤后MCP-1表达显著上调, 且与CCR2呈强相关(r=0.617, P=0.015), 与M1巨噬细胞标志物CD68呈强相关(r=0.654, P=0.001), 提示骨骼肌挫伤后MCP-1/CCR2轴可能参与了巨噬细胞的募集。
这一推测可从其他骨骼肌损伤模型得到支持。如Shireman等[6]发现, 与野生型小鼠相比, MCP-1基因缺失小鼠, 在骨骼肌缺血性损伤后第3天巨噬细胞浸润减少, 在伤后第7天仍有巨噬细胞浸润和大量坏死组织, 损害了骨骼肌再生。与野生型小鼠相比, CCR2(MCP-1的受体)基因敲除小鼠, 在心脏毒素注射骨骼肌损伤后巨噬细胞募集减少、脂肪沉积增加、VEGF表达下降, 骨骼肌再生受损[5, 26-27]。虽然MCP-1与M1巨噬细胞显著相关, 但MCP-1与M2巨噬细胞标志物CD163和CD206均无相关, 提示MCP-1可能未参与M2巨噬细胞趋化, 因为骨骼肌损伤后, M2巨噬细胞一般较晚出现, 且一般认为其由M1巨噬细胞转化而来, 而非从外周血募集[17, 28]。以上结果提示, MCP-1/CCR2轴可能参与了挫伤骨骼肌修复过程中M1巨噬细胞的趋化。
此外, SDF-1/CXCR4轴也与巨噬细胞的迁移相关。SDF-1及其受体CXCR4属于CXC趋化因子家族, 在多种细胞中表达(如C2C12成肌细胞、肌卫星细胞、造血干细胞、白细胞等)[29-31]。SDF-1/CXCR4轴常被认为与肿瘤环境中巨噬细胞募集有关[32-33]。虽然在离体状态下SDF-1可促进巨噬细胞趋化[33], 但能否促进损伤骨骼肌中巨噬细胞的募集则少有研究。本实验中, 骨骼肌挫伤后SDF-1 mRNA表达显著上调, 且SDF-1与其受体CXCR4呈相关, 但SDF-1与巨噬细胞3种标志物间均无相关性。提示在骨骼肌挫伤这一特定病理环境中, SDF-1/CXCR4可能并未参与巨噬细胞趋化。
4. 结束语
本文基于前期大量文献报道, 仅对涉及巨噬细胞趋化的2条重要趋化途径进行了探索。从结果看, MCP-1/CCR2轴可能参与了挫伤骨骼肌修复过程中M1巨噬细胞的趋化, 但仍不能排除有其他促进巨噬细胞向损伤骨骼肌趋化的途径。
-
表 1 荧光定量PCR引物序列
Table 1 Primer Sequences for PCR
目标基因 上游引物序列 下游引物序列 CD68 5’-CAAAGCTTCTGCTGTGGAAAT-3’ 5’-GACTGGTCACGGTTGCAAG-3’ CD163 5’- GCAAAAACTGGCAGTGGG -3’ 5’- GTCAAAATCACAGACGGAGC -3’ CD206 5’- GGATTGTGGAGCAGATGGAAG -3’ 5’- CTTGAATGGAAATGCACAGAC -3’ MCP-1 5’-GCTCAGCCAGATGCAGTTAAC-3’ 5’- CTCTCTCTTGAGCTTGGTGAC-3’ CCR2 5’- GAAAAGCCAACTCCTTCATCAG -3’ 5’- TCTAAGCACACCACTTCCTCTG -3’ SDF-1 5’- ACGGAAGAACCAAAGAGAAAGA -3’ 5’-CTCAGACAGCGAGGCACAT -3’ CXCR4 5’- CAAGGCCCTCAAGACGACAG-3’ 5’- CCCCCAAAAGGATGAAGGAG-3’ GAPDH 5’-ACTCCACTCACGGCAAATTC-3’ 5’-TCTCCATGGTGGTGAAGACA-3’ 表 2 趋化因子与其受体及巨噬细胞标志物的相关性
Table 2 Correlation between thechemokines and their receptors and markers of macrophages
基因 MCP-1 SDF-1 r P r P CD68 0.654 0.001 * * CD163 * * * * CD206 * * * * CCR2 0.617 0.015 — — CXCR4 — — 0.187 0.023 注:*表示无相关; —表示未进行相关分析 -
[1] TIDBALL J G.Mechanisms of muscle injury, repair, and regeneration[J].Comprehensive Physiology, 2011, 1(4):2029-2062 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=71ba6ca0fcddadcfcd6ea7bd092d2872&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[2] RELAIX F, ZAMMIT P S.Satellite cells are essential for skeletal muscle regeneration:The cell on the edge returns centre stage[J].Development, 2012, 139(16):2845-2856 doi: 10.1242/dev.069088
[3] TIDBALL J G, VILLALTA S A.Regulatory interactions between muscle and the immune system during muscle regeneration[J].American Journal of Physiology Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology, 2010, 298(5):R1173-1187 doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00735.2009
[4] KHARRAZ Y, GUERRA J, MANN C J, et al.Macrophage plasticity and the role of inflammation in skeletal muscle repair[J].Mediators of Inflammation, 2013, 2013:491-497 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_pubmedcentral.nih.gov_3572642
[5] MARTINEZ C O, MCHALE M J, WELLS J T, et al.Regulation of skeletal muscle regeneration by CCR2-activating chemokines is directly related to macrophage recruitment[J].American Journal of Physiology Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology, 2010, 299(3):R832-842 doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00797.2009
[6] SHIREMAN P K, CONTRERAS S V, OCHOA O, et al.MCP-1 deficiency causes altered inflammation with impaired skeletal muscle regeneration[J].Journal of Leukocyte Biology, 2007, 81(3):775-785 doi: 10.1189/jlb.0506356
[7] XIAO W, LIU Y, LUO B, et al.Time-dependent gene expression analysis after mouse skeletal muscle contusion[J].Journal of Sport and Health Science, 2016, 5(1):101-108 doi: 10.1016/j.jshs.2016.01.017
[8] XIAO W, LIU Y, CHEN P.Macrophage depletion impairs skeletal muscle regeneration:The roles of pro-fibrotic factors, inflammation, and oxidative stress[J].Inflammation, 2016, 39(6):2016-2028 doi: 10.1007/s10753-016-0438-8
[9] LIU X, LIU Y, ZHAO L, et al.Macrophage depletion impairs skeletal muscle regeneration:The roles of regulatory factors for muscle regeneration[J].Cell Biology International, 2017, 41(3):228-238 doi: 10.1002/cbin.v41.3
[10] LIVAK K J, SCHMITTGEN T D.Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(T)(-Delta Delta C) method[J].Methods, 2001, 25(4):402-408 doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262
[11] XIAO W, CHEN P, DONG J.Effects of overtraining on skeletal muscle growth and gene expression[J].International Journal of Sports Medicine, 2012, 33(10):846-853 doi: 10.1055/s-00000028
[12] 肖卫华, 陈佩杰, 刘宇.巨噬细胞在骨骼肌急性损伤修复中的作用研究进展[J].中国运动医学杂志, 2014, 33(3):269-274 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6710.2014.03.015 [13] CEAFALAN L C, MANOLE E, TANASE C P, et al.Interstitial outburst of angiogenic factors during skeletal muscle regeneration after acute mechanical trauma[J].Anat Rec (Hoboken), 2015, 298(11):1864-1879 doi: 10.1002/ar.23254
[14] WRIGHT C T, OPOLON P, APPELL H J, et al.Treatment of muscle injuries by local administration of autologous conditioned serum:Animal experiments using a muscle contusion model[J].International Journal of Sports Medicine, 2004, 25(8):582-587 doi: 10.1055/s-2004-821303
[15] NOZAKI M, LI Y, ZHU J, et al.Improved muscle healing after contusion injury by the inhibitory effect of suramin on myostatin, a negative regulator of muscle growth[J].The American Journal of Sports Medicine, 2008, 36(12):2354-2362 doi: 10.1177/0363546508322886
[16] 刘晓光, 赵淋淋, 曾志刚, 等.小鼠骨骼肌损伤修复过程中肌再生调节因子和血管再生因子表达规律研究[J].中国康复医学杂志, 2016, 31(12):1294-1300 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1242.2016.12.001 [17] NOVAK M L, KOH T J.Macrophage phenotypes during tissue repair[J].Journal of Leukocyte Biology, 2013, 93(6):875-881 doi: 10.1189/jlb.1012512
[18] PILLON N J, BILAN P J, FINK L N, et al.Cross-talk between skeletal muscle and immune cells:Muscle-derived mediators and metabolic implications[J].American Journal of Physiology Endocrinology and Metabolism, 2013, 304(5):E453-465 doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00553.2012
[19] KIMURA N, HIRATA S, MIYASAKA N, et al.Injury and subsequent regeneration of muscles for activation of local innate immunity to facilitate the development and relapse of autoimmune myositis in C57BL/6 mice[J].Arthritis & Rheumatology, 2015, 67(4):1107-1116 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=92bb52d50c73a0c256f5a905d425361c&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[20] TONKIN J, TEMMERMAN L, SAMPSON R D, et al.Monocyte/macrophage-derived IGF-1 orchestrates murine skeletal muscle regeneration and modulates autocrine polarization[J].Molecular Therapy:The Journal of The American Society of Gene Therapy, 2015, 23(7):1189-1200 doi: 10.1038/mt.2015.66
[21] SHONO J, SAKAGUCHI S, SUZUKI T, et al.Preliminary time-course study of antiinflammatory macrophage infiltration in crush-injured skeletal muscle[J].Animal Science Journal=Nihon Chikusan Gakkaiho, 2013, 84(11):744-750 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=679a00b09f45deaacdf9fe353032b14b
[22] DENG B, WEHLING H M, VILLALTA S A, et al.IL-10 triggers changes in macrophage phenotype that promote muscle growth and regeneration[J].Journal of Immunology, 2012, 189(7):3669-3680 doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1103180
[23] ZOU K, WANG Y, HU Y, et al.Specific tumor-derived CCL2 mediated by pyruvate kinase M2 in colorectal cancer cells contributes to macrophage recruitment in tumor microenvironment[J].Tumour Biol, 2017, 39(3):1-10 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=84bbd1da47a125a3df4e1aaeb448919b&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[24] 杨建斌, 冯红超, 宋宇峰.口腔鳞癌中单核细胞趋化蛋白-1在巨噬细胞浸润、聚集中的意义[J].中国肿瘤临床, 2005, 32(20):1155-1157 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8179.2005.20.005 [25] CARSON W F T, SALTER G S E, SCOLA M M, et al.Enhancement of macrophage inflammatory responses by CCL2 is correlated with increased miR-9 expression and downregulation of the ERK1/2 phosphatase Dusp6[J].Cell Immunol, 2017, 314:63-72 doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2017.02.005
[26] CONTRERAS S V, OCHOA O, REYES R S M, et al.Fat accumulation with altered inflammation and regeneration in skeletal muscle of CCR2-/- mice following ischemic injury[J].American Journal of Physiology Cell Physiology, 2007, 292(2):C953-967 doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00154.2006
[27] OCHOA O, SUN D, REYES R S M, et al.Delayed angiogenesis and VEGF production in CCR2-/- mice during impaired skeletal muscle regeneration[J].American Journal of Physiology Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology, 2007, 293(2):R651-661 doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00069.2007
[28] ARNOLD L, HENRY A, PORON F, et al.Inflammatory monocytes recruited after skeletal muscle injury switch into antiinflammatory macrophages to support myogenesis[J].J Exp Med, 2007, 204(5):1057-1069 doi: 10.1084/jem.20070075
[29] BRZOSKA E, KOWALSKI K, MARKOWSKA Z A, et al.Sdf-1(CXCL12) induces CD9 expression in stem cells engaged in muscle regeneration[J].Stem Cell Research & Therapy, 2015, 6:46 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=796d7994a6ea39048d098daef5e32edc&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[30] BRZOSKA E, KOWALEWSKA M, MARKOWSKA Z A, et al.Sdf-1(CXCL12) improves skeletal muscle regeneration via the mobilisation of Cxcr4 and CD34 expressing cells[J].Biology of The Cell/Under The Auspices of The European Cell Biology Organization, 2012, 104(12):722-737 doi: 10.1111/boc.v104.12
[31] RATAJCZAK M Z, MAJKA M, KUCIA M, et al.Expression of functional CXCR4 by muscle satellite cells and secretion of SDF-1 by muscle-derived fibroblasts is associated with the presence of both muscle progenitors in bone marrow and hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells in muscles[J].Stem Cells, 2003, 21(3):363-371 doi: 10.1634/stemcells.21-3-363
[32] 杨志峰, 杨清玲, 陈昌杰.趋化因子SDF-1与受体CXCR4的研究进展[J].分子诊断与治疗杂志, 2011, 3(1):58-61 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6929.2011.01.015 [33] 李鹏程, 徐茜, 胡燕华.蛋白激酶C对SDF-1诱导巨噬细胞趋化及血管内皮生长因子转录的调节作用[J].华中科技大学学报(医学版), 2008, 37(1):93-96 doi: 10.3870/j.issn.1672-0741.2008.01.024 -
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 李佳,丁见,陈欢,缪化春,龚鑫,丁艳霞. COX-2在骨骼肌纤维化中的机制探究. 包头医学院学报. 2024(11): 15-18+35 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 刘琳,刘庆广,黄强民. 创伤性肌筋膜触发点的形成对大鼠骨骼肌肌梭内NT-3及受体TrkC的表达影响. 南京体育学院学报. 2023(07): 44-49 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 刘杏,魏晓菡,邓洁,李仲铭. 骨骼肌钝挫伤兔模型制备与打击力度的关系. 中国组织工程研究. 2021(02): 196-200 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 高璨,梁辰,张建平,杨杨,马云,詹晖. 肌骨超声技术在第18届亚运会中国优秀运动员运动损伤诊治中的应用. 中国体育科技. 2020(07): 108-113 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: