Expression and Application of Differential Protein in Urine for Male Athletes after Exercises with Different Intensities
-
摘要:目的 应用蛋白质组学技术,检测不同强度跑台运动后运动员尿液中差异蛋白的表达,探讨不同强度运动后尿液蛋白质组分的变化特点及其与人体免疫功能、运动性疲劳的关联性,为运动生化监控提供科学依据和实用方法。方法 应用双向电泳法,分析8名男性运动员分别以55%、75%、85%、95%最大摄氧量(VO2max)的强度进行跑台运动后其尿液蛋白质组图谱的差异性表达,选取运动后差异蛋白表达量上调≥5倍且具有重复性的蛋白点,用基质辅助激光解吸电离串联飞行时间质谱法(MALDI-TOF-TOF-MS)进行质谱分析。结果 经双向电泳确定的4种不同强度运动后尿液蛋白质组的差异性蛋白点共275个,其中,下调蛋白点85个,上调蛋白点190个;对差异蛋白表达量上调≥5倍且具有重复性的蛋白点进行质谱鉴定,共鉴定出29种蛋白,包括载脂蛋白、锌-α2-糖蛋白、免疫球蛋白、白蛋白、补体蛋白C3、甘露糖结合凝集素相关蛋白19、维生素D结合蛋白等;生物信息学分析结果表明,这些差异蛋白的功能主要与机体免疫调节和炎症反应的生物过程关系密切。结论 蛋白质组学分析可以更好地诠释运动后尿液蛋白质组分的变化,其中差异表达的载脂蛋白、锌-α2-糖蛋白与运动后能量代谢有关,免疫球蛋白、白蛋白、补体蛋白C3、甘露糖结合凝集素相关蛋白19、维生素D结合蛋白与运动后免疫调节有关,这为考察运动训练后人体免疫功能和疲劳状态的变化提供了理论依据与应用方法。Abstract:Objectives Proteomics principles and techniques were used to detect and screen out the expression of differential proteins in urine of athletes after exercise with different intensities; the changes of urinary protein components and the correlations among the changes, human immune function and exercise fatigue were investigated, which provided scientific basis and practical methods for exercise biochemical monitoring.Methods Based on Two-dimensional electrophoresis(2-DE), differential expression of urine proteome of 8 male athletes was analyzed after exercises of 55%, 75%, 85% and 95% VO2max intensity, respectively; the protein expressed levels which were up-regulated by at least 5-fold and with repeatability were screened and analyzed using matrixassisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry.Results A total of 275 differentially expressed protein points was detected after different exercise intensities, down-regulated protein points were 85 and up-regulated 190.After screening expressed levels which were up-regulated by at least 5-fold protein, a total of 29 protein was identified, showing a close relation to the biological processes of immune regulation and inflammatory response.Conclusions Proteomics better explains what happens to the urine proteome after different exercises, among which, apolipoprotein and zinc-α2-glycoprotein are related to lipid metabolism after exercise; immunoglobulin, albumin, complement component C3, mannose-binding lectin protein 19 and Vitamin D binding protein are related to immune regulation. The theoretical basis and application method are provided for the evaluation of the effects of exercise training on human immune function and fatigue.
-
Keywords:
- exercise /
- urine /
- proteome /
- two-dimensional electrophoresis /
- mass spectrometry /
- male athlete
-
尿蛋白的组成和数量已成为评价运动后负荷强度简便、实用的指标[1],但现有评价指标多采用尿白蛋白、β2微球蛋白、尿总蛋白等几个常见蛋白[2-4],对于尿液蛋白质组整体的变化研究甚少;随着科技的发展,蛋白质组学技术无疑成为诠释尿蛋白携带信息最有效的方法[5]。双向电泳(2-DE)法和质谱(MS)技术的联合可以系统性地分析和鉴定尿液中的所有蛋白质分子并研究其生物学功能。目前尿液蛋白质组研究在医学领域已取得一定成果,尿液蛋白质组分的变化成为多种疾病发生、发展的生物标志物[6-9]。在体育科学领域,有关尿液蛋白质组学的研究报道较少。本文从蛋白质组学整体的角度,分析4种不同强度运动后运动员尿液蛋白质组图谱差异性表达的变化,探讨运动后尿液蛋白质组分变化与人体免疫功能、疲劳程度的关联性,有利于筛选尿液中对评定运动负荷及身体机能具有重要意义的标志性蛋白,为运动训练的科学监控提供实验依据和实用方法。
1. 研究对象与方法
1.1 研究对象
研究对象为广州体育学院运动训练专业学生,男性,均为国家二级运动员。首先对25名受试者进行最大摄氧量(VO2max)测试,其中16名受试者出现VO2max,从中筛选专业相同的8名受试者为正式研究对象,平均年龄、身高、体质量、心率、训练年限和VO2max分别为(21.6±2.4)岁、(175.8±4.2)cm、(64.0±4.2)kg、(57.8±6.48)次/min、(4.8±1.3)a和(3 559±316.1)mL/min。受试者对本文研究均知情,并自愿签署知情同意书。
1.2 运动方案
根据受试者VO2max测试结果,确定每名受试者运动强度分别达55%VO2max、75%VO2max、85%VO2max、95%VO2max时对应的跑台速度(表 1),4个强度的跑台运动总时间一致,具体方案见表 2,每个强度间测试至少间隔2 d,测试期间除正常上课外均不进行其他形式运动。
表 1 每名受试者4种强度对应的速度Table 1. Speeds corresponding to four intensities for per subject编号 55%VO2max 75%VO2max 85%VO2max 95%VO2max 速度/(km·h-1) 坡度/(°) 距离/km 速度/(km·h-1) 坡度/(°) 距离/km 速度/(km·h-1) 坡度/(°) 距离/km 速度/(km·h-1) 坡度/(°) 距离/km 1 11.0 0 7.3 13.7 1 9.1 14.8 2 9.9 16.7 2 11.2 2 9.2 0 6.1 11.5 1 7.7 13.0 2 8.7 15.5 2 10.4 3 10.0 0 6.7 14.0 1 9.3 16.0 2 10.7 18.0 2 12.0 4 9.4 0 6.3 12.2 1 8.2 14.2 2 9.5 15.4 2 10.3 5 9.8 0 6.5 12.2 1 8.2 13.8 2 9.2 15.4 2 10.3 6 9.0 0 6.0 11.0 1 7.4 15.0 2 10.0 17.0 2 11.4 7 9.0 0 6.0 11.0 1 7.4 14.0 2 9.3 16.0 2 10.7 8 10.0 0 6.7 12.0 1 8.0 14.0 2 9.3 15.4 2 10.7 表 2 不同运动强度方案Table 2. The exercise programme of different intensities组别 运动组数 每组运动时间/min 组间休息时间/min 坡度/(°) 55%VO2max 2 20 5 0 75%VO2max 4 10 5 1 85%VO2max 5 8 5 2 95%VO2max 8 5 5 2 1.3 样品采集
尿液采集:按检测操作要求收集8名受试者运动前(晨起)、运动后15 min的尿液,分别存储于50 mL的无菌离心管。为避免蛋白酶解,每组采集运动前(晨起)、运动后的尿液后,各组分别取8名受试者10 mL的尿液进行混合,加入蛋白酶抑制剂PMSF(1 mmol/L),-80℃冻存作为待测尿液蛋白质组分指标的尿样;剩余尿样直接用于尿蛋白的测试。
血液采集与测试:采集运动前、运动后即刻肘静脉血5 mL,测定血尿素(blood urea,BU)、血清肌酸激酶(creatine kinase,CK)。采集指尖血测定运动前后血乳酸(blood lactic acid,BLA)。
1.4 评测指标及方法
采用基质辅助激光解吸电离串联飞行时间质谱法(MALDI-TOF-TOF-MS)进行尿液蛋白质组学分析;采用德国血乳酸盐分析仪(型号:EKF-C-Line GP)测试血乳酸;采用试剂盒(试剂盒均购于南京建成生物工程研究所)检测血尿素和血清肌酸激酶;应用双缩脲法测定尿总蛋白(TP),仪器为S22PC分光光度计,试剂均购于南京建成生物工程研究所;以每分钟排泄量(μg/min)表示尿蛋白含量。
《主观体力感觉等级表》(RPE)为6~20分的等级量表(6分表明根本不费力,20分表明精疲力竭)。受试者在实验前后应用量表进行测评。
1.5 蛋白提取
复融后的样品于4 ℃下以3 345g离心20 min,分离上清,分别用孔径0.45 μm和0.22 μm的滤膜过滤一次,加入丙酮过夜。沉淀的蛋白在4℃下以13 780g离心20 min,弃去上清,-80 ℃冻存备用。用600 μL Tris饱和酚将蛋白团块充分裂解后,加入600 μL提取液,在4 ℃下以13 780g离心20 min,吸出上层酚相,移至EP管;重复操作1次。最后加入含5倍酚体积的沉淀液使蛋白沉淀,-20 ℃下保存过夜。沉淀蛋白团块在4 ℃下以13 780g离心20 min,去上清;同时加入1 mL甲醇溶液,反复吹打洗涤蛋白,以13 780g离心20 min,去上清;重复操作1次。晾干后-80 ℃冻存备用。
1.6 双向电泳
1.6.1 固相等点聚焦
干燥后的蛋白质经再水化液(RB)溶解和Bradford法定量后,加入上样液(质量分数为1%的二硫苏糖醇,DTT)、质量分数为1%的固相pH梯度干胶条(IPG Buffer)、1×溴酚蓝(BPB)、RB至460 μL,上样量120 μg。胶条经泡胀过夜(10~12 h)后放入等电聚焦盘中。等电聚焦程序:300 V 0.5 h、700 V 0.5 h、1 500 V 1.5 h、9 000 V 3 h、9 000 V 5 h,总电压为64 kV。
1.6.2 聚丙烯酰胺凝胶垂直电泳(SDS-PAGE)
将平衡后的胶条移至质量分数为12.5%的凝胶上端,用质量分数为0.8%的低熔点琼脂糖和质量分数为1.5%的普通琼脂糖封闭。在2-DE实验过程中,先在2 W/gel的功率条件下跑45 min,后功率加大至17 W/gel,直至溴酚蓝指示剂达到底部边缘时停止电泳。17 W/gel功率电泳用时共计4.5 h。
1.7 凝胶染色与图像分析
采用考马斯亮蓝G-250染色法按照固定、漂洗、考染、漂洗的步骤进行凝胶染色。采用UMAX Powerlook 1100凝聚图像扫描仪进行胶图扫描,利用Image Master 2D platinum 5.0软件对扫描的图像进行背景消减、斑点检测、蛋白匹配等系统分析,比较图谱蛋白斑点差异。
1.8 质谱分析和生物信息学分析
选取差异蛋白斑点中重复性好、表达清晰、界限明显者进行蛋白酶胶内酶切。利用德国布鲁克(Bruker Dalton)Autoflex Speed™ MALDI-TOF-TOF-MS质谱仪进行质谱分析。利用BioTools(Bruker Dalton)软件搜索美国国家生物技术信息中心(National Center for Biotechnology Information,NCBI)数据库,找出匹配的蛋白质,使用Metascape(http://metascape.org)对其进行生物信息学分析;选择对应的物种“H.sapinens”,得到靶点的基因本体(GO)分类富集分析结果(Metascape数据库更新时间为2019年8月19日)。
1.9 数理统计
所有数据利用SPSS 19.0软件进行统计,计量资料以均数±标准差($ \overline{x} $±s)表示,采用独立样本配对t检验进行统计分析,统计学显著水平为P<0.05和P<0.01。
2. 研究结果
2.1 不同强度运动前后身体机能指标的变化
4种不同强度运动后,8名男运动员血尿素、血乳酸、血清肌酸激酶、尿总蛋白与运动前比较均显著升高(P<0.05),RPE评分在各强度运动后也显著升高(P<0.05)(表 3)。
表 3 不同强度运动前后身体机能有关指标的变化Table 3. Changes of indicators related to body function after exercise of different intensities组别 血尿素/(mol·L-1) 血乳酸/(mol·L-1) 血清肌酸激酶/(U·L-1) 尿总蛋白/ (μg·min-1) RPE评分 运动前 运动后 运动前 运动后 运动前 运动后 运动前 运动后 运动前 运动后 55%VO2max 4.11±1.08 5.75±0.82** 1.58±0.57 4.98±1.94* 126.24±58.70 213.15±98.84* 2.34±2.85 6.63±4.57* 9.48±1.18 12.31±2.18* 75%VO2max 4.13±1.12 6.50±0.53** 1.35±0.26 10.21±3.79** 124.14±56.70 312.81±184.23* 4.81±6.64 35.78±29.78* 9.16±1.32 14.41±2.33* 85%VO2max 4.08±1.06 7.21±1.47** 1.65±0.53 12.23±3.54** 119.22±48.70 404.70±201.84** 3.58±3.15 91.56±42.54** 9.05±1.41 18.23±2.06** 95%VO2max 4.01±1.02 6.87±1.11** 1.49±0.47 13.12±4.49** 120.21±58.70 434.25±267.11** 2.72±1.84 69.71±28.78** 9.21±1.23 17.72±2.57** 注:n=8;显著性检测为各强度运动前和运动后比较,*表示P<0.05,**表示P<0.01;RPE表示《主观体力感觉等级表》。 2.2 不同强度运动前后尿液蛋白质2-DE图谱特征
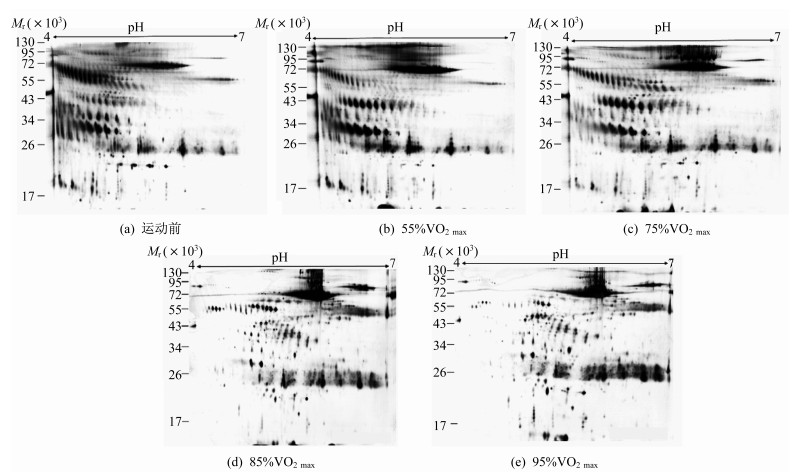
在相同条件下对运动前(晨尿)及4种不同强度跑台运动后尿液进行2-DE图谱(图 1)鉴定,结果可见:运动前(晨尿)蛋白质相对分子质量主要集中在20 000~80 000;运动后蛋白质相对分子质量主要集中在20 000~95 000,大于95 000和小于20 000的蛋白质分子很少,且各点染色深浅和面积有一定差异,表明蛋白质含量不同。运动前(晨起)蛋白质的pH值多集中在4.0~5.0;运动后蛋白质的pH值多集中在4.5~6.0。运动前(晨起)尿液蛋白质2-DE图谱左侧斑点较多,右侧斑点偏少,且极碱性蛋白很少,说明尿液中酸性蛋白质多于碱性蛋白质;运动后斑点的颜色和位置发生不同程度的变化,随着强度的不断增加,右侧斑点较多且颜色和面积逐渐增加。对运动员在不同强度跑台运动前(晨起)、运动后的尿液蛋白质2-DE图谱进行软件分析、人工确认并比较,发现不同强度跑台运动前(晨起)与运动后的尿蛋白差异表达明显,集中表现在2-DE图谱斑点的增减、面积大小及染色的深浅方面。
2.3 不同强度运动前后尿液蛋白质2-DE图谱差异性表达
经软件检测运动前(晨起)和不同强度运动后尿液蛋白质2-DE图谱,共鉴定出差异蛋白275个,下调蛋白点65个,消失蛋白点20个,上调蛋白点127个,新增蛋白点63个,具体情况见表 4。差异蛋白的数量与运动强度成正比;随着强度的升高差异蛋白的相对分子质量逐渐增加,且碱性蛋白数量逐渐增多。
表 4 不同强度运动前后差异蛋白表达量上调/下调蛋白点数目分布Table 4. The number and change folds of differentially expressed proteins after exercise of different intensities组别 下调蛋白点数量 上调蛋白点数量 <2倍 ≥2倍 ≥5倍 ≥10倍 消失 <2倍 ≥2倍 ≥5倍 ≥10倍 新增 55%VO2max 5 5 0 0 5 7 17 6 0 0 75%VO2max 9 12 0 1 5 5 15 2 0 4 85%VO2max 0 4 2 4 1 6 12 10 8 24 95%VO2max 3 11 2 7 9 3 14 9 13 35 2.4 质谱鉴定结果
选择不同强度运动后差异蛋白表达量上调≥5倍且具有重复性的蛋白点,利用MALDI-TOF-TOF-MS质谱仪对这些差异性蛋白质斑点进行检测,将获得的肽谱和肽段氨基酸在NCBI数据库中检索,最终鉴定出29种差异蛋白(表 5)。其中很多蛋白的数据库搜索结果为同一种蛋白,在很大程度上可能与蛋白翻译、修饰以及蛋白降解等多种情况致使同一个蛋白的不同修饰类型或不同碎片出现在凝胶的不同位置有关。
表 5 不同强度运动后差异表达蛋白点质谱鉴定结果一览Table 5. Protein expression levels in the urine samples from athletes after exercise of different intensities identified by MALDI-TOF-TOF-MS组别 编号 NCBI登录号 蛋白名称(英文名称) 相对分子质量 等电点 55%
VO2max2-11 gi|343197759 免疫球蛋白κ链(immunoglobulin kappa chain) 24 352 6.99 2-20 gi|90108664 载脂蛋白A1(apolipoprotein A1) 28 061 5.27 2-24 gi|50513645 甘露糖结合凝集素相关蛋白19(MBL-associated protein 19) 19 531 5.44 75%
VO2max4-10 gi|4699583 锌-α2-糖蛋白(zinc-α2-glycoprotein) 31 854 5.7 4-17 gi|1633319 血管细胞黏附分子-1(vascular cell adhesion molecule-1) 22 149 4.93 4-20 gi|78101271 补体蛋白C3(complement component 3) 40 204 4.79 85%
VO2max6-4 gi|20810124 CD177蛋白(CD177 protein) 47 985 5.87 6-8 gi|114147359 免疫球蛋白重链(immunoglobulin heavy chain) 13 620 6.97 6-20 gi|18655424 维生素D结合蛋白(vitamin D binding protein) 52 780 5.17 6-21 gi|21730549 维生素D结合蛋白(vitamin D binding protein) 52 807 5.22 6-23 gi|58737017 前列腺酸性磷酸酶(prostatic acid phosphatase) 40 702 5.66 6-24 gi|55669910 白蛋白(albumin) 67 174 5.57 6-26 gi|31615330 甲状腺素结合前白蛋白(albumin complexed with thyroxine) 68 406 5.66 6-30 gi|11493459 白蛋白[albumin (PRO2619)] 58 513 5.96 6-31 gi|763431 白蛋白(albumin) 53 416 5.69 6-38 gi|17028367 凝溶胶蛋白(gelsolin) 31 052 4.85 6-39 gi|4699583 锌-α2-糖蛋白(zinc-α2-glycoprotein) 31 854 5.70 6-44 gi|119585669 激肽释放酶(kallikrein) 101 521 6.21 6-47 gi|168988718 白蛋白(albumin) 67 773 5.63 6-49 gi|229526 本-周蛋白(Ben-Jones protein) 23 779 8.75 6-50 gi|576259 淀粉样物质(amyloid) 23 358 6.12 6-57 gi|18953 前列腺特异抗原前体(prostate specific antigen precursor) 19 431 5.68 95%
VO2max8-5 gi|168988718 白蛋白(albumin) 67 773 5.63 8-6 gi|55669910 白蛋白(albumin) 67 174 5.57 8-7 gi|47124258 淀粉酶α1(amylase alpha 1) 56 859 8.82 8-9 gi|11493459 白蛋白[albumin(PRO2619)] 58 513 5.96 8-19 gi|169249224 免疫球蛋白重链保守α1(immunoglobulin heavy chain constant alpha 1) 19 738 4.94 8-24 gi|229601 免疫球蛋白G1(immunoglobulin G1) 49 801 8.8 8-25 gi|6980876 胰石蛋白(lithostathine) 16 522 5.32 8-37 gi|119626074 白蛋白(albumin) 48 568 5.97 8-46 gi|58176763 锌-α2-糖蛋白(zinc-α2-glycoprotein) 32 354 5.71 8-53 gi|7770217 白蛋白[albumin (PRO2675)] 33 466 6.14 8-58 gi|119592329 激肽释放酶3(kallikrein 3) 24 056 6.82 8-59 gi|343197759 免疫球蛋白κ链(immunoglobulin kappa chain) 24 352 6.99 组别 编号 预期值 匹配肽段 相对分子质量(实验) 相对分子质量(计算) 序列覆盖率/% 分数 变化倍数 55%
VO2max2-11 1.50×10-8 5 1 916.922 8 1 916.951 3 35 132 ↑6.20 2-20 2.40×10-20 13 1 225.540 2 1 225.536 4 46 250 ↑5.62 2-24 9.70×10-29 8 986.504 8 986.497 4 42 334 ↑8.57 75%
VO2max4-10 6.10×10-14 4 2 402.176 3 2 402.201 9 29 186 ↑9.35 4-17 3.90×10-17 7 1 206.603 7 1 206.624 4 42 218 ↑9.47 4-20 3.90×10-9 4 1 249.620 4 1 249.615 9 16 138 New 85%
VO2max6-4 1.20×10-9 7 3 034.515 2 3 034.460 7 21 143 New 6-8 4.90×10-6 6 1 880.977 4 1 880.995 6 89 107 New 6-20 1.90×10-19 7 1 528.766 7 1 528.777 3 19 241 New 6-21 6.10×10-18 7 1 528.766 7 1 528.777 3 19 226 ↑12.9 6-23 1.50×10-11 5 880.519 1 880.517 1 14 162 New 6-24 9.70×10-17 17 1 148.633 7 1 148.607 7 27 214 New 6-26 3.10×10-17 17 1 286.676 9 1 286.677 2 35 219 New 6-30 7.70×10-11 10 1 212.611 7 1 212.625 1 25 155 ↑5.4 6-31 2.40×10-14 7 2 649.251 0 2 649.256 7 12 190 ↑6.38 6-38 1.20×10-9 3 2 885.559 9 2 885.425 4 44 143 New 6-39 1.20×10-25 13 2 402.229 8 2 402.201 9 43 303 New 6-44 7.70×10-7 11 2 232.108 0 2 232.095 9 5 115 ↑48.54 6-47 2.40×10-17 14 1 225.577 1 1 225.597 9 21 220 New 6-49 2.20×10-4 3 1 944.979 3 1 945.019 7 23 90 New 6-50 2.40×10-8 7 763.447 3 763.438 1 29 130 New 6-57 6.10×10-14 5 1 076.511 2 1 076.496 1 27 186 ↑62.04 95%
VO2max8-5 2.40×10-22 22 1 225.585 2 1 225.597 9 40 270 New 8-6 3.90×10-22 18 932.523 6 932.511 3 33 268 New 8-7 2.40×10-12 7 1 286.676 9 1 286.677 2 19 170 New 8-9 2.40×10-24 15 1 073.579 5 1 073.535 3 33 290 New 8-19 9.10×10-4 3 1 212.611 7 1 212.625 1 19 84 ↑16.28 8-24 5.50×10-5 6 1 698.737 2 1 698.755 9 16 96 New 8-25 8.30×10-4 3 1 266.568 4 1 266.566 3 26 85 ↑14.62 8-37 4.90×10-22 12 1 531.761 8 1 531.799 4 35 267 ↑26.25 8-46 1.50×10-24 11 973.477 5 973.480 4 35 292 ↑15.67 8-53 3.10×10-20 11 1 622.797 5 1 622.780 3 44 249 ↑182.35 8-58 7.70×10-21 9 1 076.497 9 1 076.496 1 39 255 ↑120.33 8-59 1.70×10-4 5 1 916.947 2 1 916.951 3 28 92 New 2.5 生物信息学分析结果
使用Metascape数据库对差异蛋白进行富集通路分析,发现运动后差异蛋白表达主要参与了2条GO富集通路,其功能与机体免疫调节、炎症反应的生物过程关系密切。
3. 讨论
随着运动科学的发展,各种生理生化指标常用于运动训练强度的监控,最常见的样本有血液和尿液,通过检测运动前后血液和尿液的某些成分变化,可全面了解机体各项机能指标的变化。已被训练实践广泛接受和采纳的血液指标有血清肌酸激酶、血乳酸、血尿素等;尿液指标有尿总蛋白、尿白蛋白等,可反馈运动员训练期间的身体机能、训练负荷、机体疲劳与恢复等信息。由于尿液具有取样方便,无损伤,易被运动员接受,且测定简易、快速,便于在运动中反复测定等优点,其成为运动训练监控的首选样本。
3.1 不同强度运动后尿液中差异蛋白表达变化
尿液中蛋白质种类和数量的变化可反映机体生理负荷刺激发生、发展及预后的各种信息,在运动应激过程中会引起肾小管和肾小球超微结构的改变和肾功能的下降[10];因此,可用尿蛋白评定训练量,特别是评定训练强度。Davis等[11]和Spahr等[12]用液相色谱串联质谱(LC-MS/MS)法分析了酶切后的混合尿样,共鉴定出124个尿液蛋白质,丰富了尿液蛋白质组分的信息。Samudrala等[13]为了监测运动效果,应用质子转移反应质谱技术检测尿蛋白,结果证明,尿液蛋白质组分可以较全面地反映运动员运动后机体代谢的基本状况,尿液蛋白质组分可以作为监测运动效果的生物标志物。本文分析不同强度运动前后尿液2-DE图谱,共鉴定差异蛋白275个,包含了多种上调、下调、消失和新增蛋白点,且差异蛋白的数量与运动强度成正比,其中55%VO2max组表达上调大于5倍的蛋白有免疫球蛋白、脂蛋白、甘露糖结合凝集素相关蛋白19(MBL-associated protein 19);而75%VO2max组表达上调大于5倍的蛋白有锌-α2-糖蛋白(zinc-α2-glycoprotein)、血管细胞黏附分子-1(vascular cell adhesion molecule-1),以及补体蛋白C3(complement component 3);85%VO2max组和95%VO2max组运动后蛋白上调倍数增加,数目增多,而且新增蛋白点增多,并出现多个免疫球蛋白、白蛋白及其碎片。由此可见,尿液蛋白质组蕴藏着丰富的运动应激后机体代谢信息,蛋白质组学技术可以更好地探究尿液蛋白质组的变化,更加全面、整体地监测运动训练。
3.2 不同强度运动后尿液蛋白表达与人体免疫功能
研究表明,运动过程中一定的运动强度会打破人体的免疫系统和内分泌之间的平衡,使免疫增强类信息物与免疫抑制类信息物之间发生失衡,机体免疫功能低下是影响运动训练及身体机能最常见的医学问题[14]。如果在运动训练过程中及早发现免疫功能的变化,可以尽早避免免疫功能降低,保障运动训练顺利进行。既往研究多数仅从某一方面反映机体免疫功能的变化情况,欠缺整体性和预警性,且需多次采血,指标测试比较繁杂。近几年来,蛋白质组学技术的检查与研究结果发现,由于运动项目不同、运动负荷不同以及运动员的身体机能状况的差异,所检测出的尿液蛋白质组分都不同,且具有显著性差异[15],可见尿液蛋白质组分可用于评定运动负荷及身体机能。徐国琴等[16]在探讨递增运动机体免疫力降低过程中发现,尿液中的白蛋白、锌-α2-糖蛋白、前列腺特异性抗原会显著增加,提示这些蛋白有待作为检测机体免疫功能的尿液指标。蔺海旗[17]探讨30 km耐力运动对尿液蛋白质组图谱差异性表达的影响,筛选出尿液中的前列腺特异性抗原、维生素D结合蛋白(vitamin D binding protein,DBP)、锌-α2-糖蛋白、本-周蛋白、β-肌动蛋白和白蛋白,作为有运动应激特点的尿液标志性蛋白质。综上所述,尿液蛋白质组分的变化更能全面、整体地反映机体的变化。
55%VO2max组运动后尿液中上调蛋白——甘露糖结合凝集素相关蛋白19属于凝集素家族,能激活和调节补体系统[18],提高机体的免疫功能,同时该强度组免疫球蛋白增多,也提示了免疫功能的增强。75%VO2max组运动后血管细胞黏附分子-1表达量上调,可能与运动刺激引发机体炎症反应有关;而补体蛋白C3作为运动后新增蛋白也证明了这一点,补体是激活3条补体调控途径的核心,广泛参与机体免疫和炎症反应,促进机体免疫增强。85%VO2max组运动后新增蛋白——DBP作为多基因簇家族的成员之一,具有多种生理功能,包括携带维生素D及其代谢产物的转运、脂肪酸的结合和肌动蛋白的清除[19]。DBP同时参与机体免疫反应,通过部分去糖化转变为巨噬细胞活化因子(MAF),即VD-MAF,随之刺激组织的巨噬细胞活化,并可介导巨噬细胞的凋亡。85%VO2max组运动后DBP还可以通过增强补体蛋白C5介导的信号传递而发挥免疫调节功能,与循环血中的中性粒细胞结合,刺激对靶细胞的化学趋化作用,向炎症部位集中免疫细胞。85%VO2max组运动后DBP作为新增点出现,可能与运动强度负荷有关。高强度间歇运动后代谢产物大量堆积以及局部出现炎症,致使细胞在应激条件下分泌的DBP增多,从而加强机体对代谢物的清除等功能,激活机体免疫功能,而新增的免疫球蛋白和表达量上升的激肽释放酶(kallikrein)也表明机体炎症增加。其中的激肽释放酶是参与生物体内重要炎症调节过程的蛋白[20],提示高强度间歇运动可能导致机体炎症增加及免疫功能降低。
目前,对DBP与运动的作用关系及其机制知之甚少,有待进一步深入研究与解析。95%VO2max组运动后胰石蛋白(lithostathine)和激肽释放酶表达量大幅度上调,胰石蛋白主要与胰腺炎症的发生、发展及转归密切相关[19]。激肽释放酶参与生物体内重要炎症调节过程[20],提示高强度运动导致机体炎症增加,而且85%VO2max组和95%VO2max组运动后尿液中白蛋白的残基、碎片较多,多数都为新增蛋白,这可能与高强度运动引起肾小球滤过膜通透性的改变以及白蛋白膜电荷的改变有关,这一结果与定量测试尿白蛋白结果趋势一致。在前人研究中也有类似状况:Kohler等[21]发现耐力运动后尿液蛋白质图谱中检测出白蛋白以及其碎片,认为是由于运动刺激机体所引起,但同时也不排除相应机体患有肾小球肾炎疾病;蔺海旗[17]发现30 km耐力跑后尿液2-DE图谱中白蛋白及其碎片增多,认为除了与运动刺激机体引起肾小球通透性增加有关以外,还与蛋白质自身在电泳中表达的位置有关。而本文发现白蛋白及其碎片只在95%VO2max组运动后出现,这可能是因为运动打破机体系统的内稳态,内稳态在被中低强度运动打破后快速在恢复期重建,而高强度运动使机体炎症增加、免疫功能下降,内稳态很难重建,因此导致白蛋白及其碎片大量排出。
3.3 不同强度运动后尿液蛋白表达与运动性疲劳
有训练就有疲劳,适当的疲劳产生可以刺激机体超代偿恢复,提高运动能力,过度运动疲劳会损害身体健康,严重影响运动能力。在运动过程中,生化指标的监测可以准确、真实地反映身体机能状况,其中血乳酸是常用于监测运动强度的指标。本文发现,55%VO2max组运动后即刻血乳酸值约为4.98 mol/L,75%VO2max组运动后即刻血乳酸值约为10.21 mol/L,85%VO2max组运动后即刻血乳酸值约为12.23 mol/L,而95%VO2max组运动后即刻血乳酸值约为13.12 mol/L。Poortmans[22]的研究结果表明,乳酸过度积累可引起尿液酸度增加,使尿蛋白排出量与血乳酸呈指数关系。本文也发现,尿蛋白的排出量随着强度的增加而增加。在正常生理状态下,当尿素的生成和排泄处于平衡状态时,血尿素水平保持相对稳定;当运动后血尿素比运动前增加值超过3 mmol/L时,或运动后超过8.33 mmol/L,则认为运动量大,运动员已达疲劳阈值[23]。运动前后血尿素差值随运动强度的增加而增加,85%VO2max组运动前后差值为3.11 mmol/L,表明受试者机体承受大负荷运动,机体接近疲劳阈值。研究[24]结果表明,运动后血清肌酸激酶浓度的变化可能与运动员运动能力有关,这可作为过度训练的监测指标。
本文发现,各强度运动后血清肌酸激酶浓度的变化均显著升高,75%VO2max组、85%VO2max组和95%VO2max组运动后血清肌酸激酶浓度均超过300 U/L,达到疲劳阈值,且浓度随着运动强度的增加而不断升高,表明随着运动强度的增加,受试者运动能力下降,疲劳感增强。RPE量表的结果也验证了疲劳感随着运动强度的升高而逐渐增加。运动员运动后尿蛋白的排出量与运动时间、以乳酸高的糖酵解供能为主的运动负荷密切相关。载脂蛋白A1(apolipoprotein A1)和锌-α2-糖蛋白是与能量代谢相关的蛋白,它们在降低体质量、减少脂肪含量及调控能量代谢方面具有重要作用[25]。锌-α2-糖蛋白可增加机体能量消耗和脂质利用,本文锌-α2-糖蛋白在75%VO2max组、85%VO2max组和95%VO2max组运动后表达量均上调,且85%VO2max组运动后为新增点出现,这很可能与高强度、长时间运动引起机体乳酸堆积,疲劳加深,为了满足运动时的能量需求,而引起锌-α2-糖蛋白合成率增加,促进脂肪分解,从而加强能量供应有关。Poortmans[22]研究发现,在剧烈运动后尿液中的锌-α2-糖蛋白排出量增强了20倍。同时,Kohler等[21]应用2-DE+MS技术在长距离耐力运动后的受试者尿液中也检测出锌-α2-糖蛋白,与本文结果一致,提示锌-α2-糖蛋白可能与运动疲劳有关,是否能作为运动疲劳监测蛋白还需深入研究。
综上所述,血液和尿液中的各种生化指标不仅可以评定运动强度,还可以很好地监控运动疲劳和机体免疫能力。血液指标需要反复多次取血,运动员较难接受;而本文应用2-DE法分析尿液蛋白质组分,2-DE法中第1向基于蛋白质的等电点不同用等电聚焦分离,第2向则按相对分子质量的不同用SDS-PAGE分离,能把复杂蛋白混合物中的蛋白质在二维平面上分开,可检测到4 ng蛋白;通过差异分析或其他方法找到感兴趣的蛋白后,就可以从凝胶中或膜上切取这些目标蛋白质进行质谱分析,其分辨率、灵敏度和精确度较高,能科学、准确地评定运动负荷。由于尿液获取简便易行,没有创伤性,可重复多次取样,不会引起受试者的抵触情绪,因此被广泛应用于运动负荷和身体机能的评定中。本文由于实验条件限制,未对不同强度运动后的差异性蛋白及机制进行深入探讨。在后续研究中,笔者将建立基因敲除小鼠的运动模型,进一步研究其差异蛋白的表达及作用机制。
4. 结论
(1)采用双向电泳质谱法(2DE-MALDI-TOF)成功分析出不同强度运动后尿蛋白多肽序列质谱图,更好地诠释了运动后尿液蛋白质组的变化,共鉴定差异蛋白275个,且差异蛋白变化与运动强度成正比。
(2)将差异蛋白中表达量上调≥5倍且具有重复性的蛋白点在NCBI数据库中进行检索,共检索出29种蛋白,通过生物信息学分析,发现差异蛋白主要与机体免疫调节和炎症反应关系密切,其中免疫球蛋白、白蛋白、补体蛋白、甘露糖结合凝集素相关蛋白19、DBP与运动后免疫调节有关。该发现可为运动训练监控提供新的理论依据与方法。
(3)载脂蛋白、锌-α2-糖蛋白与运动疲劳有关,可作为监测运动性疲劳的新指标。
-
表 1 每名受试者4种强度对应的速度
Table 1 Speeds corresponding to four intensities for per subject
编号 55%VO2max 75%VO2max 85%VO2max 95%VO2max 速度/(km·h-1) 坡度/(°) 距离/km 速度/(km·h-1) 坡度/(°) 距离/km 速度/(km·h-1) 坡度/(°) 距离/km 速度/(km·h-1) 坡度/(°) 距离/km 1 11.0 0 7.3 13.7 1 9.1 14.8 2 9.9 16.7 2 11.2 2 9.2 0 6.1 11.5 1 7.7 13.0 2 8.7 15.5 2 10.4 3 10.0 0 6.7 14.0 1 9.3 16.0 2 10.7 18.0 2 12.0 4 9.4 0 6.3 12.2 1 8.2 14.2 2 9.5 15.4 2 10.3 5 9.8 0 6.5 12.2 1 8.2 13.8 2 9.2 15.4 2 10.3 6 9.0 0 6.0 11.0 1 7.4 15.0 2 10.0 17.0 2 11.4 7 9.0 0 6.0 11.0 1 7.4 14.0 2 9.3 16.0 2 10.7 8 10.0 0 6.7 12.0 1 8.0 14.0 2 9.3 15.4 2 10.7 表 2 不同运动强度方案
Table 2 The exercise programme of different intensities
组别 运动组数 每组运动时间/min 组间休息时间/min 坡度/(°) 55%VO2max 2 20 5 0 75%VO2max 4 10 5 1 85%VO2max 5 8 5 2 95%VO2max 8 5 5 2 表 3 不同强度运动前后身体机能有关指标的变化
Table 3 Changes of indicators related to body function after exercise of different intensities
组别 血尿素/(mol·L-1) 血乳酸/(mol·L-1) 血清肌酸激酶/(U·L-1) 尿总蛋白/ (μg·min-1) RPE评分 运动前 运动后 运动前 运动后 运动前 运动后 运动前 运动后 运动前 运动后 55%VO2max 4.11±1.08 5.75±0.82** 1.58±0.57 4.98±1.94* 126.24±58.70 213.15±98.84* 2.34±2.85 6.63±4.57* 9.48±1.18 12.31±2.18* 75%VO2max 4.13±1.12 6.50±0.53** 1.35±0.26 10.21±3.79** 124.14±56.70 312.81±184.23* 4.81±6.64 35.78±29.78* 9.16±1.32 14.41±2.33* 85%VO2max 4.08±1.06 7.21±1.47** 1.65±0.53 12.23±3.54** 119.22±48.70 404.70±201.84** 3.58±3.15 91.56±42.54** 9.05±1.41 18.23±2.06** 95%VO2max 4.01±1.02 6.87±1.11** 1.49±0.47 13.12±4.49** 120.21±58.70 434.25±267.11** 2.72±1.84 69.71±28.78** 9.21±1.23 17.72±2.57** 注:n=8;显著性检测为各强度运动前和运动后比较,*表示P<0.05,**表示P<0.01;RPE表示《主观体力感觉等级表》。 表 4 不同强度运动前后差异蛋白表达量上调/下调蛋白点数目分布
Table 4 The number and change folds of differentially expressed proteins after exercise of different intensities
组别 下调蛋白点数量 上调蛋白点数量 <2倍 ≥2倍 ≥5倍 ≥10倍 消失 <2倍 ≥2倍 ≥5倍 ≥10倍 新增 55%VO2max 5 5 0 0 5 7 17 6 0 0 75%VO2max 9 12 0 1 5 5 15 2 0 4 85%VO2max 0 4 2 4 1 6 12 10 8 24 95%VO2max 3 11 2 7 9 3 14 9 13 35 表 5 不同强度运动后差异表达蛋白点质谱鉴定结果一览
Table 5 Protein expression levels in the urine samples from athletes after exercise of different intensities identified by MALDI-TOF-TOF-MS
组别 编号 NCBI登录号 蛋白名称(英文名称) 相对分子质量 等电点 55%
VO2max2-11 gi|343197759 免疫球蛋白κ链(immunoglobulin kappa chain) 24 352 6.99 2-20 gi|90108664 载脂蛋白A1(apolipoprotein A1) 28 061 5.27 2-24 gi|50513645 甘露糖结合凝集素相关蛋白19(MBL-associated protein 19) 19 531 5.44 75%
VO2max4-10 gi|4699583 锌-α2-糖蛋白(zinc-α2-glycoprotein) 31 854 5.7 4-17 gi|1633319 血管细胞黏附分子-1(vascular cell adhesion molecule-1) 22 149 4.93 4-20 gi|78101271 补体蛋白C3(complement component 3) 40 204 4.79 85%
VO2max6-4 gi|20810124 CD177蛋白(CD177 protein) 47 985 5.87 6-8 gi|114147359 免疫球蛋白重链(immunoglobulin heavy chain) 13 620 6.97 6-20 gi|18655424 维生素D结合蛋白(vitamin D binding protein) 52 780 5.17 6-21 gi|21730549 维生素D结合蛋白(vitamin D binding protein) 52 807 5.22 6-23 gi|58737017 前列腺酸性磷酸酶(prostatic acid phosphatase) 40 702 5.66 6-24 gi|55669910 白蛋白(albumin) 67 174 5.57 6-26 gi|31615330 甲状腺素结合前白蛋白(albumin complexed with thyroxine) 68 406 5.66 6-30 gi|11493459 白蛋白[albumin (PRO2619)] 58 513 5.96 6-31 gi|763431 白蛋白(albumin) 53 416 5.69 6-38 gi|17028367 凝溶胶蛋白(gelsolin) 31 052 4.85 6-39 gi|4699583 锌-α2-糖蛋白(zinc-α2-glycoprotein) 31 854 5.70 6-44 gi|119585669 激肽释放酶(kallikrein) 101 521 6.21 6-47 gi|168988718 白蛋白(albumin) 67 773 5.63 6-49 gi|229526 本-周蛋白(Ben-Jones protein) 23 779 8.75 6-50 gi|576259 淀粉样物质(amyloid) 23 358 6.12 6-57 gi|18953 前列腺特异抗原前体(prostate specific antigen precursor) 19 431 5.68 95%
VO2max8-5 gi|168988718 白蛋白(albumin) 67 773 5.63 8-6 gi|55669910 白蛋白(albumin) 67 174 5.57 8-7 gi|47124258 淀粉酶α1(amylase alpha 1) 56 859 8.82 8-9 gi|11493459 白蛋白[albumin(PRO2619)] 58 513 5.96 8-19 gi|169249224 免疫球蛋白重链保守α1(immunoglobulin heavy chain constant alpha 1) 19 738 4.94 8-24 gi|229601 免疫球蛋白G1(immunoglobulin G1) 49 801 8.8 8-25 gi|6980876 胰石蛋白(lithostathine) 16 522 5.32 8-37 gi|119626074 白蛋白(albumin) 48 568 5.97 8-46 gi|58176763 锌-α2-糖蛋白(zinc-α2-glycoprotein) 32 354 5.71 8-53 gi|7770217 白蛋白[albumin (PRO2675)] 33 466 6.14 8-58 gi|119592329 激肽释放酶3(kallikrein 3) 24 056 6.82 8-59 gi|343197759 免疫球蛋白κ链(immunoglobulin kappa chain) 24 352 6.99 组别 编号 预期值 匹配肽段 相对分子质量(实验) 相对分子质量(计算) 序列覆盖率/% 分数 变化倍数 55%
VO2max2-11 1.50×10-8 5 1 916.922 8 1 916.951 3 35 132 ↑6.20 2-20 2.40×10-20 13 1 225.540 2 1 225.536 4 46 250 ↑5.62 2-24 9.70×10-29 8 986.504 8 986.497 4 42 334 ↑8.57 75%
VO2max4-10 6.10×10-14 4 2 402.176 3 2 402.201 9 29 186 ↑9.35 4-17 3.90×10-17 7 1 206.603 7 1 206.624 4 42 218 ↑9.47 4-20 3.90×10-9 4 1 249.620 4 1 249.615 9 16 138 New 85%
VO2max6-4 1.20×10-9 7 3 034.515 2 3 034.460 7 21 143 New 6-8 4.90×10-6 6 1 880.977 4 1 880.995 6 89 107 New 6-20 1.90×10-19 7 1 528.766 7 1 528.777 3 19 241 New 6-21 6.10×10-18 7 1 528.766 7 1 528.777 3 19 226 ↑12.9 6-23 1.50×10-11 5 880.519 1 880.517 1 14 162 New 6-24 9.70×10-17 17 1 148.633 7 1 148.607 7 27 214 New 6-26 3.10×10-17 17 1 286.676 9 1 286.677 2 35 219 New 6-30 7.70×10-11 10 1 212.611 7 1 212.625 1 25 155 ↑5.4 6-31 2.40×10-14 7 2 649.251 0 2 649.256 7 12 190 ↑6.38 6-38 1.20×10-9 3 2 885.559 9 2 885.425 4 44 143 New 6-39 1.20×10-25 13 2 402.229 8 2 402.201 9 43 303 New 6-44 7.70×10-7 11 2 232.108 0 2 232.095 9 5 115 ↑48.54 6-47 2.40×10-17 14 1 225.577 1 1 225.597 9 21 220 New 6-49 2.20×10-4 3 1 944.979 3 1 945.019 7 23 90 New 6-50 2.40×10-8 7 763.447 3 763.438 1 29 130 New 6-57 6.10×10-14 5 1 076.511 2 1 076.496 1 27 186 ↑62.04 95%
VO2max8-5 2.40×10-22 22 1 225.585 2 1 225.597 9 40 270 New 8-6 3.90×10-22 18 932.523 6 932.511 3 33 268 New 8-7 2.40×10-12 7 1 286.676 9 1 286.677 2 19 170 New 8-9 2.40×10-24 15 1 073.579 5 1 073.535 3 33 290 New 8-19 9.10×10-4 3 1 212.611 7 1 212.625 1 19 84 ↑16.28 8-24 5.50×10-5 6 1 698.737 2 1 698.755 9 16 96 New 8-25 8.30×10-4 3 1 266.568 4 1 266.566 3 26 85 ↑14.62 8-37 4.90×10-22 12 1 531.761 8 1 531.799 4 35 267 ↑26.25 8-46 1.50×10-24 11 973.477 5 973.480 4 35 292 ↑15.67 8-53 3.10×10-20 11 1 622.797 5 1 622.780 3 44 249 ↑182.35 8-58 7.70×10-21 9 1 076.497 9 1 076.496 1 39 255 ↑120.33 8-59 1.70×10-4 5 1 916.947 2 1 916.951 3 28 92 New -
[1] 曹建民, 张爱芳, 徐晓阳, 等. 女子手球比赛时生理、生化指标及运动负荷指标的研究[J]. 北京体育大学学报, 2000, 23(3): 332-334 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3612.2000.03.018 [2] 王勇, 陈峰. 散打运动员专项训练后的尿液成分变化分析[J]. 上饶师范学院学报, 2019, 39(3): 111-115 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2237.2019.03.021 [3] 杨玲, 翁锡全, 林文弢, 等. 不同负荷运动对RAAS的影响[J]. 韶关学院学报, 2019, 40(9): 77-81 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5348.2019.09.017 [4] 段晓贤. 高校网球选修课准备活动操的创编及其运动负荷的生理生化评定[D]. 广州: 广州体育学院, 2018: 39 [5] 雷婷, 赵旭宏, 张曼. 正常人尿蛋白质组学研究[J]. 广东医学, 2010, 31(3): 300-302 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9448.2010.03.012 [6] WANG Z, HILL S, LUTHER J M, et al. Proteomic analysis of urine exosome by multidimensional protein identification technology[J]. Proteomics, 2012, 12(2): 329-338 doi: 10.1002/pmic.201100477
[7] 黄爱文. 儿童激素耐药型与激素敏感型肾病综合征尿蛋白组学的初步研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2007: 40 [8] AREGGER F, PILOP C, UEHLINGER D E, et al. Urinary proteomics before and after extracorporeal circulation in patients with and without acute kidney injury[J]. Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, 2010, 139(3): 692-700 doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2009.11.015
[9] MUSANTE L, CANDIANO G, BRUSCHI M, et al. Characterization of plasma factors that alter the permeability to albumin within isolated glomeruli[J]. Proteomics, 2012, 22(2): 197-205 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/11519620_Characterization_of_plasma_factors_that_alter_the_permeability_to_albumin_within_isolated_glomeruli
[10] KOHLER M, SCHANZER W, THEVIS M. Effects of exercise on the urinary proteome[J]. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 2015, 845: 121-131 doi: 10.1007/978-94-017-9523-4_12
[11] DAVIS M T, SPAHR C S, MCGINLEY M D, et al. Towards defining the urinary proteome using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Ⅱ. Limitations of complex mixture analyses[J]. Proteomics, 2001, 1(1): 108-117 doi: 10.1002/1615-9861(200101)1:1<108::AID-PROT108>3.0.CO;2-5
[12] SPAHR C S, DAVIS M T, MCGINLEY M D, et al. Towards defining the urinary proteome using liquid chromatography-tan-dem mass spectrometry. I. Profiling an unfractionated tryptic digest[J]. Proteomics, 2001, 1(1): 93-107 doi: 10.1002/1615-9861(200101)1:1<93::AID-PROT93>3.0.CO;2-3
[13] SAMUDRALA D, GEURTS B, BROWN P A, et al. Changes in urine headspace composition as an effect of strenuous walking[J]. Metabolomics, 2015, 11(6): 1656-1666 doi: 10.1007/s11306-015-0813-8
[14] COLBEY C, COX A J, PYNE D B, et al. Upper respiratory symptoms, gut health and mucosal immunity in athletes[J]. Sports Medicine, 2018, 48(1): 65-77 doi: 10.1007/s40279-017-0846-4
[15] 林文弢, 徐国琴, 翁锡全. 尿液蛋白质组学研究现状及其在体育科学中的应用[J]. 广州体育学院学报, 2010, 30(6): 72-76 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-323X.2010.06.017 [16] 徐国琴, 翁锡全, 孟艳, 等. 运动性免疫机能低下发生过程中尿蛋白质组分变化特点研究[J]. 中国运动医学杂志, 2018, 37(11): 921-926 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6710.2018.11.005 [17] 蔺海旗. 男子30公里跑后身体机能相关生化指标及尿蛋白组份变化的研究[D]. 广州: 广州体育学院, 2012: 41 [18] SOREN E D, THIEL S, NIELSEN O, et al. MAp19, the alternative splice product of the MASP-2 gene[J]. Journal of Immunological Methods, 2011, 373(1-2): 89-101 doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2011.08.006
[19] 李玲, 孙子林. 胰腺应激蛋白PSP/reg对胰腺星状细胞活性的影响[J]. 江苏医药, 2010, 36(23): 2795-2798 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YIYA201023026.htm [20] 刘畅, 姚玉宇, 马根山, 等. 人血浆组织激肽释放酶结合蛋白与冠状动脉病变程度相关性研究[J]. 南京医科大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 36(10): 1208-1212 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-NJYK201610013.htm [21] KOHLER M, WALPURGIS K, THOMAS A, et al. Effects of endurance exercise on the urinary proteome analyzed by 2-D PAGE and Orbit rap MS[J]. Proteomics Clinical Applications, 2010, 4: 568-576 doi: 10.1002/prca.200900209
[22] POORTMANS J R. Exercise and renal function[J]. Sports Medicine, 1984, 1(2): 125-153 doi: 10.2165/00007256-198401020-00003
[23] 林文弢. 运动生物化学[M]. 北京: 人民体育出版社, 2009: 164 [24] ACKEL C, VANCINI R L, CASTELO A, et al. Absence of the predisposing factors and signs and symptoms usually associated with overreaching and overtraining in physical fitness centers[J]. Clinics(Sao Paulo), 2010, 65(11): 1-6 doi: 10.1590/S1807-59322010001100019
[25] WEI X, LIU X, TAN C, et al. Expression and function of zinc-α2-glycoprotein[J]. Neurosis Bull, 2019, 35(3): 540-550 doi: 10.1007/s12264-018-00332-x
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 季炜然,孟林盛. 基于深度学习和心电信号的运动疲劳识别方法. 印刷与数字媒体技术研究. 2024(02): 135-144 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 殷飞,虞沁宸. 关于体力活动提升中老年人免疫力综述研究. 南京体育学院学报. 2022(08): 53-60 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: