Influencing Mechanism of Exercise, Social Capital on Mental and Physical Health of Rural and Urban Residents
-
摘要:
使用CLDS 2016数据对体育锻炼、社会资本对我国城乡居民身心健康的影响机制进行实证检验,发现社会资本对体育锻炼的健康促进效应具有中介作用:参加体育锻炼不仅能直接影响居民的身心健康水平,也能通过提高居民的集体和个体社会资本存量间接影响居民的身心健康水平。通过城乡对比发现,城市居民的体育锻炼和社会资本均对身心健康有显著影响,而农村居民参加体育锻炼对提高身心健康水平并无显著的直接作用,农村居民反而更多地依靠参加体育锻炼后带来的集体和个体社会资本的增长来提高身心健康水平,农村居民的社会资本在体育锻炼和健康之间的中介效应比城市居民更高。
Abstract:Data from CLDS 2016 has been employed to empirically test the influence and mechanism of exercise as well as social capital on the physical and mental health of urban and rural residents in China. It is found that the effect of exercise on health improvement is mediated by social capital. Sports participation improves mental and physical health of residents directly and indirectly by increasing their collective and individual social capital. When separating the sample into urban and rural groups, the effect of exercise on mental and physical health is found significant only in the urban residents group. For rural residents, exercise acts more likely as a way to increase collective and individual social capital, which further improves their mental and physical health. Comparing to urban residents, the mediating effect of social capital is stronger for rural residents.
-
“健康中国”是全面建成小康社会的重要目标,习近平总书记强调,全民健身是全体人民增强体魄、健康生活的基础和保障。“十三五”规划将建设“健康中国”正式上升为国家战略,特别提出要“发展体育事业,推广全民健身,增强人民体质”;“十四五”规划将“到2035年我国将建成社会主义现代化体育强国”设定为我国体育发展目标。通过体育锻炼提高身体健康水平是全社会的共识和常识,随着“生物—心理—社会”现代医学模式的不断发展,社会资本作为重要的“社会”因素也成为健康研究的重要议题。大量关于社会资本与健康的实证研究表明,个体和集体社会资本对个体的身心健康有显著的促进作用。作为影响体育运动和健康的重要因素,社会资本应被置于“健康中国”与体育强国建设背景下、结合我国现实情况深入探讨。
过往关于体育锻炼、社会资本与健康的研究主要探讨两两之间的关系,较少讨论三者之间的影响机制;且由于调查数据的限制,这些研究往往只局限于单一地区的群体,如单独研究城市居民或农村居民,很少有两者的对比性研究。本文使用全国性调查数据,在以往理论和研究的基础上进一步探究体育锻炼、社会资本对身体健康的作用路径及其城乡差异。
1. 文献回顾与研究假设
1.1 社会资本的概念与测量
自20世纪80年代布迪厄(Bourdieu)[1]和科尔曼(Coleman)[2]先后提出社会资本的概念以来,社会资本因其强大的解释力受到各学科的青睐,成为社会科学研究中一个重要的理论概念,被广泛运用于社会学、经济学、管理学以及体育与公共卫生等各学科研究。社会资本拥有强大解释力的一个重要原因是其概念定义较为宽泛[1-5],在不同的研究中,其概念可以有不同的含义[6]。有学者[7]对社会资本的概念和理论进行了详细的综述,认为学术界关于社会资本定义和理论的分歧与争论主要由研究者所选择分析层次的差异造成[8]。按照社会资本的分析层次,研究者将社会资本分为集体社会资本和个体社会资本2种类别,并对其定义和测量方法进行了详细的回顾[6, 8-9]。
波茨、林南、边燕杰等是个体社会资本研究的代表性学者。目前学术界普遍采用林南[10]对个体社会资本的定义:社会资本是一种嵌入于社会网络和社会关系中的可以在有目的的行动中获取或动员的资源。在个体层次上,社会资本分析关注3个方面:对社会资本的投资、社会资本的获取和动员以及社会资本的回报,即个体如何对社会关系和社会网络进行投资,如何获取和使用嵌于个体社会关系和社会网络的资源,以及如何获得工具性行动中的回报和保持情感性行动中的收益[1, 8, 10]。
由于个体社会资本是嵌入个体社会网络中的资源,对其测量主要是对个体社会网络情况的测量。测量个体社会网络的关键是网络类型、网络生成方法和分析指标。根据社会关系类型,社会网络可以进一步分为“日常接触网”“重要问题讨论网”“春节拜年网”“社交餐饮网”“工作求职网”“社会参与网”等,目前针对每种类型的网络均已发展出一套标准的题器和量表。在网络生成方面,大多数研究者通常采用提名法(name-generator)[11]或定位法(position-generator)[12]生成以每个被调查者为中心延伸出去的被调查者“个体中心网络” (ego-centered network)[13]。在分析指标方面,个体所拥有网络的结构(如网络规模、密度、同质性、异质性、内聚性和封闭性等)、网络中蕴含资源的多少(如资源的范围、最高可达性、多样性或异质性以及资源的构成等)以及个人在网络结构中所处的位置(如结构洞等)是测量个体社会网络资本的常用指标。
帕特南(Putnam)[5, 14]是较早开始研究集体社会资本的学者,他将社会资本定义为“社会组织的特征,诸如信任、规范以及社会网络,它们能够通过促进合作行为来提高社会的效率”。有学者[6, 9]将集体社会资本归纳为“一种内部社会资本或公共物品,除了宏观的群体内部的社会联结与互信外,集体社会资本也包括促成集体行动并创造资源的群体的结构方式”。国外一些学者[15]将集体社会资本分为基于客观的、外部的、可观测的、人际互动(如规则、程序、组织成员身份等)的“结构性(structural)社会资本”和基于共同的规范、价值观、态度与信仰的“认知性(cognitive)社会资本”[16-19] 。在测量上,“结构性社会资本”主要依据个体的社会组织成员身份(organizational membership)进行测量,其指标为受访者参加特定社会组织(如居委会、业主委员会、体育俱乐部、志愿者团体等)的数量。“认知性社会资本”则主要基于心理量表来测量受访者对集体的信任、邻里互惠互助、人际交往频率、凝聚力、认同感与归属感、利益共同感等方面的认知和感受。也有研究[5, 14, 20-25]以社区(或区域、国家等)为单位对这些指标进行加总(如计算社区成员平均社会活动参与率、社区平均信任水平等)来衡量社区(或区域、国家等)所拥有集体社会资本的水平。
1.2 体育运动与社会资本
体育运动与社会资本的研究始于20世纪90年代,帕特南[5]以体育社团和体育俱乐部的数量测量社会资本,并探讨了参加体育运动对培育社会资本的作用[14],引发了学界对体育运动与社会资本的广泛关注和讨论。有学者[26-29]对国内外相关研究进行了系统性综述,认为该领域的研究分别从2个不同的视角展开,边燕杰[29]将其归纳为“大众体育视域下的社会资本建构”和“社会资本视域下的大众体育发展”,前者主要探讨体育运动对社会资本生成的影响,而后者主要关注社会资本对促进体育运动参与的作用。
诸多研究表明,体育运动有助于社会资本的生成和维持。一部分研究者关注体育组织(如体育运动俱乐部、社区体育社团、社区体育志愿者组织等)参与对社会资本的影响[30],发现:参加体育运动俱乐部(如高尔夫球、保龄球俱乐部)等有助于个体社会资本(尤其是关系更强的“黏着型”社会资本)[31]的生成;而参加社区体育组织对社区和个体层面的集体和个体社会资本都存在显著的正向影响[32]。社区体育组织是社会资本生产和再生产的潜在场所,对个体和社区层面的信任、合作和社会网络的生成具有促进作用,尤其是社区体育志愿者组织能够更加明显地促进信任和互惠,志愿者网络成员之间可产生关系紧密的“黏着型”社会资本。研究[26, 33-34]还发现,体育俱乐部的类型和地理位置差异,以及社区结构和地理位置差异对社会资本的生成具有不同的影响。
更多的研究则关注参加体育运动和体育锻炼对社会资本的影响。有研究[14]认为,体育锻炼中产生的广泛联系为社会资本的创造提供了良好平台,无论哪种参与形式的体育锻炼方式都能直接或间接增加社会联系,有助于构建和维持跨越年龄、种族、社会经济地位等界限的社会网络,促进个体和集体社会资本的生成。一方面,经常参加体育锻炼对个人社会网络的规模、网络顶端、网络差异、网络异质性等都有显著的正向影响,有助于提高个体社会资本[28, 35-40];另一方面,参加体育锻炼也能够增强个体的普遍信任水平与社会参与[41-42],提升集体社会资本。此外,研究还发现,体育锻炼对社会资本的影响在不同的群体中存在异质性效应,体育锻炼对社会资本的影响因性别、年龄、受教育程度、婚姻状况、经济水平和锻炼频率等的差别而有所不同[42-43],且存在“马太效应”[42, 44]:相较于社会资本较低的群体,社会资本水平越高的群体参加体育锻炼越能提高其集体和个体社会资本水平。
一些研究[45-46]发现,社会资本既能促进个体参加体育运动,也有助于体育运动的发展。①个体社会资本越高,越倾向于参加体育锻炼,个体的社会网络规模、互动频率以及社会网络成员的同质性均对个人的体育参与具有促进作用。具体而言,个体社会资本存量和社会网络规模与其体育参与率存在显著关联,个体的关系网络通过提供资源、维持健康行为模式等途径影响个体体育参与,当个体的社会网络规模越大时,其网络成员中体育参与者的数量就会越多,体育资源的可及性越高,个体受到网络影响参与体育运动的可能性越大。②个人和社区层面的集体社会资本也会影响个体的体育参与。个体的社区信任度和社会参与度越高,越愿意参加体育锻炼;内部成员之间普遍信任感越强、相互之间联系越密切、对社区活动参与态度越积极的社区,其成员体育参与状况越好[28, 32, 45-50]。
由此可见,体育运动与社会资本存在相互影响:一方面,体育运动对培育个体和集体层面的社会资本有显著影响;另一方面,社会资本对促进体育参与存在不可忽视的积极作用。
1.3 社会资本与健康
社会资本的理论被普遍用于健康领域的研究,已有诸多学者对国内外社会资本与健康的研究进行了综述,将其归纳为3个层次:个体层次、集合(以社区、区域、国家等为单位的集体)层次,以及个体与集合层次的交互作用[51]。
个体层次的研究通常以自评健康(self-rated health)测量个体的身体健康状况;以霍普金斯症状清单(Hopkins Symptomes Check List,HSCL)、流调中心抑郁量表(Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale,CES-D)等心理学量表以及主观幸福感(subjective well-being)等指标测量个体的心理健康状况。在个体社会资本的测量上,研究通常按照认知性和结构性来区分社会资本的类型,并将个体社会资本、社会网络与社会支持、集体社会资本中的社会参与一并纳入结构性社会资本,与集体社会资本中的信任、互惠等认知性社会资本一起测量个体社会资本的存量。集合层次的研究则将上述指标以社区、地区或国家等为单位进行加总,或直接使用集体层面的指标测量社区的整体情况,如以社区死亡率测量社区的健康水平,以社区中公共事务的参与率测量社会资本存量等[51]。
最早将社会资本用于健康研究是在集合层面上进行的,研究[22, 51-52]发现,不同社区、地区和国家的平均信任水平和社会网络状况与其平均健康状况存在关联,总体而言,生活在社会信任水平较高地区的人往往具有更好的自评健康状况和更高的主观幸福感。对个体层面社会资本与健康关系的大部分研究[22-23, 53-57]也发现,认知性社会资本,如信任、归属感和社会凝聚力对健康具有积极影响,而结构性社会资本,如社会支持、社会网络、社区参与等也对健康存在不同程度的影响。
随着社会资本与健康研究的发展,社会资本对健康的影响得到更加细致的探讨。研究[56-57]从性别、年龄、城乡、婚姻等角度探讨在不同群体中社会资本对健康影响的异质性,发现社会资本对女性健康的影响显著高于男性,对农村居民健康的影响显著高于城市居民,对65岁以下居民健康的影响显著高于65岁以上居民,对独居个体的健康促进效应显著低于非独居个体等。也有研究[58]从社会网络的结构出发,探讨不同网络结构对健康影响的差异发现:个人的社会网络规模对身心健康具有积极作用;紧密度高、异质性低、强关系多的核心网络对精神健康有积极影响;具有相反特征的松散网络则对身体健康更有利;个人在网络中的相对地位对精神健康起着积极作用。
一些学者尝试对社会资本影响健康的机制进行分析,这些研究[52, 54, 56, 59-64]提出了社会资本影响健康的4种潜在路径:①高水平的集体社会资本(良好的社会交往和相互信任的社会环境)和个体社会资本(充分的社会支持)可以降低个人面临的压力,从而减轻压力对身心健康造成的负面影响;②社会资本有助于个体获得更多关于健康行为和健康生成的信息;③社会参与和社会交往可以产生对自己和他人的责任感,个体更有可能接受并遵循一些有利于健康的行为规范,抑制不利于健康的行为发生,从而降低危险行为发生的可能性;④社会资本提高了医疗卫生、健康设施和服务的可及性,为提高和维持健康水平提供了可能。上述对社会资本影响健康机制的分析主要停留在理论层面,而使用真实数据对其影响机制进行检验的实证研究较少。
1.4 研究假设
在全民健身与“健康中国”的大背景下,从科学的角度研究体育健身是新时期学者们关注的焦点和热点问题。通过回顾社会资本与体育锻炼、社会资本与健康的过往研究,发现社会资本作为一项重要的社会因素,对促进体育锻炼和提高身心健康水平都存在不可忽视的积极作用。但这些研究或只关注社会资本对体育锻炼的影响,或只关注社会资本对健康的影响,而鲜有将体育锻炼、社会资本和健康结合起来探讨三者之间的关系。这主要是由于研究者在进行体育锻炼与社会资本的实证研究时,较少讨论体育锻炼对健康的影响。虽然通过体育锻炼提高身体健康水平已是全社会的共识和常识,但欲厘清体育锻炼、社会资本和健康三者的关系,首先应对体育锻炼与健康的关系进行实证检验。大量研究表明,适当的体育锻炼可以增强体质,减少个人负面情绪,促进身心健康,提升生活满意度和幸福感。据此提出研究假设1:体育锻炼的健康促进效应假设。
在现实生活中,对于什么是“适当的”体育运动,不同人有不同见解,因而个体体育锻炼参与度(体育锻炼的频率、时长和强度)存在差异,从而导致体育锻炼对健康的影响存在异质性。研究[65]认为,锻炼频率与心理健康存在一定的相关关系,随着体育锻炼频率的提高,心理健康水平也相应提高。研究[66]具体分析了体育锻炼频率、锻炼时长对个体身心健康的影响,发现参加体育锻炼对个体身体和心理健康具有促进作用,但体育锻炼并不是越多越好,每周锻炼3~5次,每次30~60 min对心理健康的正向作用更强;而每个月锻炼超过23次或每次超过90 min的个体,其心理健康状况反而更差。研究[67]进一步发现,与锻炼时长、锻炼强度相比,锻炼频率对个体心理健康的影响更大,且这一影响存在性别差异—与女性相比,体育锻炼频率对于男性心理健康的影响更大。由于我国城乡居民的文化水平、观念、生活环境、经济水平等的差异,城市和农村居民的体育锻炼参与情况和身心健康状况也存在差别。研究[68]发现:城乡老年人体育锻炼水平具有显著差异,农村老年人基本不锻炼的比例较高,而城市老年人中等锻炼量与大锻炼量的比例高于农村老年人;且体育锻炼等级与心理健康的关系也存在城乡差异,与农村相比,中等锻炼量的城市低龄老年人心理健康状况更好。但也有研究[69]发现,参与体育锻炼对心理健康影响的城乡差异不具有显著性,因此有必要对体育锻炼对身心健康影响的城乡差异进行进一步检验。基于上述论证,假设1可分为2个子假设:假设1-1,总体而言,经常参加体育锻炼有助于提高个体的身心健康水平;假设1-2,体育锻炼对居民身心健康的影响存在城乡差异,体育锻炼对城市居民的健康促进效应高于农村居民。
个体和集体社会资本对健康的积极影响效应已被大量研究证实:个体的信任水平和社会参与度越高,身心健康状况越好;个体的社会网络规模越大、社会网络中蕴含的资源越多、个体从网络中调用资源的能力越强,个体的身心健康水平也越高;此外,社会资本对健康的影响在性别、年龄、阶层、城乡等不同特征的群体中存在异质性;在个体社会资本中,社会网络结构的差异也会对个体的健康带来不同程度的影响。但这些研究鲜有讨论集体和个体社会资本对身心健康影响的差别。笔者认为,集体和个体社会资本所包含的人与社会的联系具有较大差异,集体社会资本体现的是个体对所在社会环境的认知和感受,而个体社会资本体现的是个人与实实在在的个体产生的社会关系状况,因此,集体和个体社会资本对个体身心健康的影响可能存在差异。据此提出研究假设2:社会资本的健康促进效应假设。假设2分为3个子假设:假设2-1,总体而言,个人的集体和个体社会资本越高,身心健康状况越好;假设2-2,集体和个体社会资本对身心健康存在不同的影响;此外,已有实证研究发现,城乡居民的社会资本占有量及其构成存在差异 [58, 70],且社会资本对城市和农村居民的身心健康影响也存在差别[56, 58, 71],据此进一步提出假设2-3,社会资本对城市和农村居民身心健康的影响存在差异。
在社会资本、体育锻炼与幸福感的作用机制方面,研究[72]发现,社会资本在体育锻炼与幸福感之间存在中介效应。前文已阐明,参加体育运动有助于集体和个体社会资本的生成和维持,无论哪种参与形式的体育锻炼都能直接或间接地增加社会联系,“甚至在跑步时对另一位经常出现的跑步者点头致意,这些小小的举动就像把一分钱投进存钱罐,都能让社会资本得到逐渐增加”[73],而体育锻炼和社会资本都对身心健康有促进作用。由此可推论:体育锻炼和社会资本除了直接作用于身心健康外,体育锻炼还通过社会资本对身心健康产生间接影响,即社会资本在体育锻炼与身心健康之间起中介作用。据此提出研究假设3:体育锻炼、社会资本对身心健康的作用机制假设。假设3分为3个子假设:假设3-1,参加体育锻炼有助于提高个人的集体和个体社会资本存量,且社会资本对体育锻炼影响健康具有中介效应。此外,大多数居民的体育锻炼在所处社区内进行,因此参加体育锻炼有助于增强与社区的联系,提升对社区的熟悉感、信任感,也有助于拓展社区内部的社会网络。由于我国的农村社区是“熟人”社会,相较于城市,农村社区的人际联系更为紧密,集体社会资本更高;而城市地区的人际关系质量更高,因而城市地区的个体社会资本更高。基于前人“体育锻炼对社会资本的影响存在‘马太效应’”的研究结论进一步提出:假设3-2,体育锻炼对农村居民集体社会资本的促进效应高于城市居民,而对城市居民个体社会资本的促进效应高于农村居民;假设3-3,和城市相比,社会资本对体育锻炼影响健康的中介效应在农村更强。
2. 研究设计
2.1 数据来源
使用2016年中国劳动力动态调查(China Labor-force Dynamics Survey,CLDS 2016)数据。该调查以劳动力的教育、就业、劳动权益、职业流动、职业保护与健康、职业满足感和幸福感等的现状和变迁为核心,采用多阶段、多层次、与劳动力规模成比例的概率抽样方法,在全国(除港澳台、西藏、海南外)29个省(区、市)展开,共完成了401份村居社区问卷,14226份家庭问卷,21086份劳动力人口个体问卷,样本覆盖率高,具有较好的全国代表性。
2.2 变量及操作化
因变量为城乡居民的身心健康水平。在具体的测量上,参照社会资本领域的研究案例,使用受访者自评健康状况量表测量身体健康水平;使用CES-D20量表测量受访者的抑郁状况,反映受访者的心理健康水平。
自变量为城乡居民的体育锻炼参与度。CLDS 2016在调查受访者的体育锻炼情况时,首先询问受访者“最近1个月是否有规律地进行体育锻炼”;针对有规律地参加体育锻炼的受访者,再询问其体育锻炼频率(平均每周锻炼的次数)和锻炼时长(每次体育锻炼的时长)。锻炼频率和锻炼时长只针对最近1个月有规律地参加体育锻炼的受访者,而这部分样本占总样本的31.66%。为了对总样本进行统一的锻炼参与度调查,将最近1个月未进行规律体育锻炼的受访者的锻炼频率和锻炼时长赋值为0,然后使用验证性因子分析将锻炼频率和锻炼时长整合成一个综合的体育锻炼参与度变量
1 。另一个关键自变量(也是中介变量)为社会资本。集体社会资本采用受访者对社区熟悉、信任和互惠的认知和感受来测量,受访者的回答有5个等级,通过验证性因子分析生成一个综合的集体社会资本变量
2 。个体社会资本则是通过受访者的支持网络进行测量,CLDS 2016询问了受访者:在本村(社区)所拥有的关系密切、可以获得他/她的支持和帮助的熟人数量,在这些人中能够向他/她诉说心事的人的数量,可以讨论重要事情的人的数量以及可以向他/她借钱(以5000元为标准)的人的数量。用这几道题器分别测量个体的总体社会支持网规模、情感支持网规模、讨论网规模和借钱网规模,同样使用验证性因子分析生成一个综合的个体社会资本变量3 。此外,为避免内生性问题,还选取过往研究中已被证明会影响社会资本水平、个体健康状况和体育参与的社会人口和社会经济地位变量(包括性别、年龄、婚姻状况、户口类型、受教育程度、个体收入、家庭收入、家庭经济状况满意度等)作为控制变量,并按照受访者所在地区进行城乡对比。具体变量介绍和描述性统计结果如表1所示。
表 1 相关变量描述性统计结果Table 1. Descriptive statistics of relevant variables变量名称 均值(标准差/百分比) t 或 χ2 变量描述 农村(n=13013) 城市(n=7525) 身体健康状况 3.51(1.05) 3.79(0.9) −18.7*** 定序变量,自评健康状况:非常不健康=1、比较不健康=2、一般=3、比较健康=4、非常健康=5 抑郁得分 7.83 (9.4) 6.61(8.9) 9.12*** 定距变量, CES-D20量表20道题得分加总;取值范围为[0,60] 集体社会资本 0.20(0.78) −0.34(0.86) 46.20*** 定距变量,由熟悉程度、信任程度、互惠程度3个变量进行因子分析得到;取值范围为[−2.78,1.51] 熟悉程度 4.00(0.89) 3.34(1.02) 48.38*** 定序变量,和本村(社区)邻里街坊的熟悉程度:非常不熟悉=1、不太熟悉=2、一般=3、比较熟悉=4、非常熟悉=5 信任程度 3.79(0.83) 3.41(0.81) 32.4*** 定序变量,对本村(社区)邻里街坊的信任程度:非常不信任=1、不太信任=2、一般=3、比较信任=4、非常信任=5 互惠程度 3.51(0.98) 3.00(1.02) 35.49*** 定序变量,与本村(社区)邻里街坊的互助频率:非常少=1、比较少=2、一般=3、比较多=4、非常多=5 个体社会资本 −0.01(0.94) 0.02(0.88) −2.18** 定距变量,由总体社会支持网、情感支持网、讨论网和借钱网规模的因子分析得到;取值范围为[−0.58,13.27] 总体社会支持网规模 9.34(16.05) 9.36(15.19) −0.05*** 定距变量,在本村(社区)有多少个关系密切、可以获得他们支持和帮助的朋友或熟人;取值范围为[0,100] 情感支持网规模 4.12(8.06) 4.08(6.74) 0.33 定距变量,在本村(社区)关系密切的人中,有多少人可以诉说心事;取值范围为[0,100] 讨论网规模 3.47(6.75) 3.73(6.32) −2.74*** 定距变量,在本村(社区)关系密切的人中,有多少人可以讨论重要事情;取值范围为[0,100] 借钱网规模 3.06(6.81) 3.81(7.67) −7.31*** 定距变量,在本村(社区)关系密切的人中,有多少可以向他/她借钱(以5000元为标准);取值范围为[0,100] 锻炼参与度 −0.16(0.82) 0.27(0.99) −33.56*** 定距变量,由每周锻炼频率和每次锻炼时长的因子分析得到;取值范围为[−0.59,2.19] 锻炼频率 1.21(2.43) 2.24(2.82) −27.62*** 定距变量,每周锻炼次数;取值范围为[0,7] 锻炼时长 0.55(1.09) 1.2(1.42) −36.55*** 定序变量,每次锻炼时长:不锻炼=0、不足0.5 h=1、0.5~1 h=2、1~2 h=3、2 h以上=4 年龄 46.29(14.82) 42.24(13.83) 19.32*** 定距变量,受访者年龄 受教育程度 7.33(3.98) 11.11(3.91) −66.07*** 定距变量,受访者受教育年限(按照最高学历);取值范围为[0,19] 个体收入(取对数) 5.12(3.27) 6.23(3.48) −22.84*** 定距变量,受访者月收入取对数;取值范围为[0,12.61] 家庭收入(取对数) 7.58(1.51) 8.38(1.3) −38.48*** 定距变量,受访者家庭月收入取对数;取值范围为[0,16.3] 家庭经济状况满意度 3.18(1.07) 3.35(1.04) −11.34*** 定序变量,受访者对家庭经济状况满意程度:非常不满意=1、不太满意=2、一般=3、比较满意=4、非常满意=5 性别 6317 (48.54) 3446(45.79) 14.45*** 虚拟变量,受访者性别:女性=0、男性=1 婚姻状况 10897(83.74) 5778(76.78) 151*** 虚拟变量,受访者当前婚姻状态:未婚=0、已婚=1 户口类型 712(5.47) 4957(65.87) 0.009*** 虚拟变量,是否为居民户口:非居民户口=0、居民户口=1 注:*** 表示P<0.01,** 表示P<0.05。 CLDS 2016共收集个体样本21086个,在剔除健康状况等关键变量缺失样本后,所使用的样本量为20538个,其中:农村样本共13013个,占总样本的63.36%;城市样本共7525个,占总样本的36.64%。表1展示了农村和城市样本在各变量上的分布,t检验(对虚拟变量进行χ2检验)结果显示,除情感支持网规模外,城市样本和农村样本在身心健康、体育锻炼、个体和集体社会资本以及社会人口学、社会经济地位变量上的分布都存在显著差异。总体而言:相较于农村居民,城市居民身心健康状况更好,体育锻炼参与度更高,个体和家庭的社会经济地位更高,个体社会资本存量更高;农村居民的集体社会资本存量则显著高于城市居民。因此,有必要对农村和城市居民的体育锻炼、社会资本和健康状况的关系进行分别讨论和对比。
2.3 研究方法
使用数据驱动的探索和理论指导的实证相结合的方式展开研究。首先使用高斯图模型(Gaussian Graphical Model)中的罚似然图模型(Graphical LASSO,GLASSO)[74-75]建构所有原始变量(不含因子分析生成的变量)之间的网络关系,从而对变量之间的关系进行探索。在高斯图模型中,每个节点表示1个变量,2个节点之间的连线表示2个变量存在相关关系。GLASSO模型通过加入惩罚项对各变量的偏相关系数进行约束,可以在一定程度上消除变量之间的伪相关,使得原本条件独立的变量之间不存在相关关系。模型的惩罚力度可以通过参数λ(λ∈[0,1])加以控制,λ取值越大,对系数的惩罚力度越强,所得到的偏相关系数矩阵越稀疏,网络连线越少 [76-77]。使用基于拓展的贝叶斯信息准则(Extended Bayesian Information Criterion,EBIC)的GLASSO模型对变量网络进行估计,EBIC GLASSO模型是一个机器学习模型,在BIC的基础上,EBIC通过超参数γ(γ∈[0,0.5])进一步控制模型对简洁度的偏好,γ取值越大,所估计出的模型越简洁,即变量的网络越稀疏。当γ=0时,EBIC等同于普通的BIC。根据BIC准则,BIC越小代表模型拟合度越好且越简洁。在设定好参数γ后,EBIC GLASSO模型自动在[0,1]范围内选取100个值作为λ的取值放入模型进行估计,并自动择100个模型中EBIC最小的模型作为最优模型。EBIC GLASSO模型可通过R软件的Bootnet和qgraph程序包来实现[78-79]。
与回归模型不同,高斯图模型不仅可反映多个自变量对因变量的影响,同时也能反映自变量之间的相互关系,为探索潜在的影响路径提供数据上的启示:如果A、B、C这3个变量中,A与B之间有连接,B与C之间有连接,而A与C之间没有连接,则说明A不直接影响C,而需通过B这个中介变量对C产生影响[79]。此外,作为一种图模型,其网络结构的特性也可为分析提供线索,例如,变量网络中所形成的社团结构能够指导研究者选择对哪些变量进行因子分析,被广泛运用于心理学研究[79-81]。通过对网络节点中心性的分析也能帮助研究者找到最重要的变量,在对变量之间的关系进行初步探索后,使用基于最小二乘法(OLS)的多元线性回归模型对假设中的直接效应(包括体育锻炼对健康的影响、社会资本对健康的影响以及体育锻炼对社会资本的影响)进行检验,并使用Bootstrap中介检验法验证中介效应。需要说明的是,自评健康状况为定序分类变量,但考虑到后续中介效应检验要求因变量为连续变量,且为与心理健康状况(抑郁得分,为连续变量)相统一,在分析时将自评健康视为连续变量,使用OLS多元线性回归模型进行估计。
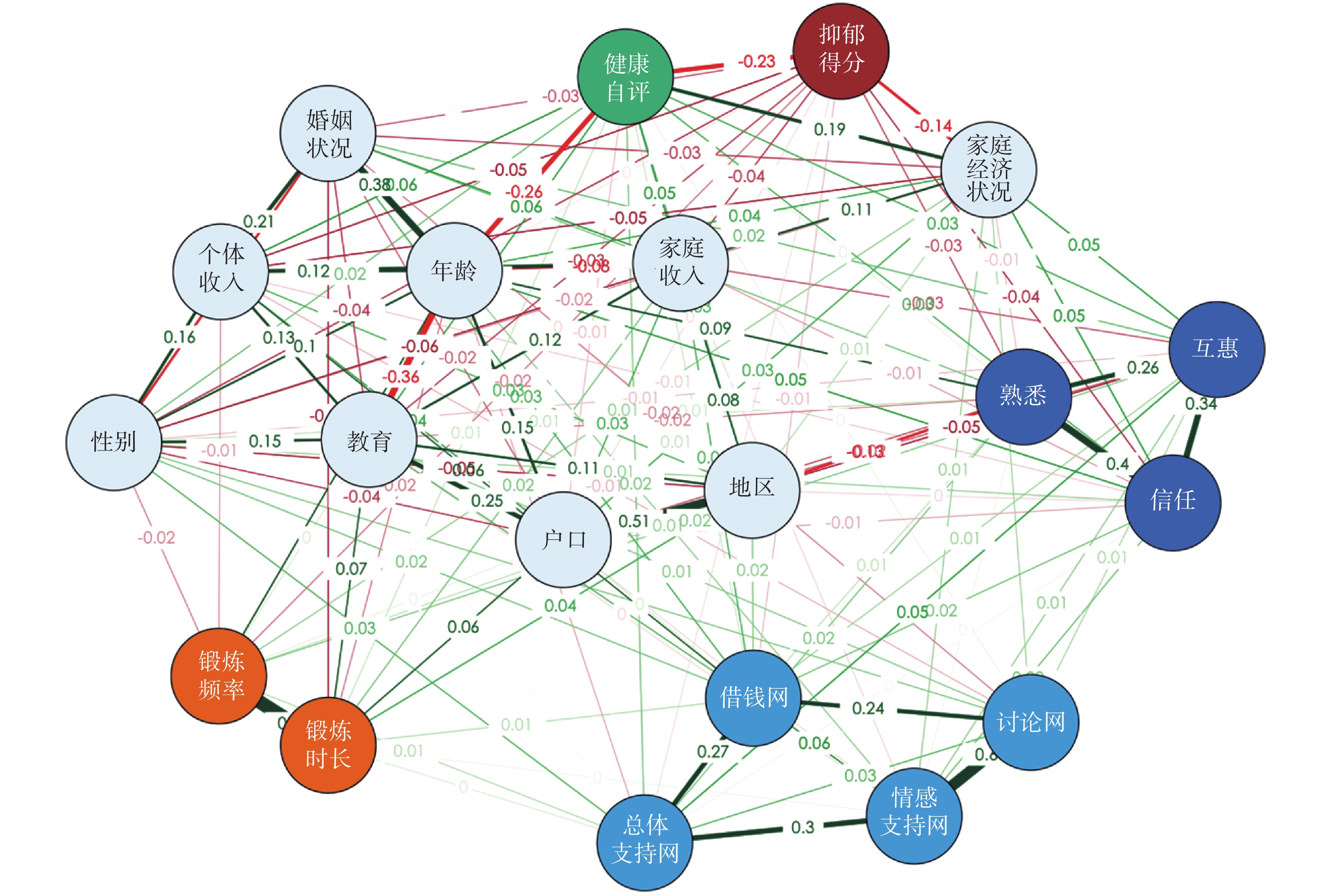
图1为使用EBIC GLASSO模型建构出的原始(不包含因子分析生成)变量网络。从图1可以直观地看出集体社会资本的测量变量(熟悉、信任、互惠)、个体社会资本的测量变量(总体社会支持网、情感支持网、讨论网、借钱网),以及体育锻炼参与度的测量变量分别形成了3个内部联系紧密的子群体,前文基于社会资本测量理论对这些变量进行因子分析的做法得到了数据上的验证。此外,从这一变量网络可看出,身心健康、集体/个体社会资本、体育锻炼和控制变量之间都存在或多或少的联系,前文假设的各种关系也得以初步验证。
3. 实证分析结果
在使用数据驱动的方式对变量之间的关系进行初步探索后,接下来使用OLS多元线性回归模型对前文提出的假设进行验证。
3.1 体育锻炼的健康促进效应
为检验假设1,先从总体上分析体育锻炼参与度对身心健康的影响效应,再讨论体育锻炼对城乡居民身心健康的影响差异。
体育锻炼对健康的影响效应如表2所示。总体而言,全样本模型结果显示,体育锻炼对城乡居民的身体、心理健康都有显著的积极影响:体育锻炼参与度越高,居民的自评健康状况越好,身体健康状况越好;且参加体育锻炼有助于抵抗消极情绪,体育锻炼参与度越高,越有助于减轻抑郁状况。对比体育锻炼对身心健康的影响可发现,体育锻炼对心理健康的影响(系数为−0.408)远远大于对身体健康的影响(系数为0.028),假设1-1得到验证。
表 2 体育锻炼对身心健康的影响效应Table 2. The effect of exercise on physical and mental health变量 全样本模型 交互模型 农村模型 城市模型 自评健康 抑郁得分 自评健康 抑郁得分 自评健康 抑郁得分 自评健康 抑郁得分 锻炼参与度 0.028*** −0.408*** 0.023** −0.141 0.016 −0.078 0.038*** −0.756*** 锻炼参与度×所在地区 0.01 −0.590*** 性别(男性=1) 0.093*** −1.095*** 0.093*** −1.102*** 0.121*** −1.543*** 0.036* −0.388* 年龄 −0.022*** 0.035*** −0.022*** 0.036*** −0.023*** 0.049*** −0.020*** 0.01 婚姻状况(已婚=1) 0.089*** −1.079*** 0.089*** −1.082*** 0.079*** −1.478*** 0.091*** −0.486* 受教育程度 0.015*** −0.136*** 0.015*** −0.137*** 0.017*** −0.173*** 0.011*** −0.062* 个体收入(对数) 0.025*** −0.214*** 0.025*** −0.213*** 0.030*** −0.187*** 0.016*** −0.243*** 家庭收入(对数) 0.038*** −0.324*** 0.038*** −0.324*** 0.044*** −0.406*** 0.023*** −0.109 家庭经济状况自评 0.234*** −1.919*** 0.234*** −1.924*** 0.253*** −2.189*** 0.203*** −1.508*** 所在地区(城市=1) 0.072*** 0.318* 0.234*** −1.924*** 户口类型(居民=1) −0.080*** 0.03 −0.081*** 0.098 −0.009 0.045 −0.097*** −0.027 常数项 3.163*** 18.226*** 3.162*** 18.240*** 3.032*** 19.779*** 3.511*** 15.125*** 观测值 20 538 20 538 20 538 20 538 13 013 13 013 7 525 7 525 R2 0.215 0.088 0.215 0.089 0.22 0.107 0.17 0.057 注:*** 表示P<0.01,** 表示P<0.05,*表示 P<0.1。 交互模型、农村模型和城市模型反映了居民所在地区(农村或城市)对体育锻炼的健康促进效应的影响。整体而言,体育锻炼对农村居民身体、心理健康的影响都要小于城市居民,表现为农村模型中体育锻炼参与度对自评健康和抑郁得分的回归系数绝对值均小于城市模型,且均不显著。但从交互模型上看,体育锻炼对居民身体健康影响的城乡差异不显著(交互项系数不显著,且使用基于似无相关模型的SUR检验也发现城乡系数无显著差异),而体育锻炼对心理健康影响的城乡差异在P<0.01水平上显著(SUR检验结果相同),假设1-2基本得到验证。对比农村和城市模型还可以发现,性别、年龄、受教育程度和经济状况等变量对农村居民身心健康的影响均大于城市居民。
此外,居民的身心健康也受到性别、年龄、婚姻状况、社会经济状况、地区和户口类型等因素的影响:男性的自评健康水平更高,抑郁得分更低;年龄对健康具有显著的负向影响,年龄越大,自评健康状况越差,且抑郁得分越高;已婚人群的身心健康程度显著高于未婚人群;受教育程度越高,身心健康状况越好;社会经济状况越好,身体健康状况越好,负面情绪越少;且所在地区(城乡)也对身心健康存在显著影响
4 。3.2 社会资本的健康促进效应
为检验假设2,首先使用基于因子分析得到的集体社会资本和个体社会资本变量建构全模型,检验集体社会资本和个体社会资本对身体、心理健康的影响,以检验假设2-1;接着分别讨论集体和个体社会资本的不同方面如何影响个体的身体、心理健康,以检验假设2-2;最后分析集体和个体社会资本对城乡居民身体健康影响的差异,以检验假设2-3。
社会资本对身心健康影响的回归分析结果如表3所示。总体而言,集体和个体社会资本对个体的身心健康具有显著的积极影响,表现为集体社会资本每增加1个单位,自评健康得分增加0.117,抑郁得分降低1.115;个体社会资本每增加1个单位,自评健康得分提高0.028,抑郁得分减少0.152,假设2-1得到验证。同时,相较于个体社会资本,集体社会资本对身体、心理健康的影响更大(经SUR检验,二者差异在P<0.01水平上显著)。
表 3 社会资本对身心健康的影响效应Table 3. The effect of social capital on physical and mental health变量 全模型 集体社会资本模型 个体社会资本模型 自评健康 抑郁得分 自评健康 抑郁得分 自评健康 抑郁得分 集体社会资本 0.117*** −1.115*** 熟悉程度 0.026*** −0.458*** 信任程度 0.065*** −0.718*** 互惠程度 0.041*** −0.076 个体社会资本 0.028*** −0.152** 总体社会支持网规模 0.002*** −0.011** 情感支持网规模 0.002 0.0001 讨论网规模 0.001 −0.013 借钱网规模 0.002 −0.018* 控制变量 已控制 已控制 已控制 已控制 已控制 已控制 常数项 3.230*** 17.783*** 2.743*** 22.395*** 3.141*** 18.545*** 观测值 20 538 20 538 20 538 20 538 20 538 20 538 R2 0.224 0.096 0.224 0.097 0.224 0.096 注:*** 表示P<0.01,**表示 P<0.05,* 表示P<0.1;由于篇幅限制,控制变量系数未列出。 集体社会资本模型和个体社会资本模型分别反映集体和个体社会资本不同方面对健康的影响。集体社会资本中的信任程度、熟悉程度能显著提高身体健康水平,降低抑郁得分,而互惠程度对身体健康具有显著的正向影响,对心理健康的影响不显著。在这3个因素中,信任程度对身体、心理健康的影响最大,这一发现与大多数研究使用信任程度测量集体社会资本的结果一致。在个体社会资本中,对身心健康影响最大的是总体社会支持网规模,总体社会支持网规模越大,健康自评状况越好,且抑郁得分越低;情感支持网规模、讨论网规模对身心健康的影响均不显著。有趣的是,借钱网规模对身体健康的影响不显著,但能显著降低抑郁得分,这可能是由于心理压力一部分来源于经济压力,遇到经济困难时获得经济支持能在一定程度上减轻心理压力。
社会资本对健康影响的城乡差异分析结果如表4所示。对比社会资本影响健康的城市模型和农村模型,集体社会资本对农村居民身体健康的影响程度高于城市居民,且这一差异具有统计学意义上的显著性(集体社会资本与所在地区的交互项系数显著,SUR检验也得到了相同的结果),但集体社会资本对心理健康的影响未发现显著的城乡差异。个体社会资本对农村居民身体健康的影响系数略低于城市居民,而对抑郁得分的影响系数绝对值略低于城市居民,但这一差异未达到统计学意义上的显著水平,假设2-3得到验证:集体社会资本对城乡居民身体健康的影响存在显著差异,集体社会资本对农村居民身体健康的影响高于城市居民。
表 4 社会资本对身心健康影响的城乡差异Table 4. The differentiation effect of social capital on physical and mental health between rural and urban residents变量 交互模型 农村模型 城市模型 自评健康 抑郁得分 自评健康 抑郁得分 自评健康 抑郁得分 集体社会资本 0.146*** −1.099*** 0.147*** −1.084*** 0.067*** −1.097*** 个体社会资本 0.029*** −0.231*** 0.025*** −0.091 0.032*** −0.187** 集体社会资本×所在地区 −0.069*** −0.037 个体社会资本×所在地区 −0.007 0.233 控制变量 已控制 已控制 已控制 已控制 已控制 已控制 常数项 3.228*** 17.793*** 3.137*** 14.810*** 3.560*** 18.973*** 观测值 20 538 20 538 13 013 7 525 7 525 13 013 R2 0.225 0.096 0.232 0.061 0.174 0.116 注:*** 表示P<0.01,** 表示P<0.05,* 表示P<0.1; 由于篇幅限制,控制变量系数未列出。 3.3 体育锻炼、社会资本对城乡居民身心健康的影响机制
接下来讨论体育锻炼、社会资本对身心健康的影响机制,以检验假设3。前文通过对过往研究的回顾和理论推演提出假设3-1:体育锻炼有助于社会资本的生成,且社会资本在体育锻炼对健康的影响中起中介作用。为检验这一中介效应假设,首先使用社会资本对体育锻炼的OLS回归模型对中介效应的前置假设—体育锻炼影响社会资本进行验证;接着使用GLASSO模型,在控制其他变量的情况下,对体育锻炼影响社会资本进而影响身心健康的路径进行初步探索;最后使用Bootstrap方法对中介效应进行检验,并对城乡差异进行进一步讨论。
体育锻炼的社会资本提升效应分析结果如表5所示。从全样本模型可看出,总体而言,参加体育锻炼能显著提高集体和个体社会资本存量。交互模型、农村模型和城市模型进一步对体育锻炼对社会资本影响的城乡差异进行了分析。对比农村模型和城市模型发现,体育锻炼参与度对农村和城市居民的集体和个体社会资本均有显著的正向作用,且从回归系数来看,体育锻炼对提高城市居民集体和个体社会资本的作用高于农村居民,但这一差异未达到统计学意义上的显著水平(在交互项模型中,体育锻炼与所在地区的交互项系数对于集体社会资本和个体社会资本均不显著,SUR检验也得出了相同的结果),假设3-2未得到验证。虽然在描述性分析中证实了农村居民的集体社会资本高于城市居民,而城市居民的个体社会资本高于农村居民,但体育锻炼对城乡居民的社会资本促进作用并不存在“马太效应”。
表 5 体育锻炼的社会资本提升效应Table 5. The effect of exercise on social capital promotion变量 全样本模型 交互模型 农村模型 城市模型 集体社会资本 个体社会资本 集体社会资本 个体社会资本 集体社会资本 个体社会资本 集体社会资本 个体社会资本 锻炼参与度 0.054*** 0.050*** 0.049*** 0.044*** 0.044*** 0.048*** 0.064*** 0.052*** 锻炼频率 0.011 0.013 控制变量 已控制 已控制 已控制 已控制 已控制 已控制 已控制 已控制 常数项 −0.580*** −0.581*** −0.580*** −0.581*** −0.656*** −0.539*** −0.873*** −0.731*** 观测值 20 538 20 538 20 538 20 538 13 013 13 013 7 525 7 525 R2 0.153 0.023 0.153 0.023 0.071 0.02 0.066 0.028 注:***表示P<0.01,**表示P <0.05,*表示P <0.1;由于篇幅限制,控制变量系数未列出。 进一步分析锻炼频率和锻炼时长对提升集体和个体社会资本的影响,回归结果发现:提高体育锻炼的频率更有助于增加集体社会资本,这是由于城乡居民大多数的体育锻炼在社区中展开,且一部分居民经常参加广场舞、球类运动等集体体育锻炼
5 ,经常参加体育锻炼有助于促进邻里交往,从而增加个体对社区的熟悉、信任程度,提高社区互惠程度。锻炼时长更有助于居民积累个体社会资本,这可能是因为个体社会资本衡量的是社会网络的规模,需要受访者与其他人建立紧密的社会关系,因此,参加体育锻炼的时间越长,在锻炼中与同伴的相处时间越长,更有可能建立私人之间更加亲密的人际关系。此外,社会人口特征、社会经济特征对社会资本的回归结果显示:性别、年龄、婚姻状况、家庭经济状况满意度和个体经济收入都对居民的集体和个体社会资本有显著的正向影响。受教育程度对提高个体社会资本具有显著的正向影响,但对提高集体社会资本的影响不显著;同时,家庭收入越高,个体社会资本存量越高,集体社会资本存量反而越低。值得一提的是,在描述性分析中,农村居民个体社会资本的存量显著低于城市居民,但回归结果显示,在控制了体育锻炼的作用后,城市对个体社会资本的影响为负,这也从另一个方面说明体育锻炼具有积累社会资本的作用,且这一作用可能存在城乡差异。
在验证了体育锻炼对社会资本的促进效应后,接下来分析体育锻炼、社会资本对身心健康的作用路径。首先使用GLASSO模型建构变量之间的关系,对这一路径进行数据驱动的探索。GLASSO模型分析得到的变量关系网络和变量之间正则化后的偏相关系数矩阵分别如图2和图3所示。图2中黄色的体育锻炼节点既直接与绿色的身体健康节点、红色的心理健康状况节点相连接,也间接通过连接深蓝色的集体社会资本和浅蓝色的个体社会资本节点,再与身体、心理健康节点相连接。据此可推测,除直接效应外,体育锻炼还通过社会资本影响身心健康状况。
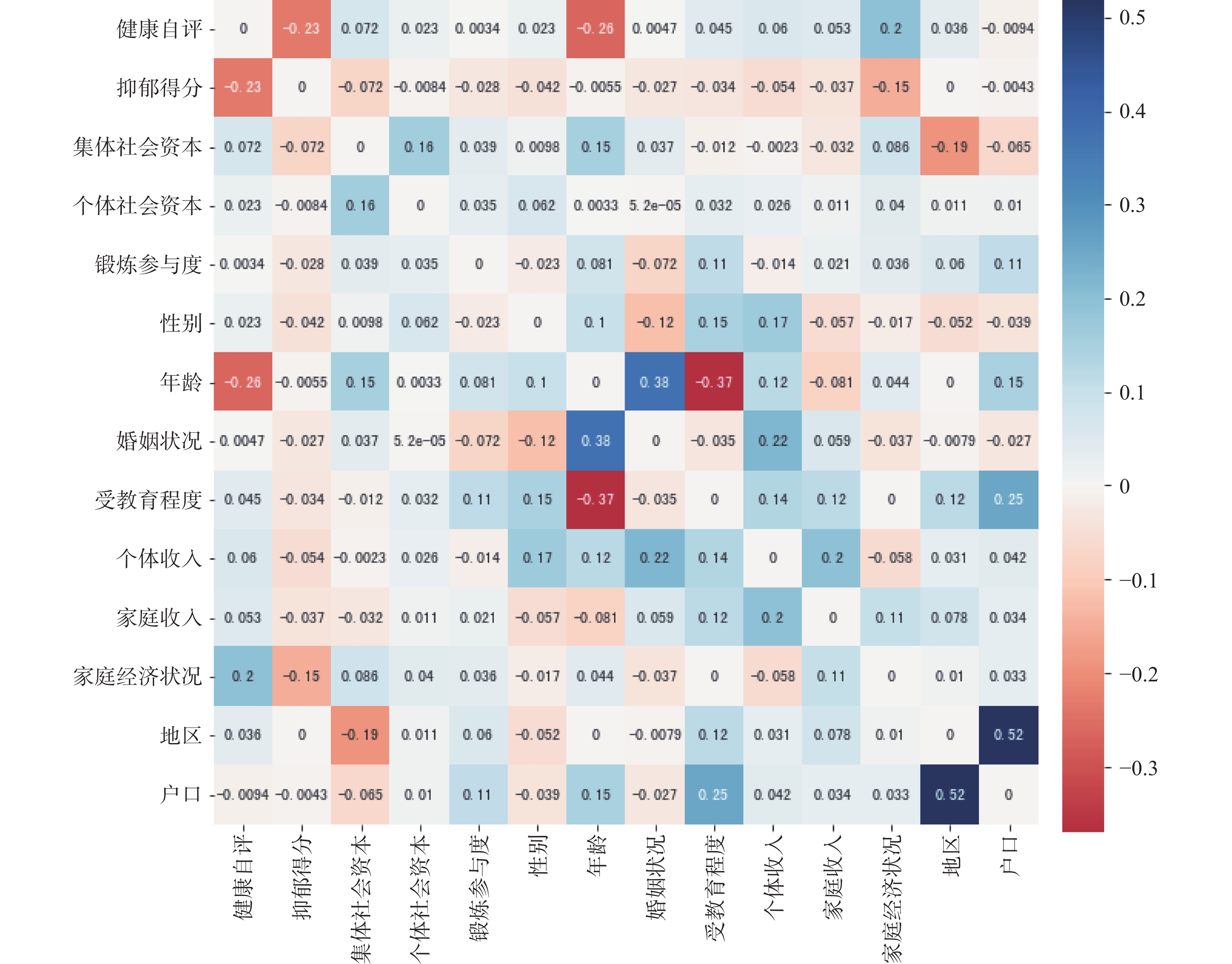
此外,GLASSO模型建构的变量网络不仅能反映关键自变量对因变量的影响,还能体现自变量之间、自变量与控制变量之间、控制变量与因变量之间的相互作用。图2中节点之间连边线条越粗表示变量之间的关系越强,红色线条表示偏相关系数为负,绿色线条表示系数为正。图2中连线过多导致线条和系数位置重叠,具体节点之间的偏相关系数可在图3中查看。在诸多影响身体健康的因素中,年龄和家庭经济状况满意度相对于其他因素而言对身体健康的影响最大:年龄越大身体健康状况越差;对家庭经济状况越满意,个体身体健康状况越好。身体健康和心理健康之间存在较强的相互关系,身体健康状况越好的人,其抑郁消极情绪也越少;个体和集体社会资本之间也存在正向关联,拥有较高集体社会资本的个体也更有可能拥有更多的个体社会资本。
上述基于GLASSO模型的数据探索初步体现了社会资本对体育锻炼的健康影响效应具有中介作用,再对中介效应系数和比例进行计算,并使用Bootstrap检验法对中介效应系数的显著性进行检验(表6)。在身体、心理健康模型中,集体社会资本和个体社会资本作为中介变量均在95%置信水平上显著(置信区间不包括0)。集体社会资本对体育锻炼身体健康促进效应的中介作用高于个体社会资本(集体社会资本的解释比例为23.69%,而个体社会资本只有7.98%);对于心理健康亦是如此,集体社会资本对体育锻炼心理健康促进效应的解释比例为14.82%,而个体社会资本仅有3.67%。城乡居民的对比分析发现,社会资本对农村居民体育锻炼参与的身心健康促进效应的中介作用高于城市居民。在身体健康模型中,农村居民的集体社会资本对体育锻炼健康促进效应的解释比例达42.89%,而城市居民只有11.61%;农村居民的个体社会资本对体育锻炼健康促进效应的解释比例达14.15%,而城市居民只有5.44%。在心理健康模型中,这一差距更加明显,农村居民的集体社会资本对体育锻炼健康促进效应的解释比例高达64.53%,而城市居民仅有8.84%;农村居民的个体社会资本对体育锻炼健康促进效应的解释比例达21.3%,而城市居民仅有1.41%。至此,假设3-1、假设3-3得到验证:社会资本对体育锻炼的身心健康促进效应具有中介作用,且这一中介作用存在城乡差异。
表 6 社会资本的中介效应检验结果Table 6. The mediating effect of social capital类别 系数 Bootstrap标准误 95%置信区间下限 95%置信区间上限 中介效应比例/% 身体健康模型(自评健康状况) 集体社会资本 总体 0.007 0.001 0.005 0.008 23.69 农村 0.007 0.001 0.004 0.010 42.89 城市 0.004 0.001 0.003 0.007 11.61 个体社会资本 总体 0.002 0.001 0.001 0.003 7.98 农村 0.002 0.001 0.001 0.004 14.15 城市 0.002 0.001 0.001 0.004 5.44 心理健康模型(抑郁得分) 集体社会资本 总体 −0.060 0.008 −0.077 −0.045 14.82 农村 −0.051 0.011 −0.071 −0.030 64.53 城市 −0.067 0.013 −0.093 −0.044 8.84 个体社会资本 总体 −0.015 0.004 −0.023 −0.008 3.67 农村 −0.017 0.005 −0.028 −0.007 21.30 城市 −0.011 0.007 −0.025 0.004 1.41 注:Bootstrap再抽样次数=1000次。 4. 结论与建议
本文探讨了社会资本、体育锻炼对城乡居民身心健康的影响,得出如下结论:
(1)体育锻炼和社会资本对提高城乡居民的身心健康水平皆有显著的正向影响,且参加体育锻炼不仅能直接影响身心健康,也能通过提高城乡居民的社会资本间接提高个体的身心健康水平。我国居民的体育锻炼通常是在社区进行,且不少居民乐于参加球类、太极拳、广场舞等体育锻炼,因此:提高锻炼频率能够有效增加与社区成员的联系和对社区的熟悉度、信任感,也能促进社区内互惠互助行为的产生,有助于培育良好的社区氛围;而延长锻炼时间能够与同伴进行更加长期、深入的交流,有助于建立更多密切的人际关系,从而扩大个体的社会支持网络;良好的社区氛围和有力的社会支持网络有助于减轻个体所受到的压力和促进健康信息的传播,有利于个体对卫生、健康服务和设施的获取,从而提高和维持个体的身心健康水平。
(2)对比城乡状况发现,对于农村居民而言,相较于体育锻炼,农村居民的身心健康更多地受到社会资本的影响(表现为体育锻炼对农村居民的健康影响不显著,但社会资本对身心健康具有显著的影响),且农村居民参与体育锻炼主要是通过提高社会资本来影响健康。这一发现一方面说明农村地区的人际联系更加紧密,农村居民的身心健康更容易受到人际关系的影响;另一方面也可能是因为我国体育资源分配不均,农村的公共体育设施较少,且城乡居民的体育运动知识水平不同,因此,农村居民参与体育锻炼无法达到和城市居民同等的健康促进效应。
以上结论可以提供以下政策性的启示:①应继续大力发展体育事业,推广全民健身;②应加强社区体育基础设施建设,发展和鼓励居民参加更多的集体性体育锻炼,培育居民的集体社会资本和社会支持网络,以提高居民的身心健康水平;③应平衡体育资源的分布,补足农村公共体育设施的短板,在农村大力开展体育和健康知识宣传,帮助农村居民更加有效地通过体育锻炼提高身心健康水平。
作者贡献声明:梁玉成:提出论文选题、研究问题及分析方法,审核、修改论文;作者贡献声明:贾小双:调研、整理文献,分析数据,撰写、修改论文。1 ①锻炼频率和锻炼时长的因子负载系数均为0.87,虽然KMO值(0.5)较小,但根据Bartlett球形检验结果(P<0.001)和 SMC值(0.69)判断可以进行因子分析。2 ②熟悉程度、信任程度、互惠程度的因子负载系数分别为0.72、0.74和0.69,KMO值为0.71。3 ③总体社会支持网规模、情感支持网规模、讨论网规模和借钱网规模的因子负载系数分别为0.66、0.85、0.83和0.63,KMO值为0.74。4 ①此外,笔者还具体分析了锻炼频率和锻炼时长如何影响身心健康。回归结果显示:锻炼时长对身体健康水平具有显著的促进作用(回归系数为 0.033,P=0.01),而对减轻抑郁程度的作用不显著( 回归系数为 −0.061,P=0.59);锻炼频率对身体健康的促进作用不显著( 回归系数为 0.006,P=0.29),而对抵抗抑郁情绪的作用显著( 回归系数为 −0.260,P<0.01)。因篇幅限制,未列出回归分析结果。 5 ①CLDS 2016询问了参加体育锻炼受访者日常的锻炼方式,在6626位回答了该题的受访者中,75.75%的受访者日常通过走路、跑步的方式锻炼,15%的受访者通过球类运动、气功、太极拳、广场舞,以及使用社区体育器材等进行锻炼。 -
表 1 相关变量描述性统计结果
Table 1 Descriptive statistics of relevant variables
变量名称 均值(标准差/百分比) t 或 χ2 变量描述 农村(n=13013) 城市(n=7525) 身体健康状况 3.51(1.05) 3.79(0.9) −18.7*** 定序变量,自评健康状况:非常不健康=1、比较不健康=2、一般=3、比较健康=4、非常健康=5 抑郁得分 7.83 (9.4) 6.61(8.9) 9.12*** 定距变量, CES-D20量表20道题得分加总;取值范围为[0,60] 集体社会资本 0.20(0.78) −0.34(0.86) 46.20*** 定距变量,由熟悉程度、信任程度、互惠程度3个变量进行因子分析得到;取值范围为[−2.78,1.51] 熟悉程度 4.00(0.89) 3.34(1.02) 48.38*** 定序变量,和本村(社区)邻里街坊的熟悉程度:非常不熟悉=1、不太熟悉=2、一般=3、比较熟悉=4、非常熟悉=5 信任程度 3.79(0.83) 3.41(0.81) 32.4*** 定序变量,对本村(社区)邻里街坊的信任程度:非常不信任=1、不太信任=2、一般=3、比较信任=4、非常信任=5 互惠程度 3.51(0.98) 3.00(1.02) 35.49*** 定序变量,与本村(社区)邻里街坊的互助频率:非常少=1、比较少=2、一般=3、比较多=4、非常多=5 个体社会资本 −0.01(0.94) 0.02(0.88) −2.18** 定距变量,由总体社会支持网、情感支持网、讨论网和借钱网规模的因子分析得到;取值范围为[−0.58,13.27] 总体社会支持网规模 9.34(16.05) 9.36(15.19) −0.05*** 定距变量,在本村(社区)有多少个关系密切、可以获得他们支持和帮助的朋友或熟人;取值范围为[0,100] 情感支持网规模 4.12(8.06) 4.08(6.74) 0.33 定距变量,在本村(社区)关系密切的人中,有多少人可以诉说心事;取值范围为[0,100] 讨论网规模 3.47(6.75) 3.73(6.32) −2.74*** 定距变量,在本村(社区)关系密切的人中,有多少人可以讨论重要事情;取值范围为[0,100] 借钱网规模 3.06(6.81) 3.81(7.67) −7.31*** 定距变量,在本村(社区)关系密切的人中,有多少可以向他/她借钱(以5000元为标准);取值范围为[0,100] 锻炼参与度 −0.16(0.82) 0.27(0.99) −33.56*** 定距变量,由每周锻炼频率和每次锻炼时长的因子分析得到;取值范围为[−0.59,2.19] 锻炼频率 1.21(2.43) 2.24(2.82) −27.62*** 定距变量,每周锻炼次数;取值范围为[0,7] 锻炼时长 0.55(1.09) 1.2(1.42) −36.55*** 定序变量,每次锻炼时长:不锻炼=0、不足0.5 h=1、0.5~1 h=2、1~2 h=3、2 h以上=4 年龄 46.29(14.82) 42.24(13.83) 19.32*** 定距变量,受访者年龄 受教育程度 7.33(3.98) 11.11(3.91) −66.07*** 定距变量,受访者受教育年限(按照最高学历);取值范围为[0,19] 个体收入(取对数) 5.12(3.27) 6.23(3.48) −22.84*** 定距变量,受访者月收入取对数;取值范围为[0,12.61] 家庭收入(取对数) 7.58(1.51) 8.38(1.3) −38.48*** 定距变量,受访者家庭月收入取对数;取值范围为[0,16.3] 家庭经济状况满意度 3.18(1.07) 3.35(1.04) −11.34*** 定序变量,受访者对家庭经济状况满意程度:非常不满意=1、不太满意=2、一般=3、比较满意=4、非常满意=5 性别 6317 (48.54) 3446(45.79) 14.45*** 虚拟变量,受访者性别:女性=0、男性=1 婚姻状况 10897(83.74) 5778(76.78) 151*** 虚拟变量,受访者当前婚姻状态:未婚=0、已婚=1 户口类型 712(5.47) 4957(65.87) 0.009*** 虚拟变量,是否为居民户口:非居民户口=0、居民户口=1 注:*** 表示P<0.01,** 表示P<0.05。 表 2 体育锻炼对身心健康的影响效应
Table 2 The effect of exercise on physical and mental health
变量 全样本模型 交互模型 农村模型 城市模型 自评健康 抑郁得分 自评健康 抑郁得分 自评健康 抑郁得分 自评健康 抑郁得分 锻炼参与度 0.028*** −0.408*** 0.023** −0.141 0.016 −0.078 0.038*** −0.756*** 锻炼参与度×所在地区 0.01 −0.590*** 性别(男性=1) 0.093*** −1.095*** 0.093*** −1.102*** 0.121*** −1.543*** 0.036* −0.388* 年龄 −0.022*** 0.035*** −0.022*** 0.036*** −0.023*** 0.049*** −0.020*** 0.01 婚姻状况(已婚=1) 0.089*** −1.079*** 0.089*** −1.082*** 0.079*** −1.478*** 0.091*** −0.486* 受教育程度 0.015*** −0.136*** 0.015*** −0.137*** 0.017*** −0.173*** 0.011*** −0.062* 个体收入(对数) 0.025*** −0.214*** 0.025*** −0.213*** 0.030*** −0.187*** 0.016*** −0.243*** 家庭收入(对数) 0.038*** −0.324*** 0.038*** −0.324*** 0.044*** −0.406*** 0.023*** −0.109 家庭经济状况自评 0.234*** −1.919*** 0.234*** −1.924*** 0.253*** −2.189*** 0.203*** −1.508*** 所在地区(城市=1) 0.072*** 0.318* 0.234*** −1.924*** 户口类型(居民=1) −0.080*** 0.03 −0.081*** 0.098 −0.009 0.045 −0.097*** −0.027 常数项 3.163*** 18.226*** 3.162*** 18.240*** 3.032*** 19.779*** 3.511*** 15.125*** 观测值 20 538 20 538 20 538 20 538 13 013 13 013 7 525 7 525 R2 0.215 0.088 0.215 0.089 0.22 0.107 0.17 0.057 注:*** 表示P<0.01,** 表示P<0.05,*表示 P<0.1。 表 3 社会资本对身心健康的影响效应
Table 3 The effect of social capital on physical and mental health
变量 全模型 集体社会资本模型 个体社会资本模型 自评健康 抑郁得分 自评健康 抑郁得分 自评健康 抑郁得分 集体社会资本 0.117*** −1.115*** 熟悉程度 0.026*** −0.458*** 信任程度 0.065*** −0.718*** 互惠程度 0.041*** −0.076 个体社会资本 0.028*** −0.152** 总体社会支持网规模 0.002*** −0.011** 情感支持网规模 0.002 0.0001 讨论网规模 0.001 −0.013 借钱网规模 0.002 −0.018* 控制变量 已控制 已控制 已控制 已控制 已控制 已控制 常数项 3.230*** 17.783*** 2.743*** 22.395*** 3.141*** 18.545*** 观测值 20 538 20 538 20 538 20 538 20 538 20 538 R2 0.224 0.096 0.224 0.097 0.224 0.096 注:*** 表示P<0.01,**表示 P<0.05,* 表示P<0.1;由于篇幅限制,控制变量系数未列出。 表 4 社会资本对身心健康影响的城乡差异
Table 4 The differentiation effect of social capital on physical and mental health between rural and urban residents
变量 交互模型 农村模型 城市模型 自评健康 抑郁得分 自评健康 抑郁得分 自评健康 抑郁得分 集体社会资本 0.146*** −1.099*** 0.147*** −1.084*** 0.067*** −1.097*** 个体社会资本 0.029*** −0.231*** 0.025*** −0.091 0.032*** −0.187** 集体社会资本×所在地区 −0.069*** −0.037 个体社会资本×所在地区 −0.007 0.233 控制变量 已控制 已控制 已控制 已控制 已控制 已控制 常数项 3.228*** 17.793*** 3.137*** 14.810*** 3.560*** 18.973*** 观测值 20 538 20 538 13 013 7 525 7 525 13 013 R2 0.225 0.096 0.232 0.061 0.174 0.116 注:*** 表示P<0.01,** 表示P<0.05,* 表示P<0.1; 由于篇幅限制,控制变量系数未列出。 表 5 体育锻炼的社会资本提升效应
Table 5 The effect of exercise on social capital promotion
变量 全样本模型 交互模型 农村模型 城市模型 集体社会资本 个体社会资本 集体社会资本 个体社会资本 集体社会资本 个体社会资本 集体社会资本 个体社会资本 锻炼参与度 0.054*** 0.050*** 0.049*** 0.044*** 0.044*** 0.048*** 0.064*** 0.052*** 锻炼频率 0.011 0.013 控制变量 已控制 已控制 已控制 已控制 已控制 已控制 已控制 已控制 常数项 −0.580*** −0.581*** −0.580*** −0.581*** −0.656*** −0.539*** −0.873*** −0.731*** 观测值 20 538 20 538 20 538 20 538 13 013 13 013 7 525 7 525 R2 0.153 0.023 0.153 0.023 0.071 0.02 0.066 0.028 注:***表示P<0.01,**表示P <0.05,*表示P <0.1;由于篇幅限制,控制变量系数未列出。 表 6 社会资本的中介效应检验结果
Table 6 The mediating effect of social capital
类别 系数 Bootstrap标准误 95%置信区间下限 95%置信区间上限 中介效应比例/% 身体健康模型(自评健康状况) 集体社会资本 总体 0.007 0.001 0.005 0.008 23.69 农村 0.007 0.001 0.004 0.010 42.89 城市 0.004 0.001 0.003 0.007 11.61 个体社会资本 总体 0.002 0.001 0.001 0.003 7.98 农村 0.002 0.001 0.001 0.004 14.15 城市 0.002 0.001 0.001 0.004 5.44 心理健康模型(抑郁得分) 集体社会资本 总体 −0.060 0.008 −0.077 −0.045 14.82 农村 −0.051 0.011 −0.071 −0.030 64.53 城市 −0.067 0.013 −0.093 −0.044 8.84 个体社会资本 总体 −0.015 0.004 −0.023 −0.008 3.67 农村 −0.017 0.005 −0.028 −0.007 21.30 城市 −0.011 0.007 −0.025 0.004 1.41 注:Bootstrap再抽样次数=1000次。 -
[1] BOURDIEU P. The forms of capital[M]// RICHARDSON J G. Handbook of theory and research for the sociology of education. Westport CT: Greenwood Press, 1986: 241-258
[2] COLEMAN J S. Social capital in the creation of human capital[J]. American Journal of Sociology,1988,94:S95-S120 doi: 10.1086/228943
[3] PORTES A. Social capital:Its origins and applications in modern sociology[J]. Annual Review of Sociology,1998,24:1-24 doi: 10.1146/annurev.soc.24.1.1
[4] LIN N. Building a network theory of social capital[J]. Connections,1999,22(1):28-51
[5] PUTNAM R D, LEONARDI R, NONETTI R Y. Making democracy work: Civic traditions in modern Italy[M]. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1994: 195-201
[6] 赵延东,罗家德.如何测量社会资本:一个经验研究综述[J]. 国外社会科学,2005(2):18-24 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4777.2005.02.003 [7] 张文宏.中国社会网络与社会资本研究30年:上[J]. 江海学刊,2011(2):104-112 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-856X.2011.02.015 [8] 张文宏.社会资本:理论争辩与经验研究[J]. 社会学研究,2003(4):23-35 [9] 罗家德,方震平.社区社会资本的衡量:一个引入社会网观点的衡量方法[J]. 江苏社会科学,2014(1):114-124 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8671.2014.01.015 [10] 林南. 社会资本: 关于社会结构与行动的理论[M]. 张磊, 译. 上海: 上海人民出版社, 2005: 23-24 [11] BURT R S. Network items and the general social survey[J]. Social Networks,1984,6(4):293-339 doi: 10.1016/0378-8733(84)90007-8
[12] LIN N,DUMIN M. Access to occupations through social ties[J]. Social Networks,1986,8(4):365-385 doi: 10.1016/0378-8733(86)90003-1
[13] BERNARD H R,JOHNSEN E C,KILLWORTH P D,et al. Comparing four different methods for measuring personal social networks[J]. Social Networks,1990,12(3):179-215 doi: 10.1016/0378-8733(90)90005-T
[14] PUTNAM R D.Bowling alone: The collapse and revival of American community[M]. New York: Simon & Schuster, 2000: 42-121
[15] UPHOFF N,WIJAYARATNA C M. Demonstrated benefits from social capital:The productivity of farmer organizations in Gal Oya,Sri Lanka[J]. World Development,2000,28(11):1875-1890 doi: 10.1016/S0305-750X(00)00063-2
[16] HARPHAM T,GRANT E,THOMAS E. Measuring social capital within health surveys:Key issues[J]. Health Policy and Planning,2002,17(1):106-111 doi: 10.1093/heapol/17.1.106
[17] MCKENZIE K,WHITLEY R,WEICH S. Social capital and mental health[J]. British Journal of Psychiatry,2002,181(4):280-283 doi: 10.1192/bjp.181.4.280
[18] KRISHNA A. Moving from the stock of social capital to the flow of benefits:The role of agency[J]. World Development,2001,29(6):925-943 doi: 10.1016/S0305-750X(01)00020-1
[19] ISLAM M K,MERLO J,KAWACHI I,et al. Social capital and health:Does egalitarianism matter? A literature review[J]. International Journal for Equity in Health,2006,5:3 doi: 10.1186/1475-9276-5-3
[20] 桂勇,黄荣贵.社区社会资本测量:一项基于经验数据的研究[J]. 社会学研究,2008,23(3):122-142,244 [21] 项军.城市“社区性”量表构建研究[J]. 社会,2011,31(1):131-158 [22] YIP W,SUBRAMANIAN S V,MITCHELL A D,et al. Does social capital enhance health and well-being? Evidence from rural China[J]. Social Science & Medicine,2007,64(1):35-49
[23] WANG H M,SCHLESINGER M,WANG H,et al. The flip-side of social capital:The distinctive influences of trust and mistrust on health in rural China[J]. Social Science & Medicine,2009,68(1):133-142
[24] PAXTON P. Is social capital declining in the United States? A multiple indicator assessment[J]. American Journal of Sociology,1999,105(1):88-127 doi: 10.1086/210268
[25] 福山. 信任: 社会道德与繁荣的创造[M]. 李宛容, 译. 呼和浩特: 远方出版社, 1998: 35-46 [26] 周结友,裴立新.国外体育运动与社会资本研究:缘起、成果与启示[J]. 体育科学,2014,34(7):73-82,96 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-677X.2014.07.011 [27] 仇军,杨涛.体育与社会资本研究述评[J]. 体育学刊,2012,19(5):14-21 [28] 张晓丽,黄谦.社会资本对体育健身的影响及作用路径理论探析[J]. 西安体育学院学报,2018,35(6):657-662 [29] 边燕杰.社会资本与大众体育[J]. 上海体育学院学报,2020,44(4):1-11 [30] 张瑞云, 李海霞. 体育组织参与对青少年体育社会资本的影响[C]. 南宁: 全国体育科学大会论文集, 2015: 1428 [31] COALTER F. Sports clubs,social capital and social regeneration:'Ill-defined interventions with hard to follow outcomes'?[J]. Sport in Society,2007,10(4):537-559 doi: 10.1080/17430430701388723
[32] 黄谦,张晓丽,葛小雨.体育参与促进社会资本生成的路径和方式:基于2014年《中国家庭追踪调查》数据的实证分析[J]. 中国体育科技,2019,55(7):63-70 [33] OKAYASU I,KAWAHARA Y,NOGAWA H. The relationship between community sport clubs and social capital in Japan:A comparative study between the comprehensive community sport clubs and the traditional community sports clubs[J]. International Review for the Sociology of Sport,2010,45(2):163-186 doi: 10.1177/1012690210362027
[34] SEIPPEL Ø. Sport,civil society and social integration:The case of Norwegian voluntary sport organizations[J]. Journal of Civil Society,2005,1(3):247-265 doi: 10.1080/17448680500484483
[35] 田恩庆,仇军,方震平,等.“5·12”灾后重建中体育参与对个体社会资本和身体健康的影响[J]. 成都体育学院学报,2014,40(11):43-49 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9154.2014.11.011 [36] OTTESEN L,JEPPESEN R S,KRUSTRUP B R. The development of social capital through football and running:Studying an intervention program for inactive women[J]. Scandinavian Journal of Medicine & Science in Sports,2010,20:118-131
[37] 于永慧.参加大众体育与个人社会网络的关系分析:和其他休闲活动类型相比较[J]. 天津体育学院学报,2005(6):74-76 [38] COALTER F. A wider social role for sport: Who's keepingthe score[M].London and New York: Routledge Press, 2007: 49-64
[39] ARAI H,NAGATSUKA M,HIRAI K. The relationship between regular exercise and social capital among Japanese community residents[J]. International Journal of Sport and Health Science,2008,6:188-193 doi: 10.5432/ijshs.IJSHS20080352
[40] DI BARTOLOMEO G,PAPA S. The effects of physical activity on social interactions:The case of trust and trustworthiness[J]. Journal of Sports Economics,2019,20(1):50-71 doi: 10.1177/1527002517717299
[41] JARVIE G. Communitarianism,sport and social capital:'Neighbourly Insights into Scottish Sport'[J]. International Review for the Sociology of Sport,2003,38(2):139-153 doi: 10.1177/1012690203038002001
[42] 张晓丽,雷鸣,黄谦.体育锻炼能提升社会资本吗?:基于2014 JSNET调查数据的实证分析[J]. 上海体育学院学报,2019,43(3):76-84 [43] 彭大松.体育锻炼中的社会分层:现象、机制与思考[J]. 体育科学,2012,32(5):24-33 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-677X.2012.05.003 [44] 梁玉成,张琦.城市居民的体育锻炼模式与集体社会资本:一个异质社会空间的视角[J]. 上海体育学院学报,2020,44(4):12-22 [45] SPANIER P A,ALLISON K R. General social support and physical activity:An analysis of the Ontario health survey[J]. Canadian Journal of Public Health,2001,92(3):210-213 doi: 10.1007/BF03404308
[46] 钟建伟. 大众体育参与与社会资本生成: 基于城市居民调查的研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2010: 1 [47] GREINER K A,LI C,KAWACHI I,et al. The relationships of social participation and community ratings to health and health behaviors in areas with high and low population density[J]. Social Science & Medicine,2004,59(11):2303-2312
[48] UESHIMA K,FUJIWARA T,TAKAO S,et al. Does social capital promote physical activity? A population-based study in Japan[J]. PLoS One,2010,5(8):e12135 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012135
[49] KIM J R,JEONG B,PARK K S,et al. Association of social capital at the individual level with physical activity in communities with high mortality in Korea[J]. Health Promotion International,2016,32(5):850-859
[50] 唐刚,李雪梅,彭英.社会资本视域下“村改社”社区居民体育参与实证研究:以成渝试验区为例[J]. 山东体育科技,2017,39(3):12-17 [51] 梁童心,齐亚强.对社会资本与健康关系研究的回顾与反思[J]. 天津社会科学,2015,6(2):103-104 [52] KAWACHI I,KENNEDY B P,GLASS R. Social capital and self-rated health:A contextual analysis[J]. American Journal of Public Health,1999,89(8):1187-1193 doi: 10.2105/AJPH.89.8.1187
[53] ROSE R. How much does social capital add to individual health?[J]. Social Science & Medicine,2000,51(9):1421-1435
[54] 周子力,毛宗福.社会资本测量及其在健康领域应用[J]. 中国公共卫生,2016,32(9):1287-1292 doi: 10.11847/zgggws2016-32-09-41 [55] 赵斌,刘米娜.收入、社会资本、健康与城市居民幸福感的实证分析[J]. 统计与决策,2013(20):96-99 [56] 薛新东,刘国恩.社会资本决定健康状况吗:来自中国健康与养老追踪调查的证据[J]. 财贸经济,2012(8):113-121 [57] 孙博文,李雪松,伍新木.社会资本的健康促进效应研究[J]. 中国人口科学,2016(6):98-106,128 [58] 赵延东.社会网络与城乡居民的身心健康[J]. 社会,2008,28(5):1-19,224 [59] FOLLAND S. An economic model of social capital and health[J]. Health Economics,Policy,and Law,2008,3(4):333-348
[60] 李玉霞,曲江斌,赵娜.社会资本在健康领域的应用现状[J]. 卫生软科学,2006,20(6):562-564,577 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-2800.2006.06.021 [61] WELLMAN B,LIN N,DEAN A,et al. Social support,life events,and depression[J]. Contemporary Sociology,1988,17(2):237 doi: 10.2307/2070619
[62] LIN N,SIMEONE R S,ENSEL W M,et al. Social support,stressful life events,and illness:A model and an empirical test[J]. Journal of Health and Social Behavior,1979,20(2):108-119 doi: 10.2307/2136433
[63] 郭克强,李宇阳,郁希阳,等.家庭社会资本通过健康素养对健康状况影响的路径研究[J]. 中国全科医学,2021,24(10):1249-1253 [64] 缪晓雷,边燕杰.防疫社会资本、体育锻炼与身心健康[J]. 上海体育学院学报,2020,44(12):1-12 [65] 郭德法.体育锻炼频率与大学生心理健康的研究[J]. 中国科技信息,2008(4):208-209 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8972.2008.04.122 [66] CHEKROUD S R,GUEORGUIEVA R,ZHEUTLIN A B,et al. Association between physical exercise and mental health in 1.2 million individuals in the USA between 2011 and 2015:A cross-sectional study[J]. The Lancet Psychiatry,2018,5(9):739-746 doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(18)30227-X
[67] GRASDALSMOEN M, ERIKSEN H R, LØNNING K J, et al. Physical exercise, mental health problems, and suicide attempts in university students[J]. BMC Psychiatry, 2020, 20(1): 1-11
[68] 胡芳芳,张娇,高兆溶,等.城乡社区低龄老人体育锻炼与心理健康的关系[J]. 中国心理卫生杂志,2021,35(9):739-744 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6729.2021.09.007 [69] 方黎明,郭静.体育锻炼促进了健康公平吗?:体育锻炼对中国城乡居民抑郁风险的影响[J]. 体育科学,2019,39(10):65-74 [70] 胡荣,胡康.城乡居民社会资本构成的差异[J]. 厦门大学学报(哲学社会科学版),2008(6):64-70 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0438-0460.2008.06.009 [71] 池上新.社会网络、心理资本与居民健康的城乡比较[J]. 人口与发展,2014,20(3):96-103,112 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1668.2014.03.015 [72] 雷鸣.体育锻炼如何提升幸福感:论社会资本的中介作用[J]. 上海体育学院学报,2020,44(4):23-30 [73] 帕特南. 独自打保龄: 美国社区的衰落与复兴[M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 2011: 7 [74] FRIEDMAN J,HASTIE T,TIBSHIRANI R. Sparse inverse covariance estimation with the Graphical LASSO[J]. Biostatistics,2007,9(3):432-441
[75] FRIEDMAN J H, HASTIE T, TIBSHIRANI R. Glasso: Graphical LASSO: Estimation of Gaussian graphical models[EB/OL]. [2021-12-22]. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=glasso
[76] JUNG A,HANNAK G,GOERTZ N. Graphical LASSO based model selection for time series[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters,2015,22(10):1781-1785 doi: 10.1109/LSP.2015.2425434
[77] MEINSHAUSEN N,BÜHLMANN P. High-dimensional graphs and variable selection with the LASSO[J]. The Annals of Statistics,2006,34(3):1436-1462
[78] FOYGEL R,DRTON M. Extended bayesian information criteria for Gaussian Graphical Models[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems,2010,11:604-612
[79] EPSKAMP S,FRIED E I. A tutorial on regularized partial correlation networks[J]. Psychological Methods,2018,23(4):617-634 doi: 10.1037/met0000167
[80] JAYA E S,HILLMANN T E,REININGER K M,et al. Loneliness and psychotic symptoms:The mediating role of depression[J]. Cognitive Therapy and Research,2017,41(1):106-116 doi: 10.1007/s10608-016-9799-4
[81] EPSKAMP S, WALDORP L J, MÕTTUS R, et al. Discovering psychological dynamics: The Gaussian graphical model in cross-sectional and time-series data[EB/OL]. [2021-12-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1609.04156v2
-
期刊类型引用(21)
1. 李卓,罗雅楠. 互联网使用与流动老年人身心健康的关系及机制研究. 云南民族大学学报(哲学社会科学版). 2024(01): 95-109 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张宇争,徐阳,凌巍. 社会资本对农民主观幸福感的影响——基于CGSS2017的实证分析. 统计理论与实践. 2024(01): 55-61 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 钟华梅,许文鑫. 体育锻炼参与的主观福利效应研究——基于中国家庭追踪调查数据的实证分析. 西安体育学院学报. 2024(01): 62-75 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 张倩雯,罗金萍,孙嘉颖,王康,尹文强,陈钟鸣,马东平. 基于健康生态学模型的潍坊市居民自测健康状况及影响因素研究. 中国卫生事业管理. 2024(03): 344-349 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 姜勇,王晓宇. 城市社区体育“协商治理”发展的本土逻辑、价值定位与未来向度. 南京体育学院学报. 2024(01): 39-45 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 汪如锋,聂小琳,李九祥. 我国大学生体质健康资本保障路径研究——高校体育生活化视角. 南京体育学院学报. 2024(04): 53-59+2 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 吕行,杜莉华,陈阳. “作为方法的时间”:基于过程性时间量化研究的框架重构与方法革新. 新闻与写作. 2024(07): 62-75 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 孟敏. 乡村振兴背景下城乡公共体育服务优化及设施建设对策. 湖北第二师范学院学报. 2024(06): 30-33 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 王晶晶,冯强,范超群,王成龙,王梅. 中国20~79岁居民心理健康现状及其与体育锻炼的关系. 中华行为医学与脑科学杂志. 2024(08): 699-705 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 袁青. 南粤古驿道体育赛事提升村民社会资本的实践经验与启示. 文体用品与科技. 2024(19): 40-42 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 马艳红,梁响玲. 健康中国背景下我国女性体育锻炼行为变迁的影响因素研究——基于中国综合社会调查(CGSS)数据的实证检验. 体育与科学. 2024(06): 95-104 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 赵炎. 德州市德城区城市居民体育锻炼现状调查与分析. 文体用品与科技. 2023(03): 40-42 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 郭珂吟,因杰秀,朴顺哲,张震. 十二周体适能训练对肥胖大学生体成分的影响. 当代体育科技. 2023(08): 16-19+25 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 李利强,李玉林,霍小亮,吴进. 我国城镇居民健康生活方式与主观幸福感的关系:体育锻炼和健康状态的链式中介作用. 中国健康心理学杂志. 2023(08): 1155-1161 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 陈文鑫,吴佑年. 体育锻炼对农村留守儿童心理韧性影响的交叉滞后分析. 湖北文理学院学报. 2023(09): 85-88 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 蒲毕文,邓星华,吴开霖. 健康中国建设背景下我国居民进行体育锻炼影响其主观幸福感的实证研究:基于CGSS的相关数据分析. 首都体育学院学报. 2023(05): 556-567+584 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. 李琼,李娜,王海军,张丽. 河北省农村居民体育健康促进路径研究. 当代体育科技. 2023(30): 109-111 .  百度学术
百度学术
18. 潘磊. 智能化工作方式对劳动者体育锻炼参与的影响. 西安体育学院学报. 2023(05): 554-563+593 .  百度学术
百度学术
19. 肖红,宋耀伟. 我国城镇居民文化资本、体育锻炼与主观健康关系研究——基于CGSS2017数据的实证分析. 西安体育学院学报. 2022(05): 570-580 .  百度学术
百度学术
20. 孙中锋,谈兆杰. 老龄时代的健康中国:社会经济地位与老年人健康状况——基于CGSS 2017数据的实证分析. 福建农林大学学报(哲学社会科学版). 2022(06): 68-79 .  百度学术
百度学术
21. 王海霞,许金富,魏德样. COVID-19疫情下体育锻炼对居民抑郁风险的影响及作用机制——基于CFPS调查数据的实证分析. 山东体育学院学报. 2022(05): 100-110 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(18)




 下载:
下载: