Associations Among Habitual Behavior, Implementation Intention and Physical Activity of Adolescents: Application of Model of Extended Theory of Planned Behavior
-
摘要: 在计划行为理论(TPB)的基础上,引入身体活动习惯行为与执行意向,构建扩展TPB(METPB)模型,检验该模型对9~19岁青少年群体的中高强度身体活动(MVPA)的适用性,探讨该模型对小学、初中及高中阶段青少年MVPA影响的差异。结果显示:假设模型的拟合度可以接受,纳入习惯行为与执行意向后,METPB显著地提高了其对身体活动行为的解释力。态度和感知行为控制对MVPA行为意向有显著性影响,解释了31.4%的行为意向方差;行为意向和习惯行为对MVPA行为有显著性影响,解释了18.7%的行为方差;执行意向加强了行为意向朝实际行为的转换。METPB模型对于不同学习阶段青少年MVPA意向及行为的影响有显著性差异。其中:主观规范对小学生与初中生MVPA意向产生了显著性影响,而对高中生的MVPA意向并无显著性影响;感知行为控制对3个阶段学生的MVPA意向产生的影响随着学习阶段的上升不断增强。建议:在对于青少年身体活动的干预中,政府、家庭、学校应重视培养学生对于身体活动参与的正确态度,提高其参与身体活动的意愿,培养其参与身体活动的行为习惯,且在对青少年身体活动干预时考虑学习阶段的差异。Abstract: The habitual behavior and implementation intention into the theory of planned behavior(TPB)was studied to be a model of extended TPB(METPB)and this model was tested with moderate to vigorous physical activity(MVPA)of adolescents aged 9~19 years.The differences in the prediction of METPB of MVPA were examined among primary, secondary and high school students. It is founded that the model of hypothesized relationships demonstrated a good fit with the data, and the METPB has a higher predictive ability than the TPB model, after including habitual behavior and implementation intention.The findings revealed that attitude and perceive behavioral control is significantly associated with MVPA intention, which explained 31.4% variance of intention.Behavioral intention and implementation intention are significantly associated with MVPA behavior, which explained 18.7% variance of behavior.Implementation mediated the influence intention on behavior.There is a significant difference in the influence of METPB variables on MVPA of adolescents in primary, secondary and high school students. Subjective norm is significantly associated with MVPA intention of primary and middle school students instead of high school students.The stronger association between perceived behavioral control and MVPA behavior goes with the higher learning stage.The government, school, and parents should put emphasis on the improvement of adolescent attitude towards PA, intention to participate in PA, and PA habit to promote adolescent PA participation. The differences among primary, secondary, and high school students should be taken into consideration when designing intervention.
-
1. 问题的提出
从1985年开始,我国共进行了5次全国青少年体质健康调查,前4次调查结果显示我国青少年的体质在近20年持续下降,学生肥胖检出率不断提升。2010年,第5次全国学生体质健康调查结果显示,学生体质与健康状况总体有所改善,但肥胖检出率仍在持续提升。我国青少年体质健康调研结果[1]显示,身体活动不足是其体质下降与肥胖率升高的主要原因。研究指出,长期性、规律性的身体活动能够降低青少年慢性疾病(如心血管疾病)的发病率,控制超重和肥胖发生率及精神疾病发生的危险性。青少年时期是学习运动技能和形成良好运动习惯的黄金时期[2],了解青少年身体活动水平及其影响因素非常重要。
近年来,身体活动的研究正逐步走向理论化与模型化。有多种心理学理论被应用于身体活动行为的研究,例如自我决定理论、期望价值理论、阶段发展理论以及计划行为理论,其中计划行为理论(theory of planned behavior, TPB)的应用最为广泛。本文以Ajzen[3]提出的TPB模型为基础框架,纳入青少年在日常生活中所形成的身体活动“习惯行为”(habitual behavior),以及在特定情境下形成的身体活动“执行意向”(implementation intention),对模型基于中高强度身体活动(moderate to vigorous physical activity, MVPA)情境进行修正,构建解释青少年身体活动行为的扩展TPB模型(model of extended theory of planned behavior, METPB),并对其进行实证检验,从而为改善青少年参与身体活动的意向与行为提供促进策略。
2. 理论视角与模型设定
2.1 TPB模型及应用
Ajzen [3]提出的TPB认为行为意向(behavioral intention)与感知行为控制(perceived behavior control)是影响行为(behavior)最直接的因素,而态度(attitude)、主观规范(subjective norm)和感知行为控制综合决定了行为意向。其中:行为意向反映了个人参与某项行为的意愿;态度指行为主体对特定行为积极或消极结果的总体评价;主观规范反映的是重要的他人(如父母、教师或朋友)或团体对个体行为的态度与看法;感知行为控制是指个体感知到执行某特定行为的难易程度。
国外大量实证研究[4-6]验证了TPB解释和预测青少年身体活动的效力。Martin等[4]发现TPB模型能解释8%~9%美国儿童的MVPA方差,参与意向是预测其MVPA行为的唯一变量。态度、行为规范与感知行为控制则解释了45%的MVPA行为意向方差。Trost等[5]聚焦于美国6年级学生的身体活动意向与行为,发现态度和主观规范与MVPA意向显著相关,解释了其13%的行为意向方差,而感知行为控制与行为意向均与MVPA行为显著相关,解释了6%的行为方差。Mummery等[6]也运用TPB调查了加拿大儿童与青少年的MVPA的参与意向,结果显示:态度、行为规范与感知行为控制三变量解释了47%的行为意向方差。在这些研究中,TPB模型均显示出良好的解释效力。然而,Ajzen[3]认为,TPB模型并不完美,对一些具体情境下行为的研究还需要考虑其他特定的因素。由此,一些学者提出METPB,在研究中纳入其他变量提高TPB对于行为的预测与解释力度。在目前的青少年身体活动研究中,纳入的变量有自我身份定位、锻炼习惯行为、自我锻炼效能、描述性准则、个人道德准则、家庭支持、朋友支持、社会供给等,大量实证研究[7-10]已证明这些变量不同程度地提高了计划行为理论对于身体活动水平的解释力。
研究[11-12]发现TPB模型在预测个体行为时会受到人口统计学因素(如性别和年龄)的影响。国内外研究发现青少年在不同学习阶段,其参与身体活动的水平并不一致。其中,大部分研究发现随着年龄或年级的增长,其MVPA的参与时间不断上升。Mummery等[6]运用TPB模型预测3、5、8、11年级学生的身体活动意向与行为,发现不同年级学生的TPB模型干预存在显著性差异,其中,相比于3年级与8年级学生,5年级学生的行为态度对身体活动参与意向的影响更为显著,而感知行为控制对于8年级和11年级学生的影响要显著强于3年级学生。
在我国,少数研究运用METPB解释与预测了青少年身体活动与锻炼行为。冯玉娟等[13-14]在TPB的基础上引入了“自我决定动机”,探索影响高中生与大学生身体活动意向和行为的心理因素。方敏[15]在TPB的意向与行为之间引入新的变量——“行为计划”,探讨青少年的锻炼行为。李业敏[16]对TPB进行了更为完整的修订,将“计划”“家人社会支持”“朋友社会支持”“自我效能”作为意向和行为的第三变量。上述研究发现这些变量都有效提升了TPB对身体活动行为的预测解释力。但我国目前还没有研究探讨过TPB模型对不同年龄或学习阶段青少年身体活动影响的差异。
2.2 习惯行为、执行意向与身体活动
TPB理论是建立在个体有意识的决定基础之上的。然而,部分学者认为除了有意识决定过程外,没有特定目的或意识的自发认知过程也有可能会解释行为(如习惯行为、执行意向等),将这些变量纳入TPB模型可能会增强它对行为的解释力,这在有关出行、旅游、吸烟等的实证研究中也得到了证实[17-18]。同样,对于经常从事身体活动的青少年而言,其参与身体活动的行为并非有意识决定的结果,而可能只是一种习惯的驱使或遇到了与参与身体活动相符的特定情境,但TPB模型无法对此进行解释。目前我国鲜有研究在TPB模型中纳入这类无意识变量解释身体活动意向或行为。
人们总是以某种模式执行行为,只要这种行为发生过,其重复发生的概率就非常大。当这种以目标为导向的行为在特定的相似的行为背景下反复出现时,该行为就构成了一种习惯行为[7]。不同于有意行为,习惯行为是一种完全无意识的自动化行动过程。许多学者认为习惯行为和行为意向对行为的影响可以相互替代。具体而言,当个体处于全新的环境中,并无以往的经验可以帮助做出选择时,其往往通过深思熟虑后形成以目标为导向的行为意向,并开始实施与其对应的后续行为,而如果目标所要求的行动是一种其过去经常从事的日常行为,则主要以无意识的习惯为主导,进而影响其未来的行为[19]。Conner等[20]的元分析也证明了习惯行为与行为意向和行为有直接关系,并且能分别解释7.2%的行为意向方差和13%的行为方差。因此,本文将习惯行为纳入青少年身体活动分析中,能够影响行为意向并配合行为意向一起对个体选择身体活动参与的行为起到更为全面和有效的解释。
执行意向是一种有效的自我调节策略,被称为“如果-那么”计划,是将一个预期的情境(机会或时机)与一个确定的目标定向行为联系起来,明确说明个体在什么时间、地点以及如何追求一个特定目标的计划。这个概念包含了2个成分:“如果”成分,指采取适当行为的预期情境;“那么”成分,指促进目标实现的行为反应。执行意向的具体形式:如果遇到情境Y,那么我会采取行动以达到目标X[21]。例如“如果我正好在微信上(情境),我就会去朋友圈发表评论(目标)”。形成执行意向使得预期的情境和目标定向行为之间形成了强烈的关联,建立行为意向和实际行为之间联系的中介变量[21]。目前国外有实证研究[7]证明了执行意向是行为意向与行为之间的中介变量,能促进身体活动意向转化为身体活动参与行为,使其有效且无意识地进行身体活动参与目标的定向反应。因此,将执行意向纳入TPB模型,意味着当个体遇到预期的情境,行为意向可以通过执行意向转化为行为,但如果未遇到预期的情境,行为意向则直接决定了行为参与。
2.3 概念模型与研究假设
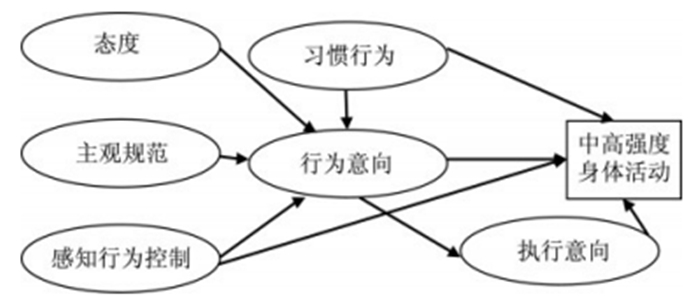
基于上述理论分析,以METPB为基本框架,提出青少年身体活动参与研究的概念模型(图 1)。研究目的:①METPB各因素对于青少年MVPA参与意向的影响;②METPB对于青少年MVPA参与行为的影响;③METPB对于不同学习阶段(小学、初中、高中)学生MVPA参与影响的差异。基于研究目的与概念模型,提出如下研究假设:
H1:态度、主观规范、感知行为控制、习惯行为对青少年MVPA参与意向有显著的正向影响。
H2:行为意向、感知行为控制、习惯行为对MVPA行为有直接、显著的正向影响。
H3:执行意向在青少年MVPA行为意向与行为之间起中介作用。
H4:METPB模型变量对于青少年MVPA的影响在不同学习阶段存在差异。
3. 研究方法
采用仪器测量法与问卷调查法分别测量青少年1周中平均每天MVPA时间和METPB各变量。
3.1 测试及调查对象
于2015年3—6月间开展测试与调查工作。按照分层抽样原则,以市区和郊区为考虑因素,选取上海市杨浦区、浦东新区与宝山区3个区,每个区抽取1所小学(3~5年级)、1所初中(初1~初3)与1所高中(高1~高2)。在所抽取的学校中以年级为单位,每个年级随机抽取1个班级为对象进行身体活动测试,共选取24个班级1 063名学生。按照自愿参与的原则,研究组成员向被邀请参与研究的学生及其监护人发放知情同意书,并详细介绍研究目的、过程、获益及可能带来的不便。最终共有817名学生及监护人签署了自愿参加测试的知情同意书。测试员运用加速度计对这817名学生进行1周身体活动测量,并对他们进行问卷调查,共发放问卷817份,回收783份,有效问卷为751份,问卷的有效回收率为92%。
3.2 测试、调查工具及指标
3.2.1 身体活动测试工具及指标
运用Actigraph GT3X型人体运动能耗监测仪(加速度计)测量MVPA时间。加速度计是目前测量儿童青少年身体活动及能量消耗最有效的工具之一,已广泛运用于国内外儿童青少年身体活动研究[22-25]。
3.2.2 METPB变量评价工具及指标
问卷分为3部分。第1部分是样本的基本信息,包括年龄、性别、所在学校等。第2部分为Hagger等[24]制定的TPB量表,此量表已广泛运用于国内外青少年身体活动影响因素的相关研究[4, 6, 25]。量表共4个维度(态度、主观规范、感知行为控制、行为意向)10个题项。第3部分为习惯行为与执行意向量表。习惯行为量表采用Wang[26]制定的量表,包含3个题项,主要通过了解青少年在过去一段时间内某种特定行为发生的频率体现其习惯行为,频率越高,代表其习惯保持得越稳定。对于执行意向,采用Brickell等[7]研究中的6个题项进行测量,主要了解参与者对于参与身体活动的时间、地点、方式的计划及实施,计划及实施越充足,则其执行意向越高。以上量表均采用Likert 7级量表法,表 1对所使用的测量量表进行了简单描述。
表 1 验证性因子分析结果Table 1. Confirmatory factor analysis results测量维度与测量题项 标准化因子载荷 CR AVE Cronbach’s α系数 行为意向 0.915 0.783 0.808 我计划在下周最少参与3次身体活动 0.892 我希望在下周最少参与3次身体活动 0.886 我会在下周最少参与3次身体活动 0.877 态度 0.852 0.657 0.915 认为在下周最少参与3次身体活动是差的—好的 0.826 认为在下周最少参与3次身体活动让我无聊—兴奋 0.829 认为在下周最少参与3次身体活动是无趣的—有趣的 0.775 主观规范 0.752 0.513 0.826 我的父母认为我下周要参与3次身体活动 0.736 我的朋友认为我下周要参与3次身体活动 0.814 我的老师认为我下周要参与3次身体活动 0.537 感知行为控制 0.717 0.559 0.719 可以完全决定下周参与3次身体活动 0.462 可以基本决定下周参与3次身体活动 0.763 对于下周最少参与3次身体活动选择上的控制力 0.733 习惯行为 0.781 0.546 0.792 过去1周参与身体活动的次数 0.714 过去4周参与身体活动的次数 0.835 过去3个月参与身体活动的次数 0.657 执行意向 0.896 0.596 0.727 我计划好了下周参与身体活动的时间 0.909 我计划好了下周参与身体活动的地点 0.883 我计划好了下周参与身体活动的方式 0.787 我已经在计划的时间完成了身体活动 0.578 我已经在计划的地点完成了身体活动 0.662 我已经按计划的方式完成了身体活动 0.763 信度反映了同一变量所有题项答案的一致性程度,通常用Cronbach’s α系数来衡量。总量表的Cronbach’s α系数为0.749,表 1所列5个分量表的Cronbach’s α系数均大于0.7,由此判定,本文使用的量表具有较好的信度。
还对问卷效度进行了检验,在内容效度方面,研究运用回译方法进行问卷翻译内容的有效性检验:笔者将英文问卷翻译成中文,再由1位英语专业的教授将其回译为英语,然后与原版英文问卷进行对照,对于有疑问的地方2人进行讨论与商议,并进行相应的修改。中文版问卷形成后笔者向5位专家发放问卷效度检验表,3位认为有效,另外2位专家分别提出了修改意见,根据专家意见对问卷进行了修改。专家认为只有1个题项“在我身边的人的影响”测量主观规范不够客观与全面,因此,将其修改为“父母、教师、朋友的影响”3个题项。
运用因子分析检验量表的结构效度。首先利用SPSS 21.0进行因子分析,结果发现KMO值为0.805,并通过Bartlett’s球型检验(P < 0.001), 累积方差解释比例达82%。在此基础上,运用AMOS 24.0进行验证型因子分析,结果显示:CMIN/df=4.171,CFI=0.903,IFI=0.903,NFI=0.891, RMSEA=0.079, 尽管RMSEA和NFI值均稍偏离可接受标准值0.060与0.900,但其他指标均在标准值以内[26],因此,验证型因子分析整体的模拟程度可以接受。除题项“可以完全决定下周参与3次身体活动”的因子载荷低于0.5予以删除外,每个观测指标在相应潜变量上的标准化因子载荷均大于0.5且小于1。此外,组合信度(CR)分布在0.717~0.915,均在大于0.7的可接受水平。采用Fornell等[27]建议的方法,通过潜变量平均方差萃取值(AVE)的平方根与潜变量之间相关系数的比较检验潜变量的区分效度。如表 2所示,所有因子的AVE平方根均大于与其他因子的相关系数,显示出了良好的区分效度。因此,通过对量表信效度的分析可见,所收集的数据质量较高,满足做进一步分析的要求。
表 2 预测模型各变量的相关性和描述性统计结果Table 2. Correlation and descriptive statistical results of variables in the prediction model态度 主观规范 感知行为控制 行为习惯 执行意向 行为意向 MVPA行为 M SD 态度 0.811 0.145* 0.316* 0.006 0.048 0.294* 0.171* 4.922 1.721 主观规范 0.716 0.304* 0.064 0.173* 0.201* 0.072 5.214 1.792 感知行为控制 0.748 0.056 0.045 0.542* 0.164* 4.621 1.594 行为习惯 0.739 0.472* 0.006 0.114* 3.327 1.825 执行意向 0.772 0.088* 0.109* 4.489 1.409 行为意向 0.885 0.336* 3.906 1.751 MVPA行为 28.146 10.925 注:此矩阵对角线为AVE的平方根,对角线上方为各因子之间的相关系数;因MVPA并非量表测量变量,故无AVE值;*表示P < 0.05,**表示P < 0.01, ***表示P < 0.001。 3.3 测试及调查过程
仪器发放前,由测试员讲解研究目的,然后向受试学生发放仪器。仪器发放过程中,测试员记录学生姓名以及仪器编号,并讲解佩戴仪器的规范和注意事项。按照测试要求,受试学生将加速度计通过1根有弹性的带子佩戴在右髋部,在接受测量的1周内连续7 d必须佩戴仪器(睡觉、洗澡、游泳时除外)。佩戴加速度计后,受试学生可进行正常的学校活动和日常生活。测试开始后,测试员每天去学校检查与监督学生佩戴仪器的情况。加速度计从发放的第2天0点开始记录数据,直至第8天由测试员将其收回。
测试完成后,运用加速度计分析软件Actilife 6.5对数据进行有效性筛选和统计分析,采用60 s的时间间隔(epoch)记录加速度测量数据,以每天佩戴时间不少于10 h为1个有效日,1周至少佩戴3个有效日(2个上学日+1个周末日)为最低标准筛选有效的身体活动数据[22]。通过数据分析,在817名参与测试的学生中,604名学生的身体活动测试数据为有效数据,有效率为74%。加速度计记录数据时以“count”为计量单位,根据count值可将身体活动可分为不同的强度。选取Zhu等[23]研制的符合中国儿童青少年的强度分类标准,将身体活动分为“静坐不动”(SPA)、“轻度活动”(LPA)、“中等强度活动”(MPA)和“高强度活动”(VPA)等4个等级。选取测量所得数据中的MVPA时间(MVPA时间=MPA时间+VPA时间)作为青少年身体活动数据进行分析。
受试学生进行身体活动测量前1周,测试人员向所有参与身体活动测量的受试青少年发放问卷,并向受试者说明问卷填写注意要点,要求问卷每一道题都要如实填写,填写过程大约为20 min,填写完毕由发放者检查无误后当场收回问卷。
3.4 统计学分析
采用的数据统计学分析方法主要包括:①运用SPSS 21.0对问卷进行统计和分析,采用均数和标准差对青少年中高强度身体活动时间及METPB的各变量进行描述性统计分析;②运用AMOS 24.0应用结构方程对假设模型进行验证;③运用多群组结构方程方法进一步分析METPB对不同学习阶段(小学、初中、高中)青少年身体活动参与意向与行为的影响。
4. 研究结果
4.1 样本基本特征
对身体活动测试有效数据与调查问卷有效问卷进行筛选后,数据有效样本为588人。其中,23人的调查数据缺失,运用删除法删除缺失值,最后的样本为562人。男生284名,占50.5%;女生278名,占49.5%。平均年龄为12.51岁(SD=2.44),年龄跨度为9~19岁。小学生(3~5年级)190名,占33.8%;初中生(初1~初3)217名,占38.6%;高中生(高1与高2)155名,占27.6%。
4.2 青少年身体活动及METPB变量的描述性分析结果
描述性分析结果显示,青少年平均每天参与MVPA时间为28 min,低于国际卫生组织提出的每天60 min MVPA的推荐量。单因素方差分析结果显示,不同学习阶段青少年的MVPA时间存在显著性差异,F(2,562)=2.871,P=0.031,其中初中阶段青少年的MVPA时间最长(M=29.67, SD=10.59),高中阶段青少年的MVPA时间最短(M=26.07, SD=10.54)。METPB各变量中,除了行为意向与习惯行为之外,其他变量的均值大部分都高于Likert 7级量表的中值4。同时,相关分析结果显示,METPB中除了少量变量(如行为习惯与态度、主观规范及感知行为控制)之间不相关外,其他各变量之间的相关性显著(表 2),适合进行结构方程模型检验。
4.3 模型拟合与假设检验结果
综合选择卡方自由度比(χ2/df)、相对拟合指数(CFI)、塔克-刘易斯指数(TLI)、标准化残差均方根(SRMR)和近似误差平方根(RMSEA)等指标全面检验结构模型的拟合情况。Hu等[28]所设标准为:当χ2/df小于3时模型拟合较好;当χ2/df在3和5之间时观测数据与模型基本拟合,模型可以接受;当χ2/df大于5时则表示观测数据与模型拟合度不好。CFI和TLI这2个指标大于0.09,越接近1越好;RMSEA的值小于0.06、SRMR的值小于0.08时模型通常会有较好的拟合度,越接近0表明观测数据和模型拟合度越好[28]。
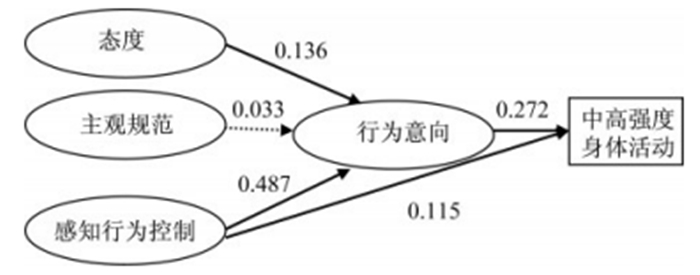
首先对TPB模型(图 2)进行检验,结果为χ2/df=4.5, P < 0.01;CFI=0.972;TLI=0.908, SRMR=0.042; RMSEA=0.08。模型的拟合度较好,各指标均可接受。各自变量对行为意向的解释力为30.2%, 对行为的解释力为11.3%。态度(β=0.136, P < 0.01)与感知行为控制(β=0.487, P < 0.01)显著影响了身体活动参与的行为意向,行为意向(β=0.272, P < 0.01)与感知行为控制(β=0.115, P < 0.05)显著影响了身体活动参与行为。
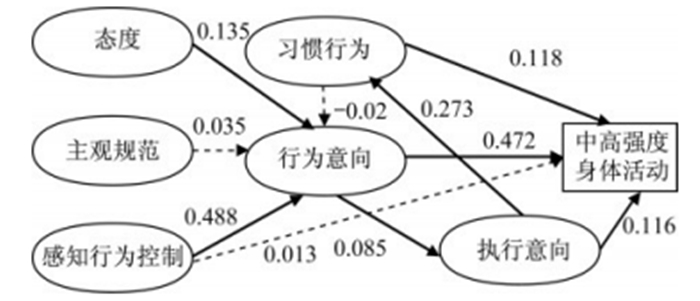
对METPB预测模型(图 3)进行检验,结果显示:χ2/df=1.528, P < 0.01;CFI=0.705;TLI=0.436, SRMR=0.983;RMSEA=0.160。模型的拟合不佳。根据模型的修正提示,模型应增加“执行意向→习惯行为”路径。目前有些学者认为执行意向会促进习惯的养成或改变,执行意向建立的自动化联结会加强习惯联结,这在一些准实验研究如改变饮食习惯和注意力焦点控制等中已得到证实[29]。因此,为寻求更好的拟合模型,增加“执行意向→习惯行为”路径,修正后模型的检验结果为:χ2/df=2.17, P < 0.05;CFI=0.980;TLI=0.953,SRMR=0.031;RMSEA=0.046。修正后的模型与样本数据拟合良好。
提出的假设大部分得到了数据的支持。数据分析结果显示:态度(β=0.135,P < 0.01)和感知行为控制(β=0.488, P < 0.01)对MVPA行为意向具有显著性影响,但主观规范(β=0.035,P > 0.05)和习惯行为(β=0.118,p > 0.05)与MVPA行为意向无显著相关性,部分支持H1;行为意向(β=0.472,P < 0.01)和习惯行为(β=0.118,P < 0.01)与MVPA行为显著相关,但感知行为控制(β=0.013,P > 0.05)与MVPA行为无显著相关,因此部分支持H2。从图 3可以看出,行为意向除了对MVPA行为有直接影响外,还可通过执行意向的中介作用对MVPA行为产生影响,这一路径的间接效应为0.01,支持H3。此外,结果还显示,执行意向对习惯行为有显著性影响(β=0.273,P < 0.01)。研究的自变量解释了31.4%的MVPA行为意向方差以及18.7%的MVPA行为方差。与TPB模型相比,METPB对行为意向的解释力变化率为ΔR2=0.13,对身体活动参与行为的解释力变化率为ΔR2=0.74。
4.4 METPB对小学、初中、高中学生MVPA意向与行为影响的差异
运用多群组结构方程模型分析METPB影响因素对于青少年MVPA参与意向及行为影响的差异。首先检验不同性别青少年群组间未受限制模型(基准模型的拟合优度), 该模型的拟合优度指标为:χ2/df=4.977, P < 0.001; CFI=0.940; TLI=0.902,RMSEA=0.054。这说明不同学习阶段青少年群组的METPB影响因素结构方程模型是可接受的。其次,限制小学、初中及高中学生的结构方程中的结构路径系数都相等(此模型称为平行模型),对小学、初中及高中学生的平行模型与基准模型的χ2值差异进行比较,结果见表 3。数据分析结果显示,不同学习阶段青少年在主观规范→MVPA意向与感知行为控制→MVPA意向2条结构路径上的标准化回归系数存在显著差异。其中:主观规范对小学生与初中生的MVPA意向产生了显著性影响,而对高中生的MVPA意向并无显著性影响;感知行为控制对3个不同阶段学生的MVPA意向都产生了显著性影响,且从小学、初中到高中,其相关性不断增强。
表 3 不同学习阶段青少年METPB路径系数和卡方检验结果Table 3. The results of METPB path coefficient and chi-square test in adolescents at different learning stagesM0基准模型 群组 标准化回归系数 χ2/df CFI TLI RMSEA △χ2 P 4.977 0.940 0.902 0.054 M1态度→MVPA意向 小学 0.172* 4.616 0.943 0.894 0.051 0.391 0.823 初中 0.180* 高中 0.120 M2主观规范→MVPA意向 小学 0.119* 5.012 0.921 0.851 0.055 13.060 0.001 初中 0.183* 高中 -0.004 M3感知行为控制→MVPA意向 小学 0.184* 4.879 0.928 0.865 0.053 8.825 0.012 初中 0.567** 高中 0.593** M4行为意向→MVPA行为 小学 0.041 4.633 0.942 0.892 0.051 0.956 0.620 初中 1.804** 高中 1.630** M5感知行为控制→MVPA行为 小学 0.428 4.635 0.942 0.892 0.051 1.015 0.602 初中 0.969 高中 1.194* M6习惯行为→MVAP行为 小学 0.028 4.639 0.942 0.892 0.051 1.124 0.570 初中 0.982* 高中 0.607 M7习惯行为→MVAP意向 小学 0.064 4.694 0.939 0.896 0.052 2.890 0.236 初中 0.041 高中 0.080 M8行为意向→执行意向 小学 0.041 4.623 0.943 0.893 0.051 0.636 0.728 初中 0.910* 高中 0.068 M9执行意向→MVPA行为 小学 0.503* 4.801 0.933 0.874 0.053 6.308 0.053 初中 0.024 高中 0.997* 注:∗表示P < 0.05,∗∗表示P < 0.01。 5. 分析与讨论
5.1 METPB的模型验证
本文将习惯行为与执行意向纳入一般的TPB模型,构建并验证了METPB在青少年身体活动意向与行为上的解释和预测力。该模型假设态度、主观规范、感知行为控制以及习惯行为能够有效预测身体活动意向,行为意向、感知行为控制、习惯行为能够有效预测身体活动参与行为,执行意向是行为意向影响身体活动参与行为的中介变量,研究结果部分支持了研究假设。
结果显示, TPB模型解释了30.2%的青少年MVPA行为意向方差以及11.2%的MVPA行为方差,而METPB的自变量解释了31.4%的MVPA行为意向方差以及18.7%的MVPA行为方差。因此,纳入习惯行为与执行意向2个变量的METPB增加了对青少年身体活动意向与行为的解释力。此结果证实了METPB可以加强TPB对意向与行为的解释效力[7-10]。此外,以往国内外的相关研究皆显示,TPB模型对行为意向的预测力要远高于对行为的预测力。通过对72项运用TPB预测身体活动意向与行为的研究进行总结与归纳, 发现大部分行为变化没能得到有效解释,如:Hagger等[24]在其元分析中发现TPB可以解释44.5%的锻炼意向方差,但只能解释27.4%的身体活动行为方差,这表示在青少年身体活动行为意向与行为之间存在更加有意义的变量[28];部分学者[13]也提出后续研究应探索更多能够使意向转化为行为的心理因素。本文证明了除行为意向与感知行为控制外,习惯行为与执行意向在很大程度上弥补了TPB模型对于行为的解释。
5.2 态度、主观规范、感知行为控制与MVAP行为意向及行为的关系
在TPB模型变量中,态度与感知行为控制对MVPA行为意向有显著的正向影响,但主观规范与MVPA行为意向却无显著相关性。此结果与以往的国内外研究结果基本一致[7-9, 13]。这表明培养青少年对于身体活动正面的认知与态度,为其参与身体活动提供便利的场地、设施、器材、氛围,改善其运动技能,可以增强其参与身体活动的意愿。主观规范对青少年MVPA行为意向的影响无统计学意义,可能有以下两方面的原因:①根据青少年身心发展规律,受试的初中及高中生处于青春期早期,也就是叛逆期,这段时期也是青少年自主性形成期,表现为渴望独立、自我决定、抗拒其他人的影响、寻求自己的主观感觉等特征,从而导致父母、教师以及朋友的意见并不能对其MVPA行为意向产生显著性影响[24]。②“万般皆下品,唯有读书高”的传统观念让父母、教师、朋友等身边人更多关注学生的学习成绩而忽视了参与身体活动的状况,从而导致周围人群的态度并未对青少年身体活动参与意向产生显著性影响。在对青少年MVPA行为的预测方面,行为意向对其有显著性影响,而感知行为控制与其无显著相关性,这与以往大多数研究[17-19]结论不一致。此研究结果表明,有强烈参与意向的青少年有更高的参与身体活动的积极性,MVPA时间更长,而受到周围环境(场地、设施、时间、技能)的影响更小。
Ajzen [3]指出,在TPB模型中,感知行为控制影响效力的高低主要取决于个体对其行为实施的场地、设施、时间等外界环境的控制程度。近年,我国政府高度重视学生的体质与身体活动参与状况,面向青少年开展和实施了“阳光体育运动”,进一步完善了中小学体育场馆设施的建设,并增加了体育课以及体育锻炼的时间。这些举措的实施让青少年感受到了自身对环境、设施、场地等方面的掌控。因此,在参与身体活动时较少考虑外界环境的制约,而主要由其本身的意愿所决定。
5.3 习惯行为、执行意向与青少年MVPA行为意向及行为的关系
笔者发现,习惯行为对于青少年MVPA行为有显著性影响,但与其MVPA行为意向无显著相关性。本文研究结果也进一步证明了Gardner[19]提出的个体习惯行为与行为意向是2种互相平行、相互替代的变量的观点。即在没有形成身体活动习惯之前,青少年的身体活动行为主要由行为意向决定,而当习惯形成之后,则主要由其习惯来主导。习惯行为对于青少年MVPA参与行为的显著影响也凸显了培养青少年参与身体活动习惯的重要性,其习惯的养成将在很大程度上提高青少年的身体活动参与水平,从而改善其体质。然而,本文结果显示青少年习惯行为虽然与MVPA行为有显著性相关,但其效力(β=0.118,P < 0.01)却低于行为意向(β=0.472,P < 0.01),这说明大部分青少年参与身体活动是经过其有意识思考的结果,而非无意识的习惯养成导致。从本文的描述性分析看,上海市青少年在过去1周、1个月及3个月的身体活动参与频率都低于Likert 7级量表的中值,这说明青少年还未形成参与身体活动的习惯,这也解释了行为习惯对于MVPA行为的影响力不如行为意向的影响力大这一研究结果。
关于执行意向对于身体活动的影响,目前国内基本无研究涉及。执行意向是计划、情境与实施的结合,在身体活动中主要表现为个体对其未来身体活动参与的时间、地点、方式以及在此情境下其自动执行活动的计划。例如,A计划在下周的周1、3、5下午5点在操场慢跑0.5 h,那么当时间推移至这些时间段时,A可能会自觉去操场进行慢跑。笔者发现执行意向是身体活动行为意向转化为实际行为的中介变量,即形成了身体活动参与执行意向的青少年更有可能克服实际困难,将其通过谨慎思考而决定的行为意向(极有可能并不会付诸实际行动)自动化,从而提升其行为意向转变为实际参与身体活动行为的转化率,缩小意向和行为的距离,改善了TPB模型中存在意向和行为不一致的弊端。值得注意的是本文中的MVPA是基于1 d的体力活动测量的,包括了青少年在学校中参与的体育课、体育锻炼课等情境,这些情境下所参与的身体活动大多是学校规定的,并不能完全反映青少年自身的意愿。因此,未来的研究可特别着眼于青少年在自我选择的闲暇时间内的身体活动参与来探讨其执行意向对其身体活动参与行为的影响。
在对于TPB模型的修正中,笔者发现习惯行为与执行意向2个自动化模式发挥了某种程度的作用,执行意向对习惯行为有显著的正向影响,这说明执行意向建立的目标行为自动化模式可以帮助身体活动习惯的养成。目前国外关于身体活动参与的研究也运用实验的方法证明了执行意向能促进行为习惯的养成或改变[27],即青少年可以通过多次计划未来的身体活动情境,并在此情境下参与身体活动, 形成无意识的身体活动参与习惯。
5.4 不同学习阶段的差异
本文研究结果显示,在小学、初中与高中阶段,METPB对于身体活动参与的影响存在显著性差异,差异主要体现在“主观规范→MVPA意向”与“感知行为控制→MVPA意向”2条结构路径。这进一步证明了TPB模型在预测个体行为时会受到人口统计学因素的影响[3]。其中,主观规范对小学生与初中生MVPA意向产生了显著性影响,而对高中生的MVPA意向并无显著性影响。这说明父母、教师与朋友对小学与初中阶段青少年参与身体活动的态度对其影响更大。主要原因在于高中阶段,随着青春期的到来,个体自主性和独立性增强,心理社会认知也逐步发展,青少年试图以各种方式挣脱父母与教师的保护[30]。许多实证研究[29, 31]也证明了随着年龄的增长,青少年的身体活动参与受其父母与教师的影响越来越弱。其次,感知行为控制对小学、初中及高中生的MVPA意向的影响随着学习阶段的上升不断增强。此研究结果与Mummery等[6]的研究发现一致,这可能是由于从小学至高中,随着年龄的增长,青少年参与的身体活动越来越复杂,对技术、场地及设施等方面的要求越来越高。小学生进行的身体活动只是简单的走、跑、跳或投,但高中生则可能会参与更高技术要求的身体活动(如户外攀岩、网球等),这对于场地设施以及自身能力的要求也越来越高,从而导致感知行为控制对其参与身体活动行为的制约不断上升。
6. 结论、建议及不足
以TPB为框架,通过将习惯行为与执行意向纳入一般的TPB模型,对其进行基于身体活动情境的修正,研究结果证明了TPB纳入习惯行为与执行意向后,显著地提高了对身体活动行为的解释力。
在青少年身体活动过程中,青少年的参与态度和对于参与困难程度的感知在其MVPA参与意向的形成中起到了关键作用。青少年的MVPA参与行为则主要由其参与意向和是否拥有参与习惯所决定。同时,执行意向不但促进了MVPA参与意向向参与行为的转换,而且也是促进身体活动习惯行为的有效策略。基于此,在对青少年身体活动的干预中,教师与父母应尊重青少年自身的意愿,并为其身体活动提供更多的内容、项目、手段与方式以供选择,切忌运用强制的手段推进青少年身体活动参与。政府、学校、家庭应着重激发青少年参与身体活动的兴趣,通过政府的宣传、学校与家庭教育让青少年了解身体活动的益处,培养其对身体活动参与的正确态度与观念,从而提高其身体活动行为意向。促成青少年养成参与身体活动的习惯是提高其身体活动参与行为的有效途径。基于执行意向对习惯的影响,教师或家长应帮助青少年制定可行的参与身体活动的计划,并监督其在相应的情境下按计划执行与实施,从而有效地培养其养成身体活动参与的习惯。
METPB对于青少年身体活动参与的影响随着学习阶段不同也有所变化,因此,对于青少年身体活动进行干预时需考虑学习阶段的差异。建议在小学与初中阶段更多地加强父母、教师对其身体活动参与的正确引导,培养其对于身体活动参与的正确态度,鼓励及支持其参与身体活动。对于高中生而言,则应更多地关注其各种身体活动技能与能力的培养以及为其身体活动参与提供场地设施和时间上的支持。
本文仍存在一些不足之处需在后续研究中予以完善。①加速度计测量与问卷调查中缺失将近一半的样本,导致本文的总体样本数量较少,今后的研究中应增大样本量。②采用的是横断面研究,将来可考虑对同类被试样本的身体活动意向及行为进行追踪调查,验证METPB影响因素对行为意向及行为意向对实际行为的预测效果。③虽然对执行意向的影响进行了分析与研究,但由于研究目的所限,未能进一步对执行意向的内在作用机制进行分析,未来可在后续研究中继续展开。④未来可以考虑进一步在TPB中纳入更多的心理影响因素,或者和其他心理行为模型如自我决定理论模型结合,提高TPB对于青少年身体活动意向与行为的解释力。
-
表 1 验证性因子分析结果
Table 1 Confirmatory factor analysis results
测量维度与测量题项 标准化因子载荷 CR AVE Cronbach’s α系数 行为意向 0.915 0.783 0.808 我计划在下周最少参与3次身体活动 0.892 我希望在下周最少参与3次身体活动 0.886 我会在下周最少参与3次身体活动 0.877 态度 0.852 0.657 0.915 认为在下周最少参与3次身体活动是差的—好的 0.826 认为在下周最少参与3次身体活动让我无聊—兴奋 0.829 认为在下周最少参与3次身体活动是无趣的—有趣的 0.775 主观规范 0.752 0.513 0.826 我的父母认为我下周要参与3次身体活动 0.736 我的朋友认为我下周要参与3次身体活动 0.814 我的老师认为我下周要参与3次身体活动 0.537 感知行为控制 0.717 0.559 0.719 可以完全决定下周参与3次身体活动 0.462 可以基本决定下周参与3次身体活动 0.763 对于下周最少参与3次身体活动选择上的控制力 0.733 习惯行为 0.781 0.546 0.792 过去1周参与身体活动的次数 0.714 过去4周参与身体活动的次数 0.835 过去3个月参与身体活动的次数 0.657 执行意向 0.896 0.596 0.727 我计划好了下周参与身体活动的时间 0.909 我计划好了下周参与身体活动的地点 0.883 我计划好了下周参与身体活动的方式 0.787 我已经在计划的时间完成了身体活动 0.578 我已经在计划的地点完成了身体活动 0.662 我已经按计划的方式完成了身体活动 0.763 表 2 预测模型各变量的相关性和描述性统计结果
Table 2 Correlation and descriptive statistical results of variables in the prediction model
态度 主观规范 感知行为控制 行为习惯 执行意向 行为意向 MVPA行为 M SD 态度 0.811 0.145* 0.316* 0.006 0.048 0.294* 0.171* 4.922 1.721 主观规范 0.716 0.304* 0.064 0.173* 0.201* 0.072 5.214 1.792 感知行为控制 0.748 0.056 0.045 0.542* 0.164* 4.621 1.594 行为习惯 0.739 0.472* 0.006 0.114* 3.327 1.825 执行意向 0.772 0.088* 0.109* 4.489 1.409 行为意向 0.885 0.336* 3.906 1.751 MVPA行为 28.146 10.925 注:此矩阵对角线为AVE的平方根,对角线上方为各因子之间的相关系数;因MVPA并非量表测量变量,故无AVE值;*表示P < 0.05,**表示P < 0.01, ***表示P < 0.001。 表 3 不同学习阶段青少年METPB路径系数和卡方检验结果
Table 3 The results of METPB path coefficient and chi-square test in adolescents at different learning stages
M0基准模型 群组 标准化回归系数 χ2/df CFI TLI RMSEA △χ2 P 4.977 0.940 0.902 0.054 M1态度→MVPA意向 小学 0.172* 4.616 0.943 0.894 0.051 0.391 0.823 初中 0.180* 高中 0.120 M2主观规范→MVPA意向 小学 0.119* 5.012 0.921 0.851 0.055 13.060 0.001 初中 0.183* 高中 -0.004 M3感知行为控制→MVPA意向 小学 0.184* 4.879 0.928 0.865 0.053 8.825 0.012 初中 0.567** 高中 0.593** M4行为意向→MVPA行为 小学 0.041 4.633 0.942 0.892 0.051 0.956 0.620 初中 1.804** 高中 1.630** M5感知行为控制→MVPA行为 小学 0.428 4.635 0.942 0.892 0.051 1.015 0.602 初中 0.969 高中 1.194* M6习惯行为→MVAP行为 小学 0.028 4.639 0.942 0.892 0.051 1.124 0.570 初中 0.982* 高中 0.607 M7习惯行为→MVAP意向 小学 0.064 4.694 0.939 0.896 0.052 2.890 0.236 初中 0.041 高中 0.080 M8行为意向→执行意向 小学 0.041 4.623 0.943 0.893 0.051 0.636 0.728 初中 0.910* 高中 0.068 M9执行意向→MVPA行为 小学 0.503* 4.801 0.933 0.874 0.053 6.308 0.053 初中 0.024 高中 0.997* 注:∗表示P < 0.05,∗∗表示P < 0.01。 -
[1] 教育部.2010年全国学生体质与健康调查结果[R]. 2011-09-02 [2] 刘述芝, 邹志春.国外青少年体力活动与健康促进研究现状[J].哈尔滨体育学院学报, 2010, 28(6):5-8 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2808.2010.06.002 [3] AJZEN I. The theory of planned behavior[J]. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 1991, 50(2):179-211 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_doaj-articles_2b2ad57a8744e7e9e97e2f9e44499dda
[4] MARTIN J J, MCCAUGHTRY N, SHEN B. Predicting physical activity in Arab American school children[J]. Journal of Teaching in Physical Education, 2008, 27(2):205-219 doi: 10.1123/jtpe.27.2.205
[5] TROST S, SAUNDER R, WARD D. Determinants of physical activity in middle school children[J]. American Journal of Health Behavior, 2002, 26(2):95-102 doi: 10.5993/AJHB.26.2.2
[6] MUMMERY W, SPENCE J, HUDEC J. Understanding physical activity intention in Candian school children and youth:An application of the theory of planned behavior[J]. Research Quarterly for Exercise and Sport, 2000, 71(2):116-24 doi: 10.1080/02701367.2000.10608889
[7] BRICKELL T A, CHATZISARANTIS N L D, PRETTY G M. Using past behavior and spontaneous implementation intentions to enhance the utility of the theory of planned behavior in predicting exercise[J]. British Journal of Health Psychology, 2006, 11(2):249-262 doi: 10.1348/135910705X52471
[8] HAGGER M S, CHATZISARANTIS N, BIDDLE S J, et al. Antecedents of children's physical activity intentions and behaviour:Predictive validity and longitudinal effects[J]. Psychology & Health, 2001, 16(4):391-407 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=10cc71b905000e4d73af352c59a920e6&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[9] HAMILTON K, WHITE K M. Extending the theory of planned behavior:The role of self and social influences in predicting adolescent regular moderate-to-vigorous physical activity[J]. Journal of Sport & Exercise Psychology, 2008, 30(1):56-74 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=0a6354453d8cbc3b4147dd164293753c&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[10] RIES F, HEIN V, PIHU M, et al. Self-identity as a component of the theory of planned behavior in predicting physical activity[J]. European Physical Education Review, 2012, 18(3):322-334 doi: 10.1177/1356336X12450792
[11] GRØNTVED A, PEDERSEN G S, ANDERSEN L B, et al. Personal characteristics and demographic factors associated with objectively measured physical activity in children attending preschool[J]. Pediatric Exercise Science, 2009, 21(2):209-219 doi: 10.1123/pes.21.2.209
[12] WANG C, CHEN P J, ZHUANG J. A national survey of physical activity and sedentary behavior of Chinese city children and youth using accelerometers[J]. Research Quarterly for Exercise and Sport, 2013, 84(sup2):12-28 doi: 10.1080/02701367.2013.850993
[13] 冯玉娟, 毛志雄.高中生身体活动意向和行为的促进策略:自我决定动机对TPB的贡献[J].体育科学, 2014, 34(8):64-69 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-677X.2014.08.007 [14] 冯玉娟, 毛志雄, 车广伟.大学生身体活动行为预测干预模型的构建:自主动机与TPB扩展模型的结合[J].北京体育大学学报, 2015, 38(5):72-76 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-BJTD201505014.htm [15] 方敏.计划行为理论的概化:青少年锻炼行为的预测模式[J].天津体育学院学报, 2010, 25(3):224-227 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0000.2010.03.010 [16] 李业敏.锻炼意向与行为的关系: 计划, 自我效能与社会支持的作用[D].北京: 北京体育大学, 2010: 21-25 http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10043-2010123372.htm [17] 景鹏, 隽志才, 查奇芬.扩展计划行为理论框架下基于MIMIC模型的城际出行行为分析[J].管理工程学报, 2016(4):61-68 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/glgcxb201604008 [18] 王林, 时勘, 赵杨.行为执行意向的理论观点及相关研究[J].心理科学, 2014, 37(4):875-879 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xlkx201404018 [19] GARDNER B. Modeling motivation and habit in stable travel mode contexts[J]. Transportation Research Part F:Traffic Psycology and Behaviour, 2009, 12(1):68-76 doi: 10.1016/j.trf.2008.08.001
[20] CONNER M, SMITH N, MCMILIAN B. Examining normative pressure in the theory of planned beahviour:Impact of gender and passengers on intentions to break the speed limit[J]. Current Psychology, 2003, 22(3):252-263 doi: 10.1007/s12144-003-1020-8
[21] GOLLWITZER P M. Implementation intention:Strong effects of simple plans[J]. American Psychologist, 1999, 54(7):493-503 doi: 10.1037/0003-066X.54.7.493
[22] ANDERSON C B, HAGGER C B, HAGSTROMER M, et al. Validation of the PDPAR as an adolescent diary:Effect of accelerometer cut points[J]. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise, 2005, 37(7):1224-1230 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=ba8dba725c05fae90ae51860c60c35af&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[23] ZHU Z, CHEN P, ZHUANG J. Intensity classification accuracy of accelerometer-measured physical activities in Chinese children and youth[J]. Research Quarterly for Exercise and Sport, 2013, 84(sup 2):S4-S11 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=10.1080/02701367.2013.850919
[24] HAGGER M S, CHATZISARANTIS N L D, BIDDLE S J H. A meta-analytic review of the theories of reasoned action and planned behavior in physical activity:Predictive validity and the contribution of additional variables[J]. Journal of Sport & Exercise Psychology, 2002, 24(1):3-32 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=0691c95155359cf2858bd95f72fb1c40&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[25] 康茜, 王丽娟.基于计划行为理论分析青少年休闲性体力活动的影响因素[J].中国学校卫生, 2016, 37(6):851-855 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgxxws201606013 [26] WANG X. The role of anticipated negative emotions and past behavior in individuals'physical activity intentions and behaviors[J]. Psychology of Sport and Exercise, 2011, 12(3):300-305 doi: 10.1016/j.psychsport.2010.09.007
[27] FORNELL C, LARCKER D F. Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error[J]. Journal of Marketing Research, 1985, 66(6):39-50 doi: 10.2307-3151312/
[28] HU L, BENTLE P M. Cut-off criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis:Conventional criteria versus new alternatives[J]. Structural Equation Modeling:A Multidisciplinary Journal, 1999, 6(1):1-55 doi: 10.1080/10705519909540118
[29] ACHTZIGER A, GOLLWITZER P M, SHEERAN P. Implementation intentions and shielding goal striving from unwanted thoughts and feelings[J]. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 2008, 34(3):381-393 doi: 10.1177/0146167207311201
[30] 高岩, 王先亮.父母支持、同伴友谊质量对青少年运动动机与投入影响[J].天津体育学院学报, 2015, 30(6):480-486 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tjtyxyxb201506004 [31] KIRBY J, LEVIN K A, INCHLEY J. Parental and peer influences on physical activity among Scottish adolescents:A longitudinal study[J]. Journal of Physical Activity and Health, 2011, 8(6):785-793 doi: 10.1123/jpah.8.6.785
-
期刊类型引用(30)
1. 孙高峰,潘小非. 健身App需求支持对青少年锻炼坚持性的影响:自主动机与执行意向中介作用. 北京体育大学学报. 2025(03): 104-113 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 李树旺,李京律,杨抒奕,梁媛. 经济新常态下我国滑雪旅游产业高质量发展研究——基于3个雪季的数据预测及市场细分. 武汉体育学院学报. 2024(01): 1-12+29 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 马宇轩,王会宗. 基于拓展计划行为理论的电子竞技用户行为SEM模型构建及分析. 广州体育学院学报. 2024(01): 25-33+90 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 叶治东,王乐鹏. 国际学生中医药文化接触对其中医导向行为的影响研究. 亚太传统医药. 2024(05): 6-13 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 李成. 社会生态学理论视域下青少年运动健康行为评估指标研究. 体育师友. 2024(03): 33-38+55 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 谢福杨,邓朝辉. 女大学生锻炼意图影响因素分析——基于拓展计划行为理论. 福建技术师范学院学报. 2024(05): 132-140 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 孙晓岚,周巧珠,李占肖,柴会荣. 首次发病的老年缺血性脑卒中患者锻炼行为感知与锻炼行为执行意向、社会支持的现况研究. 现代临床护理. 2023(01): 9-15 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 王阳. 基于计划行为理论的普通学校教师融合教育行为意向研究. 中国特殊教育. 2023(03): 19-28 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 李康,周少林,马国才. 大学生运动动机对其锻炼行为的影响:实施意向与自我认同感的链式中介效应. 湖北体育科技. 2023(03): 193-198 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 郑东和,陈垣鑫. Z世代体育类短视频信息接触对锻炼意向的影响研究. 福建体育科技. 2023(02): 12-17 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 张茹,陈一萍,淮盼盼,乔彩虹,杨辉. 基于时限性自我调节理论的执行意向策略对中青年脑卒中病人康复锻炼行为执行意向的影响. 护理研究. 2023(18): 3368-3373 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 白茜. 以体育人视角下青少年体育运动习惯养成策略研究. 南京体育学院学报. 2023(07): 69-73 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 方雪薇,岳建军. 校园移动干预技术对大学生体育锻炼行为影响的实证研究——基于计划行为理论的解释与干预. 山东体育科技. 2023(05): 64-71 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 谢懿. 性别视角下青少年体育意识的代际传递——基于家庭支持氛围的中介效应的分析. 现代基础教育研究. 2023(03): 152-158 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 袁梦阳,朱银峰,傅佳青. 基于计划行为理论的大学生垃圾分类行为初探. 广西教育学院学报. 2023(04): 186-190 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 王丽娟. 5~18岁儿童青少年24 h活动研究:现状、影响因素与健康效应. 中国体育科技. 2022(01): 46-56 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. 梁金辉. 北京2022年冬奥会举办地青少年参与冰雪运动的驱动因素研究——基于TPB框架. 中国体育科技. 2022(04): 10-16 .  百度学术
百度学术
18. 魏星. 基于TPB理论探讨高血压伴冠心病患者家属参与心脏康复训练的影响因素. 心血管病防治知识. 2022(13): 88-91 .  百度学术
百度学术
19. 彭忠金. 基于计划行为理论的高校大学生体育锻炼行为意向研究——以哈尔滨体育学院为例. 当代体育科技. 2022(21): 195-198 .  百度学术
百度学术
20. 陈锦,刘萍,刘木子. 长期使用健身App大学生的体育锻炼影响因素研究. 体育科技文献通报. 2022(08): 125-127 .  百度学术
百度学术
21. 昂晨,杨喆,王静,关志逊,薛岚. 高原徒步登山中急性高原病的风险因素及预防建议——基于贡嘎山徒步登山路线的实证研究. 体育科学. 2022(07): 85-97 .  百度学术
百度学术
22. 朱良昊. 大学生体育锻炼意向与习惯强度的关系:行动计划、锻炼行为的多重中介作用. 湖北体育科技. 2022(11): 974-981 .  百度学术
百度学术
23. 周玉兰,王丽娟. 不同学段体育课中教师因素对学生身体活动水平的影响. 体育学刊. 2021(02): 118-124 .  百度学术
百度学术
24. 梁金辉,周传斌. 2022年北京冬奥会举办地青少年支持冬奥行为意向影响机理研究. 山东体育学院学报. 2021(04): 61-68 .  百度学术
百度学术
25. 宫淑文,贾霞,都新萍. 基于计划行为理论视角的带教模式在血液内科实习护生中的应用. 中华现代护理杂志. 2021(29): 3981-3985 .  百度学术
百度学术
26. 王佳卉,王玉秀. 大学生体测增值关注与锻炼坚持性的关系——内部动机与执行意向的链式中介作用. 体育学刊. 2021(06): 111-118 .  百度学术
百度学术
27. 邱小燕,唐敏,许姮. 基于计划行为理论的整合模式在妊娠期高血压疾病患者中的应用. 齐鲁护理杂志. 2021(23): 1-4 .  百度学术
百度学术
28. 王瑜. 培养初中生良好体育行为习惯的对策研究. 文体用品与科技. 2021(24): 131-132 .  百度学术
百度学术
29. 陈晨. 青少年的体育锻炼与体育消费. 中国青年研究. 2020(07): 14-21 .  百度学术
百度学术
30. 葛小雨,黄谦,荀阳,刘天彧,李帅然. 利用体育类APP进行体育锻炼的行为意向影响研究. 西安体育学院学报. 2020(05): 558-567 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(50)




 下载:
下载: