Method, Dose and Pathway of Different Exercise Types to Intrahepatic Lipid in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
-
摘要:目的 探讨不同类型运动干预降低非酒精性脂肪性肝病(NAFLD)患者肝内脂质含量的靶向作用和量效关系。方法 在Web of Science、PubMed、中国知网、万方及维普网等数据库检索文献,依据纳入与排除标准最终筛选出21篇文献进行分析,比较有氧运动、抗阻运动、高强度间歇运动及组合运动干预NAFLD患者的方案及效果差异。结果 有氧运动主要通过分解消耗脂肪降低肝内脂质含量,抗阻运动主要通过促进骨骼肌吸收游离脂肪酸减少肝内脂质堆积。虽然目前有氧运动联合抗阻运动的效果与单纯有氧运动或抗阻运动的短期效果在统计学上难以区分,但从长期效果看,结合抗阻运动能保持骨骼肌对游离脂肪酸的利用率,高强度间歇运动可有效改善肝硬化和恢复Kupffer细胞功能。结论 有氧运动、抗阻运动和高强度间歇运动单独干预或组合干预均可降低NAFLD患者的肝内脂质含量,但剂量选择和靶向作用不同,高强度间歇运动相对更高效、省时,推荐NAFLD患者采取组合干预形式。Abstract:Objective To analyze the targeting effect of different exercises on intrahepatic lipid(IHL) content of patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease(NAFLD) and the exercise dose levels.Methods By searching literature in the databases such as Web of Science(WoS), PubMed and CNKI etc., 21 articles were filtered and analyzed according to inclusion & exclusion criteria eventually. The program and effect of aerobic exercise (AE), resistance exercise (RE) and high-intensity interval training(HⅡT) and combination of exercise intervention were compared in NAFLD patients.Results AE reduced IHL content by consuming adipose tissue; RE reduced the accumulation of IHL by promoting the absorption of non-esterified fatty acid(NEFA) in skeletal muscles mainly with the effective increase of muscle mass and strength.Although the short-term effect of AE+RE was statistically indistinguishable from AT or RE alone, combination of RE could maintain the utilization rate of NEFA by skeletal muscle and promote the formation of a virtuous cycle of systemic metabolism as a long-term benefit.Conclusions Different types of exercise can reduce intrahepatic lipid(IHL) content of patients with NAFLD, but the dose and targeted role are different.HⅡT is more efficient and timesaving.The combination of the both is still recommended for NAFLD patients when time and space conditions are available.
-
非酒精性脂肪性肝病(non-alcoholic fatty liver disease,NAFLD)以肝内脂质堆积过量为特征,伴随胰岛素抵抗,并与遗传易感、肥胖和代谢综合征密切相关,包括非酒精性单纯性脂肪肝病、非酒精性脂肪性肝炎、肝硬化及肝细胞癌等,且患者无过量饮酒史。目前NAFLD的发病率逐年升高,文献[1]报道NAFLD的全球患病率约为25.24%,美国患病率为10%~30%,欧洲与亚洲也报道了相似的患病率[2-3],中国患病率为15%~30%[4],造成了严重的社会经济负担[1, 5-9]。氢质子磁共振波谱技术(1H proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy,1H⁃MRS)[10]实现了对人体肝内脂质含量的无创检测和定量分析,其推广应用使NAFLD的检出率明显增高[11-14]。影响肝内脂质含量的因素有脂质进入肝脏、脂质新生、肝脏脂质氧化、肝内脂质进入血液循环等,这些因素单独或协同发挥作用,如果向肝脏输送的脂质含量超过了肝脏脂质氧化和分泌的总和,则肝内脂质含量增加,就可能发展为NAFLD。
久坐不动的生活方式是导致NAFLD发生的重要原因之一[8, 15]。NAFLD患者的活动量低于一般人群[16-17],活动量与肝内脂质水平成反比,与年龄、性别、体质量指数和胰岛素抵抗等混杂因素无关[18]。研究[19]发现,超过80%的NAFLD患者活动量未达到体力活动指南推荐水平,即每周进行3次或3次以上30 min的中等强度运动。2012—2018年,欧洲肝脏研究协会、美国肝病研究协会、NAFLD亚太工作组及中华医学会肝病学分会相继发布了NAFLD相关防治指南[5-6, 8, 20-21],这些指南及NAFLD相关实验研究[22-24]均提出,改变不良的生活方式、坚持规律科学的体育锻炼可有效预防和逆转NAFLD,减轻肝脂肪变性,减少肝脂肪含量。但这些指南和研究关于运动的具体建议不尽相同,并认为防治NAFLD的运动类型、运动强度、运动剂量及适用人群仍需继续探讨。本文比较有氧运动、抗阻运动、高强度间歇运动及2种或2种以上运动方式的组合运动干预NAFLD人群的方案及效果差异,解析不同类型运动干预实现的靶向作用和量效关系规律,为NAFLD易感人群选择运动方式、强度、频率及持续时间提供参考。
1. NAFLD的运动干预文献来源
参考上述指南[5-6, 8, 20-21],以主题词“non-alcoholic fatty liver disease”或“NAFLD”或“非酒精性脂肪肝”和“aerobic exercise”或“aerobic training”或“有氧运动”或“resistance exercise”或“resistance training”或“抗阻运动”或“high-intensity interval exercise”或“high-intensity interval training”或“HIIT”或“高强度间歇运动”和“1H proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy”或“1H-MRS”或“氢质子磁共振波谱技术”或“hepatic fat content”或“HFC”或“肝脏脂肪含量”或“intrahepatic lipid”或“IHL”或“肝内脂质”,检索2007年1月1日—2019年12月31日被Web of Science、PubMed、中国知网、万方及维普网等数据库收录的文献共1 046篇。排除会议论文、摘要、评论、书信、综述、专利、方案、运动结合药物及NAFLD诊断信息不全的论文1 025篇,最终筛选出21篇文献,探讨运动干预对NAFLD的靶向作用和剂量选择,比较不同类型运动干预对NAFLD患者肝内脂质含量的影响。
2. 不同类型运动干预NAFLD的效果
体力活动与肝内脂质含量呈负相关[18],运动可通过增加能量消耗改善NAFLD[25]。国内外肝病研究协会关于防治NAFLD的运动建议有所不同。中华医学会肝病学分会发布的《非酒精性脂肪性肝病防治指南(2018更新版)》建议NAFLD患者每天坚持中等强度有氧运动30 min、每周5次,或每天进行高强度有氧运动20 min、每周3次,同时做8~10组抗阻运动、每周2次[21, 26]。欧洲肝脏研究协会发布的NAFLD防治指南[27]建议,NAFLD患者可遵循国际社会认可的糖尿病预防实验推荐的运动方式,即每周至少150 min中等强度身体活动(快步走)、至少75 min高强度运动(慢跑)、2次肌肉力量训练和2次灵敏性训练,这一运动处方与美国运动医学会提出的一般人群运动建议(每周3~5次中等强度有氧运动,每次运动40 min,至少持续8周,以显著提高最大摄氧量)[28]一致。NAFLD亚太工作组[20]也推荐上述运动处方,但认为防治NAFLD的运动强度、运动量及运动类型仍需进一步探讨。美国肝病研究协会提出,运动可以减少NAFLD患者的肝脂肪变性,但未对所需的运动方式、强度及运动量给出建议。目前有氧运动、抗阻运动、高强度间歇运动及2种或2种以上运动方式组合干预对NAFLD患者的靶向效应尚不清晰。本文筛选出的21篇文献中关于以上几种运动方式的干预效果见表 1。
表 1 不同类型运动干预NAFLD的剂量与效果Table 1. Dose selection and effect of different exercise intervention on NAFLD文献 研究对象 n 年龄/岁 运动
类型运动干预方案 干预
时间干预效果 Zhang等[26] 肥胖成年人 220 54±7.0 AE 快步走(强度维持在最大心率的45%~55%)、跑步(强度维持在最大心率的65%~80%),每周150 min 12个月 体质量下降,体脂率下降,腰围下降,内脏脂肪含量下降,肝内脂质含量下降 Promrat等[29] 超重/肥胖
成年人31 49±11.0 AE 跑步、蹬功率车,中等强度体力活动,10 000步/d,每周200 min 48周 体质量下降,肝脏组织学表现改善 Wong等[30] 超重成年人 154 51±9.0 AE 中等强度AE,每次30 min,每周3~5次 12个月 体质量下降,腰围下降,肝内脂质含量下降 Johnson等[31] 肥胖成年人 19 49±2.0 AE 蹬功率车,强度维持在峰值摄氧量的50%~70%,每次30~45 min,每周3次 4周 肝内脂质含量下降,内脏脂肪含量下降,峰值摄氧量上升 Keating等[32] 超重/肥胖
成年人47 44.0±3.0 AE 蹬功率车,LO∶HI组运动强度维持在峰值摄氧量的50%,每次60 min,每周3次;HI∶LO组运动强度维持在峰值摄氧量的70%,每次45 min,每周3次;LO∶LO组运动强度维持在峰值摄氧量的50%,每次45 min,每周3次 8周 肝内脂质含量下降,内脏脂肪含量下降,腰围下降,峰值摄氧量上升 Sullivan等[33] 肥胖成年人 18 47.5±3.1 AE 运动强度维持在峰值摄氧量的45%~55%,每天30~60 min,每周5 d 16周 肝内脂质含量下降 Van der Heijden等[34] 肥胖青少年 29 15.0±1.0 AE 蹬功率车,运动强度维持在峰值摄氧量的70%,每次30 min,每周2次 12周 肝内脂质含量下降,内脏脂肪含量下降,胰岛素抵抗下降,峰值摄氧量上升 Shojaee-Moradie等[35] 久坐超重
男性17 50.0±2.6 AE 运动强度维持在峰值摄氧量的60%~85%,每次20 min,每周3次 6周 肝脏脂肪含量无显著变化 Bacchi等[11] 超重/肥胖
成年人31 56.0±2.0 RE RE训练3组动作,每组动作重复10次,1次重复最大力量的70%~80%,每周3次;跑步、自行车等AE,运动强度维持在最大心率的60%~65%,每次60 min,每周3次 4个月 2组肝内脂质含量、内脏脂肪含量下降,1/4的患者肝内脂肪变性消失,胰岛素敏感性升高,2组总体脂肪质量、内脏脂肪、皮下脂肪组织、糖化血红蛋白均降低 Hallsworth等[12] 久坐肥胖
成年人19 52.0±13.3 RE RE训练8个动作,每次45~60 min、2~3组、8个动作,1次重复最大力量的50%~70%,每周3次 8周 肝内脂质含量下降,改善血糖控制和胰岛素抵抗 Zelber-Sagi等[36] 超重/肥胖
成年人82 40.0±11.0 RE RE训练3组动作,3次重复最大力量,每周增加0.5 kg直至4 kg,重复8~12次,每次40 min 12周 肝内脂质、体脂、低密度脂蛋白、胆固醇水平均下降,胰岛素敏感性升高 Hallsworth等[37] 久坐肥胖
成年人23 54.0±10.0 HIIT 蹬功率车HIIT方案:第1周高强度运动2 min(自我疲劳程度评分为16~17分),之后每周增加10 s;3 min恢复,恢复期包括90 s的被动恢复及60 s的上肢轻度阻力迷你带训练,每个动作间隔15 s;3 min放松;每次持续30~40 min,每周3次 12周 肝内脂质含量、体脂、丙氨酸、天冬氨酸转氨酶水平均下降 Cassidy等[38] 肥胖老年人,2型糖尿病患者 28 61.0±9.0 HIIT 蹬功率车HIIT方案:第1周高强度运动2 min(自我疲劳程度评分为16~17分),之后每周增加10 s;3 min恢复,恢复期包括90 s的被动恢复及60 s的上肢轻度阻力迷你带训练,每个动作间隔15 s;3 min放松;每次持续30~40 min,每周4次 12周 肝内脂质含量、体脂含量均下降,心脏结构改善,糖化血红蛋白水平下降 Lee等[13] 肥胖青少年,男 32 对照组14.8±1.4;AE组15.2±1.9;RE组14.6±1.5 AE vs RE AE组:第1周运动强度为最大摄氧量的40%,每次40 min;第2~12周运动强度为最大摄氧量的60%~75%,每次60 min;每周3次。RE组:10个动作、2组、8~12次重复,持续60 min,每次重复最大力量的60%(第1~4周)至疲劳(第5~12周),每周3次 3个月 2组肝内脂质、体质量、体脂、内脏脂肪水平均下降 Lee等[14] 肥胖青少年,女 32 Con组
15.0±2.2;AE组14.6±1.9;RE组14.8±1.9AE vs RE AE组:第1周运动强度为最大摄氧量的40%,每次40 min;第2~12周运动强度为最大摄氧量的60%~75%,每次60 min;每周3次。RE组:10个动作、2组、8~12次重复,持续60 min,每次重复最大力量的60%(第1~4周)至疲劳(第5~12周);每周3次 3个月 AE组肝内脂质、体脂、内脏脂肪含量均下降;RE组肝内脂质含量无显著性变化,体脂含量下降 Slentz等[39] 超重/肥胖
久坐成年人196 49.0±11.0 AE vs RE RE训练,8个动作、3组、8~12次重复,每周3次;AE训练,强度维持在峰值摄氧量的75%,每周19.2 km;RE+AE训练 8个月 AE组肝内脂质、内脏脂肪、丙氨酸转氨酶、胰岛素抵抗、总脂肪及腹部皮下脂肪含量均显著降低;RE组皮下脂肪含量减少,其他指标均未见明显改善。在改善内脏脂肪、肝脾比值和腹部总脂肪方面,AE比RE更有效。AE+RE训练的效果与单纯AE训练相比无显著性差异 De Piano等[40] 肥胖青少年 58 16.5±1.4 AE+RE 跑步、蹬功率车,运动强度维持在峰值摄氧量的50%~70%,每次60 min,每周3次;主要肌肉群RE训练,6~20次重复最大力量,每次30 min,每周3次 12个月 体质量、内脏脂肪、体脂水平均下降,炎症标志物和食欲肽浓度均降低 Brouwers等[41] 男性NAFLD患者和男性健康成年人 22 NAFLD: 54.5± 6.8;Con:57.6±8.1 AE+RE AE组:蹬功率车,运动强度为最大摄氧量的70%,每次30 min,每周2次。RE组:3组动作,重复10次,1次重复最大力量的60%,重点锻炼大肌肉群 12周 高脂肪和低脂肪含量者的肝内脂质含量均降低。运动训练对2组肝内脂质含量的影响相似 Cheng等[42] 糖尿病前期及NAFLD患者 115 对照组:60.0±3.4;
AE组:59.0 ±4.4;
饮食干预组:60.0±4.1;
AE结合饮食干预组:60.0±3.5AE/AE+饮食干预 AE组:北欧式健步走,运动强度维持在峰值摄氧量的60%~75%,每次30~60 min,每周2~3次。饮食干预组:38% 碳水化合物,膳食纤维12 g/d 8.6个月 所有干预组肝内脂质含量均下降,但AE结合饮食干预组下降幅度更明显,且只有结合组糖化血红蛋白显著下降 Winn等[43] 肥胖成年人 18 41.0±14.0 HIIT vs AE HIIT组:4 min强度维持在峰值摄氧量80%的运动和3 min强度维持在峰值摄氧量50%的运动交替。AE组:运动强度维持在峰值摄氧量的55%,持续60 min 4周 肝内脂质含量下降,2个干预组之间效果差异无统计学意义 Oh等[44] 久坐肥胖
成年人61 RE组:51.2±1.9;HIIT组:48.6 ±1.8;AE组:48.2± 2.3 HIIT vs AE vs RE 所有训练每周3次。RE组:2009年美国运动医学学会推荐的仰卧起坐、腿部按压、腿部伸展、腿部弯曲、胸部按压、坐式划船和下拉7个动作,1次重复最大力量,负荷率每个月增加1次。HIIT组:蹬功率车,3组3 min强度维持在峰值摄氧量80%~85%的运动,2组2 min强度维持在峰值摄氧量50%的运动。AE组:40 min强度维持在峰值摄氧量60%~65%的运动 12周 所有运动训练组肝内脂质含量下降,只有HIIT在改善肝硬化和恢复Kupffer细胞功能方面有效 注:年龄数据以平均数±标准差形式表示;NAFLD表示非酒精性脂肪性肝病,AE表示有氧运动,RE表示抗阻运动,HIIT表示高强度间歇运动,Con组表示对照组。 2.1 有氧运动干预
有氧运动是人体在氧气供应充分的情况下进行的体育运动。有氧运动改善NAFLD患者肝脏状况可能是通过减轻体质量实现的[8]。肥胖是NAFLD最常见的危险因素,减重被认为是防治NAFLD的有效措施[45]。体质量减轻的程度与肝脏组织学的改善水平相关,减轻3%~5%的体质量能改善肝脏脂肪变性,减轻10%的体质量则能改善肝脏脂肪的轻微炎症,但前提是未出现肝脏纤维化[6]。Promrat等[29]研究发现,通过48周、每周200 min的中等强度有氧运动干预,不仅可有效降低NAFLD患者的体质量,而且能明显改善患者的肝脏组织学表现。Wong等[30]研究发现,通过采用以社区为基础的12个月每周3~5次中等强度有氧运动的生活方式干预后,NAFLD患者的体质量、腰围及肝内脂质含量均下降。
Zhang等[26]的研究结果显示,中等强度和高强度有氧运动在改善中老年NAFLD患者肝脏状况方面的效果同样显著,并且这种效果可能为体质量减轻所致。该研究共纳入220例NAFLD患者(其中54%为女性患者,平均年龄约为54岁,平均体质量约为72 kg,平均体质量指数约为28 kg/m2,平均肝内脂质含量约为18%),并随机分为3组:①不运动对照组。②中高强度有氧运动组,患者在运动监控人员监督下慢跑,运动强度维持在最大心率的65%~80%,每天30 min,每周5 d,共6个月;之后快步走,运动强度维持在最大心率的45%~55%,每天30 min,每周5 d,共6个月。③中等强度有氧运动组,患者在运动监控人员监督下每天进行30 min中等强度运动,每周5 d,共12个月。干预6个月时,与不运动对照组相比,中高强度有氧运动组和中等强度有氧运动组患者肝内脂质含量下降幅度较大(分别为5.0%和4.2%),但2个运动组之间无显著性差异。干预12个月时,中高强度有氧运动组(3.8%)和中等强度有氧运动组(3.5%)肝内脂质含量的下降幅度比不运动的对照组大,但2个运动组之间亦无显著性差异。运动训练6个月和12个月对NAFLD患者肝内脂质含量的有益作用在调整体质量影响后仍然显著。不减重的运动训练也可降低肝内脂质含量,且差异有显著性[46]。以上研究结果表明,运动对肝内脂质含量的影响是通过体质量下降和运动本身的独立减重效应调节的。
即使未减轻体质量,持续时间至少4周的规律有氧运动也能降低肥胖患者的肝内脂质含量,这表明有氧运动的益处并不完全取决于体质量的降低[31]。Keating等[32]对47例NAFLD患者分组进行8周3种不同运动强度和剂量的有氧运动干预,包括LO∶HI组(蹬功率车,强度为峰值摄氧量的50%,每次60 min,每周3次)、HI∶LO组(蹬功率车,强度为峰值摄氧量的70%,每次45 min,每周3次)、LO∶LO组(蹬功率车,强度为峰值摄氧量的50%,每次45 min,每周3次)。结果显示:3种有氧运动方案都降低了患者的肝内脂质和内脏脂肪含量,不同剂量和强度有氧运动对肝内脂质含量的减少效果无差异。Johnson等[31]研究发现,4周的有氧功率车运动减少了12%的内脏脂肪组织体积和21%的肝脏甘油三酯浓度,且差异均显著(P < 0.01、P < 0.05),但未改变体质量、股外侧肌内甘油三酯浓度和腹部皮下脂肪组织体积。Sullivan等[33]按照美国卫生与公众服务部的体育活动指南,对18例肥胖NAFLD患者进行为期16周、每周平均持续时间为(224±22)min、强度为峰值摄氧量45%~55%的有氧运动训练干预,结果提示,该干预方案对肝内脂质含量有小而有益的影响,但不能改善肥胖NAFLD患者的肝脂蛋白动力学表现。Van der Heijden等[34]对西班牙久坐肥胖青少年进行12周的有氧运动干预后,受试者的肝内脂质和内脏脂肪含量均下降,胰岛素抵抗下降,峰值摄氧量上升,但体质量未显著降低。这一结果表明,一个合适的有氧运动干预方案虽未达到减重效果,但可以有效减少成年人或青少年NAFLD患者内脏及肝脏脂肪的积累,并减少胰岛素抵抗。
中等强度有氧运动在减少肝内脂质含量方面可能与剧烈有氧运动的效果相当,然而大多数人更有可能坚持中等强度的锻炼,而不是高强度的锻炼,运动干预的依从性往往很难控制。在Zhang等[26]的研究中受试者依从性较高,运动监控效果较好。有氧运动对肝内脂质的影响可以通过体质量下降和运动本身的减重独立效应调节。一项纳入20项随机对照实验、共1 073例NAFLD患者的meta分析[47]显示,即使体质量无显著变化,运动也能对肝内脂质产生有益影响。这可能因为一段时间的有氧运动虽然未能改变总体质量,却可以改变身体成分,如内脏脂质含量下降,去脂体质量增加[12, 33, 42, 47]。内脏脂质含量的降低是造成肝内脂质含量变化的重要因素。虽然减重被公认为NAFLD患者有效的干预措施[22],但未必是降低患者肝内脂质含量所必须达到的唯一目标。
另外,2017年Cheng等[42]通过对比北欧式健步走、饮食控制及2种方式结合的干预方式对糖尿病前期合并NAFLD患者的效果,发现3个干预组患者的肝内脂质含量均下降,但有氧运动结合饮食干预组的下降幅度更明显,且仅有氧运动结合饮食干预组的糖化血红蛋白显著下降。可见有氧运动干预的形式可以不局限于实验室环境中的功率车训练、快步走和跑步。北欧式健步走借助健走杖不仅可动员运动者的上肢肌肉,使能量消耗增加,而且能有效保护膝关节,缓解脊椎和腿部压力,多点支撑还可以增强身体的平衡能力从而保证运动时的安全性,较适宜中老年人。坚持有氧运动的同时减少碳水化合物并增加膳食纤维的饮食控制更有助于改善NAFLD患者的肝脏脂肪堆积。
2.2 抗阻运动干预
抗阻运动是指肌肉在克服外来阻力时进行的主动运动。抗阻运动对心肺耐力要求较低,是增加肌肉力量、质量及耐力的有效手段[45]。Hallsworth等[12]研究发现,持续8周的抗阻运动训练可以降低NAFLD患者的肝内脂质含量,并改善血糖水平和胰岛素抵抗。因此,在本文检索到的文献中,产生降低肝内脂质含量效果的抗阻运动训练干预的持续时间长于有氧运动最短干预持续时间(4周)。Zelber-Sagi等[36]通过3个月的抗阻运动训练干预研究发现,抗阻运动训练能改善NAFLD患者的肝内脂质含量和低密度脂蛋白,可作为NAFLD治疗的补充。Bacchi等[11]通过对比4个月抗阻运动训练和有氧运动的干预效果发现,2种运动干预方式都可以降低NAFLD患者的肝内脂质、内脏脂肪含量,有1/4的患者肝脂肪变性消失、胰岛素敏感性升高,而2组的总体脂肪质量、内脏脂肪质量、腹部皮下脂肪组织、糖化血红蛋白均降低。Lee等[13-14]分别对肥胖青少年男生和女生进行了有氧运动干预和抗阻运动干预的对比研究,发现相比空白对照组,有氧运动和抗阻运动干预均能有效降低肥胖男生的肝内脂质含量、体质量、体脂及内脏脂肪含量,女生进行有氧运动可产生与男生相同的效果,然而抗阻运动干预仅能降低女生的体脂,对肝内脂质含量并无显著影响。
2.3 高强度间歇运动干预
高强度间歇运动是指短时间的极量强度运动穿插短时间恢复期(低强度运动或安静休息)的运动。这种运动方案通过提高运动强度并显著缩短运动持续时间,大幅度减少了运动量。运动中适度的间歇能减缓不适症状的出现,更易于患者接受训练和坚持完成训练[48]。高强度间歇运动能有效减少肝内脂质含量,改善肝纤维化和炎症[37-38, 45]。
Hallsworth等[37]和Cassidy等[38]使用相同的高强度间歇运动干预方案分别对肥胖成年人和2型糖尿病肥胖老年人进行干预,结果显示,高强度间歇运动可有效降低肝内脂质含量,并且可以改善2型糖尿病肥胖老年人的心脏结构。Winn等[43]研究表明,能量匹配的高强度和中等强度运动对降低肝内脂质含量和NAFLD风险有效,并且该作用不取决于腹部脂肪或体质量的减少。Oh等[44]通过对比高强度间歇运动与抗阻运动、有氧运动对NAFLD患者的干预效果发现,3种运动干预方案都可以降低患者的肝内脂质含量,但只有高强度间歇运动可有效改善肝硬化和恢复Kupffer细胞功能,这些益处可能与检测到的体质量和内脏脂肪减少无关,而是通过调节体内脂肪酸代谢和肥胖相关炎症获得的。
2.4 多运动方式组合干预
Brouwers等[41]研究发现,通过12周有氧运动与抗阻运动结合的运动训练,NAFLD患者和肝内脂质含量正常者的肝内脂质含量均降低,2组受试者肝内脂质含量降低的程度相似。De Piano等[40]对肥胖青少年进行为期12个月的运动干预研究发现,与单纯的有氧运动干预相比,有氧运动和抗阻运动组合的运动方案对改善肥胖青少年NAFLD患者炎症标志物和降低食欲肽浓度的积极作用更显著。Slentz等[39]通过比较有氧运动训练、抗阻运动训练及2种运动组合干预方案对超重人群肝内脂质堆积的改善效果发现,有氧运动训练比抗阻运动训练更有效,2种运动组合干预方案与单纯有氧运动训练的效果差异无统计学意义。这一结果表明,对于欲减少内脏脂肪和脂肪肝浸润、改善胰岛素抵抗和丙氨酸转氨酶水平的超重和肥胖个体,适量的有氧运动较有氧运动与抗阻运动组合训练的方式更省时。然而,抗阻训练可以改善胰岛素敏感性、肌肉力量和功能,有研究[49]表明肌肉减少症与NAFLD风险有关。根据心血管疾病风险控制中阻力训练的临床建议,目前证据[50]表明,抗阻训练应作为有氧运动训练的补充而不是取而代之。对加速训练(在振动平台上进行的抗阻训练)和混合训练(涉及肌肉的自主和电收缩)的初步研究[51-53]表明,创新的复合运动方案也可能降低NAFLD患者的肝脏脂肪含量。
3. 不同类型运动干预NAFLD的靶向作用与剂量选择
既往研究[54]表明,有氧运动、抗阻运动和高强度间歇运动单独干预或组合干预均可降低NAFLD患者的肝内脂质含量。在本文回顾的文献报道关于NAFLD患者的有氧运动方案中,出现肝内脂质含量下降效果的最短的干预时间为4周[31](采用蹬功率车的方式进行30 min强度为峰值摄氧量50%~70%的持续运动,每周3次),最长的干预时间为12个月[26](快走,强度维持在最大心率的45%~55%;跑步,强度维持在最大心率的65%~80%;每周150 min)。一项研究[36]报道,经过6周的有氧运动训练后,超重健康男性的肝内脂质含量无变化,但该研究的运动剂量较小,仅限于每周3次,1次持续20 min。由此可见,若要达到肝内脂质含量下降的效果,有氧运动干预应遵循一定的剂量效应关系。干预持续周期需至少4周,若干预周期较长,所需要的运动强度(不低于最大心率的45%~55%)和频率(不低于3次/周)相对较低。虽然未发现确切证据(差异有统计学意义)证明稍高强度、低剂量的有氧运动比中等强度、稍高剂量的有氧运动在降低肝内脂质含量方面更有效,运动强度和持续时间的结构性组合方式的干预效果似乎稍弱,但是低于上述限度[36]无法实现这一目标。对于NAFLD患者而言,有氧运动干预可适用于各个年龄段,常伴随体质量下降,对运动场地的要求也较低,方便在社区推广。但往往对患者的心肺耐力有一定要求,持续时间较长的有氧运动干预会导致疲劳和不适,老年或病态的肥胖NAFLD患者可能难以进行。
针对心肺耐力不足、肌肉量较低或超重且不能耐受有氧运动的NAFLD患者,抗阻运动是更好的选择。本文回顾的能产生肝内脂质含量下降效果的抗阻运动训练干预时间最短为8周,最长为12个月,抗阻运动训练方案大多采用器械练习的方式,1次重复最大力量的50%~80%负荷持续运动超过45 min,每周3次,持续时间超过3个月。抗阻运动训练能够增加患者的肌肉力量和质量,但是由于需要专用器械和具体的训练方法,其开展易受场地、设备、教练员等方面的限制,并且动作变形可能会导致患者发生关节损伤,在训练中应有专业教练员及时纠正并加强自身防护。
对NAFLD患者产生显著效益的高强度间歇运动方案为采用跑步或蹬功率车的方式,每周3次至少13 min强度大于峰值摄氧量80%的持续运动,持续运动12周[37-38];另一种方案是4 min强度为峰值摄氧量80%的运动搭配3 min强度为峰值摄氧量50%的运动,每次60 min,持续运动4周[43]。无论是在时效还是在量效方面,相较于有氧运动和抗阻运动,高强度间歇运动的优势明显,且只有高强度间歇运动可有效改善肝硬化和恢复Kupffer细胞功能。由于运动持续时间及干预周期都较短,高强度间歇运动干预凸显其经济性和时效性,很好地解决了运动干预NAFLD的靶向性和量效问题。然而,无论高强度间歇运动方案的具体运动形式如何变化,都是典型的技能习得性运动,训练离不开专业人员的科学指导。而且心肺耐力较差及同时伴有其他慢性代谢疾病的NAFLD患者进行高强度运动的风险高,在实施运动方案前需要进行科学的健康评估。这取决于体育及医学测评手段和工具的科学性、深度融合及介入程度,也是未来科学健身在慢性疾病防治和康复方面能否充分发挥作用的关键环节。
在12个月长期的运动干预研究中,相比单纯的有氧运动干预,有氧运动和抗阻运动相结合的运动方案对改善NAFLD肥胖青少年患者的炎症生物标志物和降低食欲肽浓度的积极作用更显著[40, 54]。也有研究[40]通过比较8个月有氧运动训练、抗阻运动训练及2种运动结合的运动干预方案对超重人群肝内脂质含量堆积的干预效果,发现有氧运动训练比抗阻运动训练更有效,而有氧运动加抗阻运动训练的效果与单纯有氧运动训练的效果在统计学上难以区分。然而,抗阻运动可以改善胰岛素敏感性、肌肉力量和功能,肌肉减少症与NAFLD风险之间存在关联[49]。根据心血管疾病风险控制中抗阻运动的临床建议,目前的证据表明,抗阻运动应补充而不是取代有氧运动训练。
4. 运动对人体肝内脂质含量的影响途径
虽然运动训练减少肝内脂质含量的研究是可复制的,但运动训练影响人类肝内脂质含量的机制仍未明确。到底是运动直接影响了肝内脂质,还是体力活动使能量消耗增加致负能量平衡,负能量平衡导致肝内脂质作为底物被调动起来,为能量不足提供燃料?
4.1 肝脏脂肪代谢通路与NAFLD
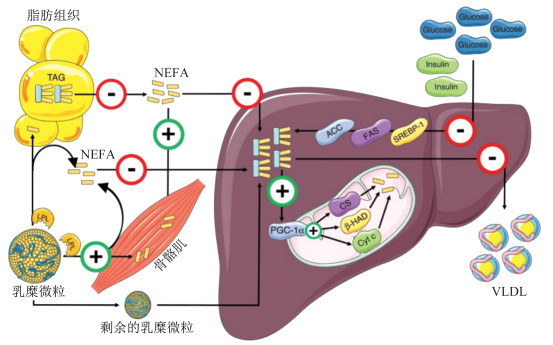
脂肪组织通过分解将游离脂肪酸(non-esterified fatty acid,NEFA)释放到血浆中,脂肪组织分解过多将导致空腹和餐后血浆NEFA升高,最终在肝脏部位被吸收。食物中的脂肪通过乳糜微粒运输。脂肪组织和骨骼肌通过脂蛋白脂肪酶的作用吸收脂肪酸,这些脂肪酸来源于乳糜微粒-甘油三酯储备,而剩余的乳糜微粒被肝脏吸收。然而,当膳食脂肪利用率很高时,乳糜微粒-甘油三酯储备溢出释放脂肪酸进入血浆NEFA池,这些NEFA可被肝脏吸收。此外,高胰岛素血症会通过激活脂质新生增加肝脏对葡萄糖的吸收。为了代偿肝脏脂肪运载和合成的增加,极低密度脂蛋白(very low density lipoprotein,VLDL)和甘油三酯线粒体氧化上调导致肝脏分泌更多甘油三酯,最终肝内脂质含量升高。
4.2 运动训练影响肝内脂质的通路
运动训练可提高胰岛素敏感性,增加脂肪酸氧化,减轻氧化应激和炎症,调节肠道菌群内环境稳态[55-59],降低NAFLD的患病率。运动训练可改善或减轻NAFLD患者的肝脂肪变性[23],是治疗NAFLD的基础[22]。
如上所述,肝内脂质积累是由于脂质传递到肝脏的改变、肝脏脂质氧化的改变、肝内脂质分泌到循环的改变或这些因素的综合作用。运动训练降低肝内脂质含量,可能是通过影响人体内1条或多条信号通路实现的(图 1)[25]。有证据[31]表明,即使体质量没有减轻,持续时间至少4周的规律有氧运动也能降低肥胖患者的肝内脂质含量。有氧运动训练降低空腹和餐后NEFA,很可能是通过减少脂肪分解实现的,但运动训练影响脂肪分解的具体机制尚不清楚。抗阻运动可改善胰岛素敏感性、肌肉力量和功能。有氧运动或抗阻运动训练可改善全身脂肪氧化,增加了骨骼肌对NEFA的吸收,这可能降低肝脏对血浆NEFA的吸收,从而改变脂肪酸从肝脏到骨骼肌的分配。例如,与健康的、久坐不动的人相比,运动员的骨骼肌从血液摄取了较多的NEFA,而肝脏保留的NEFA低于20%。12周的有氧运动联合抗阻运动训练还可提高全身胰岛素敏感性,从而改善胰岛素介导的血浆NEFA抑制[25, 60]。
![]() 图 1 运动训练降低肝脏内脂质含量的信号通路[25]注:红色圆圈代表运动训练对肝脏脂质代谢的抑制通路,绿色圆圈代表运动训练对肝脏脂质代谢的上调路径;TAG表示甘油三酯,NEFA表示游离脂肪酸,LPL表示肝内脂质,ACC表示乙酰辅酶A羧化酶,FAS表示脂肪酸合酶,SREBP-1表示固醇调节元件结合蛋白1,PGC-1α表示过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ共激活剂1α,CS表示柠檬酸合成酶,β-HAD表示β三羟基酰基辅酶A脱氢酶,Cyt c表示细胞色素c,Glucose表示葡萄糖,Insulin表示胰岛素,VLDL表示极低密度脂蛋白。Figure 1. Signal pathway of exercise training reducing lipid content in liver[25]
图 1 运动训练降低肝脏内脂质含量的信号通路[25]注:红色圆圈代表运动训练对肝脏脂质代谢的抑制通路,绿色圆圈代表运动训练对肝脏脂质代谢的上调路径;TAG表示甘油三酯,NEFA表示游离脂肪酸,LPL表示肝内脂质,ACC表示乙酰辅酶A羧化酶,FAS表示脂肪酸合酶,SREBP-1表示固醇调节元件结合蛋白1,PGC-1α表示过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ共激活剂1α,CS表示柠檬酸合成酶,β-HAD表示β三羟基酰基辅酶A脱氢酶,Cyt c表示细胞色素c,Glucose表示葡萄糖,Insulin表示胰岛素,VLDL表示极低密度脂蛋白。Figure 1. Signal pathway of exercise training reducing lipid content in liver[25]运动训练除了对血浆NEFA水平有影响外,还可能调节餐后脂质代谢。运动训练可降低高脂膳食后的血清甘油三酯浓度,运动员和久坐男性之间甘油三酯半衰期的差异,可能是由于运动训练对脂蛋白脂肪酶介导的甘油三酯向骨骼肌迁移的直接作用所致[25]。无论是一次性高强度有氧运动,还是长期中等强度有氧运动耐力训练,无论男女,人体骨骼肌中脂蛋白脂肪酶的活性均增强,骨骼肌对乳糜微粒的吸收均增加,肝脏对乳糜微粒的运载量降低。已知肝素可促使内皮结合部位的脂蛋白脂肪酶释放到循环血液中,健康、久坐的个体在经过20周有氧运动训练后,输注肝素后血浆中的脂蛋白脂肪酶活性增强。肝素输注后不久测得的脂蛋白脂肪酶活性是来自骨骼肌而非脂肪组织的。这一结果表明,通过有氧运动训练,餐后甘油三酯更有可能被骨骼肌吸收[25]。肝脂肪酶在脂蛋白重构及从乳糜微粒、高密度脂蛋白、中等密度脂蛋白和低密度脂蛋白中水解甘油三酯和磷脂等方面发挥重要作用,使甘油三酯被肝脏吸收。经过20周的有氧运动训练后,肝素输注后的肝脂肪酶活性显著降低,这可能导致餐后肝脏对甘油三酯的摄取降低。虽然这些研究结果间接表明,餐后脂肪通过运动训练流向骨骼肌而远离肝脏,但对餐后肝脏脂肪储存的影响尚未得到直接证明。在本文检索到的文献中,产生降低肝内脂质含量效果的抗阻运动训练干预的持续时间(8周)[12]长于有氧运动及高强度间歇运动的最短干预持续时间(4周)[31, 43]。NAFLD患者若坚持抗阻运动训练3个月可改善其肝内脂质含量,并改善体脂分布和低密度脂蛋白水平[11]。
虽然人们认为VLDL代谢通常不是人类NAFLD发生的潜在因素,但运动训练仍然可以通过改变VLDL代谢影响肝内脂质含量。目前还没有研究探讨运动训练诱导VLDL代谢变化对人肝内脂质含量的影响,但有研究探讨了运动训练对VLDL分泌和清除的影响。高强度间歇运动或有氧运动训练似乎也会降低肝脏VLDL-甘油三酯的分泌,这虽然证明了肝脏代谢的有益适应,但不能解释为什么运动训练会降低肝内脂质含量,因为VLDL-甘油三酯分泌的降低理论上会导致更多的肝内脂质储存。因此,减少VLDL-甘油三酯的分泌很可能是运动训练后肝内脂质含量降低的结果[61]。
运动训练降低人体血浆胰岛素水平是脂质新生激活的一个关键因素,由此推测,运动训练可能降低脂质新生活性。动物实验研究[62-64]结果显示,运动训练降低了肝脏脂肪酸合成的关键酶乙酰辅酶A羧化酶和脂肪酸合酶的活性,运动训练对大鼠肝内脂质含量的影响与脂质新生活性之间似乎存在联系。运动训练可显著降低空腹血糖和空腹胰岛素水平,已知胰岛素可通过调节葡萄糖代谢刺激脂质新生[65],因此,运动训练可能通过降低血浆中胰岛素和葡萄糖的浓度而减弱脂质新生。有证据表明,在进行有氧运动训练的个体中,血浆胰岛素和葡萄糖的浓度较低,是因为有氧运动训练改善了全身的胰岛素敏感性。虽然没有关于人体脂质新生活性的直接数据,但在人体中观察到的低血糖和/或胰岛素水平与在动物模型中一致。在运动训练前后,对脂质新生活性的直接测量有助于进一步认识人类运动训练降低肝内脂质含量的作用机制。
此外,动物实验研究[63-64]结果显示,单纯有氧运动训练或有氧运动训练同时控制热量摄入可有效减少动物肝内脂质含量,伴随过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ共激活剂1α表达的增加,并且作为线粒体功能标志物的线粒体蛋白质(包括细胞色素c、β三羟基酰基辅酶A脱氢酶和柠檬酸合成酶)含量也同时增加。尚未见有关运动训练对人体肝脏线粒体功能影响的研究报道,未来或许可使用磷磁共振波谱法测量肝脏线粒体功能与运动训练中肝内脂质含量变化的关系,以确定在啮齿动物中的观察结果是否也适用于人类。
5. 影响人体肝内脂质含量的其他因素
随着研究的深入,NAFLD发病的可能机制也在不断被揭示,从Day等[66]提出的“二次打击”假说不足以解释NAFLD发生的分子和代谢变化,到Buzzetti等[67]提出的“多重打击”假说考虑到遗传易感人群同时受到胰岛素抵抗、脂肪组织堆积及分泌激素、营养因素、肠道菌群、遗传及表观遗传因子等多种因素协同作用的影响,逐渐为NAFLD的发生机制提供了更准确的解释。
与增加运动训练同样重要的似乎是避免久坐[55]。大量基于人群的研究[55, 68]结果表明,久坐不动的时间是胰岛素抵抗综合征的独立预测因子,并一致认为这与中度甚至剧烈的体力活动水平无关。不锻炼的原因包括心肺适能下降[19]、疲劳[69]、与体质量相关的关节疾病[70]、心血管疾病和心理因素[71]等。
除了运动,增加可溶性纤维的摄入可能在减少脂质含量和提升胰岛素敏感性方面发挥了重要作用。Cheng等[42]研究表明,当纤维摄入量较少时,即使增加纤维摄入量到推荐的水平,也会对健康造成重要影响。早期对NAFLD患者运动获益与方案的研究一直存在争议,因为运动伴随着饮食的改变,或是饮食诱导的减肥,运动是否对NAFLD具有独立影响存在争议。最近,更多的对照研究不仅证明运动对降低肝内脂质含量有效,而且也开始探索其潜在的机制。虽然运动对肝内脂质含量降低有显著的临床意义(肝内脂质含量相对减少20%~30%),但与减肥(减少80%)相比,运动的干预效果并不明显[72]。通过节食方法控制体质量比单纯运动对肝脏脂肪产生更大的影响。然而,完全分离运动和饮食可能没有好处,研究[73]表明在NAFLD患者中,心肺健康是饮食干预的决定因素。这就形成了一个矛盾:心肺健康水平较低且认为锻炼较为困难的人,对饮食诱导的生活方式干预的反应也较低。此外,高水平的体力活动(每周200~300 min)对保持减肥效果至关重要,因为运动对NAFLD的治疗有独立的作用,它为减肥困难的人提供了另一种治疗选择。
6. 结论
有氧运动、抗阻运动和高强度间歇运动单独干预或组合干预均可降低NAFLD患者的肝内脂质含量,但剂量选择和靶向作用不同。有氧运动干预达到肝内脂质含量下降效果的持续时间需至少4周,运动强度和持续时间的结构性组合方式似乎影响力稍弱,但是低于一定限度的有氧运动干预无法实现肝内脂质含量下降。有氧运动通过分解消耗脂肪降低肝内脂质含量,抗阻运动主要通过有效增大肌肉力量和质量促进骨骼肌吸收NEFA减少肝脏脂质堆积。产生降低肝内脂质含量效果的抗阻运动训练干预持续时间(8周)长于有氧运动及高强度间歇运动最短干预持续时间(4周)。从长期效果出发则推荐NAFLD患者采取有氧运动与抗阻运动组合的干预形式,但高强度间歇运动相对更高效、省时,且只有高强度间歇运动才能有效改善肝硬化和恢复Kupffer细胞功能。运动训练降低肝内脂质含量最可能的途径是降低肝脏对血液循环中脂质的吸收和新生,以及增加肝内甘油三酯氧化。运动训练对肝脏代谢的有益影响及其与全身代谢的相互作用所涉及的潜在通路需要进一步研究。
-
图 1 运动训练降低肝脏内脂质含量的信号通路[25]
注:红色圆圈代表运动训练对肝脏脂质代谢的抑制通路,绿色圆圈代表运动训练对肝脏脂质代谢的上调路径;TAG表示甘油三酯,NEFA表示游离脂肪酸,LPL表示肝内脂质,ACC表示乙酰辅酶A羧化酶,FAS表示脂肪酸合酶,SREBP-1表示固醇调节元件结合蛋白1,PGC-1α表示过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ共激活剂1α,CS表示柠檬酸合成酶,β-HAD表示β三羟基酰基辅酶A脱氢酶,Cyt c表示细胞色素c,Glucose表示葡萄糖,Insulin表示胰岛素,VLDL表示极低密度脂蛋白。
Figure 1. Signal pathway of exercise training reducing lipid content in liver[25]
表 1 不同类型运动干预NAFLD的剂量与效果
Table 1 Dose selection and effect of different exercise intervention on NAFLD
文献 研究对象 n 年龄/岁 运动
类型运动干预方案 干预
时间干预效果 Zhang等[26] 肥胖成年人 220 54±7.0 AE 快步走(强度维持在最大心率的45%~55%)、跑步(强度维持在最大心率的65%~80%),每周150 min 12个月 体质量下降,体脂率下降,腰围下降,内脏脂肪含量下降,肝内脂质含量下降 Promrat等[29] 超重/肥胖
成年人31 49±11.0 AE 跑步、蹬功率车,中等强度体力活动,10 000步/d,每周200 min 48周 体质量下降,肝脏组织学表现改善 Wong等[30] 超重成年人 154 51±9.0 AE 中等强度AE,每次30 min,每周3~5次 12个月 体质量下降,腰围下降,肝内脂质含量下降 Johnson等[31] 肥胖成年人 19 49±2.0 AE 蹬功率车,强度维持在峰值摄氧量的50%~70%,每次30~45 min,每周3次 4周 肝内脂质含量下降,内脏脂肪含量下降,峰值摄氧量上升 Keating等[32] 超重/肥胖
成年人47 44.0±3.0 AE 蹬功率车,LO∶HI组运动强度维持在峰值摄氧量的50%,每次60 min,每周3次;HI∶LO组运动强度维持在峰值摄氧量的70%,每次45 min,每周3次;LO∶LO组运动强度维持在峰值摄氧量的50%,每次45 min,每周3次 8周 肝内脂质含量下降,内脏脂肪含量下降,腰围下降,峰值摄氧量上升 Sullivan等[33] 肥胖成年人 18 47.5±3.1 AE 运动强度维持在峰值摄氧量的45%~55%,每天30~60 min,每周5 d 16周 肝内脂质含量下降 Van der Heijden等[34] 肥胖青少年 29 15.0±1.0 AE 蹬功率车,运动强度维持在峰值摄氧量的70%,每次30 min,每周2次 12周 肝内脂质含量下降,内脏脂肪含量下降,胰岛素抵抗下降,峰值摄氧量上升 Shojaee-Moradie等[35] 久坐超重
男性17 50.0±2.6 AE 运动强度维持在峰值摄氧量的60%~85%,每次20 min,每周3次 6周 肝脏脂肪含量无显著变化 Bacchi等[11] 超重/肥胖
成年人31 56.0±2.0 RE RE训练3组动作,每组动作重复10次,1次重复最大力量的70%~80%,每周3次;跑步、自行车等AE,运动强度维持在最大心率的60%~65%,每次60 min,每周3次 4个月 2组肝内脂质含量、内脏脂肪含量下降,1/4的患者肝内脂肪变性消失,胰岛素敏感性升高,2组总体脂肪质量、内脏脂肪、皮下脂肪组织、糖化血红蛋白均降低 Hallsworth等[12] 久坐肥胖
成年人19 52.0±13.3 RE RE训练8个动作,每次45~60 min、2~3组、8个动作,1次重复最大力量的50%~70%,每周3次 8周 肝内脂质含量下降,改善血糖控制和胰岛素抵抗 Zelber-Sagi等[36] 超重/肥胖
成年人82 40.0±11.0 RE RE训练3组动作,3次重复最大力量,每周增加0.5 kg直至4 kg,重复8~12次,每次40 min 12周 肝内脂质、体脂、低密度脂蛋白、胆固醇水平均下降,胰岛素敏感性升高 Hallsworth等[37] 久坐肥胖
成年人23 54.0±10.0 HIIT 蹬功率车HIIT方案:第1周高强度运动2 min(自我疲劳程度评分为16~17分),之后每周增加10 s;3 min恢复,恢复期包括90 s的被动恢复及60 s的上肢轻度阻力迷你带训练,每个动作间隔15 s;3 min放松;每次持续30~40 min,每周3次 12周 肝内脂质含量、体脂、丙氨酸、天冬氨酸转氨酶水平均下降 Cassidy等[38] 肥胖老年人,2型糖尿病患者 28 61.0±9.0 HIIT 蹬功率车HIIT方案:第1周高强度运动2 min(自我疲劳程度评分为16~17分),之后每周增加10 s;3 min恢复,恢复期包括90 s的被动恢复及60 s的上肢轻度阻力迷你带训练,每个动作间隔15 s;3 min放松;每次持续30~40 min,每周4次 12周 肝内脂质含量、体脂含量均下降,心脏结构改善,糖化血红蛋白水平下降 Lee等[13] 肥胖青少年,男 32 对照组14.8±1.4;AE组15.2±1.9;RE组14.6±1.5 AE vs RE AE组:第1周运动强度为最大摄氧量的40%,每次40 min;第2~12周运动强度为最大摄氧量的60%~75%,每次60 min;每周3次。RE组:10个动作、2组、8~12次重复,持续60 min,每次重复最大力量的60%(第1~4周)至疲劳(第5~12周),每周3次 3个月 2组肝内脂质、体质量、体脂、内脏脂肪水平均下降 Lee等[14] 肥胖青少年,女 32 Con组
15.0±2.2;AE组14.6±1.9;RE组14.8±1.9AE vs RE AE组:第1周运动强度为最大摄氧量的40%,每次40 min;第2~12周运动强度为最大摄氧量的60%~75%,每次60 min;每周3次。RE组:10个动作、2组、8~12次重复,持续60 min,每次重复最大力量的60%(第1~4周)至疲劳(第5~12周);每周3次 3个月 AE组肝内脂质、体脂、内脏脂肪含量均下降;RE组肝内脂质含量无显著性变化,体脂含量下降 Slentz等[39] 超重/肥胖
久坐成年人196 49.0±11.0 AE vs RE RE训练,8个动作、3组、8~12次重复,每周3次;AE训练,强度维持在峰值摄氧量的75%,每周19.2 km;RE+AE训练 8个月 AE组肝内脂质、内脏脂肪、丙氨酸转氨酶、胰岛素抵抗、总脂肪及腹部皮下脂肪含量均显著降低;RE组皮下脂肪含量减少,其他指标均未见明显改善。在改善内脏脂肪、肝脾比值和腹部总脂肪方面,AE比RE更有效。AE+RE训练的效果与单纯AE训练相比无显著性差异 De Piano等[40] 肥胖青少年 58 16.5±1.4 AE+RE 跑步、蹬功率车,运动强度维持在峰值摄氧量的50%~70%,每次60 min,每周3次;主要肌肉群RE训练,6~20次重复最大力量,每次30 min,每周3次 12个月 体质量、内脏脂肪、体脂水平均下降,炎症标志物和食欲肽浓度均降低 Brouwers等[41] 男性NAFLD患者和男性健康成年人 22 NAFLD: 54.5± 6.8;Con:57.6±8.1 AE+RE AE组:蹬功率车,运动强度为最大摄氧量的70%,每次30 min,每周2次。RE组:3组动作,重复10次,1次重复最大力量的60%,重点锻炼大肌肉群 12周 高脂肪和低脂肪含量者的肝内脂质含量均降低。运动训练对2组肝内脂质含量的影响相似 Cheng等[42] 糖尿病前期及NAFLD患者 115 对照组:60.0±3.4;
AE组:59.0 ±4.4;
饮食干预组:60.0±4.1;
AE结合饮食干预组:60.0±3.5AE/AE+饮食干预 AE组:北欧式健步走,运动强度维持在峰值摄氧量的60%~75%,每次30~60 min,每周2~3次。饮食干预组:38% 碳水化合物,膳食纤维12 g/d 8.6个月 所有干预组肝内脂质含量均下降,但AE结合饮食干预组下降幅度更明显,且只有结合组糖化血红蛋白显著下降 Winn等[43] 肥胖成年人 18 41.0±14.0 HIIT vs AE HIIT组:4 min强度维持在峰值摄氧量80%的运动和3 min强度维持在峰值摄氧量50%的运动交替。AE组:运动强度维持在峰值摄氧量的55%,持续60 min 4周 肝内脂质含量下降,2个干预组之间效果差异无统计学意义 Oh等[44] 久坐肥胖
成年人61 RE组:51.2±1.9;HIIT组:48.6 ±1.8;AE组:48.2± 2.3 HIIT vs AE vs RE 所有训练每周3次。RE组:2009年美国运动医学学会推荐的仰卧起坐、腿部按压、腿部伸展、腿部弯曲、胸部按压、坐式划船和下拉7个动作,1次重复最大力量,负荷率每个月增加1次。HIIT组:蹬功率车,3组3 min强度维持在峰值摄氧量80%~85%的运动,2组2 min强度维持在峰值摄氧量50%的运动。AE组:40 min强度维持在峰值摄氧量60%~65%的运动 12周 所有运动训练组肝内脂质含量下降,只有HIIT在改善肝硬化和恢复Kupffer细胞功能方面有效 注:年龄数据以平均数±标准差形式表示;NAFLD表示非酒精性脂肪性肝病,AE表示有氧运动,RE表示抗阻运动,HIIT表示高强度间歇运动,Con组表示对照组。 -
[1] YOUNOSSI Z M, KOENIG A B, ABDELATIF D, et al. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes[J]. Hepatology, 2016, 64(1): 73-84 doi: 10.1002/hep.28431
[2] BAMBHA K, BELT P, ABRAHAM M, et al. Ethnicity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Hepatology, 2012, 55(3): 769-780 doi: 10.1002/hep.24726
[3] FARRELL G C, WONG V W, CHITTURI S. NAFLD in Asia: As common and important as in the West[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2013, 10(5): 307-318 doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2013.34
[4] STINE J G, WENTWORTH B J, ZIMMET A, et al. Systematic review with meta-analysis: Risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis without cirrhosis compared to other liver diseases[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2018, 48(7): 696-703 doi: 10.1111/apt.14937
[5] TOPLAK H, STAUBER R, SOURIJ H. EASL-EASD-EASO clinical practice guidelines for the management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Guidelines, clinical reality and health economic aspects[J]. Diabetologia, 2016, 59(6): 1148-1149 doi: 10.1007/s00125-016-3941-4
[6] CHALASANI N, YOUNOSSI Z, LAVINE J E, et al. The diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, American College of Gastroenterology, and the American Gastroenterological Association[J]. Hepatology, 2012, 55(6): 2005-2023 doi: 10.1002/hep.25762
[7] MIKOLASEVIC I, MILIC S, WENSVEEN T T, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A multisystem disease?[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2016, 22(43): 9488-9505 doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i43.9488
[8] CHALASANI N, YOUNOSSI Z, LAVINE J E, et al. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases[J]. Hepatology, 2018, 67(1): 328-357 doi: 10.1002/hep.29367
[9] 赵红, 谢雯. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病的中西医结合治疗现状[J]. 中国临床医生杂志, 2020, 48(1): 16-18 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZLYS202001007.htm [10] BANERJEE R, PAVLIDES M, TUNNICLIFFE E M, et al. Multiparametric magnetic resonance for the non-invasive diagnosis of liver disease[J]. J Hepatol, 2014, 60(1): 69-77 doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.09.002
[11] BACCHI E, NEGRI C, TARGHER G, et al. Both resistance training and aerobic training reduce hepatic fat content in type 2 diabetic subjects with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (the RAED2 randomized trial)[J]. Hepatology, 2013, 58(4): 1287-1295 doi: 10.1002/hep.26393
[12] HALLSWORTH K, FATTAKHOVA G, HOLLINGSWORTH K G, et al. Resistance exercise reduces liver fat and its mediators in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease independent of weight loss[J]. Gut, 2011, 60(9): 1278-1283 doi: 10.1136/gut.2011.242073
[13] LEE S, BACHA F, HANNON T, et al. Effects of aerobic versus resistance exercise without caloric restriction on abdominal fat, intrahepatic lipid, and insulin sensitivity in obese adolescent boys: A randomized, controlled trial[J]. Diabetes, 2012, 61(11): 2787-2795 doi: 10.2337/db12-0214
[14] LEE S, DELDIN A R, WHITE D, et al. Aerobic exercise but not resistance exercise reduces intrahepatic lipid content and visceral fat and improves insulin sensitivity in obese adolescent girls: A randomized controlled trial[J]. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 2013, 305(10): E1222-E1229 doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00285.2013
[15] 荆文, 李传芬, 冯连世. 运动激活AMPK改善非酒精性脂肪肝的研究进展[J]. 体育科学, 2019, 39(10): 91-97 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TYKX201910011.htm [16] PRICE J K, SRIVASTAVA R, BAI C, et al. Comparison of activity level among patients with chronic liver disease[J]. Disabil Rehabil, 2013, 35(11): 907-912 doi: 10.3109/09638288.2012.712601
[17] ZELBER-SAGI S, NITZAN-KALUSKI D, GOLDSMITH R, et al. Role of leisure-time physical activity in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A population-based study[J]. Hepatology, 2008, 48(6): 1791-1798 doi: 10.1002/hep.22525
[18] PERSEGHIN G, LATTUADA G, DE COBELLI F, et al. Habitual physical activity is associated with intrahepatic fat content in humans[J]. Diabetes Care, 2007, 30(3): 683-688 doi: 10.2337/dc06-2032
[19] JOANNE B K. Health-related fitness and physical activity in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Hepatology(Baltimore, Md), 2008, 47(4): 1158-1166 doi: 10.1002/hep.22137/full
[20] CHITTURI S, WONG V W, CHAN W K, et al. The Asiapacific working party on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease guidelines 2017: Part 2: Management and special groups[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018, 33(1): 86-98 doi: 10.1111/jgh.13856
[21] 中华医学会肝病学分会脂肪肝和酒精性肝病学组, 中国医师协会脂肪性肝病专家委员会. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病防治指南: 2018更新版[J]. 现代医药卫生, 2018, 34(5): 641-649 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5519.2018.05.001 [22] SCHWEITZER G G, KLEIN S. Exercise and NAFLD: Is it worth the effort?[J]. Hepatology, 2017, 66(5): 1691-1694 doi: 10.1002/hep.29356
[23] GEHRKE N, BIEDENBACH J, HUBER Y, et al. Voluntary exercise in mice fed an obesogenic diet alters the hepatic immune phenotype and improves metabolic parameters: An animal model of life style intervention in NAFLD[J]. Sci Rep, 2019, 9: 4007 doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-38321-9
[24] ROMERO-GÓMEZ M, ZELBER-SAGI S, TRENELL M. Treatment of NAFLD with diet, physical activity and exercise[J]. J Hepatol, 2017, 67(4): 829-846 doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.05.016
[25] BROUWERS B, HESSELINK M K, SCHRAUWEN P, et al. Effects of exercise training on intrahepatic lipid content in humans[J]. Diabetologia, 2016, 59(10): 2068-2079 doi: 10.1007/s00125-016-4037-x
[26] ZHANG H J, HE J, PAN L L, et al. Effects of moderate and vigorous exercise on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized clinical trial[J]. JAMA Intern Med, 2016, 176(8): 1074-1082 doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2016.3202
[27] RATZIU V, BELLENTANI S, CORTEZ-PINTO H, et al. A position statement on NAFLD/NASH based on the EASL 2009 special conference[J]. J Hepatol, 2010, 53(2): 372-384 doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2010.04.008
[28] HELMERHORST H J, WIJNDAELE K, BRAGE S, et al. Objectively measured sedentary time may predict insulin resistance independent of moderate- and vigorous-intensity physical activity[J]. Diabetes, 2009, 8(58): 1776-1779 http://drc.bmj.com/lookup/ijlink?linkType=ABST&journalCode=diabetes&resid=58/8/1776&atom=%2Fbmjdrc%2F5%2F1%2Fe000306.atom
[29] PROMRAT K, KLEINER D E, NIEMEIER H M, et al. Randomized controlled trial testing the effects of weight loss on nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Hepatology, 2010, 51(1): 121-129 doi: 10.1002/hep.23276
[30] WONG V W, CHAN R S, WONG G L, et al. Communitybased lifestyle modification programme for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized controlled trial[J]. J Hepatol, 2013, 59(3): 536-542 doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.04.013
[31] JOHNSON N A, SACHINWALLA T, WALTON D W, et al. Aerobic exercise training reduces hepatic and visceral lipids in obese individuals without weight loss[J]. Hepatology, 2009, 50(4): 1105-1112 doi: 10.1002/hep.23129
[32] KEATING S E, HACKETT D A, PARKER H M, et al. Effect of aerobic exercise training dose on liver fat and visceral adiposity[J]. J Hepatol, 2015, 63(1): 174-182 doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.02.022
[33] SULLIVAN S, KIRK E P, MITTENDORFER B, et al. Randomized trial of exercise effect on intrahepatic triglyceride content and lipid kinetics in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Hepatology, 2012, 55(6): 1738-1745 doi: 10.1002/hep.25548
[34] VAN DER HEIJDEN G J, WANG Z J, CHU Z D, et al. A 12-week aerobic exercise program reduces hepatic fat accumulation and insulin resistance in obese, hispanic adolescents[J]. Obesity, 2010, 18(2): 384-390 doi: 10.1038/oby.2009.274
[35] SHOJAEE-MORADIE F, BAYNES K C, PENTECOST C, et al. Exercise training reduces fatty acid availability and improves the insulin sensitivity of glucose metabolism[J]. Diabetologia, 2007, 50(2): 404-413 doi: 10.1007/s00125-006-0498-7
[36] ZELBER-SAGI S, BUCH A, YESHUA H, et al. Effect of resistance training on non-alcoholic fatty-liver disease a randomized-clinical trial[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2014, 20(15): 4382-4392 doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i15.4382
[37] HALLSWORTH K, THOMA C, HOLLINGSWORTH K G, et al. Modified high-intensity interval training reduces liver fat and improves cardiac function in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized controlled trial[J]. Clin Sci (Lond), 2015, 129(12): 1097-1105 doi: 10.1042/CS20150308
[38] CASSIDY S, THOMA C, HALLSWORTH K, et al. High intensity intermittent exercise improves cardiac structure and function and reduces liver fat in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomised controlled trial[J]. Diabetologia, 2016, 59(1): 56-66 doi: 10.1007/s00125-015-3741-2
[39] SLENTZ C A, BATEMAN L A, WILLIS L H, et al. Effects of aerobic vs. resistance training on visceral and liver fat stores, liver enzymes, and insulin resistance by HOMA in overweight adults from STRRIDE AT/RT[J]. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 2011, 301(5): E1033-E1039 doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00291.2011
[40] DE PIANO A, DE MELLO M T, DE L SANCHES P, et al. Long-term effects of aerobic plus resistance training on the adipokines and neuropeptides in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease obese adolescents[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2012, 24(11): 1313-1324 http://labs.europepmc.org/abstract/MED/22932160
[41] BROUWERS B, SCHRAUWEN-HINDERLING V B, JELENIK T, et al. Exercise training reduces intrahepatic lipid content in people with and people without nonalcoholic fatty liver[J]. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 2018, 314(2): E165-E173 doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00266.2017
[42] CHENG S L, GE J, ZHAO C, et al. Effect of aerobic exercise and diet on liver fat in pre-diabetic patients with non-alcoholic-fatty-liver-disease: A randomized controlled trial[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 15952 doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-16159-x
[43] WINN N C, LIU Y, RECTOR R S, et al. Energy-matched moderate and high intensity exercise training improves nonalcoholic fatty liver disease risk independent of changes in body mass or abdominal adiposity: A randomized trial[J]. Metabolism, 2018, 78: 128-140 doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2017.08.012
[44] OH S, SO R, SHIDA T, et al. High-intensity aerobic exercise improves both hepatic fat content and stiffness in sedentary obese men with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7: 43029 doi: 10.1038/srep43029
[45] 甄志平, 罗超, 李湘平, 等. 运动干预非酒精性脂肪肝病的研究进展[J]. 中国预防医学杂志, 2019, 20(1): 73-77 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYC201901019.htm [46] KEATING S E, HACKETT D A, GEORGE J, et al. Exercise and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Hepatol, 2012, 57(1): 157-166 doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2012.02.023
[47] KATSAGONI C N, GEORGOULIS M, PAPATHEODORIDIS G V, et al. Effects of lifestyle interventions on clinical characteristics of patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A meta-analysis[J]. Metabolism, 2017, 68: 119-132 doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2016.12.006
[48] 张戈. 高强度间歇训练: 运动量和锻炼效果研究进展[J]. 中国运动医学杂志, 2016, 35(2): 184-188 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YDYX201602016.htm [49] HONG H C, HWANG S Y, CHOI H Y, et al. Relationship between sarcopenia and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: The Korean sarcopenic obesity study[J]. Hepatology, 2014, 59(5): 1772-1778 doi: 10.1002/hep.26716
[50] WILLIAMS M A, HASKELL W L, ADES P A, et al. Resistance exercise in individuals with and without cardiovascular disease: 2007 update: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association Council on Clinical Cardiology and Council on Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism[J]. Circulation, 2007, 116(5): 572-584 doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.185214
[51] KEATING S E, ADAMS L A. Exercise in NAFLD: Just do it[J]. J Hepatol, 2016, 65(4): 671-673 doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.06.022
[52] OH S, SHIDA T, SAWAI A, et al. Acceleration training for managing nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A pilot study[J]. Ther Clin Risk Manag, 2014, 10: 925-936 http://europepmc.org/articles/pmc4230176/
[53] OH S, MARUYAMA T, EGUCHI K, et al. Therapeutic effect of hybrid training of voluntary and electrical muscle contractions in middle-aged obese women with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A pilot trial[J]. Ther Clin Risk Manag, 2015, 11: 371-380 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4354454/
[54] EL-AGROUDY N N, KURZBACH A, RODIONOV R N, et al. Are lifestyle therapies effective for NAFLD treatment?[J]. Trends Endocrinol Metab, 2019, 30(10): 701-709 doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2019.07.013
[55] HEALY G N, WIJNDAELE K, DUNSTAN D W, et al. Objectively measured sedentary time, physical activity, and metabolic risk[J]. Diabetes Care, 2008, 31(2): 369-371 doi: 10.2337/dc07-1795
[56] BRUNNER K T, HENNEBERG C J, WILECHANSKY R M, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and obesity treatment[J]. Curr Obes Rep, 2019, 8(3): 220-228 doi: 10.1007/s13679-019-00345-1
[57] CHO J, LEE I, KIM D, et al. Effect of aerobic exercise training on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease induced by a high fat diet in C57BL/6 mice[J]. J Exerc Nutrition Biochem, 2014, 18(4): 339-346 doi: 10.5717/jenb.2014.18.4.339
[58] FARZANEGI P, DANA A, EBRAHIMPOOR Z, et al. Mechanisms of beneficial effects of exercise training on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): Roles of oxidative stress and inflammation[J]. Eur J Sport Sci, 2019, 19(7): 994-1003 doi: 10.1080/17461391.2019.1571114
[59] KALAKI-JOUYBARI F, SHANAKI M, DELFAN M, et al. High-intensity interval training(HⅡT) alleviated NAFLD feature via miR-122 induction in liver of high-fat highfructose diet induced diabetic rats[J]. Arch Physiol Biochem, 2020, 126(3): 242-249 doi: 10.1080/13813455.2018.1510968
[60] MEEX R C, SCHRAUWEN-HINDERLING V B, MOONEN-KORNIPS E, et al. Restoration of muscle mitochondrial function and metabolic flexibility in type 2 diabetes by exercise training is paralleled by increased myocellular fat storage and improved insulin sensitivity[J]. Diabetes, 2010, 59(3): 572-579 doi: 10.2337/db09-1322
[61] TSEKOURAS Y E, MAGKOS F, KELLAS Y, et al. Highintensity interval aerobic training reduces hepatic very lowdensity lipoprotein-triglyceride secretion rate in men[J]. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 2008, 295(4): E851-E858 doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.90545.2008
[62] RECTOR R S, THYFAULT J P, MORRIS R T, et al. Daily exercise increases hepatic fatty acid oxidation and prevents steatosis in otsuka long-evans tokushima fatty rats[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2008, 294(3): G619-G626 doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00428.2007
[63] LINDEN M A, FLETCHER J A, MORRIS E M, et al. Combining metformin and aerobic exercise training in the treatment of type 2 diabetes and NAFLD in OLETF rats[J]. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 2014, 306(3): E300-E310 doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00427.2013
[64] RECTOR R S, UPTERGROVE G M, MORRIS E M, et al. Daily exercise vs. caloric restriction for prevention of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the OLETF rat model[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2011, 300(5): G874-G883 doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00510.2010
[65] AMEER F, SCANDIUZZI L, HASNAIN S, et al. De novo lipogenesis in health and disease[J]. Metabolism, 2014, 63(7): 895-902 doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2014.04.003
[66] DAY C P, JAMES O F. Steatohepatitis: A tale of two "hits"?[J]. Gastroenterology, 1998, 114(4): 842-845 doi: 10.1016/S0016-5085(98)70599-2
[67] BUZZETTI E, PINZANI M, TSOCHATZIS E A. The multiple-hit pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease(NAFLD)[J]. Metabolism, 2016, 65: 1038-1048 doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2015.12.012
[68] PETERSEN C B, NIELSEN A J, BAUMAN A, et al. Joint association of physical activity in leisure and total sitting time with metabolic syndrome amongst 15, 235 Danish adults: A cross-sectional study[J]. Prev Med, 2014, 69: 5-7 doi: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2014.08.022
[69] NEWTON J L, JONES D E, HENDERSON E, et al. Fatigue in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease(NAFLD) is significant and associates with inactivity and excessive daytime sleepiness but not with liver disease severity or insulin resistance[J]. Gut, 2008, 57(6): 807-813 doi: 10.1136/gut.2007.139303
[70] CHURCH T S, KUK J L, ROSS R, et al. Association of cardiorespiratory fitness, body mass index, and waist circumference to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Gastroenterology, 2006, 130(7): 2023-2030 doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2006.03.019
[71] FRITH J, DAY C P, ROBINSON L, et al. Potential strategies to improve uptake of exercise interventions in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Hepatol, 2010, 52(1): 112-116 doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2009.10.010
[72] THOMA C, DAY C P, TRENELL M I. Lifestyle interventions for the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in adults: A systematic review[J]. J Hepatol, 2012, 56(1): 255-266 doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2011.06.010
[73] KANTARTZIS K, THAMER C, PETER A, et al. High cardiorespiratory fitness is an independent predictor of the reduction in liver fat during a lifestyle intervention in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Gut, 2009, 58(9): 1281-1288 doi: 10.1136/gut.2008.151977
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 张素明. 限时饮食联合运动促进减肥的研究进展. 体育科技文献通报. 2024(10): 266-270 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 酒梦娜,孙佳森,雷玮,杨莉莉,杨小翠,肖翔. 二甲双胍联合达格列净对MAFLD患者血脂水平及肝脂肪含量的影响. 中国临床实用医学. 2024(06): 20-25 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 徐嘉兰,江远,徐文华,黄小花. 基于王氏养生三法的中医体质调节在非酒精性脂肪性肝病患者中的应用分析. 现代医院. 2021(12): 1959-1962 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)




 下载:
下载: