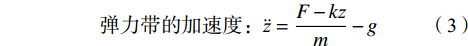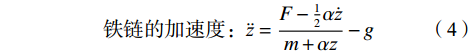Effects of Variable Resistance Training on Strength Performance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
-
摘要:目的
系统评价可变阻力训练对最大力量和爆发力表现的急性干预和训练干预效果,为在实践中科学运用可变阻力训练提供证据支持。
方法通过CNKI及PubMed、Web of Science、SPORTDiscus等数据库检索文献,采用Brughelli改进的质量评分表评价文献质量。应用Stata 16.0软件分别进行数据合并、亚组分析、绘制森林图、异质性分析、meta回归、发表偏倚评价。
结果急性干预共纳入8篇文献,与恒定阻力训练相比,可变阻力训练能更有效地诱导激活后增强效应(postactivation potentiation,PAP)(SMD=0.37,95%CI:0.18~0.56,P<0.001),且采用强度相同的设计方式诱导的PAP有非常显著性差异(P<0.001)。4~7 min间歇时间诱导的PAP趋向显著性(P=0.05),8~12 min诱导的PAP有非常显著性差异(P<0.001)。采用较大的可变阻力诱导的PAP可能更好(P=0.064)。训练干预共纳入12篇文献,与恒定阻力训练相比,可变阻力训练能更有效地提高最大力量表现(SMD=0.25,95%CI:0.05~0.45,P<0.05),且<7周的训练周期(P=0.04)以及使用铁链作为可变阻力设备(P=0.01)的训练效果更佳。可变阻力训练可能更有益于提高爆发力表现(SMD=0.26,95%CI:−0.03~0.55,P=0.08),且强度相同的设计方式以及使用弹力带作为可变阻力设备的训练效果可能更佳(P=0.08)。
结论设计可变阻力训练方案时,采用强度相同的设计方式以及较大的可变阻力是诱导PAP的最佳策略,且在干预后4~12 min的效果最佳。<7周以及使用铁链的训练策略对最大力量表现的训练效果更好;采用强度相同的设计方式以及使用弹力带的训练策略对提升爆发力表现可能效果更佳,但可变阻力不宜过大。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo evaluate the acute intervention and training intervention effects of variable resistance training on maximal strength and power, and to provide strong evidence for the scientific application of performing variable resistance training.
MethodsA literature search was conducted by using the PubMed, Web of Science, SPORTDiscus and CNKI electronic databases. A modified version of quality scoring system by Brughelli was used to assess each study. The data combining, subgroup analyses, forest plot, heterogeneity, meta-regression, publication bias were used and assessed with Stata 16.0 version.
Results8 studies were included on acute intervention. Compared to constant resistance training, variable resistance training significantly induced larger PAP (SMD=0.37, 95%CI: 0.18-0.56, P<0.001). PAP in 4-7 min recovery intervals tended to be significant (P=0.05), PAP in 8-12 min recovery intervals was significantly larger (P<0.001). The larger contribution of variable resistance could be more beneficial in inducing PAP (P=0.064). 12 studies were included on training intervention. Compared to constant resistance training, variable resistance training significantly improved maximal strength (SMD=0.25, 95%CI: 0.05-0.45, P<0.05); the intervention duration <7 weeks (P=0.04) and using chains as the variable resistance equipment (P=0.01) had a significantly larger effect on maximal strength. Variable resistance training could be more beneficial in improving power performance (SMD=0.26, 95% CI: −0.03-0.55, P=0.08), and the same relative load scheme and elastic band as the variable resistance equipment could be even better (P=0.08).
ConclusionsWhen manipulating variable resistance training, the same load and larger contribution of variable resistance was an optimal strategy to induce PAP, and the 4-12 min recovery interval was a better choice. Utilizing shorter than 7-week intervention and chains as the variable resistance equipment was an ideal strategy in improving maximal strength performance. Using the same load scheme and elastic band may be an ideal strategy in improving power performance, but the contribution of variable resistance should not be too large.
-
Keywords:
- variable resistance training /
- elastic band /
- chain /
- maximal strength /
- power /
- postactivation potentiation
-
在现代竞技体育中,如何提升体能是训练理论与实践的核心问题[1]。作为体能的重要组成部分,最大力量和爆发力是参与大部分运动必须具备的关键能力[2]。通常而言,抗阻训练能通过提高神经适应性或肌肉横断面积以改善力量表现[3]。因此,高效的抗阻训练是提高运动员竞技能力的重要保障。
近年来,一种将自由重量与弹力带或铁链相结合的抗阻训练方式被科研人员所关注,其被称为可变阻力训练(Variable Resistance Training,VRT)[4]。研究[3]认为,VRT渐变的负荷能改变运动范围内(range of motion)的生物力学特征,从而产生与恒定阻力训练(Constant Resistance Training,CRT)不同的神经肌肉适应性。以往研究表明,VRT在动作顶部的超负荷(overloading)可加快离心阶段的速度[5-6],从而有利于提高肌肉的牵拉缩短周期效率[4, 7]。此外,有研究[6, 8]认为,离心初始的超负荷能更有效地刺激中枢神经系统以提高神经元的放电频率,激活的运动单位在离心末期由于较低的强度会产生盈余,这可能会进一步提高向心阶段的力量表现。另外,根据人体的“上升力量曲线”模型[4],VRT在向心阶段渐增的负荷特征更适应肌肉的发力能力,由此能产生更快的动作速度[9]以及使参与收缩的运动单位数目增加[10]。基于相关神经肌肉表现的改善[5-10],部分学者[7, 11-12]认为,VRT可能更有益于优化肌肉的力量能力。近年的研究也进一步证实了VRT比CRT能够获得更大的急性[13]和长期[14]训练效益。尽管如此,由于设计VRT的方法学有较多的考虑因素[7],如可变阻力的设计方式(VRT与CRT的相对强度大小)、可变阻力大小以及可变阻力设备(铁链或弹力带)等,而采用不同的设计策略会产生显著不同的急性神经肌肉反应[5, 8, 15],这可能会进而影响VRT的训练效益[16-17]。因此,为科学有效地应用VRT,有必要深入探究不同的VRT设计策略对力量表现的影响。
激活后增强效应(Postactivation Potentiation, PAP)是一种由预先次最大强度抗阻训练引起的肌肉发力能力急性增强的生理现象[18]。国内学者较多地探讨了传统抗阻训练诱导PAP的强度和时域特征[19-22],较少关注VRT的干预效果。尽管国外研究证实了VRT比CRT能更有效地诱导PAP[13],但也存在不一致的结论[16, 23]。另外,有meta分析[24]结果显示,VRT与CRT对最大力量的训练效果相似,但该研究未合并爆发力指标,且仅纳入了≥7周的研究报告,结果具有一定的局限性。近期国内学者[25]采用定性的方法综述了VRT对最大力量、动作速度和功率输出的影响,认为VRT对爆发力的训练效果可能更显著。尽管综述提示了研究间出现不一致结果的可能原因,但并未对VRT的设计策略进行更全面的评价,且单纯的定性研究结论在某种程度上不能更有效地指导运动训练实践。基于上述背景,本文采用meta分析的方法系统评价VRT与CRT对最大力量和爆发力表现的急性干预和训练干预效果,将VRT的相关设计策略作为调节变量进一步分析,以期为在实践中科学地制定VRT训练策略提供证据支持。
1. 研究方法
遵循《系统综述与meta分析优先报告条目》(Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses,PRISMA)[26]的要求对纳入文献进行数据整理和统计分析。
1.1 文献检索
通过PubMed、Web of Science、SPORTDiscus、CNKI等数据库,检索截至2021年6月9日发表的文献。以(“弹力带”或“阻力带”或“铁链”或“可变阻力训练”)和(“深蹲”或“卧推”或“硬拉”或“奥林匹克举”)为中文检索词进行检索;以("elastic band" OR "rubber band" OR "theraband" OR "elastic tubing" OR "chain" OR "variable resistance" OR "accommodating resistance") AND ("resistance training" OR "free weight" OR "squat" OR "bench press" OR "deadlift" OR "weightlifting") AND ("power" OR "strength" OR "force" OR "performance" OR "speed" OR "jump" OR "1RM")为英文检索词进行布尔逻辑检索。追溯前人综述和纳入文献的参考文献,以补充获取相关文献。
1.2 纳入和排除标准
根据考克兰系统评价PICO原则,文献纳入标准包括:①研究对象为健康成年人;②干预与对照措施为需对比VRT与CRT2种训练方式对力量表现的影响效果;③结局指标为干预前后的力量表现指标。
文献排除标准包括:①存在VRT和CRT 2种训练方式的生物力学特征对比;②VRT未与自由重量训练相结合;③CRT组未被作为对照组。
1.3 文献的筛选
文献检索完成后,由2位研究人员分别采用独立双盲的方式按照上述纳入和排除标准筛选文献。首先将文献导入Endnote X9软件中进行去重,阅读题目和摘要进行初筛,对剩余文献进行全文下载并筛选。然后2位研究人员对提取的文献进行对比,若有分歧,通过与第3位研究者共同讨论决定是否纳入本文。
1.4 数据提取与编码
根据纳入标准,数据提取信息包括:①文献基本信息(作者姓名、发表年份);②样本量;③受试者特征(年龄、性别、训练经历);④干预措施类型(急性干预或训练干预的干预周期、干预频率、训练量、干预类型等)。⑤结局指标(相关结果指标前后测的平均数和标准差)。如果文献中数据缺失,通过E-mail联系作者提供缺失的数据,利用Web Plot Digitizer软件(Version 4.1;E,USA)提取仅以图形报告的结果数据(平均数±标准差)。2位研究人员使用表格独立对数据进行提取,然后合并数据,若出现分歧,与第3位研究人员协商解决。
1.5 文献质量评价
采用Brughelli等[27]的质量评分表对纳入的研究进行评价,该评分表是基于健康治疗和康复中常用的量表进行修订改进的。该表有9个评估标准,本文的急性干预效果只采用其中的8个标准,其中标准6(实际训练时间)不适用。每个标准采用0~2分的方式计算(0=否定,1=可能,2=肯定)。将每篇文献的最终分数转换成百分比,得分大于80%的研究纳入分析[28]。文献质量评分由2位研究人员独立进行,如有分歧,与第3位研究人员协商解决。
1.6 统计分析
应用Stata 16.0软件进行数据合并、亚组分析、绘制森林图、异质性分析、meta回归、发表偏倚检验。采用随机效应模型分别确定急性干预和训练干预对结局指标的影响效应。因各文献中对最大力量和爆发力的评价单位不同,故以标准化均数差(Standard Mean Difference,SMD)及其95%置信区间(CI)作为效应尺度进行效应量合并,SMD取值0.2、0.5和0.8作为小、中、大效应量的临界值[29]。以Q统计量判断研究间的异质性,取P<0.1为显著性水平,采用I2统计量进行量化,25%、50%、75%分别表示研究间异质性的低、中和高比例[30]。
在纳入meta分析的急性干预研究中,部分研究测试多个结局指标,为避免重复性计算带来的权重增加[31],选择一个最常用的指标。如:Krčmár等[32]研究中测试了下蹲跳(CMJ)、蹲跳(SJ)、10 m冲刺跑;Nickerson等[33]研究中采集了CMJ高度和峰值功率。以上研究统一选择CMJ高度作为结局指标。将可变阻力的设计方式分为3个亚组。①强度相同:与CRT相比,VRT在动作底部的强度低,动作顶部的强度高,两者运动范围内的相对强度相同。②VRT相对强度低:VRT和CRT在动作顶部的强度相同。③VRT相对强度高:VRT和CRT在动作底部的强度相同。基于以往meta分析对诱导PAP的时间分类方法[18, 34-35],将0~3 min、4~7 min、8~12 min作为亚组进行分析。此外,将可变阻力大小作为连续型变量进行meta回归。在纳入meta分析的训练干预研究中,当研究包括多个结局指标时,纳入最常用的指标进行计算。将可变阻力设备分为2个亚组(弹力带、铁链);将训练周期分为2个亚组(<7周、≥7周);训练干预研究中可变阻力设计方式的亚组分类与急性干预研究的分类方法相同。急性干预和训练干预研究中提取的数据均为基线改变值,即干预前后差值的平均值(M)和标准差(SD),计算公式:
$$ M_{改变值}=M_{干预后}-M_{干预前} $$ (1) $$ \begin{split} &{\rm{SD}}_{改变值}= \\ &\sqrt{{{{\rm{SD}}}^{2}}_{\mathrm{干}\mathrm{预}\mathrm{前}}+{{{\rm{SD}}}^{2}}_{\mathrm{干}\mathrm{预}\mathrm{后}}-(2\times R\times {{\rm{SD}}}_{\mathrm{干}\mathrm{预}\mathrm{前}}\times {{\rm{SD}}}_{\mathrm{干}\mathrm{预}\mathrm{后}})} \end{split} $$ (2) 式(2)中,相关系数R为0.5[36]。
2. 研究结果
2.1 文献检索结果
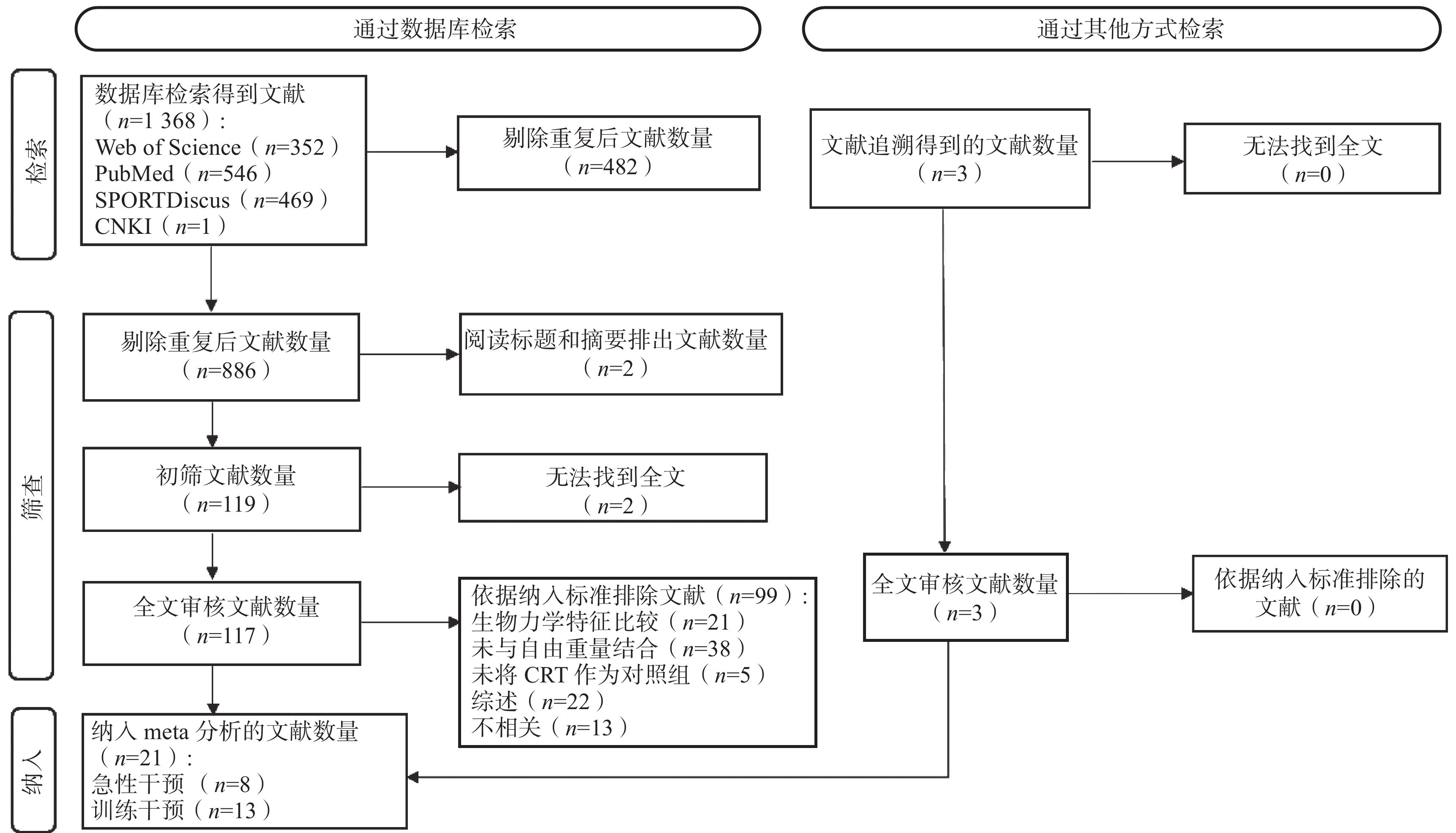
共检索到文献1368篇,剔除重复文献482篇;通过阅读标题和摘要后获得119篇;随后下载余下119篇文献全文,2篇文献无法获得全文且未与作者取得联系;阅读全文剔除99篇。此外,通过文献追溯增补3篇。最终纳入21篇,其中,急性干预研究8篇,训练干预研究13篇。具体文献筛选流程如图1所示。
2.2 纳入研究的基本特征
8篇文献报告了急性干预效果(表1),样本量共114人(男性占84%,女性占16%)。其中,6项研究只包括男性,1项研究只包括女性,1项研究同时包括男性和女性。受试者年龄平均值范围为19.9~26.0岁。8项研究均报告了可变阻力的大小,范围为13%~30%1RM,6项研究使用弹力带,2项研究使用铁链。5项研究的VRT和CRT强度相同,3项研究的VRT相对强度低。6项研究测试了爆发力动作表现,2项研究测试了深蹲最大力量表现以检验急性干预效果。
表 1 急性干预纳入研究的基本特征Table 1. Basic characteristics of the acute intervention literature included in the study作者(年份) 受试者特征 训练干预 结局指标 质量得分/% 男/女;年龄/岁 训练
时长/年训练类型;可变阻力设备 组×次数 CRT强度/1RM VRT强度(自由重量+可变阻力)/1RM 强度对比 Krčmár等[32]
(2021)0/14;
225 深蹲;弹力带 3×4 85% a:76%+17%
b:72%+25%相等 5 min、10 min:CMJ高度 93.75 Nickerson等[33] (2019) 12/0;
22未报告 深蹲;弹力带 1×3 85% 71%+28% 相等 1 min、4 min、7 min、10 min:CMJ高度 87.50 Mina等[13] (2019) 15/0;
21.75 深蹲;弹力带 1×3 85% 70%+30% 相等 30 s、4 min、
8 min、12 min:CMJ峰值功率87.50 Jones等[16] (2019) 13/0;
20.51 卧推;铁链 2×6 60% 39%+21% VRT相对强度低 2组30 s:俯卧撑峰值功率 87.50 Mina等[38] (2016) 16/0;
263 深蹲;铁链 2×3 85% 70%+30% 相等 5 min、10 min:深蹲1RM 87.50 Wyland等[23] (2015) 20/0;
23.31 深蹲;弹力带 5×3 85% 59%+26% VRT相对强度低 0、1 min、2 min、3 min、4 min:9.1 m冲刺 81.25 Mina等[39] (2014) 16/0;
263 深蹲;弹力带 2×3 85% 70%+30% 相等 5 min、10 min:深蹲1RM 100.00 Prejean等[40] (2012) 4/4;
20未报告 卧推;弹力带 3×5 85% 72%+13% VRT相对强度低 0、1.5 min:50%1RM卧推峰值功率 81.25 注:RM表示最大重复次数;CRT表示恒定阻力训练;VRT表示可变阻力训练;CMJ表示下蹲跳。 12篇文献报告了训练干预效果(表2),样本量共282人(男性占59%,女性占41%)。其中,7项研究只包括男性,3项研究只包括女性,2项研究同时包括男性和女性。受试者年龄平均值范围为17.8~24.0岁。10项研究报告了可变阻力的大小,范围为5%~44%1RM,8项研究使用弹力带,4项研究使用铁链。8项研究的VRT和CRT强度相同,2项研究的VRT相对强度低,2项研究的VRT相对强度高。干预频率为每周1~3次,多数研究的干预周期为4~12周,Shoepe等[37]的干预周期长达24周。12项研究均测试了最大力量表现,其中8项研究测试了爆发力表现以检验训练干预效果。
表 2 训练干预纳入研究的基本特征Table 2. Basic characteristics of the training intervention literature included in the study作者(年份) 受试者特征 训练干预 结局指标 质量得分/% 男/女;年龄/岁 训练
时长/年训练类型;可变阻力设备 训练
频率/
次·周−1训练周期/周 组×次数 CRT强度/1RM VRT强度(自由重量+可变阻力)/
1RMKatushabe
等[14](2020)17/0;20.47 1 深蹲、硬拉;弹力带 2 6 3×5 未报告 未报告+20% 深蹲1RM、硬拉1RM、CMJ 83.33 Arazi等[41] (2020) 0/36;23.6 >0.5 卧推、深蹲;铁链 3 8 (3~5)×(6~12) 65%~80% 50%~65%+15% 深蹲1RM、卧推1RM 83.33 Rivière等[42] (2017) 16/0;17.8 未报告 卧推;弹力带 2 6 (3~6)×(2~4) 70%~92% 50%~72%+37% 卧推1RM、卧推平均功率 83.33 Joy等[43] (2016) 14/0;未报告 1 卧推、深蹲;弹力带 1 5 3×(2~12) 40%~95% 25%~80%+30% 深蹲1RM、卧推1RM、CMJ 88.89 Andersen等[17] (2015) 0/30;24 5 深蹲、分腿蹲;弹力带 2 10 (3~4)×(6~10) 75%~85% 未报告+32%~44% 深蹲1RM、CMJ(60°) 88.89 Ataee等[44] (2014) 16/0;20.5 未报告 深蹲;铁链 3 4 3×5 85% 80%+20% 深蹲1RM、CMJ 83.33 Shoepe等[37] (2011) 10/10;20 <1 深蹲、卧推、硬拉;弹力带 3 24 (3~6)×(6~10) 67%~95% 未报告+20%~35%总负荷 深蹲1RM、卧推1RM、等速伸膝(210°) 83.33 Bellar等[45] (2011) 11/0;
23.6无训练 卧推;弹力带 2 6 5×5 85% 72%+13% 卧推1RM 88.89 Burnham等[46] (2010) 0/19;
19.81 卧推;铁链 2 8 3×(4~8) 80%~90% 75%~85%+5% 卧推1RM 83.33 Rhea等[47] (2009) 32/0;
21.41 深蹲;弹力带 2-3 12 4×10 75%~85% 未报告 深蹲1RM,CMJ 83.33 McCurdy等[48] (2009) 27/0;
20.65 卧推;铁链 2 9 (5~9)×(5~19) 55%~95% 未报告 卧推1RM 88.89 Anderson等[49] (2008) 22/22;
204 卧推、深蹲;弹力带 3 7 (3~6)×(2~10) 72%~98% 52%~78%+平均20% 深蹲1RM、卧推1RM、CMJ平均功率 94.44 注:RM表示最大重复次数;CRT表示恒定阻力训练;VRT表示可变阻力训练;CMJ表示下蹲跳。 2.3 纳入研究的质量评估
纳入的21项研究平均得分为(86.0±6.5)%,整体研究质量中等(表3)。14项研究具体说明了受试者的纳入标准,仅有8项研究具体说明了随机分配的方法。其中,Ghigiarelli等[50]研究未报告受试者纳入标准以及未具体说明可变阻力的设计方式和负荷大小等,得分低于80%被严格排除在本meta分析之外。
表 3 纳入研究的方法学质量评估Table 3. Methodological quality assessment for inclusion in the study作者(年份) 资格标准 随机分配 清晰描述
干预方式基线相似 测试易于执行 报告训练时间
(仅训练干预研究)合适的
统计方法结局指标
(均数、标准差、效应量)结论
清晰总分 Krčmár等[32](2021) 2 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 15 Nickerson等[33](2019) 2 1 2 2 2 1 2 2 14 Mina等[13](2019) 2 1 2 1 2 2 2 2 14 Jones等[16](2019) 2 2 1 2 2 2 1 2 14 Mina等[38](2016) 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 14 Wyland等[23](2015) 1 1 2 1 2 2 2 2 13 Mina等[39](2014) 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 16 Prejean等[40](2012) 0 2 2 2 2 1 2 2 13 Katushabe等[14](2020) 2 2 1 0 2 2 2 2 2 15 Arazi等[41](2020) 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 1 2 15 Rivière等[42](2017) 2 1 2 1 2 2 1 2 2 15 Joy等[43](2016) 2 2 2 1 2 2 1 2 2 16 Andersen等[17](2015) 2 2 2 1 2 2 1 2 2 16 Ataee等[44](2014) 1 1 2 1 2 2 2 2 2 15 Shoepe等[37](2011) 1 1 2 1 2 2 2 2 2 15 Bellar等[45](2011) 2 1 2 2 2 2 1 2 2 16 Burnham等[46](2010) 2 1 2 1 2 2 1 2 2 15 Rhea等[47](2009) 2 1 0 2 2 2 2 2 2 15 McCurdy等[48](2009) 2 2 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 16 Ghigiarelli等[50](2009) 0 1 1 1 2 2 1 2 2 12 Anderson等[49](2008) 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 2 2 17 2.4 急性干预和训练干预对力量表现影响的meta分析
2.4.1 急性干预对力量表现影响的meta分析
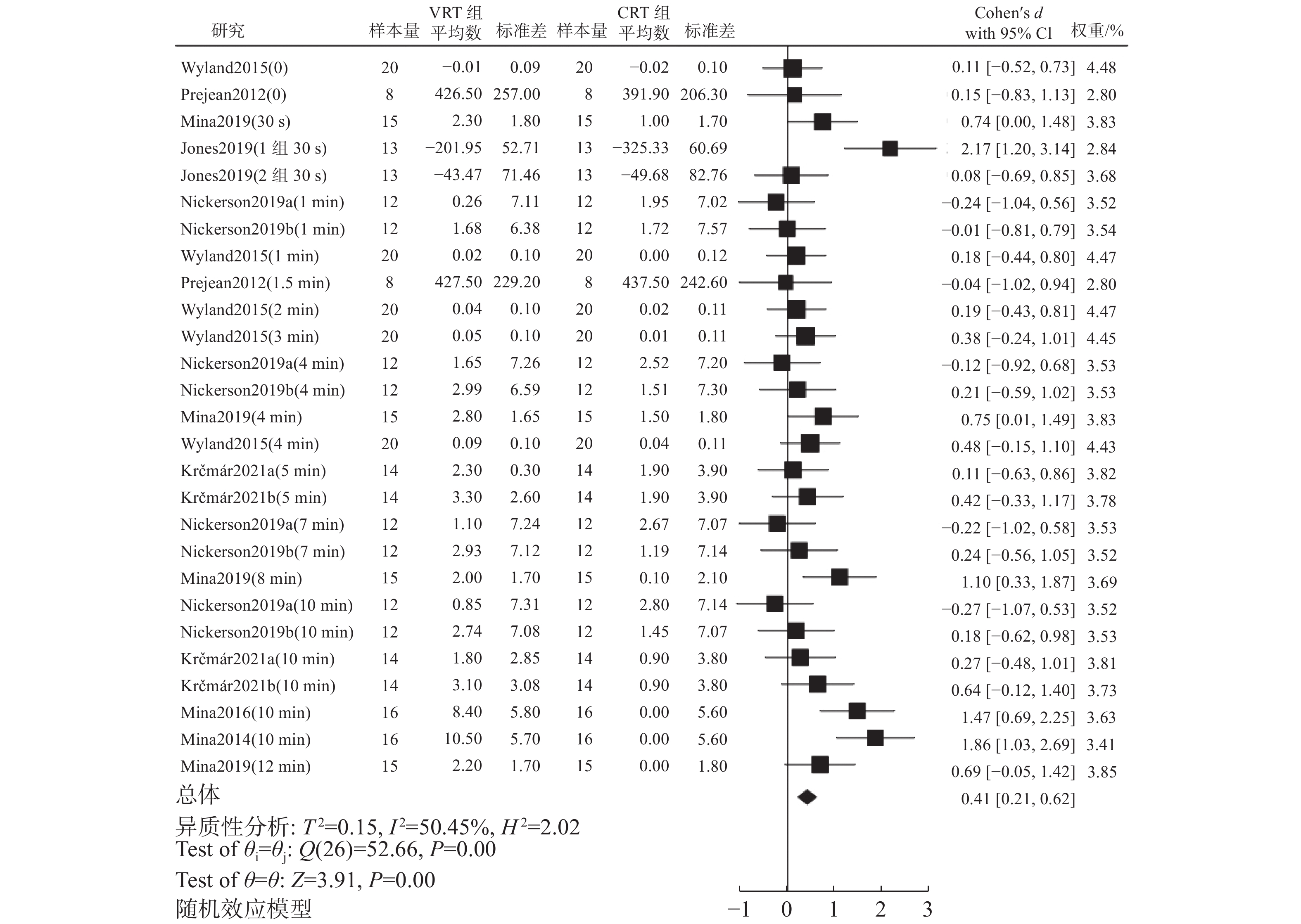
纳入的文献中有8篇急性干预研究,各研究在不同时间点对最大力量和爆发力表现进行了测试,共有27项比较。meta分析结果(图2)显示,研究间存在中度异质性(I2=50.45%,P<0.001),合并效应量SMD=0.41,95%CI为[0.21,0.62],差异有统计学意义(P<0.001)。Begg及Egger检验结果提示了无明显发表偏倚(z=0.21,P=0.84;t=0.99,P=0.33)。
对可变阻力大小进行meta回归,对间歇时间、设计方式进行亚组分析结果如下:
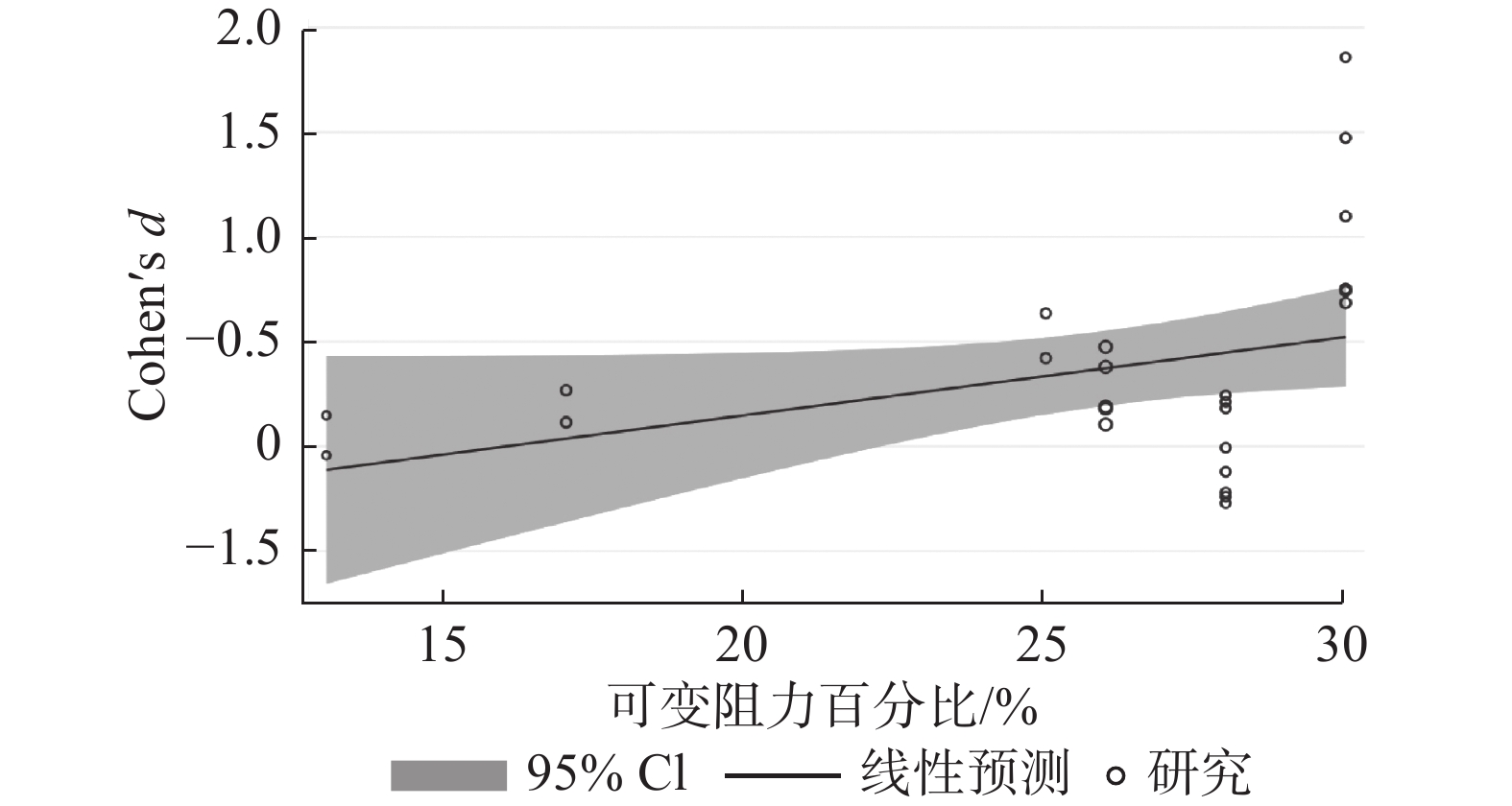
(1)meta回归结果(图3)显示:可变阻力大小作为调节变量没有统计学差异(b=2.59,95%CI为[−0.21,7.67];P=0.064)。
(2)按设计方式进行亚组分析,强度相同的亚组异质性检验结果显示,研究间存在中等程度且显著的异质性(I2=53.04%,P<0.001)。剔除Mina2014(10 min)[39]及Mina2016(10 min)[38]2项研究后,异质性明显下降(I2=7.07%,P=0.37)。进一步分析发现,上述2项研究都采用深蹲的最大力量作为检验PAP效果的指标,与其他研究采用爆发力测试不同,其他方面无明显差异。且剔除上述2项研究后,合并效应量虽有下降(剔除后的SMD=0.30,95%CI为[0.10,0.50],但结果仍具有显著性水平(P<0.001),故保留该研究进行合并分析。另外,VRT相对强度低的亚组异质性检验结果显示,研究间存在中等程度且显著的异质性(I2=46.21%,P=0.04)。剔除Jones等[16]的研究后,各研究间不存在异质性(I2=0%,P =0.97),且剔除该研究后,SMD=0.24,95%CI为[−0.02,0.49],结果不存在统计学意义(P=0.07)。进一步分析发现,Jones等[16]的研究采用的强度明显低于其他研究(60%1RM VS. 85%1RM),且VRT和CRT在2个时间点的卧推峰值功率与前测相比都有下降,通过运动表现的下降幅度来证明PAP缺乏依据,故将该研究在meta分析中排除。剔除Jones等[16]的研究后共25项比较,meta分析结果显示,SMD=0.37,95%CI为[0.18,0.56],差异有统计学意义(P<0.001)。
(3)按间歇时间进行亚组分析(表4),8~12 min间歇时间的异质性检验结果显示,剔除Mina2014(10 min)[39]及Mina2016(10 min)[38]2项研究后,异质性有明显下降(I2=28.57%,P=0.21),在剔除以上2项研究后合并效应量虽有下降(剔除后的SMD=0.45,95%CI为[0.07,0.82]),但结果仍具有显著性水平(P<0.05),故仍保留上述2项研究进行合并分析。
表 4 急性干预对力量表现影响的亚组分析Table 4. Subgroup analysis of the effect of the acute intervention on power亚组 分组标准 研究数量 异质性检验结果 meta分析结果 Q P I2/% SMD 95%CI P 设计方式 强度相同 18 36.09 0.00 53.04 0.44 [0.17, 0.71] <0.001 VRT相对强度低 7 1.33 0.97 0 0.24 [−0.02, 0.49] 0.07 间歇时间 0~3 min 9 4.12 0.85 0 0.19 [−0.05, 0.43] 0.12 4~7 min 8 4.73 0.69 0 0.26 [−0.00, 0.53] 0.05 8~12 min 8 20.77 0.00 67.02 0.74 [0.26, 1.22] <0.001 2.4.2 训练干预对最大力量表现影响的meta分析
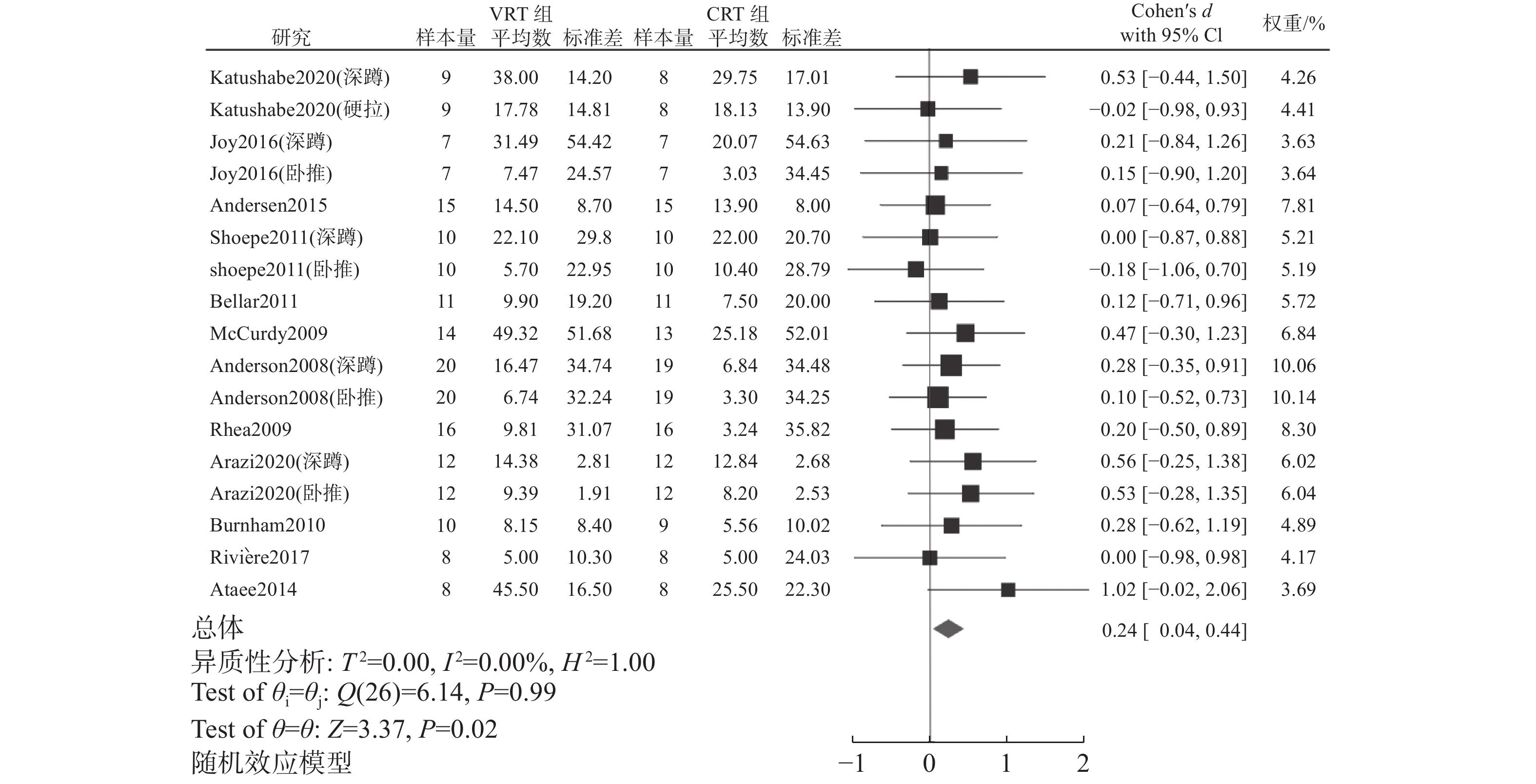
纳入的文献中有12篇训练干预对最大力量表现的研究,共有17项比较。meta分析结果(图4)显示,研究间没有异质性(I2=0%,P =0.78),SMD=0.25,95%CI为[0.05,0.45],差异有统计学意义(P=0.02)。Begg及Egger检验结果均无发表偏倚(z=0.04,P=0.98;t=0.20,P=0.84)。为进一步探究VRT对最大力量表现的最佳设计策略,对训练周期、设计方式以及可变阻力设备进行亚组分析,结果如表5所示。
表 5 训练干预对最大力量表现影响的亚组分析Table 5. Subgroup analysis of the effect of the training intervention on maximum strength亚组 分组标准 研究数量 异质性检验结果 meta分析结果 Q P I2/% SMD 95%CI P 训练周期 <7周 7 3.72 0.71 0 0.38 [0.01, 0.65] 0.04 ≥7周 10 3.00 0.96 0 0.19 [−0.05, 0.43] 0.63 设计方式 强度相同 12 7.69 0.74 0 0.17 [−0.06, 0.40] 0.15 VRT相对强度高 2 1.95 0.16 48.78 0.49 [−0.50, 1.49] 0.33 VRT相对强度低 3 0.24 0.89 0 0.47 [−0.02, 0.96] 0.06 可变阻力设备 弹力带 12 7.14 0.79 0 0.13 [−0.10, 0.37] 0.27 铁链 5 1.17 0.88 0 0.54 [0.16, 0.92] 0.01 2.4.3 训练干预对爆发力表现影响的meta分析
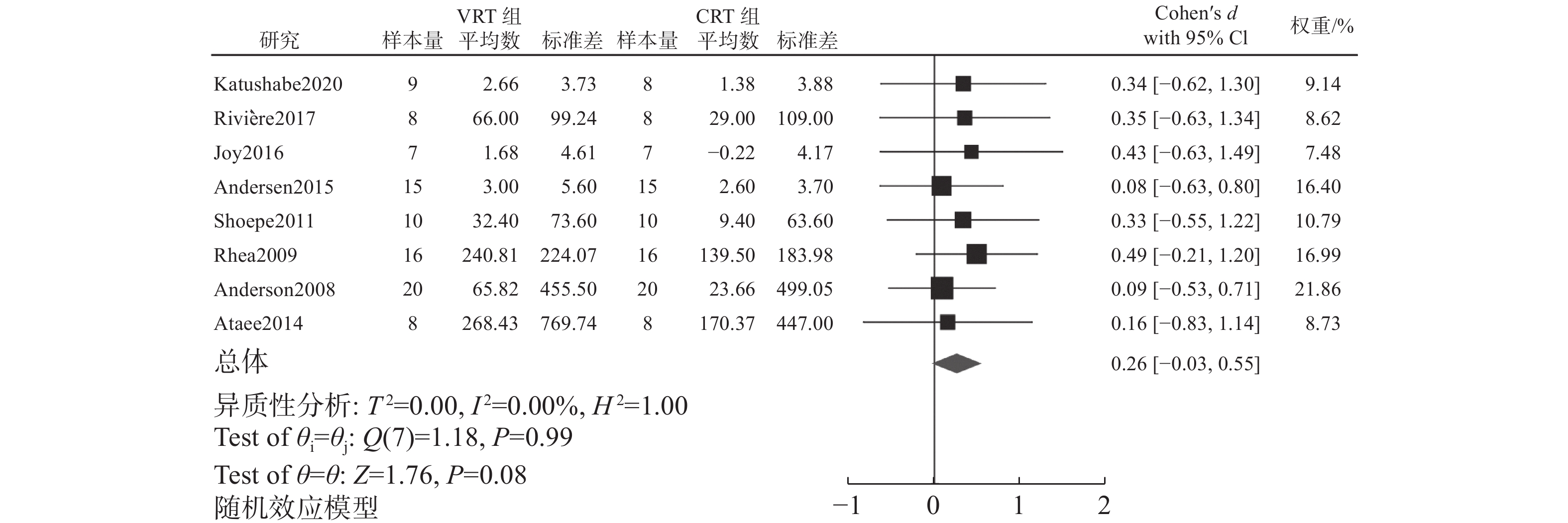
纳入的文献中有8篇训练干预对爆发力表现的研究。meta分析结果(图5)显示,研究间没有异质性(I2=0%,P =0.99),SMD=0.26,95%CI为[−0.03,0.55],差异没有统计学意义(P=0.08)。因纳入研究不足10篇,故未做Begg与Egger检验评价发表偏倚。为进一步探究VRT对爆发力表现的最佳设计策略,对训练周期、设计方式以及可变阻力设备进行亚组分析,结果如表6所示。
表 6 训练干预对爆发力表现影响的亚组分析Table 6. Subgroup analysis of the effect of the training intervention on power亚组 分组标准 研究数量 异质性检验结果 meta分析结果 Q P I2/% SMD 95%CI P 训练周期 <7周 4 0.16 0.98 0 0.32 [−0.18, 0.81] 0.21 ≥7周 4 0.96 0.81 0 0.23 [−0.12, 0.59] 0.20 设计方式 强度相同 7 1.14 0.98 0 0.27 [−0.03, 0.57] 0.08 VRT相对强度高 1 0 0 0 0.16 [−0.83, 1.14] 0.76 可变阻力设备 弹力带 7 1.14 0.98 0 0.27 [−0.03, 0.57] 0.08 铁链 1 0.00 0.00 0 0.16 [−0.83, 1.14] 0.76 3. 讨 论
3.1 急性干预效果对比
meta分析结果表明,VRT能更有效地诱导PAP(P<0.001),SMD=0.37,95%CI为[0.18,0.56]。对设计方式的亚组分析显示,强度相同的设计方式诱导的PAP合并效应量有显著差异(P<0.001)。从生物力学特征的对比研究看,采用该设计方式的VRT能更显著提高向心阶段的速度[9, 15]、峰值力量[51]及肌电活动[10]。分析认为,这种急性的神经肌肉反应是VRT能诱导更大强度PAP的主要原因。采用该设计方式的VRT比CRT在动作底部的强度更低,顶部强度更高。这一负荷特征更适应肌肉在运动范围内不同阶段的发力能力[3]。基于生物学原理,更快的收缩速度和更大的肌电活动能优先募集快肌运动单位(Ⅱ型)[52]。此外,VRT在动作顶部对机体更大强度的刺激有利于Ca2+从肌质网的释放,进而加快肌球蛋白调节轻链的磷酸化[53]。上述因素被认为是诱导PAP的潜在机制[53]。相反,采用VRT相对强度低的设计方式虽能显著提高向心阶段的速度[6],但运动范围内相对低的强度对机体的刺激较小,不足以引起肌肉活动的显著变化[54]。因此,这也解释了本文亚组分析中“VRT相对强度低的设计方式诱导的PAP合并效应量无显著变化”的结论。
除设计方式外,可变阻力大小同样是影响VRT训练效应的重要因素之一。meta回归分析结果(图3)显示,可变阻力大小作为调节变量不具有统计学意义(P=0.064)。但从图形趋势看,PAP随着可变阻力的增大而提高。分析认为,可变阻力设计方式与可变阻力大小的交互影响可能是造成这一结果的主要原因。Wyland等[23]的研究显示,可变阻力占总负荷30%的VRT组与CRT组在干预后4个时间点的冲刺跑表现均无显著区别。另有研究[40]指出,可变阻力占总负荷15%的VRT组仅显著提高了干预后即刻的卧推峰值功率,干预后90 s则无显著变化。尽管上述研究使用了较大的可变阻力,但采用相对强度低的设计方式造成VRT在运动范围内的相对强度低于CRT,由此可能导致了2种训练方式的PAP无显著差异。相反,在强度相同的设计方式研究中,Krčmár等[32]对比了不同可变阻力诱导PAP的效果,结果显示,可变阻力占总负荷35%比20%的VRT组诱导的PAP更佳。另外,多项研究[13, 38-39]证实,可变阻力占总负荷35%的VRT组能够更有效地诱导PAP。分析认为,较大的可变阻力适宜搭配强度相同的设计方式,该设计策略在运动范围的底部和顶部有较大的负荷差,这可能更有助于减轻向心阶段初期“黏滞点”的影响以及在动作末期提供更大的强度刺激,从而有利于诱导更大的PAP。
对间歇时间的亚组分析表明,VRT和CRT在0~3 min诱导的PAP无显著差异(P>0.05),VRT在4~7 min诱导的PAP趋向显著更大(P=0.05),VRT在8~12 min诱导的 PAP显著更大(P<0.001)。该结果提示,VRT诱导的PAP随着时间的推移逐渐大于CRT。根据疲劳和增强的关系[55],笔者认为,由于VRT有利于诱导更大的PAP,而较少的负荷量刺激产生的疲劳较少。在上述因素的共同作用下可能导致VRT干预后更早地出现PAP。在纳入的文献中,仅1项研究[13]证实,1组3次85%1RM的深蹲干预后,VRT组在干预后30 s即能显著地诱导PAP,且效果持续到第12 min。Nickerson等[33]的研究采用相似的负荷强度,结果显示,VRT组和CRT组在干预后1~10 min均未出现PAP。不一致的结果可能与研究纳入的受试者特征有关。此外,部分研究[56-57]指出,1组2次85%1RM的VRT能在干预后90 s诱导PAP。但上述研究由于缺乏CRT作为对照组而未被纳入本文。因此,VRT是否比CRT诱导PAP的时间效率更高,未来有必要采用随机对照试验给出实证研究依据。
综上所述并结合meta分析结果,笔者认为,设计PAP方案时,VRT适宜采用强度相同的设计方式及较大的可变阻力。为提高时间效率,VRT采用较少的负荷量刺激足以诱导PAP,且4~12 min的恢复时间效果最佳。
3.2 训练干预效果对比
3.2.1 对最大力量表现的干预效果
meta分析结果表明,VRT能更有效地提高最大力量表现(P<0.05),SMD=0.25,95%CI为[0.05,0.45]。干预周期的亚组分析显示,≥7周的训练周期对最大力量表现无统计学差异(P=0.63)。该结果与Nilo等[24]的研究结果一致。由于纳入标准和检索时间的原因,Ghigiarelli等[50]的研究未达到文献质量标准(66.67%)被排除;Cronin等[58]的研究使用仰卧式深蹲器械,与纳入标准不符被排除;Andersen等[17]和Arazi等[41]的研究被纳入。这2项研究均表示,VRT组和CRT组在8周和10周训练干预后的最大力量表现无显著差异。Arazi等[41]进一步指出,生长激素、胰岛素生长因子、皮质醇等生理指标同样无显著区别。另外,纳入文献中最长的训练周期为24周,该研究[37]同样未发现2种训练方式对最大力量表现的差异。相反,<7周的亚组分析结果显示,VRT对最大力量表现的训练效果更有优势(P=0.04),SMD=0.38,95%CI为[0.01,0.65]。Joy等[43]的研究指出,为期5周、每周1次的VRT即能更有效地提高最大力量表现。通常而言,神经层面的适应性改善被认为是短周期训练提高力量表现的主要因素[59]。以往研究[5-6, 10, 51]均证实了VRT比CRT能更有效地优化神经肌肉系统。分析认为,在周期训练初始,VRT更多地通过神经层面的改善显著地提高最大力量表现,而随着周期的延长,运动员可能逐渐适应该训练方式的刺激,进而导致神经系统对VRT敏感性的下降。另外,需特别指出的是,Katushabe等[14]的研究显示,与VRT结合的深蹲在6周干预后能更有效地提高最大力量(组间P=0.037),与VRT结合的硬拉则无显著变化(组间P=0.77)。纳入的文献中将硬拉与VRT结合的训练干预研究较少,未来有必要进一步探究硬拉与VRT结合的长期训练效果。
设计方式的亚组分析显示,强度相同、VRT相对强度高、VRT相对强度低3种设计方式对最大力量的训练效果均无显著差异(P>0.05)。该结果与急性干预不同。分析认为,在强度相同设计方式的研究中有5项研究的训练周期≥7周,2种因素的交互影响可能导致采用该设计方式的VRT不能有效地提高最大力量表现。可变阻力设备的亚组分析显示,使用铁链能更有效地提高最大力量表现(P=0.01)。有研究[3]指出,由于弹力带和铁链的属性不同,训练中使用不同的可变阻力设备会产生特异的神经肌肉反应。Ebben等[54]的研究表示,占总负荷10%的弹力带VRT和铁链VRT的峰值力量和股四头肌肌电等指标均无显著区别,但受试者表示,使用弹力带和铁链有不同的主观感觉。此外,Coker等[60]和 Berning等[61]的研究结果均显示,占总负荷5%的铁链举重和无铁链举重的生物力学特征无显著差异,但受试者表示,由于铁链的摆动需要他们施加更大的力量去稳定杠铃。以往研究已证实采用较大可变阻力比较小可变阻力能更有效地提高肌电活动[10]和峰值力量[51]。因此,采用较小的可变阻力可能是导致上述研究神经肌肉反应无显著差异的主要原因。在实际训练中,举起杠铃的过程中铁链会出现不同程度的摆动。当动作到达向心阶段末期,铁链全部悬浮于空中可能会加剧铁链的摆动。此外,当弹震式训练方式与VRT结合时,更快的动作速度同样会造成铁链较大的振动。在不稳定条件下进行抗阻训练能通过改善主动肌与协同肌的协调能力来提高神经肌肉的兴奋性[62],经过长期的训练可能更有利于改善肌肉力量。然而,目前尚缺乏支持铁链更有益于最大力量表现的直接证据,未来有必要进一步对比不同负荷的铁链和弹力带VRT对最大力量表现的训练效果。
3.2.2 对爆发力表现的干预效果
meta分析结果表明,VRT对爆发力表现的训练效果趋向显著性(P=0.08),SMD=0.26,95%CI为[−0.03,0.55]。各亚组分析结果均无统计学意义(P>0.05),而采用强度相同的设计方式和使用弹力带的亚组中,VRT的训练效果趋向显著性(P=0.08)。这一结果与大部分研究均采用上述训练策略有关。本文纳入的12篇长期干预文献中仅8篇文献报告了爆发力指标,其中7篇[14, 37, 42-44, 47, 49]结果显示:VRT比CRT对爆发力的训练效果更好,但组间无统计学差异。这一结果提示,与最大力量指标相比,VRT的爆发力训练效益欠佳,这可能与研究中采用的可变阻力大小有关。基于VRT的负荷特征,强度相同的设计方式在运动范围顶部的强度较大,虽然超负荷能有效地提高向心阶段的峰值力量[51],但同样会造成动作速度的下降[5, 63],速度的显著下降会导致功率输出的降低[8]。因此,VRT的超负荷特征可能会对以速度为目标的爆发力表现产生负面影响。然而,有研究[64]指出,超负荷能显著提高向心阶段末期的速度、力量和功率输出。这可能与向心阶段末期力量的显著提高超过了速度的降低对爆发力的影响有关。值得注意的是,Wallace等[51]对比了不同可变阻力的动力学特征,结果显示,在85%1RM的干预组中,占总负荷35%比20%的可变阻力显著地降低了峰值功率,提示采用较大可变阻力对爆发力会有负面影响。综上分析认为,可变阻力的大小影响了力-速关系,不适宜的可变阻力可能是影响爆发力表现的重要因素。未来应进一步探究提高爆发力表现的适宜可变阻力区间。
可变阻力设备的亚组分析表明,弹力带对爆发力表现可能更有效(P=0.08)。有研究[4]对2种设备的负荷特征进行了量化,发现弹力带呈曲线增加,铁链则呈线性增加。为进一步探索两者的区别,Arandjelović [65]根据力和能量原理分别推导了弹力带和铁链的加速度公式:
$$ 弹力带的加速度: \ddot{{\textit{z}}} = \frac{F-k{\textit{z}}}{m} -g $$ (3) $$ 铁链的加速度: \ddot{{\textit{z}}} = \frac{F-\frac{1}{2}\alpha \dot{{\textit{z}}}}{m+\alpha {\textit{z}}} -g $$ (4) 式(3)(4)中,z、
$ \dot{{\textit{z}}} $ 、$ \ddot{{\textit{z}}} $ 分别表示垂直位移、速度、加速度,F表示施加的力,k和αz分别表示弹力带弹性系数和悬空的铁链质量。由于弹力带的质量可以忽略不计,其加速度主要受杠铃质量以及弹力带张力的影响;使用铁链时,加速度则受铁链质量、杠铃质量以及系统速度平方的影响。研究[65]认为,弹力带可能更有利于提高向心阶段的动作速度。此外,2项研究[8, 15]采用相同的设计方式分别对2种可变阻力设备的运动学特征进行分析,结果显示:随着弹力带阻力的提高(15%、35%),VRT在60%1RM和85%1RM 2个干预组的向心阶段速度表现均有显著提高[15];相反,随着铁链负荷的增大(20%、40%),VRT在30%1RM、50%1RM和70%1RM 3个干预组的向心阶段速度表现均有显著下降[8]。尽管受试者特征可能是造成不一致结果的来源,但2项研究采用相同的运动方式以及测试方案在一定程度上说明了2种可变阻力设备可能存在不同的运动学特征[3]。由于目前尚无直接对比2种可变阻力设备速度特征的证据,且本文仅纳入1篇铁链对爆发力影响的研究[44],对该结果解释时仍需谨慎。综上所述并结合meta分析结果,笔者认为:<7周的VRT训练周期更有利于提高最大力量表现,且铁链作为可变阻力设备更具优势;强度相同的设计方式以及弹力带作为可变阻力设备的VRT对爆发力的训练效果似乎更好。可变阻力大小可能是影响爆发力表现的重要因素,过大的可变阻力可能由于速度的过度下降而影响爆发力表现。
3.3 研究的局限性
(1)在急性干预研究中,以往研究[34]证实了CRT诱导的PAP大小与运动员特征有关。本文未对受试者力量水平进行分类,尚不清楚VRT诱导的PAP是否受运动员特征影响;对可变阻力大小的meta回归未进一步对设计方式进行分类,合并的结果可能存在一定局限性。
(2)在训练干预研究中,多数研究未详细报告可变阻力的设计策略,如可变阻力大小,致使本文无法更深入地探讨各调节变量间的相互影响。由于部分研究未报告具体的可变阻力大小,本文未做meta回归分析;目前VRT对爆发力表现效果的研究相对较少,且仅有1篇研究使用铁链,这在一定程度上影响了爆发力结果的证据强度。
4. 结论与展望
设计PAP方案时,强度相同的设计方式以及较大的可变阻力是VRT诱导PAP的最佳策略,且PAP在干预后4~12 min的效果更好。较少的负荷量刺激可能更有利于提高诱导PAP的时间效率;设计周期训练方案时,<7周以及使用铁链的VRT训练策略对最大力量表现的训练效益更大。采用强度相同的设计方式以及使用弹力带的VRT训练策略对爆发力表现的干预效果更好,但过大的可变阻力可能导致速度的过度下降而影响爆发力表现。
针对可变阻力的设计方式、恒定阻力和可变阻力大小的负荷分配以及弹力带和铁链的区别等影响VRT训练效益的相关因素,研究人员有必要进一步深入探究,并重点关注不同训练策略之间的交互影响以及有益于爆发力的适宜可变阻力大小等。未来研究还应从实际应用角度出发,探寻提高诱导PAP时间效率的干预方案,以及如何将VRT有效应用到周期训练计划中以优化神经肌肉系统,从而实现力量表现的突破。
作者贡献声明:石林:提出论文主题,统计处理数据,撰写论文;作者贡献声明:韩冬:梳理论文逻辑思路,审核、指导修改论文;作者贡献声明:蔡治东:提取、处理数据,修改论文;作者贡献声明:郭炜、陈贞祥:调研文献,核实数据。 -
表 1 急性干预纳入研究的基本特征
Table 1 Basic characteristics of the acute intervention literature included in the study
作者(年份) 受试者特征 训练干预 结局指标 质量得分/% 男/女;年龄/岁 训练
时长/年训练类型;可变阻力设备 组×次数 CRT强度/1RM VRT强度(自由重量+可变阻力)/1RM 强度对比 Krčmár等[32]
(2021)0/14;
225 深蹲;弹力带 3×4 85% a:76%+17%
b:72%+25%相等 5 min、10 min:CMJ高度 93.75 Nickerson等[33] (2019) 12/0;
22未报告 深蹲;弹力带 1×3 85% 71%+28% 相等 1 min、4 min、7 min、10 min:CMJ高度 87.50 Mina等[13] (2019) 15/0;
21.75 深蹲;弹力带 1×3 85% 70%+30% 相等 30 s、4 min、
8 min、12 min:CMJ峰值功率87.50 Jones等[16] (2019) 13/0;
20.51 卧推;铁链 2×6 60% 39%+21% VRT相对强度低 2组30 s:俯卧撑峰值功率 87.50 Mina等[38] (2016) 16/0;
263 深蹲;铁链 2×3 85% 70%+30% 相等 5 min、10 min:深蹲1RM 87.50 Wyland等[23] (2015) 20/0;
23.31 深蹲;弹力带 5×3 85% 59%+26% VRT相对强度低 0、1 min、2 min、3 min、4 min:9.1 m冲刺 81.25 Mina等[39] (2014) 16/0;
263 深蹲;弹力带 2×3 85% 70%+30% 相等 5 min、10 min:深蹲1RM 100.00 Prejean等[40] (2012) 4/4;
20未报告 卧推;弹力带 3×5 85% 72%+13% VRT相对强度低 0、1.5 min:50%1RM卧推峰值功率 81.25 注:RM表示最大重复次数;CRT表示恒定阻力训练;VRT表示可变阻力训练;CMJ表示下蹲跳。 表 2 训练干预纳入研究的基本特征
Table 2 Basic characteristics of the training intervention literature included in the study
作者(年份) 受试者特征 训练干预 结局指标 质量得分/% 男/女;年龄/岁 训练
时长/年训练类型;可变阻力设备 训练
频率/
次·周−1训练周期/周 组×次数 CRT强度/1RM VRT强度(自由重量+可变阻力)/
1RMKatushabe
等[14](2020)17/0;20.47 1 深蹲、硬拉;弹力带 2 6 3×5 未报告 未报告+20% 深蹲1RM、硬拉1RM、CMJ 83.33 Arazi等[41] (2020) 0/36;23.6 >0.5 卧推、深蹲;铁链 3 8 (3~5)×(6~12) 65%~80% 50%~65%+15% 深蹲1RM、卧推1RM 83.33 Rivière等[42] (2017) 16/0;17.8 未报告 卧推;弹力带 2 6 (3~6)×(2~4) 70%~92% 50%~72%+37% 卧推1RM、卧推平均功率 83.33 Joy等[43] (2016) 14/0;未报告 1 卧推、深蹲;弹力带 1 5 3×(2~12) 40%~95% 25%~80%+30% 深蹲1RM、卧推1RM、CMJ 88.89 Andersen等[17] (2015) 0/30;24 5 深蹲、分腿蹲;弹力带 2 10 (3~4)×(6~10) 75%~85% 未报告+32%~44% 深蹲1RM、CMJ(60°) 88.89 Ataee等[44] (2014) 16/0;20.5 未报告 深蹲;铁链 3 4 3×5 85% 80%+20% 深蹲1RM、CMJ 83.33 Shoepe等[37] (2011) 10/10;20 <1 深蹲、卧推、硬拉;弹力带 3 24 (3~6)×(6~10) 67%~95% 未报告+20%~35%总负荷 深蹲1RM、卧推1RM、等速伸膝(210°) 83.33 Bellar等[45] (2011) 11/0;
23.6无训练 卧推;弹力带 2 6 5×5 85% 72%+13% 卧推1RM 88.89 Burnham等[46] (2010) 0/19;
19.81 卧推;铁链 2 8 3×(4~8) 80%~90% 75%~85%+5% 卧推1RM 83.33 Rhea等[47] (2009) 32/0;
21.41 深蹲;弹力带 2-3 12 4×10 75%~85% 未报告 深蹲1RM,CMJ 83.33 McCurdy等[48] (2009) 27/0;
20.65 卧推;铁链 2 9 (5~9)×(5~19) 55%~95% 未报告 卧推1RM 88.89 Anderson等[49] (2008) 22/22;
204 卧推、深蹲;弹力带 3 7 (3~6)×(2~10) 72%~98% 52%~78%+平均20% 深蹲1RM、卧推1RM、CMJ平均功率 94.44 注:RM表示最大重复次数;CRT表示恒定阻力训练;VRT表示可变阻力训练;CMJ表示下蹲跳。 表 3 纳入研究的方法学质量评估
Table 3 Methodological quality assessment for inclusion in the study
作者(年份) 资格标准 随机分配 清晰描述
干预方式基线相似 测试易于执行 报告训练时间
(仅训练干预研究)合适的
统计方法结局指标
(均数、标准差、效应量)结论
清晰总分 Krčmár等[32](2021) 2 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 15 Nickerson等[33](2019) 2 1 2 2 2 1 2 2 14 Mina等[13](2019) 2 1 2 1 2 2 2 2 14 Jones等[16](2019) 2 2 1 2 2 2 1 2 14 Mina等[38](2016) 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 14 Wyland等[23](2015) 1 1 2 1 2 2 2 2 13 Mina等[39](2014) 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 16 Prejean等[40](2012) 0 2 2 2 2 1 2 2 13 Katushabe等[14](2020) 2 2 1 0 2 2 2 2 2 15 Arazi等[41](2020) 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 1 2 15 Rivière等[42](2017) 2 1 2 1 2 2 1 2 2 15 Joy等[43](2016) 2 2 2 1 2 2 1 2 2 16 Andersen等[17](2015) 2 2 2 1 2 2 1 2 2 16 Ataee等[44](2014) 1 1 2 1 2 2 2 2 2 15 Shoepe等[37](2011) 1 1 2 1 2 2 2 2 2 15 Bellar等[45](2011) 2 1 2 2 2 2 1 2 2 16 Burnham等[46](2010) 2 1 2 1 2 2 1 2 2 15 Rhea等[47](2009) 2 1 0 2 2 2 2 2 2 15 McCurdy等[48](2009) 2 2 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 16 Ghigiarelli等[50](2009) 0 1 1 1 2 2 1 2 2 12 Anderson等[49](2008) 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 2 2 17 表 4 急性干预对力量表现影响的亚组分析
Table 4 Subgroup analysis of the effect of the acute intervention on power
亚组 分组标准 研究数量 异质性检验结果 meta分析结果 Q P I2/% SMD 95%CI P 设计方式 强度相同 18 36.09 0.00 53.04 0.44 [0.17, 0.71] <0.001 VRT相对强度低 7 1.33 0.97 0 0.24 [−0.02, 0.49] 0.07 间歇时间 0~3 min 9 4.12 0.85 0 0.19 [−0.05, 0.43] 0.12 4~7 min 8 4.73 0.69 0 0.26 [−0.00, 0.53] 0.05 8~12 min 8 20.77 0.00 67.02 0.74 [0.26, 1.22] <0.001 表 5 训练干预对最大力量表现影响的亚组分析
Table 5 Subgroup analysis of the effect of the training intervention on maximum strength
亚组 分组标准 研究数量 异质性检验结果 meta分析结果 Q P I2/% SMD 95%CI P 训练周期 <7周 7 3.72 0.71 0 0.38 [0.01, 0.65] 0.04 ≥7周 10 3.00 0.96 0 0.19 [−0.05, 0.43] 0.63 设计方式 强度相同 12 7.69 0.74 0 0.17 [−0.06, 0.40] 0.15 VRT相对强度高 2 1.95 0.16 48.78 0.49 [−0.50, 1.49] 0.33 VRT相对强度低 3 0.24 0.89 0 0.47 [−0.02, 0.96] 0.06 可变阻力设备 弹力带 12 7.14 0.79 0 0.13 [−0.10, 0.37] 0.27 铁链 5 1.17 0.88 0 0.54 [0.16, 0.92] 0.01 表 6 训练干预对爆发力表现影响的亚组分析
Table 6 Subgroup analysis of the effect of the training intervention on power
亚组 分组标准 研究数量 异质性检验结果 meta分析结果 Q P I2/% SMD 95%CI P 训练周期 <7周 4 0.16 0.98 0 0.32 [−0.18, 0.81] 0.21 ≥7周 4 0.96 0.81 0 0.23 [−0.12, 0.59] 0.20 设计方式 强度相同 7 1.14 0.98 0 0.27 [−0.03, 0.57] 0.08 VRT相对强度高 1 0 0 0 0.16 [−0.83, 1.14] 0.76 可变阻力设备 弹力带 7 1.14 0.98 0 0.27 [−0.03, 0.57] 0.08 铁链 1 0.00 0.00 0 0.16 [−0.83, 1.14] 0.76 -
[1] 高炳宏.我国现代体能训练的现状、问题与发展路径[J]. 体育学研究,2019,2(2):73-81 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1909.2019.02.010 [2] 卢志泉,夏正亮,李玉章,等.肌肉力量的神经生物力学基础及诊断[J]. 上海体育学院学报,2019,43(3):113-120,126 [3] FROST D M,CRONIN J,NEWTON R U. A biomechanical evaluation of resistance:Fundamental concepts for training and sports performance[J]. Sports Medicine (Auckland,N. Z.),2010,40(4):303-326 doi: 10.2165/11319420-000000000-00000
[4] MCMASTER D T,CRONIN J,MCGUIGAN M. Forms of variable resistance training[J]. Strength & Conditioning Journal,2009,31(1):50-64
[5] STEVENSON M W,WARPEHA J M,DIETZ C C,et al. Acute effects of elastic bands during the free-weight barbell back squat exercise on velocity,power,and force production[J]. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research,2010,24(11):2944-2954 doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181db25de
[6] BAKER D G,NEWTON R U. Effect of kinetically altering a repetition via the use of chain resistance on velocity during the bench press[J]. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research,2009,23(7):1941-1946 doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181b3dd09
[7] WALLACE B J,BERGSTROM H C,BUTTERFIELD T A. Muscular bases and mechanisms of variable resistance training efficacy[J]. International Journal of Sports Science & Coaching,2018,13(6):1177-1188
[8] SWINTON P A,STEWART A D,KEOGH J W L,et al. Kinematic and kinetic analysis of maximal velocity deadlifts performed with and without the inclusion of chain resistance[J]. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research,2011,25(11):3163-3174 doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e318212e389
[9] GARCÍA-LÓPEZ D,HERNÁNDEZ-SÁNCHEZ S,MARTÍN E,et al. Free-weight augmentation with elastic bands improves bench press kinematics in professional rugby players[J]. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research,2016,30(9):2493-2499 doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000000374
[10] ANDERSEN V,STEIRO FIMLAND M,KNUTSON KOLNES M,et al. Electromyographic comparison of squats using constant or variable resistance[J]. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research,2016,30(12):3456-3463 doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000001451
[11] SUCHOMEL T J,NIMPHIUS S,BELLON C R,et al. The importance of muscular strength:Training considerations[J]. Sports Medicine (Auckland,N. Z.),2018,48(4):765-785 doi: 10.1007/s40279-018-0862-z
[12] KOMPF J,ARANDJELOVIĆ O. Understanding and overcoming the sticking point in resistance exercise[J]. Sports Medicine (Auckland,N. Z.),2016,46(6):751-762 doi: 10.1007/s40279-015-0460-2
[13] MINA M A,BLAZEVICH A J,TSATALAS T,et al. Variable,but not free-weight,resistance back squat exercise potentiates jump performance following a comprehensive task-specific warm-up[J]. Scandinavian Journal of Medicine & Science in Sports,2019,29(3):380-392
[14] KATUSHABE E T,KRAMER M. Effects of combined power band resistance training on sprint speed,agility,vertical jump height,and strength in collegiate soccer players[J]. International Journal of Exercise Science,2020,13(4):950-963
[15] GALPIN A J,MALYSZEK K K,DAVIS K A,et al. Acute effects of elastic bands on kinetic characteristics during the deadlift at moderate and heavy loads[J]. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research,2015,29(12):3271-3278 doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000000987
[16] JONES M T,OLIVER J M,DELGADO J C,et al. Effect of acute complex training on upper-body force and power in collegiate wrestlers[J]. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research,2019,33(4):902-909 doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000002508
[17] ANDERSEN V,FIMLAND M S,KOLNES M K,et al. Elastic bands in combination with free weights in strength training:Neuromuscular effects[J]. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research,2015,29(10):2932-2940 doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000000950
[18] 梁美富,郭文霞.骨骼肌激活后增强效应的研究进展[J]. 体育科学,2019,39(5):70-80 [19] 张雅祺.急性低氧抗阻练习对下肢肌肉募集和激活后增强效应的影响[J]. 中国体育科技,2019,55(2):37-46 [20] 刘敏,郭燕兰.后激活增强效应对不同训练水平运动员肌肉活性的影响[J]. 中国体育科技,2019,55(7):30-36 [21] 王海宁,陈万,王颖,等.高温高湿环境长时间运动后神经肌肉疲劳类型与PAP的关系[J]. 中国体育科技,2018,54(6):83-89 [22] 梁美富,张怀川,张树峰,等.不同力量水平运动员激活后增强效应的时域特征[J]. 上海体育学院学报,2020,44(6):54-61 [23] WYLAND T P,VAN DORIN J D,REYES G F C. Postactivation potentation effects from accommodating resistance combined with heavy back squats on short sprint performance[J]. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research,2015,29(11):3115-3123 doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000000991
[24] NILO DOS SANTOS W D,GENTIL P,LIMA DE ARAÚJO RIBEIRO A,et al. Effects of variable resistance training on maximal strength:A meta-analysis[J]. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research,2018,32(11):e52-e55 doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000002836
[25] 林奕贯,叶卫兵.可变阻力训练对爆发力影响的系统综述[J]. 中国体育科技,2021,57(4):56-63 [26] MOHER D,LIBERATI A,TETZLAFF J,et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses:The PRISMA statement[J]. PLoS Medicine,2009,6(7):e1000097 doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097
[27] BRUGHELLI M,CRONIN J,LEVIN G,et al. Understanding change of direction ability in sport:A review of resistance training studies[J]. Sports Medicine (Auckland,N. Z.),2008,38(12):1045-1063 doi: 10.2165/00007256-200838120-00007
[28] MARSHALL J,BISHOP C,TURNER A,et al. Optimal training sequences to develop lower body force,velocity,power,and jump height:A systematic review with meta-analysis[J]. Sports Medicine (Auckland,N. Z.),2021,51(6):1245-1271 doi: 10.1007/s40279-021-01430-z
[29] LE FEVRE A. Statistical power analysis[J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society:Series A (Statistics in Society),2005,168(2):465
[30] HIGGINS J P T,THOMPSON S G,DEEKS J J,et al. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses[J]. BMJ (Clinical Research Ed.),2003,327(7414):557-560 doi: 10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557
[31] LÓPEZ-LÓPEZ J A,PAGE M J,LIPSEY M W,et al. Dealing with effect size multiplicity in systematic reviews and meta-analyses[J]. Research Synthesis Methods,2018,9(3):336-351 doi: 10.1002/jrsm.1310
[32] KRČMÁR M,KRČMÁROVÁ B,BAKAĽÁR I,et al. Acute performance enhancement following squats combined with elastic bands on short sprint and vertical jump height in female athletes[J]. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research,2021,35(2):318-324 doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000003881
[33] NICKERSON B S,WILLIAMS T D,SNARR R L,et al. Individual and combined effect of inter-repetition rest and elastic bands on jumping potentiation in resistance-trained men[J]. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research,2019,33(8):2087-2093 doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000002593
[34] SEITZ L B,HAFF G G. Factors modulating post-activation potentiation of jump,sprint,throw,and upper-body ballistic performances:A systematic review with meta-analysis[J]. Sports Medicine (Auckland,N. Z.),2016,46(2):231-240 doi: 10.1007/s40279-015-0415-7
[35] 梁美富,郭文霞,孔振兴,等.激活后增强效应的间歇时间对下蹲跳高度影响的Meta分析[J]. 武汉体育学院学报,2018,52(2):49-56 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-520X.2018.02.008 [36] JUKIC I,RAMOS A G,HELMS E R,et al. Acute effects of cluster and rest redistribution set structures on mechanical,metabolic,and perceptual fatigue during and after resistance training:A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Sports Medicine (Auckland,N. Z.),2020,50(12):2209-2236 doi: 10.1007/s40279-020-01344-2
[37] SHOEPE T C,RAMIREZ D A,ROVETTI R J,et al. The effects of 24 weeks of resistance training with simultaneous elastic and free weight loading on muscular performance of novice lifters[J]. Journal of Human Kinetics,2011,29:93-106 doi: 10.2478/v10078-011-0043-8
[38] MINA M A,BLAZEVICH A J,GIAKAS G,et al. Chain-loaded variable resistance warm-up improves free-weight maximal back squat performance[J]. European Journal of Sport Science,2016,16(8):932-939 doi: 10.1080/17461391.2016.1199740
[39] MINA M A,BLAZEVICH A J,GIAKAS G,et al. Influence of variable resistance loading on subsequent free weight maximal back squat performance[J]. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research,2014,28(10):2988-2995 doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000000471
[40] PREJEAN S,JUDGE L W,PATRICK T J,et al. Acute effects of combined elastic and free-weight tension on power in the bench press lift[J]. The Sport Journal,2012,15:1-1
[41] ARAZI H,SALEK L,NIKFAL E,et al. Comparable endocrine and neuromuscular adaptations to variable vs. constant gravity-dependent resistance training among young women[J]. Journal of Translational Medicine,2020,18(1):239 doi: 10.1186/s12967-020-02411-y
[42] RIVIÈRE M,LOUIT L,STROKOSCH A,et al. Variable resistance training promotes greater strength and power adaptations than traditional resistance training in elite youth rugby league players[J]. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research,2017,31(4):947-955 doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000001574
[43] JOY J M,LOWERY R P,OLIVEIRA DE SOUZA E,et al. Elastic bands as a component of periodized resistance training[J]. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research,2016,30(8):2100-2106 doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3182986bef
[44] ATAEE J,KOOZEHCHIAN M S,KREIDER R B,et al. Effectiveness of accommodation and constant resistance training on maximal strength and power in trained athletes[J]. PeerJ,2014,2:e441 doi: 10.7717/peerj.441
[45] BELLAR D M,MULLER M D,BARKLEY J E,et al. The effects of combined elastic- and free-weight tension vs. free-weight tension on one-repetition maximum strength in the bench press[J]. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research,2011,25(2):459-463 doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181c1f8b6
[46] BURNHAM T R,RUUD J D,MCGOWAN R. Bench press training program with attached chains for female volleyball and basketball athletes[J]. Perceptual and Motor Skills,2010,110(1):61-68 doi: 10.2466/pms.110.1.61-68
[47] RHEA M R,KENN J G,DERMODY B M. Alterations in speed of squat movement and the use of accommodated resistance among college athletes training for power[J]. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research,2009,23(9):2645-2650 doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181b3e1b6
[48] MCCURDY K,LANGFORD G,ERNEST J,et al. Comparison of chain- and plate-loaded bench press training on strength,joint pain,and muscle soreness in Division II baseball players[J]. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research,2009,23(1):187-195 doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e31818892b5
[49] ANDERSON C E,SFORZO G A,SIGG J A. The effects of combining elastic and free weight resistance on strength and power in athletes[J]. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research,2008,22(2):567-574 doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181634d1e
[50] GHIGIARELLI J J,NAGLE E F,GROSS F L,et al. The effects of a 7-week heavy elastic band and weight chain program on upper-body strength and upper-body power in a sample of division 1-AA football players[J]. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research,2009,23(3):756-764 doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181a2b8a2
[51] WALLACE B J,WINCHESTER J B,MCGUIGAN M R. Effects of elastic bands on force and power characteristics during the back squat exercise[J]. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research,2006,20(2):268-272
[52] 于洪军,李成伟,于淼.肌纤维募集定律的理论溯源及其对力量训练实践的影响[J]. 体育科学,2016,36(11):56-65,74 [53] TILLIN N A,BISHOP D. Factors modulating post-activation potentiation and its effect on performance of subsequent explosive activities[J]. Sports Medicine (Auckland,N. Z.),2009,39(2):147-166 doi: 10.2165/00007256-200939020-00004
[54] EBBEN W P,JENSEN R L. Electromyographic and kinetic analysis of traditional,chain,and elastic band squats[J]. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research,2002,16(4):547-550
[55] RASSIER D E,MACINTOSH B R. Coexistence of potentiation and fatigue in skeletal muscle[J]. Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research,2000,33(5):499-508 doi: 10.1590/S0100-879X2000000500003
[56] STROKOSCH A,LOUIT L,SEITZ L,et al. Impact of accommodating resistance in potentiating horizontal-jump performance in professional rugby league players[J]. International Journal of Sports Physiology and Performance,2018,13(9):1223-1229 doi: 10.1123/ijspp.2017-0697
[57] SEITZ L B,MINA M A,HAFF G G. Postactivation potentiation of horizontal jump performance across multiple sets of a contrast protocol[J]. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research,2016,30(10):2733-2740 doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000001383
[58] CRONIN J,MCNAIR P,MARSHALL R. The effects of bungy weight training on muscle function and functional performance[J]. Journal of Sports Sciences,2003,21(1):59-71 doi: 10.1080/0264041031000071001
[59] FOLLAND J P,WILLIAMS A G. The adaptations to strength training:Morphological and neurological contributions to increased strength[J]. Sports Medicine (Auckland,N. Z.),2007,37(2):145-168 doi: 10.2165/00007256-200737020-00004
[60] COKER C A,BERNING J M,BRIGGS D L. A preliminary investigation of the biomechanical and perceptual influence of chain resistance on the performance of the snatch[J]. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research,2006,20(4):887-891
[61] BERNING J M,COKER C A,BRIGGS D. The biomechanical and perceptual influence of chain resistance on the performance of the Olympic clean[J]. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research,2008,22(2):390-395 doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e31816344e6
[62] BEHM D G,ANDERSON K G. The role of instability with resistance training[J]. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research,2006,20(3):716-722
[63] SAETERBAKKEN A H,ANDERSEN V,VAN DEN TILLAAR R. Comparison of kinematics and muscle activation in free-weight back squat with and without elastic bands[J]. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research,2016,30(4):945-952 doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000001178
[64] ISRAETEL M A,MCBRIDE J M,NUZZO J L,et al. Kinetic and kinematic differences between squats performed with and without elastic bands[J]. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research,2010,24(1):190-194 doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e31819b7995
[65] ARANDJELOVIĆ O. A mathematical model of neuromuscular adaptation to resistance training and its application in a computer simulation of accommodating loads[J]. European Journal of Applied Physiology,2010,110(3):523-538 doi: 10.1007/s00421-010-1526-3
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 徐恺,唐文静,路恒,王然. 激活后增强效应与激活后表现提升:重塑定义与认知. 中国体育科技. 2025(01): 47-58 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 汤传德. 弹力带训练方法在短跑运动力量训练中的应用. 牡丹江师范学院学报(自然科学版). 2025(01): 52-57 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 江学文,杨阳,周元超. 可变阻力训练对运动员下肢爆发力影响的Meta分析. 体育科技文献通报. 2025(01): 55-60 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 孙震,赵鲁南. 第19届世界游泳锦标赛中国队成绩分析. 中国体育教练员. 2023(01): 25-27 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 石林,韩冬,郭炜,陈贞祥. 不同运动干预诱导激活后表现增强的系统综述. 体育科研. 2023(04): 84-95 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(18)




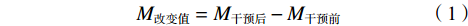
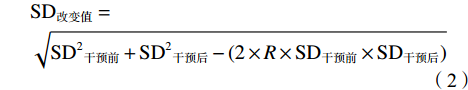
 下载:
下载: