Influence of Different Sensory Disturbance on the Balance ControlAbility of Freestyle Skiing Athletes
-
摘要:目的 探讨躯体感觉、视觉对自由式滑雪空中技巧运动员(以下简称“运动员”)平衡控制能力的影响。方法 利用平衡盘和Metitur平衡分析系统,对20名(男、女各10名)运动员进行平衡控制能力的抗干扰测试。选取人体压力中心的侧方向平均移动速度Vx和前后方向平均移动速度Vy为测试指标。采用2(性别:男、女)×2(站立方式:左腿和右腿站立)×4(感觉条件:睁眼、闭眼、睁眼+平衡盘、闭眼+平衡盘)三因素重复测量方差分析进行统计检验。结果 ① 各因素的主效应均存在显著差异(P < 0.05),站立方式×感觉条件的交互作用在Vy上有显著差异(P < 0.05);②各种感觉条件均造成平衡控制能力显著降低(P < 0.01),降低程度为,闭眼+平衡盘>睁眼+平衡盘>闭眼>睁眼;③躯体感觉对侧方向稳定性Vx的干扰显著大于前后方向稳定性Vy(P < 0.01);④躯体感觉对男子右腿的干扰显著大于左腿(P < 0.05);⑤双重感觉干扰显著大于单一感觉干扰(P < 0.01)。结论 躯体感觉和视觉干扰均会降低运动员的平衡控制能力,其中躯体感觉干扰更为严重。Abstract:Objective To explore the influence of somatosensory and visual sense on balance control ability of freestyle skiing aerial athletes.Methods Using the Balance Disc and Finland Metitur Postural Balance Measuring System, 20 athletes(10 males and 10 females)were tested for anti-interference of balance control ability; the lateral stability Vx, the front and back stability Vy of the human body pressure center were selected as the test indicators. According to gender(male, female), standing pattern(left leg or right leg)and sensory conditions(4 kinds of conditions), the 3 factors, the three-way ANOVA(2×2×4)with repeated measures was used to test the influence of different factors on the difference of balance control abilities.Results ① There was a significant difference in the main effect of each factor(P < 0.05), and a significant difference in the interaction between standing pattern and sensory condition(P < 0.05); ② All kinds of sensory conditions significantly reduced the ability of balance control(P < 0.01), with the reduction degree of closed eyes with balance disc > open eyes with balance disc > closed eyes > open eyes. ③ The somatosensory interference with side stability Vx interference was significantly higher than that of the front and back stability Vy (P < 0.01); ④ The somatosensory interference of the right leg was significantly greater than that of the left leg (P < 0.05). ⑤ Double sensory interference was significantly higher than that of single sensory interference(P < 0.01).Conclusion The interference of somatosensory and vision seriously reduces the balance control ability of athletes, and the somatosensory is more serious.
-
Keywords:
- freestyle skiing /
- aerial skill /
- athlete /
- postural control /
- balance control ability /
- somatosensory /
- visual sense
-
自由式滑雪空中技巧是一项高度危险的技巧类项目,技巧类项目均由以技术为核心,以难、美为灵魂的多元动作结构组成[1-2]。该项目是我国唯一获得冬奥会冠军的雪上项目,其动作由助滑、起跳、空中翻转和落地等4个阶段组成。欲高质量地完成动作,自由式滑雪空中技巧运动员(以下简称“运动员”)须具备较强的平衡控制能力[3]。特别是在空中翻转和落地阶段,3周台动作bdFFF的腾空高度为16~17 m,要求运动员在3 s内完成3周空翻和4周转体,并稳定站立于38°的着陆坡后再平稳滑出,着陆坡上雪的厚度为60 cm。着陆坡为不稳定的支撑面,其对运动员的躯体感觉产生极大干扰。研究[4]表明,下肢的躯体反馈是触发和调节人类自动平衡校正的关键反应。运动员在完成空中翻转时存在闭眼的现象,视觉也受到干扰,因此,躯体感觉和视觉对运动员的平衡控制能力具有较大影响。左腿或右腿在前后或侧方向的平衡控制能力下降均会造成落地动作失败甚至运动员下肢或腰部损伤,因此,运动员的躯体感觉和视觉干扰对平衡控制能力具有重要影响。
躯体感觉(本体感觉、触觉)[5-8]、视觉[9-10]和前庭功能[11-12]受到干扰时,因感觉系统提供的不精确(不对称)信息而导致人体平衡控制能力下降。例如,人站立在行驶的车上,视觉输入的信息是人体的相对运动,与躯体感觉和前庭输入的人体相对运动信息发生冲突。为解决其冲突,中枢神经系统(central nervous system,CNS)采取忽略视觉输入、依赖躯体感觉和前庭输入提供信息的方法[13],致使人体质心(center of mass,COM)分布发生变化,姿势稳定性降低。姿势的摆动为多种感觉系统融合和重新分配的动态过程。Oie等[13-14]指出,多种感觉信息以一种非线性的方式输入神经系统,每种感觉系统均对平衡控制起到了独特作用;Peterka[15]进一步指出,在安静姿势下躯体感觉和视觉对姿势稳定性的影响较大;Stoffregen等[16]认为,感觉信息是由各种感觉相互作用产生的,所有感觉系统都为提高控制和知觉的特异性提供信息。不同感觉系统之间的融合、各项目运动员躯体感觉和视觉的训练方法[17]等仍处于探索阶段。冬季运动项目在我国的兴起及2022年北京冬奥会的筹办将进一步加快我国冰雪项目的发展与竞技体育水平的提高。自由式滑雪空中技巧是我国的雪上重点优势项目,对运动员的平衡控制能力提出了更高的要求,然而,躯体感觉和视觉分别对运动员平衡控制能力的影响程度如何?这是科研人员和体能教练员亟待解决的问题。
综上所述,研究躯体感觉和视觉对运动员平衡控制能力的影响,探讨不同感觉对其平衡控制能力的影响,不同性别及不同支撑腿之间是否存在差异,分析不同感觉条件、性别和支撑腿等因素是否与平衡控制存在交互作用,以期发现运动员平衡控制的特征和存在的不足,可为制订专项平衡控制训练计划、提高运动员的平衡控制能力提供科学依据。基于此,本文假设:H1,当躯体感觉和视觉受到干扰时,男女运动员在侧方向和前后方向的平衡控制能力下降;H2,运动员躯体感觉干扰对平衡控制能力的影响大于视觉干扰;H3,当躯体感觉和视觉受到干扰时,其对不同性别运动员平衡控制能力的影响存在一定差异。
1. 研究对象与方法
1.1 研究对象与试验仪器
以国家自由式滑雪空中技巧队20名健康运动员为被试(男、女各10人)。男子:国际级运动健将6人、运动健将4人,年龄(25.35±2.69)岁,身高(174.25±2.51)cm,体质量(68.13±3.51)kg,训练年限(14.14±2.62)a。女子:国际级运动健将5人、运动健将5人,年龄(26.67±2.71)岁,身高(164.35±2.32)cm,体质量(55.76±4.18)kg,训练年限(14.78±3.13)a。向20名被试介绍试验方案并签署知情同意书,且通过了沈阳体育学院伦理委员会审核。试验前被试须熟悉整个试验要求和流程。
试验采用Metitur Good Balance 300平衡分析系统(芬兰产),Thera-Band平衡盘(美国产,质量45 g,直径22 cm),YB-150气压表(上海自动化仪表四厂产),ISOMED 2000等速肌力测试系统(德国产)等仪器。
1.2 试验方案
(1)排除优势腿因素的影响。Yoshida等[18]对前庭功能紊乱患者的研究显示,优势腿的姿势控制能力显著大于非优势腿。在试验前期对被试开展询问和调查,未发现有左右侧不对称现象;于测试前1周对被试进行左右侧膝关节和髋关节的等速肌力测试,选取向心模式下的慢速60(°)/s和快速240(°)/s,结果显示,被试双侧屈肌群和伸肌群之间均无显著差异,表明被试双侧肌力基本对称。
(2)选取感觉系统最大强度干扰条件。结合项目特征,视觉干扰选取闭眼模式;躯体感觉干扰选取气压为121.013×105 Pa的平衡盘。在沈阳体育学院的国家体育总局冬季运动项目技术诊断与机能评定重点实验室进行测试。
(3)确定试验流程。为防止疲劳,测试当天为无训练的调整日;为排除环境干扰,实验室内只有被试和主试,测试时间为20 s,试验过程中双眼与显示器屏幕同高,站立姿势、双臂下垂,单脚以平衡仪前后中线为准站立(图 1)。按照右腿睁眼、左腿睁眼、右腿闭眼、左腿闭眼、右腿睁眼+平衡盘、左腿睁眼+平衡盘、右腿闭眼+平衡盘、左腿闭眼+平衡盘等8种姿势顺序对被试进行测试。每种方式间休息120 s,在规定试验中出现非支撑侧脚触碰仪器时为动作失败,保证每种姿势获得3次测试结果。
1.3 指标参数评估
使用专业平衡仪测量压力中心(center of pressure,COP)的量化结果,移动速度为移动距离对移动时间的微分,平均移动速度为20 s测试中每秒移动速度之和的平均值。COP平均速度的具体计算公式如下:
$$ {\rm{COP}}平均速度= \left( {\frac{1}{t}} \right)\sum\limits_{i = 0}^n {\left| {co{p_{i + 1}} - co{p_i}} \right|} $$ (1) 式(1)中,t表示总测试时间,n表示第n秒,i表示起始秒数,copi表示第i秒压力中心的速度。选取COP在侧方向的平均移动速度指标Vx,代表侧方向稳定性;COP在前后方向的平均移动速度指标Vy,代表前后方向稳定性。为探讨各种感觉条件干扰对Vx和Vy的影响,分别计算出每名被试在视觉、躯体感觉和躯体感觉+视觉的Vx/Vy值,再对3种感觉干扰的Vx/Vy值进行统计学检验。
1.4 数理统计与分析
首先对每人次测试的3次各组数据求平均值以减少数据的变异,然后利用SPSS 22.0软件中的一般线性模型(general linear model)进行统计学处理。采用2(性别:男、女)×2(站立方式:左腿和右腿站立)×4(感觉条件:睁眼、闭眼、睁眼+平衡盘、闭眼+平衡盘)三因素重复测量方差分析(mixed three-factors repetitive measurement ANOVA),其中性别为被试间变量,站立方式和感觉条件为被试内变量,组成2×2×4的三因素混合试验设计,分析各因素的主效应和交互作用。当交互作用显著时需进行简单效应分析,使用Mauchly球型检验评估方差齐性,当不满足Huynh-Feldt条件时,采用Greenhouse-Geisser法矫正自由度的结果,采用LSD法进行事后比较。P < 0.05表示存在显著性差异,P < 0.01表示存在非常显著性差异。
2. 研究结果
2.1 各因素的交互作用和主效应结果
结果显示,数据符合正态分布、方差齐性、协方差具有等同性。主体内效应的Mauchly球型检验发现,在感觉条件变量中,因变量Vx和Vy的显著性结果均为P < 0.05,需对自由度进行矫正,选取其矫正后的结果。偏η2为主效应对模型的效应量(effect size),按照Cohen的评价标准,偏η2≥0.8为高效应,0.8>偏η2≥0.5为中等效应,0.5>偏η2≥0.2为低效应。
如表 1所示,站立方式×感觉条件在Vx上交互作用不显著,在Vy上交互作用显著,F(1.638)=4.850,P=0.039,偏η2=0.458,需进行简单效应分析;其他因素交互作用均不显著。简单效应分析结果显示,站立方式×感觉条件的交互作用对Vy的影响为:感觉条件在右腿站立水平时F(8,58)=976.342,P < 0.001,效应显著;在左腿站立水平时F(8,58)=651.451,P < 0.001,效应也显著。表明感觉条件对Vy的贡献受右腿和左腿站立方式的共同影响,但受右腿的影响更大。
表 1 站立方式、感觉条件和性别等因素的交互作用结果Table 1. Tests of Interaction Effects among different standing patterns, sensory conditions and genders自变量 因变量 自由度 F P 偏η2 站立方式×感觉条件 Vx 1.776 2.778 0.084 0.217 Vy 1.638 4.850 0.039* 0.458 性别×感觉条件 Vx 1.973 0.652 0.530 0.061 Vy 1.539 0.463 0.556 0.044 性别×站立方式 Vx 1.000 1.413 0.262 0.124 Vy 1.000 0.477 0.506 0.045 性别×站立方式×感觉条件 Vx 1.776 0.972 0.374 0.089 Vy 1.347 1.850 0.132 0.188 注:*表示P<0.05。 站立方式对不同感觉条件的简单效应分析结果显示:在睁眼条件下,F(1,8)=0.221,P=0.876,效应不显著;在闭眼条件下,F(1,8)=6.317,P=0.021,效应显著;在睁眼+平衡盘条件下,F(1,8)=2.032,P=0.337,效应不显著;在闭眼+平衡盘条件下,F(1,8)=12.412,P < 0.001,效应显著。这表明站立方式对Vy的贡献受睁眼、睁眼+平衡盘条件的影响不显著,受闭眼、闭眼+平衡盘条件的影响显著,但受闭眼+平衡盘条件的影响大于闭眼条件。
如表 2所示:感觉条件、站立方式和性别因素的主效应在Vx和Vy上均具有显著差异;各因素对Vx和Vy的贡献大小为,感觉条件>站立方式>性别。
表 2 性别、感觉条件和站立方式等因素的主效应分析结果Table 2. The results of main effect analyses among different genders, sensory conditions and standing patterns自变量 因变量 自由度 F P 偏η2 性别 Vx 1.000 4.603 0.037* 0.315 Vy 1.000 3.850 0.044* 0.278 感觉条件 Vx 1.973 1 187.660 0.000** 0.992 Vy 1.539 1 401.319 0.000** 0.993 站立方式 Vx 1.000 6.312 0.032* 0.521 Vy 1.000 8.676 0.014** 0.626 注:*表示P<0.05,**表示P<0.01。 2.2 不同感觉条件、站立方式和性别对平衡控制能力的影响
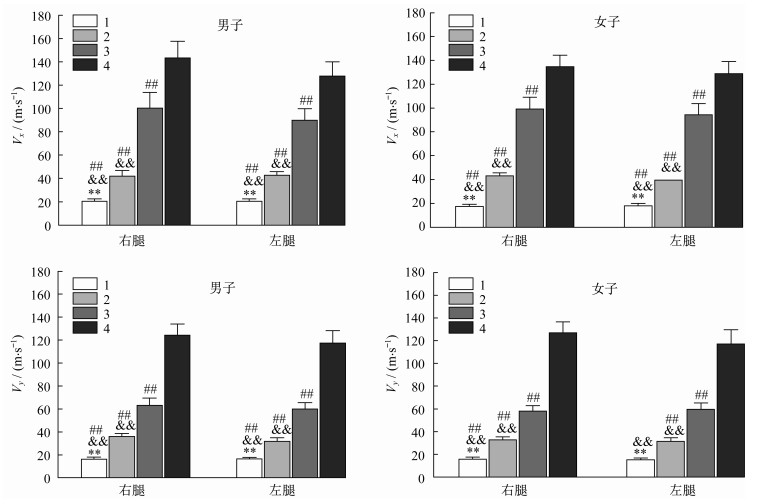
因感觉条件、站立方式和性别的主效应存在显著差异,需对各因素进行多重比较。图 2为运动员受视觉、躯体感觉和视觉+躯体感觉3种条件最大干扰时,Vx和Vy方向单腿平衡控制的结果。3种条件均显著大于无感觉条件干扰的结果;3种条件之间,躯体感觉干扰显著大于视觉干扰,躯体感觉+视觉的双重干扰显著大于躯体感觉干扰。
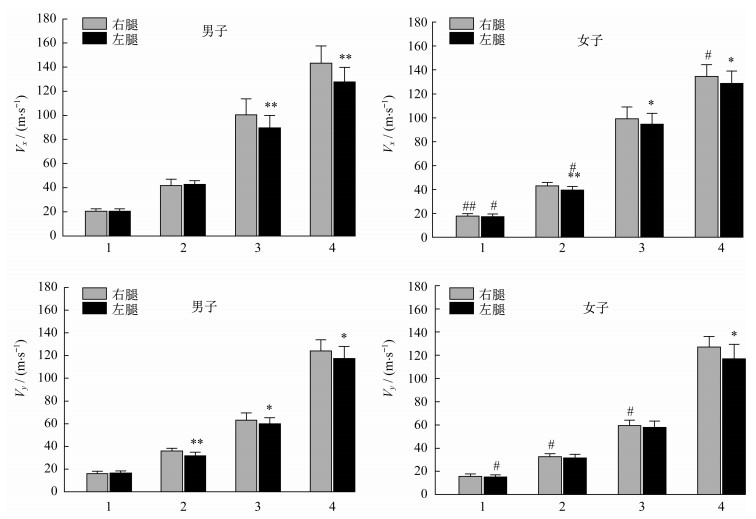
如图 3所示:在同种感觉条件和性别下的Vx指标上,男、女子在受躯体感觉和躯体感觉+视觉干扰时右腿显著大于左腿,而女子在受视觉干扰时右腿也显著大于左腿;在Vy指标上,男、女子在受躯体感觉+视觉干扰时右腿显著大于左腿,而男子在受视觉和躯体感觉干扰时右腿也显著大于左腿。
在同种感觉条件和站立方式下的Vx指标上,女子在左右腿的无干扰、左腿的视觉干扰和右腿的视觉+躯体感觉干扰条件下显著小于男子;在Vy指标上,女子在左腿的无干扰、右腿的视觉干扰和右腿的躯体感觉干扰条件下显著小于男子。
2.3 不同感觉条件对各方向平衡控制能力的影响
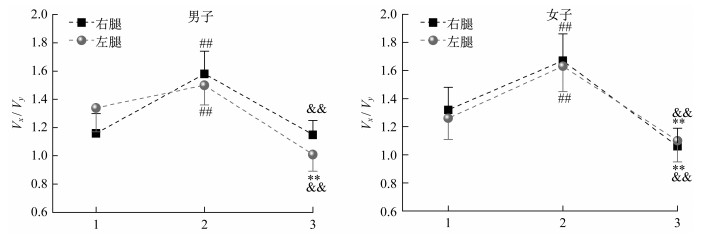
结果如图 4所示,Vx/Vy值均大于1,表明3种感觉干扰对侧方向稳定性的影响大于前后方向。
在Vx/Vy值上,躯体感觉干扰在男女运动员左、右腿均显著大于视觉干扰和视觉+躯体感觉双重干扰;在视觉干扰和视觉+躯体感觉干扰方面,除男子右腿外,均为视觉干扰显著大于视觉+躯体感觉双重干扰,即躯体感觉>视觉>视觉+躯体感觉,表明躯体感觉对侧方向稳定性影响最大,也表明视觉+躯体感觉双重干扰对Vy的影响程度更大。
3. 讨论
3.1 躯体感觉和视觉干扰对平衡控制能力的影响
当躯体感觉受到干扰时,运动员的平衡控制能力大幅下降,与无干扰相比,在侧方向和前后方向稳定性上COP移动速度平均值分别增大了3.75倍和2.79倍。目前,下肢本体感受器(如高尔基腱器、肌梭或足底皮肤感受器)的反馈被认为是触发和调节人类自动平衡校正的关键反应[19],踝关节的肌肉控制被认为是提供触发信号后产生平衡修正姿势的重要因素,胫骨前肌和腓肠肌是维持人体站立姿势的重要肌肉,在姿势摆动阶段,比目鱼肌的牵张反射在抑制跖屈方面起到了关键的拉伸作用[20]。Kim等[21]指出,足底的触觉和踝关节的本体感觉对平衡控制能力起到决定性作用,在不稳定的平衡盘上,因无法获得准确的躯体感觉信息导致姿势不稳。相关研究[22]表明:当人体感觉失调或支撑面受到干扰时,姿势控制以踝关节修正为主;随着干扰程度的增加,躯干和髋部提供主要的触发信号进行姿势修正,其平衡校正时间延迟。Bloem等[4]进一步指出,站立在硬地板上的老年人因踝关节肌力下降而被动地采取髋部调节策略,以期达到降低姿势控制的目的。由此可知,髋部调节进一步降低了姿势稳定性,因其在处理外部或内部干扰时反馈时间较慢,运动员较多地重视姿势干扰的前馈,在神经肌肉控制系统中,CNS依据躯体感觉和认知信号的输入产生经验性保护指令,在无反馈条件下直接将指令发送到效应器[23]。所以,运动员在助滑和起跳阶段均需保持直立姿势,平衡控制能力一旦下降将影响动作质量甚至导致动作失败。
此外,视觉对平衡控制能力的影响也非常显著,这与前人研究[24]结果一致。视觉提供头部的空间位置和运动信息[25],Jeka等[26]研究表明,与有视觉的被试相比,盲人的平衡控制能力较差,表现出更多的头部运动,并发现侧方向稳定性上头部运动对平衡控制能力的影响为躯干的2倍。目前已证实,使用手机可降低平衡控制能力,因看信息促使视觉固定在屏幕上而降低了视觉输入的准确性,从而导致平衡控制能力下降[27]。笔者还发现,受最大干扰时躯体感觉对平衡控制能力的影响显著大于视觉,侧方向和前后方向稳定性分别为视觉的2.36倍和1.95倍。当躯体感觉和视觉同时受干扰时,平衡控制受到的影响更大。躯体感觉为CNS提供以支撑面为参考的身体位置和运动信息。研究[28]表明,视觉、前庭功能、躯体感觉输入均会影响人体的平衡控制能力,当感觉系统受到干扰时,躯体感觉起主要作用。Horak等[29]也认为,在稳定的支撑面上,姿势控制对躯体感觉的依赖比视觉多,与本文结果一致。Dietz等[30]进一步指出,当支撑面水平移动时,相对于躯体感觉,视觉输入的作用非常小,并指出肌肉对视觉的干扰信号反应潜伏期较长,激活时间为200 ms左右,而对躯体感觉的反应较短,在80~100 ms时激活。Asadi[19]指出,单腿站立时,踝关节不稳的患者因躯体感觉信息减少而更多地依赖视觉、前庭功能甚至听觉等多个感官反馈的方式代偿,这种感觉输入的变化可改变人体的运动策略(如采取减少自由度提高身体刚度),同时降低了姿势的稳定性。因此,躯体感觉对运动员平衡控制能力具有重要影响。
3.2 不同性别、站立方式对平衡控制能力的影响
在视觉和躯体感觉受到干扰时,女运动员在部分方面抗干扰能力优于男运动员。研究指出,与男性相比,成年女性在下肢关节活动度(range of motion,ROM)[31]、刚度和肌肉激活[32]等生物力学参数以及下肢神经肌肉控制上存在差异,在急性和慢性非接触性前交叉韧带(anterior cruciate ligament,ACL)损伤方面为男性的2~3倍[33],因而女性需要更大的下肢刚度和肌肉激活以降低损伤的风险[34]。Chen等[35]指出:女性对随意姿势运动的知觉敏感性低于男性。研究[36]表明,当人体首次尝试特定方向的COP偏移时,女性对安全极限的灵敏性感知较差。脑成像研究[37]表明,女性对避免危险情况等行为起决定性作用的杏仁核-纹状体居多、对痛感的敏感程度较强,其稳定性较男性差。Li等[20]指出,踝关节周围肌肉、韧带的刚度与姿势的稳定性之间存在高度相关性。Kaminishi等[38]利用仿真技术建立站立姿势肌肉模型,结果显示肌肉刚度下降导致姿势稳定性降低。另外,推测这也与性别之间的生理学(如激素、神经肌肉)差异以及重心高低、支撑面大小有关。
当躯体感觉受到严重干扰或全部受损时,人体直立下的平衡控制能力显著下降。平衡校正以激活躯干和髋关节肌肉为主[39],髋部调节为多节控制策略,即被动地采用增加能量耗散的方式达到增加人体刚度的补偿策略[13]。躯干的刚度和惯性导致在髋关节形成铰链或重叠的多方向运动,通过臀中肌和脊柱周围激活的肌肉拉伸和卸载响应维持躯干的姿势,达到控制侧方向和前后方向稳定性的作用[19],此情况对左、右腿的对称性提出了更高的要求。笔者还发现,在不同站立方式上,男女运动员均不同程度地存在左腿平衡控制能力显著强于右腿的现象,其中男运动员在前后方向稳定性更为明显,分析其原因,推测与其长期的转体动作训练有关。自由式滑雪空中技巧的技术动作由空翻和转体构成,如男子3周台动作bdFFF由3周的空翻和4周的转体组成,在起跳阶段均以左腿为转轴左侧加速旋转,落地阶段以左腿为转轴减速制动,特别在落地阶段,需在高速下落的同时站立于60 cm厚度积雪的斜坡上[40],左腿耗散较大剩余角动量的同时还需完成对落地姿势的控制。Peterka [15]指出,在平衡控制过程中站立姿势产生较小COM偏离时,将导致重力转矩加速远离身体位置。运动员通过10多年的专项技术训练,左腿抵抗感觉系统干扰的能力强于右腿,而女运动员以难度相对较低的2周台训练为主,其常规动作为2周空翻和2周转体,因此,其影响小于男运动员。
各种干扰条件对不同方向的影响均为侧方向稳定性差于前后方向,其中躯体感觉对侧方向稳定性的影响更大,这与单腿站立时各方向的支撑面大小、关节的结构特征、肌肉的配布规律等因素有关。研究[41]表明,在人体站立时,侧方向稳定性的肌肉激活方式以近端向远端传递的反应模式为主,即髋关节和躯干周围的肌肉激活早于踝关节,而前后方向稳定性以远端向近端传递的模式为主,且近端传递模式对平衡控制能力的影响大于远端。当人体支撑面不稳时,其平衡控制以近端的髋部调节策略为主,进一步降低了姿势的稳定性[42]。侧方向稳定性降低会对运动员的起跳技术和落地动作产生较大影响,特别是落地时侧向滑行将造成落地失败甚至下肢损伤[43]。
另外,前后方向稳定性受感觉条件×站立方式的交互作用影响,站立方式中的右腿以及感觉条件中的躯体感觉干扰对平衡控制能力的影响较大,前后方向稳定性降低,在出台阶段影响人体体位角度的改变,造成空翻速度的增大或减小。速度过大会导致落地时出现背部或臀部触雪而影响落地得分,速度过小会造成落地时空翻动作未完成而被迫采用前滚翻的危险动作。因此,前后方向稳定性不足,轻者导致动作失败,严重者将导致运动员受伤。Zarei等[25]对聋哑学生感觉训练的结果表明,采取无视觉输入和干扰支撑面同步训练方法可显著提高踝关节(背屈和跖屈)的本体感觉,该训练方法和手段对自由式滑雪空中技巧项目具有一定的借鉴意义。
3.3 双重和单一感觉干扰对平衡控制能力的影响
在最大干扰时,躯体感觉+视觉>躯体感觉>视觉>无感觉干扰。Teng等[9]研究发现,成年人的躯体感觉对平衡控制能力的影响最大,其次是视觉,这与本文研究结果一致。研究[44]指出,当支撑面快速移动引起COP失衡时,神经系统优先依赖躯体感觉输入控制身体移动。在成年人神经系统损伤时,前期的恢复阶段对视觉的依赖较大,当动作熟练后,对视觉的依赖减少,而对躯体感觉的依赖增加[6]。Diener等[45]对躯体感觉的研究进一步显示,成年人站立时躯体感觉对短暂的干扰起主要作用。Jayakaran等[24]的多种感觉对姿势稳定性的研究发现,斜视儿童视觉、前庭功能和躯体感觉权重分别为28%、17%、55%,对照组分别为32%、21%、47%,并指出斜视儿童对躯体感觉的依赖性强于对照组。Foudriat等[46]进一步指出,76%的3~6岁儿童对视觉依赖性较低,躯体感觉对平衡控制能力的影响占据主导地位。结合前期研究发现,因测试方法和干扰程度不同,在对躯体感觉的最大干扰方面研究的最终结果也不尽相同,但站立姿势下躯体感觉的影响大于视觉和前庭功能,这一结果目前已被较多研究者所证实。
双重干扰大于躯体感觉或视觉的单一干扰,与Negahban等[47]提出的当视觉和支撑面同时被干扰后,进一步增加了姿势的不稳定性这一结果相一致。Jayakaran等[24]对帕金森病人同时给予视觉和触觉反馈发现,相对于单一反馈,双重反馈对姿势稳定性更有利,进一步证明了双重干扰的影响更大。Akdeniz等[48]研究视觉和躯体感觉双重干扰、视觉和前庭功能双重干扰对平衡控制能力的影响发现,视觉和躯体感觉的双重干扰对平衡控制能力的影响更大。由此可知,在落地过程中当运动员躯体感觉和视觉均受干扰时,前庭输入占主导。可推测此种双重干扰对平衡控制能力的影响巨大,运动员完成动作的难度巨大,一旦平衡控制不稳,损伤随时可能发生。从这一角度也进一步认识到自由式滑雪空中技巧为高危运动项目,因此,运动员应加强视觉和躯体感觉双重干扰训练。
影响平衡控制能力的因素很多。大量研究结果显示,躯干肌肉疲劳[49]、听力障碍[25]、体质虚弱[50-51]等因素均能导致平衡控制能力下降。Holmes等[52]发现,呼吸与姿势摆动之间具有一定的非线性耦合关系,不同的呼吸方式也会影响平衡控制能力。Kang等[53]指出,每天电脑工作6 h以上也会影响人体的平衡控制能力。另外,关节紧急制动、损伤、手术等原因[54-55]均可造成感觉通路的神经受损而导致本体感觉功能障碍。
3.4 局限性
本文仍存在一定的局限性:①受试验条件限制,很难将干扰条件控制在同一水平;②受项目特征和国家队人数的限制,样本量相对较少;③在对躯体感觉的干扰条件方面,与实际环境条件仍具有一定的差距,如躯体感觉的平衡盘与实际着陆坡上60 cm厚度的雪质之间的刚度、阻尼、弹性系数等条件不同;④运动员在实际运动中采用多种姿势控制平衡,而本文仅采用了站立姿势,未来研究仍需完善。
4. 结论
① 不同条件的干扰程度为:躯体感觉+视觉双重干扰最大,躯体感觉干扰大于视觉干扰;躯体感觉干扰对侧方向稳定性的影响大于前后方向,运动员侧方向稳定性受双重感觉干扰和右腿的共同交互影响较大。②女子的单腿抗干扰能力强于男子,左腿强于右腿;当躯体感觉受到干扰时,再增加视觉干扰,对前后方向稳定性的影响大于侧方向。③双重感觉干扰对平衡控制能力的影响较大,且大于单一干扰的叠加,建议加强躯体(特别是男子右腿)感觉和视觉双重感觉的抗干扰训练。
-
表 1 站立方式、感觉条件和性别等因素的交互作用结果
Table 1 Tests of Interaction Effects among different standing patterns, sensory conditions and genders
自变量 因变量 自由度 F P 偏η2 站立方式×感觉条件 Vx 1.776 2.778 0.084 0.217 Vy 1.638 4.850 0.039* 0.458 性别×感觉条件 Vx 1.973 0.652 0.530 0.061 Vy 1.539 0.463 0.556 0.044 性别×站立方式 Vx 1.000 1.413 0.262 0.124 Vy 1.000 0.477 0.506 0.045 性别×站立方式×感觉条件 Vx 1.776 0.972 0.374 0.089 Vy 1.347 1.850 0.132 0.188 注:*表示P<0.05。 表 2 性别、感觉条件和站立方式等因素的主效应分析结果
Table 2 The results of main effect analyses among different genders, sensory conditions and standing patterns
自变量 因变量 自由度 F P 偏η2 性别 Vx 1.000 4.603 0.037* 0.315 Vy 1.000 3.850 0.044* 0.278 感觉条件 Vx 1.973 1 187.660 0.000** 0.992 Vy 1.539 1 401.319 0.000** 0.993 站立方式 Vx 1.000 6.312 0.032* 0.521 Vy 1.000 8.676 0.014** 0.626 注:*表示P<0.05,**表示P<0.01。 -
[1] 刘兴.高水平蹦床运动员选材的基本方法与特征研究[J].沈阳体育学院学报, 2020, 39(3):63-71 [2] 杜熙茹, 谭强.新奥运周期女子平衡木成套动作编排趋势研究[J].西安体育学院学报, 2019, 36(3):350-355 [3] 娄彦涛, 郝卫亚, 王振.自由式滑雪空中技巧运动员平衡控制能力研究[J].中国体育科技, 2016, 52(4):113-126 [4] BLOEM B R, ALLUM J H, CARPENTER M G, et al. Is lower leg proprioception essential for triggering human automatic postural responses?[J]. Experimental Brain Resarch, 2000, 130(3):375-391 http://europepmc.org/abstract/med/10706436
[5] KASAHARA S, SAITO H, ANJIKI T, et al. The effect of aging on vertical postural control during the forward and backward shift of the center of pressure[J]. Gait & Posture, 2015, 42(4):448-454 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0966636215007857
[6] SCHELLDORFER S, ERNST M J, RAST F M, et al. Low back pain and postural control, effects of task difficulty on centre of pressure and spinal kinematics[J]. Gait & Posture, 2015, 41(1):112-118
[7] SWINKELS L M, SCHIE H T, VELING H, et al. The selfgenerated full body illusion is accompanied by impaired detection of somatosensory stimuli[J].Acta Psychologica, 2020, 203:102987 doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2019.102987
[8] 吴加弘, 袁陆军, 袁空军.FIFA 11+练习对高校足球运动员膝踝关节肌力、本体感觉和动态平衡的研究[J].天津体育学院学报, 2019, 34(4):344-349 [9] TENG Y L, CHEN C L, LOU S Z, et al. Postural stability of patients with schizophrenia during challenging sensory conditions:Implication of sensory integration for postural control[J].PLoS One, 2016, 11(6):e0158219
[10] HOLDEN S, BOREHAM C, DOHERTY C, et al. A longitudinal investigation into the progression of dynamic postural stability performance in adolescents[J]. Gait & Posture, 2016, 48:171-176 doi: 10.1016/j.gaitpost.2016.04.019
[11] YEH J R, LO M T, CHANG F L, et al. Complexity of human postural control in subjects with unilateral peripheral vestibular hypofunction[J]. Gait & Posture, 2014, 40(4):581-586
[12] QUITSCHA R M, FUKUNAGA J Y, GANANCA M M, et al. Evaluation of postural control in unilateral vestibular hypofunction[J].Brazilian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology, 2014, 80(4):339-345
[13] OIE K S, KIEMEL T, JEKA J J. Multisensory fusion:Simultaneous re-weighting of vision and touch for the control of human posture[J]. Cognitive Brain Research, 2002, 14(14):164-176 doi: 10.1016/S0926-6410(02)00071-X
[14] OIE K S, KIEMEL T, JEKA J J. Human multisensory fusion of vision and touch:Detecting non-linearity with small changes in the sensory environment[J]. Neuroscience Letters, 2001, 315(3):113-116
[15] PETERKA R J.Sensorimotor integration in human postural control[J].Neurophysiology, 2002, 88(3):1097-1118
[16] STOFFREGEN T A, RICCIO G E. An ecological theory of orientation and the vestibular system[J]. Psychological Review, 1988, 95(1):3-14
[17] 卢卓.中韩速度滑冰短距离项目专项体能训练体系的对比研究[J].沈阳体育学院学报, 2019, 38(3):115-120 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0560.2019.03.019 [18] YOSHIDA T, TANAKA T, YAMAMOTO M, et al. Dominant foot could affect the postural control in vestibular neuritis perceived by dynamic body balance[J]. Gait & Posture, 2018, 59:157-161
[19] ASADI A. Plyometric type neuromuscular exercise is a treatment to postural control deficits of volleyball players:A case study[J]. Revista Andaluza De Medicina Del Deporte, 2016, 9(2):75-79 doi: 10.1016/j.ramd.2016.02.004
[20] LI L, ZHANG S Q, DOBSON J. The contribution of small and large sensory afferents to postural control in patients with peripheral neuropathy[J]. Journal of Sport and Health Science, 2019, 8:218-227
[21] KIM M, LEE H H, LEE J. Does isolated somatosensory impairment affect the balance and ambulation of patients with supratentorial stroke after the acute phase?[J]. Journal of Clinical Neuroscience, 2020, 74:109-114
[22] SIMPSON J D, RENDOS N K, STEWART E M, et al. Bilateral spatiotemporal postural control impairments are present in participants with chronic ankle instability[J]. Physical Therapy in Sport, 2019, 39:1-7
[23] KNOX M F, CHIPCHASE L S, SCHABRUN S M, et al. Anticipatory and compensatory postural adjustments in people with low back pain:A systematic review and metaanalysis[J]. Spine Journal, 2018, 18(10):1934-1949 doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2018.06.008
[24] JAYAKARAN P, MITCHELL L, JOHNSON G M. Peripheral sensory information and postural control in children with strabismus[J]. Gait & Posture, 2018, 65:197-202
[25] ZAREI H, NORSATEH A A. The effect of 8 weeks proprioception training without visual input on single-limb standing balance time in deaf students:A randomized controlled trial[J]. Journal of Bodywork Movement Therapies, 2020, 24(2):63-68
[26] JEKA J J, EASTON R D, BENTZEN B L, et al. Haptic cues for orientation and postural control in sighted and blind individuals[J]. Perception & Psychophysics, 1996, 58(3):409-423
[27] LIM J, CHANG S H, LEE J, et al. Effects of smartphone texting on the visual perception and dynamic walking stability[J]. Journal of Exercise Rehabilitation, 2017, 13(1):48-54 doi: 10.12965/jer.1732920.460
[28] DIENER H C, DICHGANS J, GUSCHLBAUER B, et al. The significance of proprioception onpostural stabilization as assessed by ischemia[J]. Brain Research, 1984, 296(1):103-109
[29] HORAK F B, EARHART G M, DIETZ V.Postural responses to combinations of head and body displacements:Vestibularsomatosensory interactions[J]. Experimental Brain Resarch, 2001, 141(3):410-414
[30] DIETZ V, SCHUBERT M, DISCHER M, et al. Influence of visuoproprioceptive mismatch on postural adjustments[J].Gait & Posture, 1994, 2(2):147-155 doi: 10.1016/0966-6362(94)90002-7
[31] HOLDEN S, BOREHAM C, DOHERTY C, et al. Clinical assessment of countermovement jump landing kinematics in early adolescence:Sex differences and normative values[J]. Clinical Biomechanics, 2015, 30:469-474
[32] IGUCHI J, TATEUCHI H, TANIGUCHI M, et al. The effect of sex and fatigue on lower limb kinematics, kinetics, and muscle activity during unanticipated side-step cutting[J].Knee Surgery Sports Traumatology Arthroscopy, 2014, 22(1):41-48
[33] WALDEN M, HAGGLUND M, WERNE J, et al. The epidemiology of anterior cruciate ligament injury in football (soccer):A review of the literature from a genderrelated perspective[J]. Knee Surgery Sports Traumatology Arthroscopy, 2011, 19(1):3-10 doi: 10.1007/s00167-010-1172-7
[34] MYER G D, FORD K R, STASI S L, et al. High knee abduction moments are common risk factors for patellofemoral pain(PFP)and anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury in girls:Is PFP itself a predictor for subsequent ACL injury?[J]. British Journal of Sports Medicine, 2015, 49(2):118-122 doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2013-092536
[35] CHEN Z, HAN J, WADDINGTON G, et al. Somatosensory perception sensitivity in voluntary postural sway movements:Age gender and sway effect magnitudes[J]. Experimental Gerontology, 2019, 122:53-59
[36] TOPRAK C S, OZER K D. Immediate effects of kinesio taping on pain and postural stability in patients with chronic low back pain[J].Journal of Bodywork Movement Therapies, 2019, 23(1):206-210
[37] ENGMAN J, LINNMAN C, VAN DIJK K R A, et al. Amygdala subnuclei resting-state functional connectivity sex and estrogen differences[J]. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 2016, 63:34-42
[38] KAMINISHI K, JIANG P, CHIBA R, et al.Postural control of a musculoskeletal model against multidirectional support surface translations[J]. PLoS One, 2019, 14(3):e0212613 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0212613
[39] KAMINISHIA K, CHIBA R, TAKAKUSAKI K, et al. Investigation of the effect of tonus on the change in postural control strategy using musculoskeletal simulation[J]. Gait & Posture, 2020, 76:298-304
[40] 娄彦涛, 王振, 郝卫亚.自由式滑雪空中技巧运动员模拟落地动作的下肢生物力学特征[J].中国运动医学杂志, 2016, 35(4):333-338 [41] CASTILHO A A, LUNA N M, LUIS M, et al.The influence of anthropometric factors on postural balance:The relationship between body composition and posturographic measurements in young adults[J]. Clinics, 2012, 67(12):1433-1441 doi: 10.6061/clinics/2012(12)14
[42] HOLDEN S, BOREHAM C, DOHERTY C, et al. A longitudinal investigation into the progression of dynamic postural stability performance in adolescents[J]. Gait & Posture, 2016, 48:171-176
[43] 卞军义, 薄欣颖, 郑仕斌.青少年游泳核心稳定性训练模式的探索与实证研究[J].西安体育学院学报, 2019, 36(2):246-252 [44] BOVE M, FENOGGIO C, TACCHINO A, et al. Interaction between vision and neck proprioception in the control of stance[J]. Neuroscience, 2009, 164(4):1601-1608
[45] DIENER H C, DICHGANS J, GUSCHLBAUER B, et al. The significance of proprioception on postural stabilization as assessed by ischemia[J].Brain Research, 1984, 296(1):103-109
[46] FOUDRIAT B A, FABIO R P, ANDERSON J H. Sensory organization of balance responses in children 3-6 years of age:A normative study with diagnostic implications[J]. International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology, 1993, 27(3):255-271
[47] NEGAHBAN H, SALAVATI M, MAZAHERI M, et al. Non-linear dynamical features of center of pressure extracted by recurrence quantification analysis in people with unilateral anterior cruciate ligament injury[J].Gait & Posture, 2010, 31(4):450-455
[48] AKDENIZ S, HEPGULER S, OZTURK C, et al. The relation between vitamin D and postural balance according to clinicaltests and tetrax posturography[J]. Journal of Physical Therapy Science, 2016, 28(4):1272-1277 doi: 10.1589/jpts.28.1272
[49] GHAMKHAR L, KAHLAEE A H. The effect of trunk muscle fatigue on postural control of upright stance:A systematic review[J]. Gait & Posture, 2019, 72:167-174 doi: 10.1016/j.gaitpost.2019.06.010
[50] 杨光, 沈媛媛, 梁思雨, 等.传统与现代虚弱老年人康复性运动处方设计与应用研究[J].沈阳体育学院学报, 2019, 38(4):92-98 [51] 王锋, 吴雪萍.感觉统合力量训练对老年人双任务动态平衡能力的影响[J].天津体育学院学报, 2019, 34(4):337-343 [52] HOLMES M L, MANOR B, HSIEH W H, et al. Tai Chi training reduced coupling between respiration and postural control[J]. Neuroscience Letters, 2016, 610:60-65 doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2015.10.053
[53] KANG J H, YOUNG P R, JIN L S, et al. The effect of the forward head posture on postural balance in long time computer based worker[J]. Annals Rehabilitation Medicine, 2012, 36(1):98-104 doi: 10.5535/arm.2012.36.1.98
[54] OZCAN K B, KAHRAMAN T, KALEMCI O, et al. Gender differences in postural control in people with nonspecific chronic low back pain[J]. Gait & Posture, 2018, 64:147-151
[55] 王爱文, 罗冬梅, 毋江波.鞋前掌楔形结构对羽毛球前场蹬跨步动作的生物力学影响[J].西安体育学院学报, 2019, 36(1):88-94 -
期刊类型引用(10)
1. 廖鸣宇,朱国庆,陈文佳,邱永晨,刘博. 不同感觉条件干扰对慢性非特异性腰痛消防员姿势控制能力的影响. 中国体育科技. 2024(03): 39-50 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 任卫华,高天,刘珂,李艳辉,娄彦涛. 本体感觉训练对定向运动员平衡能力、下肢力量以及识图专项技能的影响. 上海体育大学学报. 2024(12): 92-104 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 李亚伟,冯甜,周志雄. 复合轴旋转影响青少年冰雪运动员空间认知的ERP研究. 武汉体育学院学报. 2024(12): 77-83 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 赖丽丽,刘孝斐,邹群海. 长期跑步对大学生身体静态姿势稳定性影响研究. 体育科技文献通报. 2023(03): 158-162 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 徐梦桃,范祎,李泽鹏,娄彦涛. 科技助力自由式滑雪空中技巧女子运动员备战北京冬奥会周期的应用. 沈阳体育学院学报. 2022(05): 1-7 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 邱招义,尹一全,叶茂盛,孟庆军,邱森. 提升我国冬奥项目运动员专项能力的夏季化训练措施. 北京体育大学学报. 2021(03): 2-16 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 贾宗洋. 自由式滑雪空中技巧运动员平衡控制能力分析. 体育视野. 2021(06): 68-69 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 王硕,陈子桐,史衍,任振华,穆小舟,侯富涛,翟宇. 姿势控制训练对冰球运动员加速能力和滑行能力影响的实验研究. 河北体育学院学报. 2021(05): 35-40 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 刘正宏. 表象训练在射击业余训练与比赛中的作用. 中国体育教练员. 2021(03): 77-78 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 朱瑞婷. 竞技太极拳对自由式滑雪跨项选材的影响研究. 中华武术. 2021(12): 79-81 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)





 下载:
下载: