Visual Search Behaviors in the Penalty Decision-making of Race-walking Referees
-
摘要:目的
比较不同经验水平和判罚难度条件下,竞走裁判员判罚决策的行为绩效和视觉搜索特征。
方法采用眼动追踪技术和专家—新手研究范式,采集被试在竞走执裁判罚时的行为学指标和眼动指标数据。
结果行为学指标:专家组正确率均显著高于新手组,反应时显著少于新手。在干扰条件下,新手组正确率显著降低、反应时显著升高,而专家组无显著性差异。眼动指标:专家组的注视时间、注视次数和眼跳次数均显著低于新手。在干扰条件下,新手组的注视时间、注视次数和眼跳次数均显著高于无干扰条件,专家组无显著性差异。兴趣区眼动指标显示,专家组对运动员膝和踝的注视时间显著高于新手组,注视次数显著低于新手组。可视化图像观察到,专家组注视轨迹清晰、注视热点集中;新手组注视轨迹复杂无规律,注视热点分散。
结论高水平竞走裁判员具有较好的判罚决策能力和视觉信息加工能力,判罚过程中的视觉搜索更为简洁、高效,抗场外干扰能力强,体现出自上而下的视觉加工特征,表现出专家认知优势。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo compare the decision-making ability and visual search behavior differences of race-walking referees under different experience levels and penalty difficulty conditions.
MethodsEye tracking technology and expert-novice research paradigm were used to collect behavioral indicators and eye movement indicators of subjects in the decision-making.
ResultsBehavioral indicators: The experts outperformed novices, with both higher accuracy and shorter reaction times. Under the condition of interference, the accuracy of the novices decreased significantly and the reaction time increased significantly, while the experts had no significant differences. Eye movement indicators: The fixation time, fixation count and saccade count of the experts were significantly lower than the novices. Under the interference condition, the fixation time, fixation count and saccade count of the novices were significantly higher than those under the non-interference condition, and there was no significant difference in the experts. The AOI eye movement indicators showed that the fixation time of the experts on the knee and ankle of the athletes was significantly higher than that of novices, and the fixation count was significantly lower than that of novices. The visual images showed that the fixation trajectory of the experts were clear and the fixation hotspots were concentrated while the novices' fixation trajectory was complex and irregular, and the fixation hotspots were scattered.
ConclusionHigh-level race-walking referees have good decision-making ability and visual information processing ability. The visual search in the process of ruling is more concise and efficient, and the ability to resist off-site interference is strong. It reflects the top-down processing characteristics and shows the cognitive advantages of experts.
-
体育竞赛是运动员展现训练成果的竞技舞台,裁判员在此过程中扮演着极其重要的角色[1]。作为运动比赛的执法者,裁判员在赛场上的判罚直接影响着运动员竞技水平的发挥和比赛结果。依据信息加工理论,裁判员在判罚过程中需要在极短的时间内接受大量信息源,并对有效信息进行加工和整合后做出反馈。因此,合理的视觉搜索特征对裁判员快速而准确地搜索出相关技术动作的信息源并做出准确判罚具有事半功倍的作用[2−3]。
竞走是我国优势田径项目,是奥运会、世锦赛等重大赛事上力争奖牌的重点项目[4],也是田径运动中唯一一项依靠裁判员主观意识和视觉判断进行判罚的运动。在判罚过程中,裁判员除通过肉眼观察运动技术是否符合规则外,还面临着运动员犯规判停、裁判员穿梭传送罚单、场外观众走动等现象干扰,这些干扰因素增加了裁判员判罚难度,影响着判罚决策的绩效。王万慧敏[5]对比了有干扰条件和无干扰条件下不同水平网球裁判员执裁过程中的差异,发现在干扰情境下专家组被试的反应时短于新手组。Nevill[6]等的一项定量研究发现,与那些安静观看的裁判员相比,噪声条件影响了裁判员的判罚。临场判罚极其考验裁判员的视觉搜索能力,同时也体现了个体视觉注意集中能力和抗外界干扰的能力[7]。本文试图探索有/无干扰条件下不同水平竞走裁判员判罚决策的行为绩效和视觉搜索特征。
经验优势假说认为,专家优势来自专家在信息加工方面的“软件”特征,运动专家在决策时能够显示出优越的模式识别和卓越的预判能力,这种决策优势是经过后天培养并由自实践积累而成的[8]。近年来,眼动技术的发展为了解运动领域专家优势背后的视觉搜索和认知加工特征提供了条件。专家相比新手的优越性已经在一系列运动中得到了证明。Babadi等[9]对比了不同水平击剑裁判员的视觉搜索行为和决策准确性,结果显示,与新手裁判员相比,专家裁判员的决策准确性更高,注视次数比新手裁判员少,注视位置也不同。此外,眼动研究还表明,专家关注的区域有所不同。如高水平体操裁判员在判罚时,主要注视头部和手臂,而低水平的裁判员更加注视脚部,说明专家能够利用经验引导视觉注意指向任务相关的区域[10]。竞走裁判员判罚具有一定的特殊性,对裁判员的视觉搜索能力有着极高的要求,但目前国内外有关竞走裁判员判罚决策的视觉搜索特征研究仍属空白,了解高水平竞走裁判员在判罚决策时的视觉信息加工规律以及知觉编码机制,对新手裁判员的培养具有重要的意义,为更有效地指导新手在复杂多变的运动情境中做出快速、正确并且合理的判罚提供科学参考。
综上所述,本文从眼动追踪视角出发,探讨不同水平竞走裁判员个体间的经验差异对判罚决策的影响,并分析不同判罚难度对竞走裁判员判罚决策行为绩效和视觉搜索模式的影响差异,客观揭示裁判员在判罚决策过程中的视觉搜索特征及策略,丰富运动领域视觉搜索研究的理论体系,为裁判员的选拔及培养提供理论及实践参考。
1. 研究对象与方法
1.1 研究对象
研究对象分为专家组和新手组,专家组为国际级及国家级田径裁判员,共13人(男性11名,女性2名;均多次执裁全运会、省运会等大型赛事,其中,6名被试报告总执裁场次≥200场,7名被试报告总执裁场次为150~200场)。新手组为二级田径裁判员,共20人(男性12名,女性8名;具有一定的竞走理论知识,但执裁经历少,执裁场次为3~5场,均在竞走裁判员培训实践环节参与了临场模拟判罚)。所有被试均为右利手,视力或矫正视力正常,无色弱或色盲情况,能够熟练操作计算机。实验前向被试说明实验目的和流程,并签署知情同意书。
1.2 兴趣区与眼动指标
研究主要关注不同水平竞走裁判员在有/无干扰条件下对单人运动员判罚时所关注的技术点和身体部位以及判罚过程中的视觉搜索特征,因此,对眼动指标的分析主要分为两部分:其一,不借助兴趣区直接采集被试在判罚过程中的眼动数据,以分析不同自变量条件下被试注意力整体状态的差异。其二,根据实验需求对视频划分不同兴趣区,采集不同兴趣区内的眼动数据,以分析被试在判罚过程中的注意力分配情况或注意力集中情况。结合实验目的和国际田联制定的竞走规则,将每段视频的兴趣区划分为上肢、髋关节、膝关节、踝关节(包括脚)和干扰物。对视频材料逐帧划分动态兴趣区,在移动过程中手动调整兴趣区大小与形状,保证其对研究区域全部覆盖。
整体眼动指标:①注视,即眼睛在运动公差的1°内保持静止的时间段,时间等于或大于120 ms[11]。②注视时间,指在注视点上停留的时间长短,代表被试对实验材料的感兴趣程度和/或认知加工负荷。③注视次数,指注视点的个数,代表被试对视觉信息的处理能力。④眼跳次数,2个注视点之间的眼球运动通常被称为眼跳,眼跳次数越多表明搜索的过程越长。兴趣区眼动指标:兴趣区注视时间和注视次数是指受试者在划定的感兴趣区域内注视点的停留时间及注视点的个数。
1.3 实验仪器与材料
1.3.1 实验仪器
本实验采用由瑞典著名眼动仪生产商Tobii公司生产的Tobii Pro X3-120眼动仪,采样率为120 Hz,准确度为 0.5°,精确度为 0.3°,双眼追踪。实验所用华为笔记本电脑1台,用于记录眼动数据,Dell显示器1台(23英寸,分辨率1920×1080,刷新率60 Hz),用于呈现实验材料。将眼动仪放置在Dell显示器正下方,被试与显示器之间的距离控制在55~65 cm。在眼动仪实验中各阶段的任务由眼动仪的Tobii Pro Lab软件完成,包括刺激编程、击键反应记录、眼动数据采集和可视化。
1.3.2 实验材料
选取某高校操场为拍摄地点,在天气状况较好的条件下现场拍摄竞走视频,8名一级男子竞走运动员参与实验素材拍摄。拍摄的视频材料严格模拟真实比赛情况,拍摄角度均处于裁判员在正式比赛时的站立位置及视角。查阅以往文献[12],并结合竞走领域专家和眼动技术专业人员的建议,将每段视频的时长控制在(10±2)s,其中,每段视频要求运动员的竞走速度保持在3.125~4.348 m/s[13]。最终拍摄80段视频材料,由3名国家级裁判员进行评分及答案审定,要求对每一个片段进行评估,并根据犯规类型及合理性、视频的清晰度以及生态效度进行打分(1~5分),最终筛选出判罚难易度相当、答案一致、评分高(均值>4)的视频作为实验材料。
在符合要求的材料中筛选出48段视频,8段作为练习实验的材料,其他40段为正式实验的材料。其中,无干扰实验视频材料20段,干扰实验视频材料20段,每个实验中运动员犯规与合理视频比例为1∶1,常见犯规类型腾空和曲膝比例为1∶1。单人实验视频材料仅包括运动员,无场外观众、行人的干扰;干扰实验根据竞走比赛中常见的干扰类型设置了不同的干扰情景,包括画面中同时出现罚下的运动员、摄影工作人员、骑行送单子的志愿者、场外观众等。每段视频材料难度相似,均消除了杂音的干扰,确保对实验变量的控制。
1.4 实验程序
(1)准备阶段。实验在某高校运动学习科学实验室进行,实验室不受噪声干扰,光线柔和。采用单独测试的方法,测试过程中只有主试和被试在独立环境中进行。为了确保实验结果的真实性和可靠性,实验前记录被试的基本信息并向被试讲解本次实验的目的、意义、流程、操作方法以及视频呈现方法等,要求被试以真实比赛的判罚情境对待实验。
(2)进行校准。要求被试坐在距离显示器55~65 cm处,采用5点校准法,由系统自动记录注视位置并完成校准。为保证眼动数据的准确性,要求被试必须达到实验校准要求。校准成功后进行实验练习。
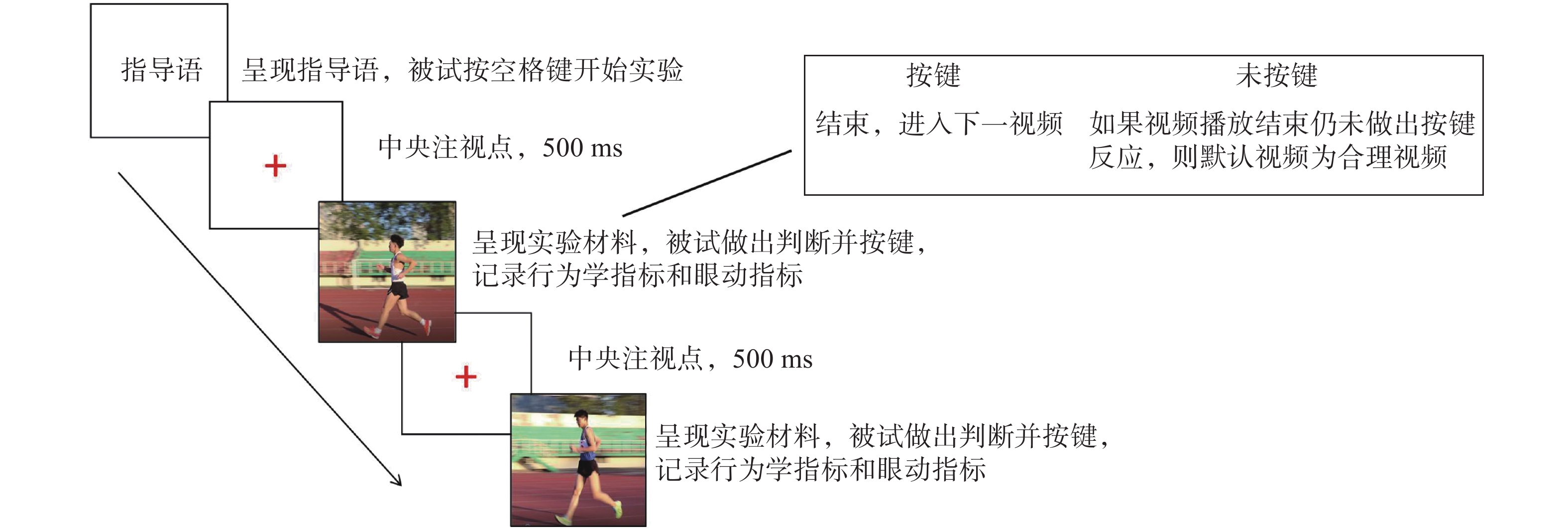
(3)进入练习阶段,被试观察8段单人竞走视频,包括犯规与合理视频两类,如果该段视频中均为合理行为按J键,如果有犯规行为按F键,在视频播放的过程中被试随时可以按键进行判断。按键后进入下一段视频,如果在视频播放结束时仍然没有判断,则进入下一段视频,默认该视频为合理视频,在每段视频结束后会有一个“+”,这是为了保证被试的视线一直在仪器可记录范围内,练习阶段主要是为了避免被试由于按键操作不熟悉而影响正式实验中的正确率及反应时指标,被试在练习阶段能够达到熟练操作按键的程度后方可开始正式实验(图1)。
(4)正式实验与练习实验过程相同。正式实验包括有干扰条件下对单人竞走运动员的判罚和无干扰条件下对单人竞走运动员的判罚2个实验,共40段视频,犯规视频与合理视频的数量比例为1∶1。其中,实验材料的呈现顺序是随机的,每段视频仅向同一个被试呈现1次。整个实验持续20 min左右。
1.5 数据分析
采用SPSS 25.0软件进行统计分析。为探讨干扰条件对不同水平竞走裁判员判罚决策的影响,采用2(组别)×2(难度)的两因素混合实验设计,考察裁判员在执裁过程中个体的视觉注意集中能力和抗外界干扰能力。因变量为行为学指标和眼动指标,行为学指标包括判罚正确率及反应时,眼动指标包括整体指标(注视时间、注视次数、眼跳次数)、兴趣区(AOI)内指标(各AOI注视时间、注视次数)以及可视化指标(注视热点图、轨迹图)。其中,对于方差分析中存在显著交互作用的变量组合,使用简单效应分析的方法对交互作用进行进一步分析。在分析过程中,对不满足球形检验的统计量采用Greenhouse-Geisser法矫正自由度和P值,事后比较采用Bonferroni法。本文中统计学差异显著性水平为α=0.05。
2. 结 果
2.1 行为学指标结果
采用2(组别:专家组、新手组)×2(判罚难度:有干扰、无干扰)两因素混合实验设计,对不同水平竞走裁判员判罚时的行为学数据进行统计分析,结果如表1、表2所示。
表 1 2组被试在有/无干扰条件下执裁时的行为学结果Table 1. Behavioral results of the two groups in the presence/absence of interference组别 正确率/% 反应时/s 无干扰 有干扰 无干扰 有干扰 专家组 0.74±0.08 0.71±0.05 5.61±0.29 5.68±0.14 新手组 0.51±0.08 0.41±0.09 6.40±0.35 6.83±0.41 表 2 2组被试行为学数据的方差分析结果Table 2. ANOVA results for behavioral data of the two groups变异来源 正确率/% 反应时/s SS df MS F P ηp2 SS df MS F P ηp2 组间 组别 0.564 1 0.564 145.491 <0.001 0.82 7.456 1 7.456 150.941 <0.001 0.83 难度 0.069 1 0.069 13.385 0.001 0.30 0.975 1 0.975 8.166 0.008 0.21 组别×难度 0.024 1 0.024 4.688 0.038 0.13 0.512 1 0.512 4.289 0.047 0.12 组内 0.159 29 0.005 3.701 29 0.128 总变异 0.816 32 12.644 32 2.1.1 正确率结果
如表2所示,组别、难度都与竞走裁判员决策正确率有很大的关系,两者的交互作用也非常显著,其P值等于0.038。由于裁判员水平、判罚难度对正确率均有显著的影响,可以作进一步简单效应分析,得出专家组和新手组在2种判罚难度下的正确率有显著性差异,无论干扰条件是否存在,专家组的正确率均高于新手组(P<0.001)。受执裁经验的影响,新手组在干扰条件下的正确率显著低于无干扰条件(P<0.001),而专家组无显著性差异(P=0.345)。
2.1.2 反应时结果
如表2所示,组别、难度都与竞走裁判员决策反应时有一定的关联,两者交互效应的P值为0.047。对数据进行进一步分析发现,专家组和新手组在2种判罚难度下的反应时存在显著性差异,无论干扰条件是否存在,专家组的反应时均低于新手组(P<0.001)。受执裁经验的影响,新手组在干扰条件下的反应时显著高于无干扰条件(P<0.001),而专家组无显著性差异(P=0.617)。
2.2 整体眼动指标结果
采用2(组别:专家组、新手组)×2(判罚难度:有干扰、无干扰)两因素混合实验设计,对不同水平竞走裁判员判罚时的眼动数据进行统计分析,结果如表3、表4所示。
表 3 2组被试在有/无干扰条件下执裁时的眼动结果Table 3. Eye movement results of the two groups in the presence/absence of interference难度 组别 注视时间/s 注视数/次 眼跳数/次 无干扰 专家组 5.21±0.11 19.38±0.51 19.93±1.95 新手组 6.10±0.16 25.31±1.80 26.40±1.61 有干扰 专家组 5.31±0.12 19.94±0.75 21.50±1.45 新手组 6.39±0.25 27.70±1.11 31.16±3.11 2.2.1 注视时间
方差分析结果显示:组别、难度都与竞走裁判员视觉搜索过程中注视时间这一眼动指标显著相关,两者交互效应的P值为0.006。进行进一步简单效应分析发现,专家组和新手组在2种判罚难度下的注视时间存在显著性差异,无论干扰条件是否存在,专家组的注视时间均低于新手组(P<0.001)。在干扰条件下新手组的注视时间显著高于无干扰条件(P<0.001),而专家组无显著性差异(P=0.059)。
表 4 对2种判罚难度的方差分析结果Table 4. List of ANOVA results for the two penalty difficulties变异来源 注视时间/s 注视数/次 眼跳数/次 SS df MS F P ηp2 SS df MS F P ηp2 SS df MS F P ηp2 组间 组别 7.612 1 7.612 327.935 <0.001 0.91 369.574 1 369.574 304.212 <0.001 0.91 512.189 1 512.189 242.506 <0.001 0.89 难度 0.632 1 0.632 35.827 <0.001 0.54 34.101 1 34.101 53.599 <0.001 0.63 157.895 1 157.895 157.895 <0.001 0.48 组别×难度 0.151 1 0.151 8.571 0.006 0.22 13.147 1 13.147 20.663 <0.001 0.40 40.189 1 40.189 7.193 0.012 0.19 组内 0.547 29 0.018 19.723 29 0.680 173.199 29 5.972 总变异 8.942 32 436.545 32 883.472 32 2.2.2 注视次数
方差分析结果显示:组别、难度都与竞走裁判员视觉搜索过程中注视次数这一眼动指标显著相关,两者交互效应的P值小于0.001。进行进一步简单效应分析发现,专家组和新手组在2种判罚难度下的注视次数存在显著性差异,无论干扰条件是否存在,专家组的注视次数均低于新手组(P<0.001)。在干扰条件下新手组的注视次数显著高于无干扰条件(P<0.001),而专家组无显著性差异(P=0.084)。
2.2.3 眼跳次数
方差分析结果显示:组别、难度都与竞走裁判员视觉搜索过程中眼跳次数这一眼动指标显著相关,两者交互效应的P值为0.012。进行进一步简单效应分析发现,专家组和新手组在2种判罚难度下的眼跳次数存在显著性差异,无论干扰条件是否存在,专家组的眼跳次数均低于新手组(P<0.001)。在干扰条件下新手组的眼跳次数显著高于无干扰条件(P<0.001),而专家组无显著性差异(P=0.101)。
2.3 各兴趣区眼动指标结果
采用2(组别:专家组、新手组)×2(判罚难度:有干扰、无干扰)两因素混合实验设计,对不同水平竞走裁判员判罚时的各兴趣区眼动数据进行统计分析。
2.3.1 AOI注视时间
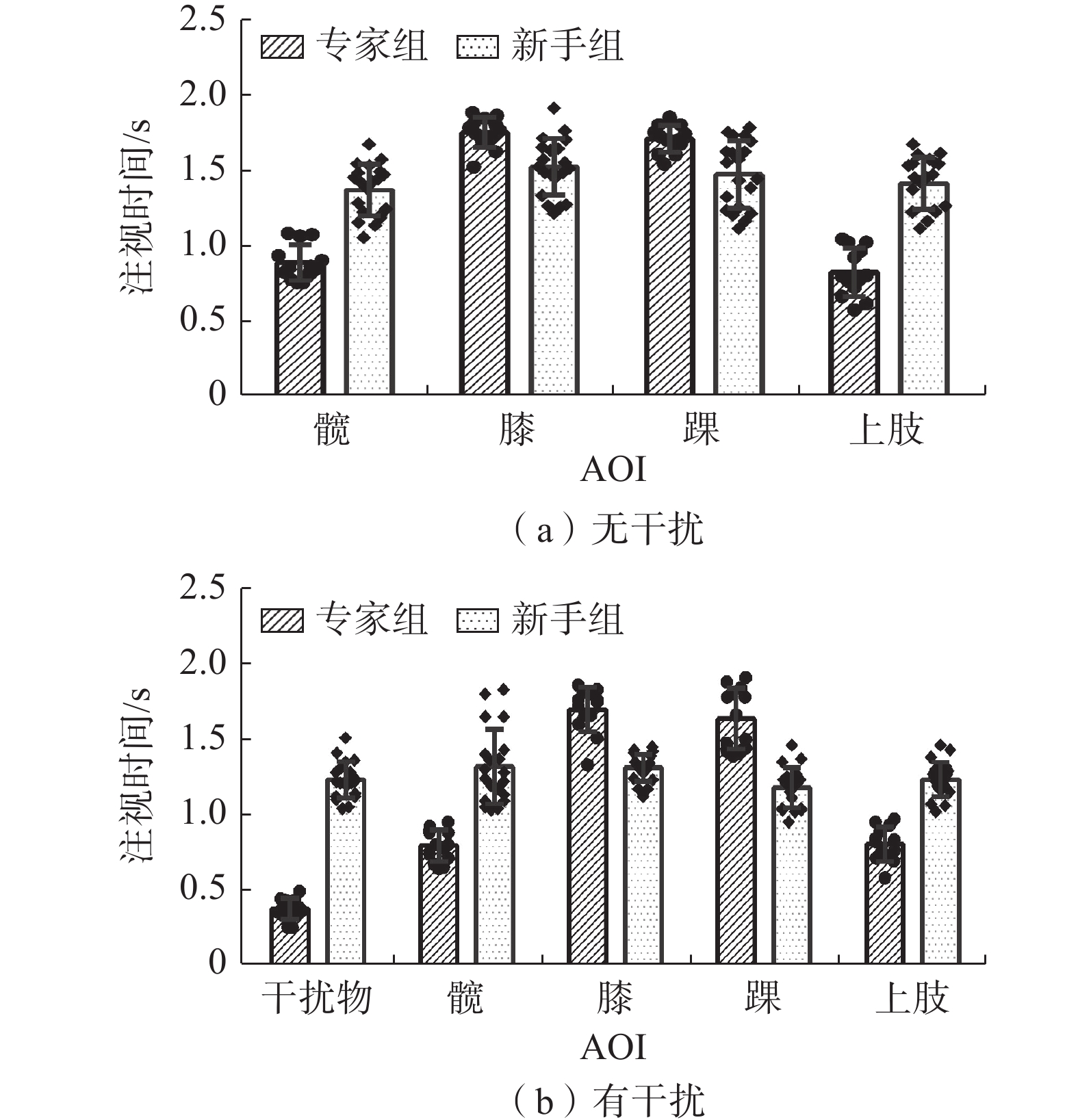
专家组和新手组在各兴趣区的注视时间分析结果如表5、表6、图2所示。髋部区域:组别主效应显著(P<0.001),专家组对运动员髋的注视时间显著低于新手组。膝部区域:判罚难度与组别的主效应(P<0.001)以及交互作用(P=0.021)均显著,进一步简单效应分析发现,无论干扰条件是否存在,专家组对运动员膝的注视时间均高于新手组(P<0.001);在干扰条件下新手组对运动员膝的注视时间显著低于无干扰条件(P<0.001)。踝部区域:判罚难度与组别的主效应(P<0.001)以及交互作用(P=0.014)均显著,进一步简单效应分析发现,无论干扰条件是否存在,专家组对运动员踝的注视时间均高于新手组(P<0.001);在干扰条件下新手组对运动员踝的注视时间显著低于无干扰条件(P<0.001)。上肢区域:判罚难度与组别的主效应(P<0.001)以及交互作用(P=0.029)均显著,进一步简单效应分析发现,无论干扰条件是否存在,专家组对运动员上肢的注视时间均低于新手组(P<0.001);在干扰条件下新手组对运动员上肢的注视时间显著低于无干扰条件(P<0.001)。
表 5 2组被试在有/无干扰条件下执裁时对各AOI注视时间Table 5. Results of the fixation time of each AOI when the two groups were performing in the presence/absence of interferences 难度 组别 髋 膝 踝 上肢 干扰物 无干扰 专家组 0.88±0.12 1.74±0.10 1.70±0.09 0.82±0.16 — 新手组 1.37±0.17 1.52±0.19 1.47±0.22 1.41±0.17 — 有干扰 专家组 0.79±0.11 1.70±0.15 1.64±0.14 0.80±0.11 0.37±0.07 新手组 1.32±0.19 1.31±0.09 1.18±0.13 1.23±0.12 1.23±0.12 注:“—”代表无对应指标。 表 6 2组被试各AOI注视时间的方差分析结果Table 6. List of ANOVA results for the fixation time in AOI for the two groups类别 变异来源 SS df MS F P ηp2 类别 变异来源 SS df MS F P ηp2 髋 组间 膝 组间 组别 2.751 1 2.751 202.235 <0.001 0.87 组别 2.065 1 2.065 66.799 <0.001 0.68 难度 1.071 1 1.071 2.287 0.141 0.07 难度 0.762 1 0.762 16.537 <0.001 0.35 组别×难度 0.064 1 0.064 0.262 0.613 0.01 组别×难度 0.136 1 0.136 5.962 0.021 0.16 组内 1.395 29 0.048 组内 0.506 29 0.017 总变异 5.281 32 总变异 2.980 32 踝 组间 上肢 组间 组别 1.103 1 1.103 61.358 <0.001 0.66 组别 3.493 1 3.493 191.832 <0.001 0.86 难度 0.621 1 0.621 17.477 <0.001 0.36 难度 0.629 1 0.629 7.367 0.011 0.19 组别×难度 0.135 1 0.135 8.570 0.014 0.18 组别×难度 0.301 1 0.301 5.209 0.029 0.14 组内 0.899 29 0.031 组内 0.620 29 0.021 总变异 2.758 32 总变异 5.043 32 2.3.2 AOI注视次数
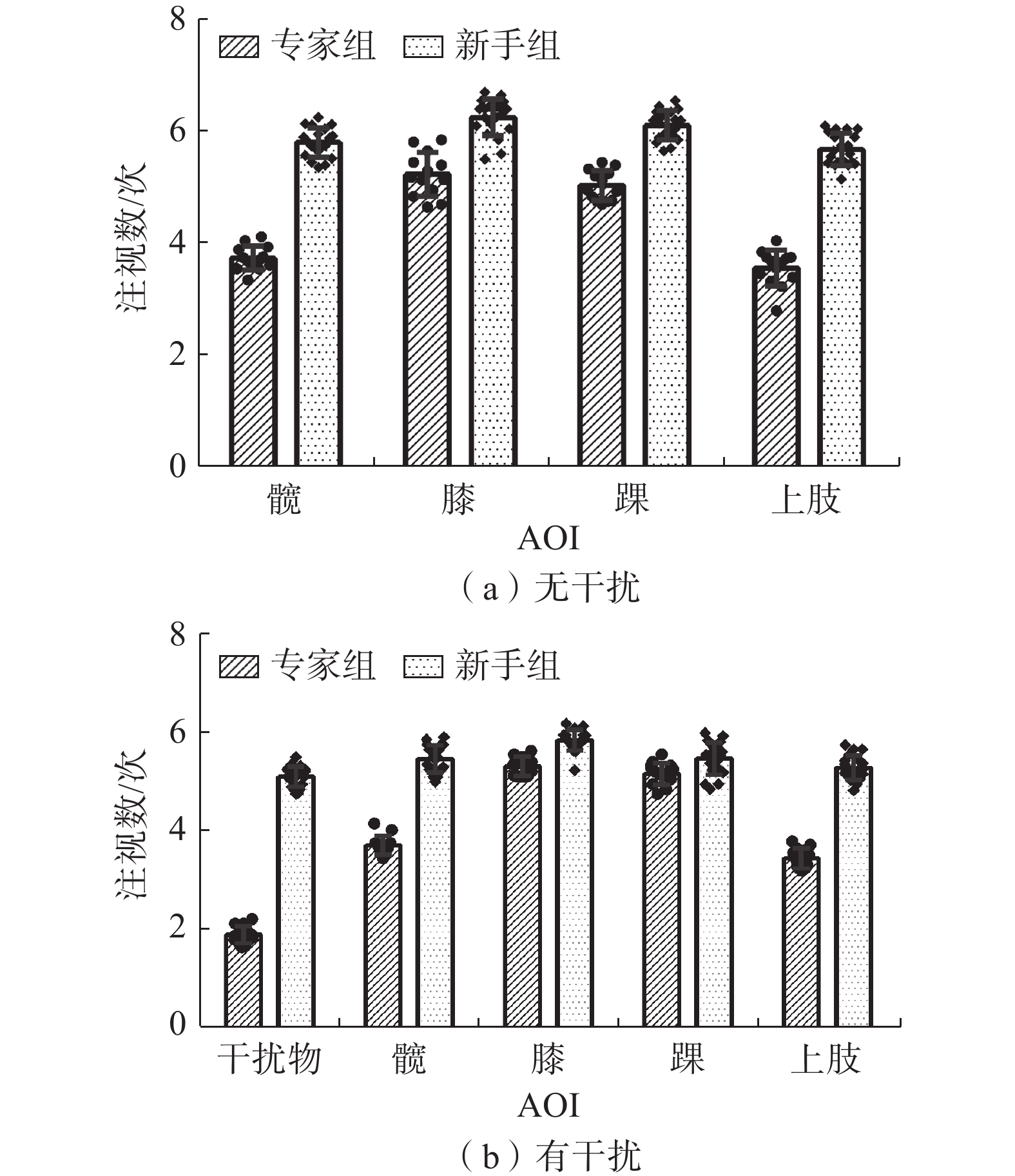
专家组和新手组在各兴趣区的注视次数分析结果如表7、表8、图3所示。髋部区域:判罚难度与组别的主效应(P<0.001)以及交互作用(P=0.003)均显著,进一步简单效应分析发现,无论干扰条件是否存在,专家组对运动员髋的注视次数均低于新手组(P<0.001);在干扰条件下新手组对运动员髋的注视次数显著低于无干扰条件(P<0.001)。膝部区域:判罚难度与组别的主效应(P<0.001)以及交互作用(P=0.002)均显著,进一步简单效应分析发现,无论干扰条件是否存在,专家组对运动员膝的注视次数均低于新手组(P<0.001);在干扰条件下新手组对运动员膝的注视次数显著低于无干扰条件(P<0.001)。踝部区域:判罚难度与组别的主效应(P<0.001)以及交互作用(P<0.001)均显著,进一步简单效应分析发现,无论干扰条件是否存在,专家组对运动员踝的注视次数均低于新手组(P<0.001);在干扰条件下新手组对运动员踝的注视次数显著低于无干扰条件(P<0.001)。上肢区域:判罚难度与组别的主效应(P<0.001)以及交互作用(P=0.027)均显著,进一步简单效应分析发现,无论干扰条件是否存在,专家组对运动员上肢的注视次数均低于新手组(P<0.001);在干扰条件下新手组对运动员上肢的注视次数显著低于无干扰条件(P<0.001)。
表 7 2组被试在有/无干扰条件下执裁时对各AOI注视次数Table 7. Results of the number of AOI fixations of the two groups in the presence/absence of interference难度 组别 髋 膝 踝 上肢 干扰物 无干扰 专家组 3.74±0.22 5.23±0.39 5.03±0.27 3.56±0.32 — 新手组 5.80±0.26 6.24±0.33 6.11±0.26 5.68±0.28 — 有干扰 专家组 3.71±0.19 5.31±0.19 5.16±0.22 3.45±0.21 1.90±0.17 新手组 5.46±0.27 5.84±0.21 5.46±0.33 5.28±0.24 5.10±0.21 注:“—”代表无对应指标。 表 8 2组被试各AOI注视次数的方差分析结果Table 8. ANOVA results for the fixation count in each AOI for the two groups at different difficulty levels类别 变异来源 SS df MS F P ηp2 类别 变异来源 SS df MS F P ηp2 髋 组间 膝 组间 组别 28.634 1 28.634 707.769 <0.001 0.96 组别 4.670 1 4.670 113.899 <0.001 0.79 难度 0.529 1 0.529 13.497 <0.001 0.30 难度 0.429 1 0.429 5.125 0.031 0.14 组别×难度 1.216 1 1.216 10.115 0.003 0.25 组别×难度 2.596 1 2.596 11.015 0.002 0.26 组内 1.312 29 0.045 组内 2.645 29 0.091 总变异 31.691 32 总变异 10.340 32 踝 组间 上肢 组间 组别 3.741 1 3.741 96.995 <0.001 0.76 组别 30.730 1 30.730 749.261 <0.001 0.96 难度 1.048 1 1.048 13.556 0.001 0.30 难度 1.000 1 1.000 16.803 <0.001 0.35 组别×难度 2.324 1 2.324 30.061 <0.001 0.49 组别×难度 0.321 1 0.321 5.389 0.027 0.15 组内 2.397 29 0.083 组内 1.844 29 0.063 总变异 9.510 32 总变异 33.985 32 2.4 可视化指标
为进一步说明兴趣区的眼动结果,本文呈现了注视热点和注视轨迹。
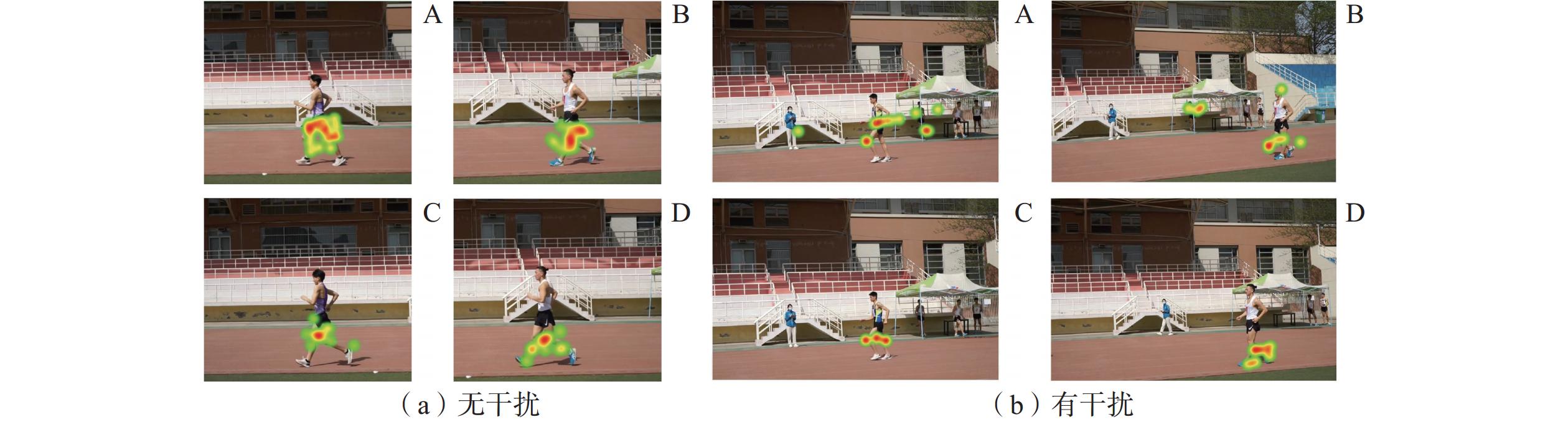
2.4.1 注视热点
受试者注视AOI的持续时间可以通过热图直观反映,其中,不同的颜色代表受试者注视该区域的不同持续时间,颜色越深表示注视时间越长。红色区域代表最长注视时间,黄色区域次之,绿色区域代表最短注视时间,无色区域表示实验参与者没有看该区域。通过图4可以看出,专家组和新手组的注视分配存在差异:专家组对运动员犯规行为的观察范围更集中,表现出目标导向的视觉搜索策略;而新手组的观察范围较大,并且在干扰条件下,除了对运动员的关注外,还表现出对干扰物的关注。
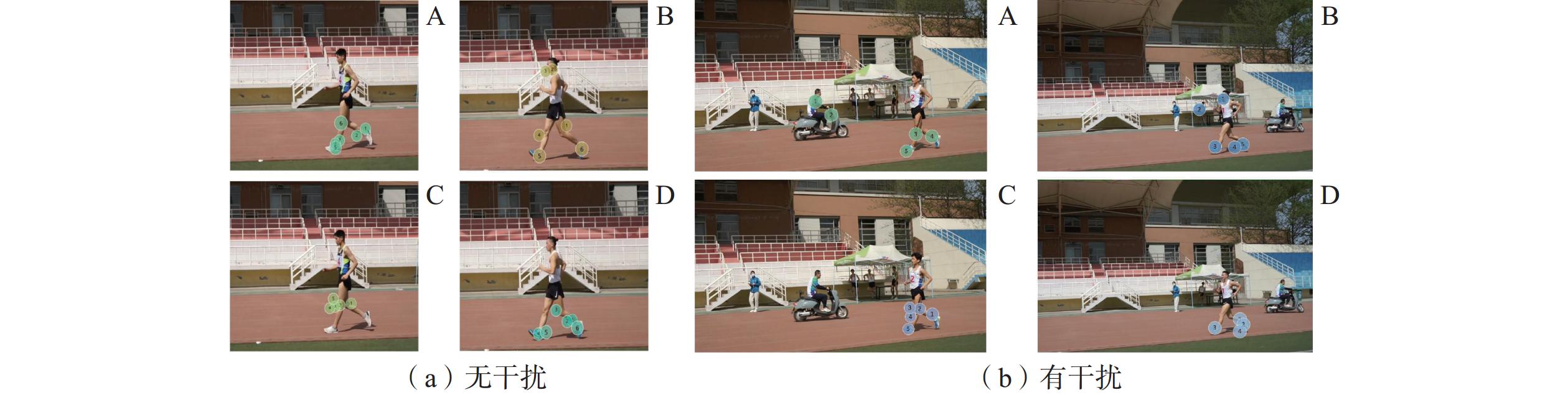
2.4.2 注视轨迹
每一个注视点之间用线连接所组成的轨迹就是注视轨迹,这是根据注视点的注视顺序相互连线形成的,各个注视点是注视轨迹的根基,其中,圆圈的大小代表在该空间中的注视时间,圆圈越大表示对该注视点的注视时间越长。通过注视轨迹(图5)可以看出:专家组注视面积小且集中,注视轨迹简洁,受犯规部位的引导,表现出自上而下目标导向的注视特征;新手组注视面积大且分散,注视点分布均无重点,注视轨迹复杂无规律。
3. 讨 论
通过比较分析发现,2种干扰条件下专家组判罚正确率均显著高于新手组,反应时均显著低于新手组,这一结果表明专家组在判罚决策上具有更好的行为绩效能力。已有研究[14]表明,个体经验与裁判员执裁表现呈现出显著的正相关。长期执裁经历和丰富的实践经验改进了高水平竞走裁判员对特定任务的知识结构和战略信息处理,使他们在判罚决策中能迅速准确地对相关任务信息进行编码并做出应答反应。新手组由于缺乏临场经验,对相关技术的掌握还不明确,大脑中没有形成快速、完整的决策机制[15]。对比2组被试在有干扰条件和无干扰条件下的行为学指标发现,新手组在干扰条件下判罚正确率降低,反应时增加,而专家组没有差异性变化。这一结果表明,专家裁判员表现出目标导向的自上而下的视觉搜索策略,而新手组受到突然出现的干扰物的影响,产生注意力分散,从而影响判罚决策,导致决策任务中行为绩效不佳的结果[16−17]。同时对专家和新手在合理视频下的决策行为指标进行对比,结果验证了专家组在2种判罚难度下正确率和反应时指标均无显著性差异,而新手组体现出显著性差异,这说明外源性、人为给予的刺激没有影响高水平竞走裁判员的执裁表现,或者说在判断标准上,高水平竞走裁判员不会因外源刺激而改变,低水平竞走裁判员则相反。
整体眼动结果显示,专家组表现出较少的注视时间、注视次数和眼跳次数,新手组则表现出相反的结果,且新手组在干扰条件下注视时间、注视次数和眼跳次数显著高于无干扰条件,专家组则无显著性差异。这表明竞走裁判员对合理视频的识别和决策能力更强。相较于低水平竞走裁判员而言,高水平竞走裁判员在进行判罚的视觉认知过程中,长期积累的经验使他们消耗的认知资源较少,因此对视觉信息加工的速度较快,表现出较短的注视时间[18]。注视时间也反映了被试处理相关信息的数量和能力,注视时间长说明被试需要处理的相关信息较多,处理能力较低[19]。低水平竞走裁判员由于缺乏专业知识的积累,在决策时需要通过更多的注视时间来确认他们的判断,对信息的加工编码需要更多的时间,在决策时收集到的信息较为琐碎和冗余,在任务中犹豫、不果断,因此表现出较长的注视时间。且在干扰条件下,随着判罚难度的增加,对低水平竞走裁判员的认知资源提出了更高的要求,增加了他们在决策时的认知负荷,故注视时间延长。高水平竞走裁判员在判罚决策时,能够将眼前的视觉信息与大脑中储存的专项知识进行比较,注视点精准且稳定,他们采用较少的注视就能够完成对视觉信息的录入、关键信息的提取和深层信息的加工,这也与前人的研究结果[20−22]一致,运动等级越高表现出的注视次数就越少。通过对眼跳次数指标的分析发现,高水平竞走裁判员在任务中表现出较少的眼跳,他们在观察运动员有无犯规行为时,对判罚的关键信息集中程度更高,视觉搜索成本低,观察更稳定,更能抓住重点。低水平竞走裁判员理论知识和实践经验薄弱,在判罚时无法区分重点信息和非重点信息,导致在搜索模式混乱,不具有高效性,表现为眼跳次数较多。研究还发现,在干扰条件下新手组的眼跳次数明显增加,说明干扰条件对低水平竞走裁判员眼跳次数的影响较大。这也与前人研究结果一致:Theeuwes等[23]考察了新目标的眼球捕获,发现在分心物条件下,个体会产生指向分心物或者附近位置的眼跳,这说明分心物会显著干扰眼跳过程,导致捕获错误,增加了对后续目标刺激的注视时间和眼跳次数。
通过划分不同的兴趣区分析被试在观看整段视频时的眼动数据,探究不同水平裁判员在各兴趣区眼动指标的差异性及关注重点。结果显示:专家组对膝和踝的注视时间显著高于低水平竞走裁判员,而对髋和上肢的注视时间显著低于新手组;在注视次数方面,专家组在各兴趣区的注视次数均低于新手组。在干扰条件下,新手组对干扰物表现出明显的注视,因此,对髋、膝、踝、上肢的注视时间和注视次数均减少,而专家组无差异性变化。在竞走项目中,对犯规的判罚类型主要包括腾空和屈膝2种,因此,膝和踝(包括足)是决定运动员技术动作是否合理的关键部位。专家组对膝和踝2个关键兴趣区的注视时间长,注视次数少,表明专家组主要将注意资源分配在运动员的膝关节及脚踝部分,他们知道注视什么地方对完成任务能够起到关键作用,因此,通过精细的加工做出准确的判断,这个过程更多采用的是目标驱动的视觉搜索方式[24]。这也表明通过经验的积累,高水平竞走裁判员能够有选择地将注意力分配给与任务相关的区域,而忽略任务冗余区域[25]。在干扰条件下新手组对干扰物表现出较长、较多的关注,并且与无干扰条件相比,对运动员膝、踝、上肢的注视时间和对髋、膝、踝、上肢的注视次数显著减少。结果表明,新手组由于将部分注视资源集中到干扰物上,在判罚中对不相关的信息加以注意,出现注意分散,浪费了有限的注意资源,从而减少了对关键区域的注视,降低了判罚效率[26]。专家组能自动忽略干扰物的影响,集中于当前的判罚任务[27]。
为进一步说明兴趣区的眼动结果,本文呈现了注视热点和注视轨迹。通过注视热点可以看出:专家组的注视主要集中于运动员的膝和踝2个动作部位,而新手组的注视比较分散,对运动员的上下肢均有关注;当同时出现运动员和干扰物时,专家组能够将注意保持在影响判罚的动作部位区,而新手组除了对运动员的观察外,还将注意分配到干扰物上,体现出专家组注意的稳定性和目标导向性。通过对注视轨迹图的分析发现,专家组的注视点更为密集,连接紧凑,大量注视点的分配与运动员技术动作的判罚密切相关,注视点形成的图形层次分明。新手组注视轨迹较为混乱,注视点分布面积较大,无重点和规律,且在干扰条件下,注视点易落于干扰物这样影响判罚并对判罚没有意义的位置。同时,针对腾空和曲膝2种不同的犯规类型而言,不同水平的裁判员也表现出不同的注视策略,低水平竞走裁判员在执裁决策时,注视轨迹大致呈现“环”形轨迹,注视范围广,且在判断运动员犯规与否以及犯规类型方面也可能存在模棱两可的状况;而高水平竞走裁判员的注视点主要集中在踝和膝区域,注视轨迹呈“线”形轨迹,简单、针对性强,表明高水平竞走裁判员受犯规区域的引导,表现出自上而下的以目标为导向的视觉搜索策略[28]。
4. 结论、不足与展望
本文发现,高水平竞走裁判员具有较好的判罚决策能力和视觉信息加工能力,在执裁过程中的视觉搜索更简洁、高效,抗场外干扰能力强,体现出自上而下的加工特点,表现出专家认知优势。这种优势是通过长期积累的实践经验建立起的快速应答的思维程序[29]。本文旨在根据高水平竞走裁判员高效的视觉注视模式,设计更为细化的竞走裁判员培养计划,为新手裁判员的预备选拔、临场执裁及赛后分析提供一个可借鉴的途径,从而提高竞走裁判员判罚的行为绩效。研究在实验材料上虽模拟了执裁场景,但与现实场景还存在一定差异,未来可设计现实场景的实验环境。此外,本文从行为学角度和眼动特征方面归纳总结了不同水平竞走裁判员在执裁过程中的视觉搜索特征,对内部机制的解释仍缺乏科学论证,未来可结合ERP、fNIRS等技术从脑机制方面探寻竞走裁判员判罚决策过程中的大脑神经机制。
作者贡献声明:刘阳:论证论文选题,撰写论文;作者贡献声明:支慧晶:分析数据;作者贡献声明:吴林珍:制作实验材料;作者贡献声明:王敏:收集、分析资料;作者贡献声明:翟琳:论证论文选题,修改论文。 -
表 1 2组被试在有/无干扰条件下执裁时的行为学结果
Table 1 Behavioral results of the two groups in the presence/absence of interference
组别 正确率/% 反应时/s 无干扰 有干扰 无干扰 有干扰 专家组 0.74±0.08 0.71±0.05 5.61±0.29 5.68±0.14 新手组 0.51±0.08 0.41±0.09 6.40±0.35 6.83±0.41 表 2 2组被试行为学数据的方差分析结果
Table 2 ANOVA results for behavioral data of the two groups
变异来源 正确率/% 反应时/s SS df MS F P ηp2 SS df MS F P ηp2 组间 组别 0.564 1 0.564 145.491 <0.001 0.82 7.456 1 7.456 150.941 <0.001 0.83 难度 0.069 1 0.069 13.385 0.001 0.30 0.975 1 0.975 8.166 0.008 0.21 组别×难度 0.024 1 0.024 4.688 0.038 0.13 0.512 1 0.512 4.289 0.047 0.12 组内 0.159 29 0.005 3.701 29 0.128 总变异 0.816 32 12.644 32 表 3 2组被试在有/无干扰条件下执裁时的眼动结果
Table 3 Eye movement results of the two groups in the presence/absence of interference
难度 组别 注视时间/s 注视数/次 眼跳数/次 无干扰 专家组 5.21±0.11 19.38±0.51 19.93±1.95 新手组 6.10±0.16 25.31±1.80 26.40±1.61 有干扰 专家组 5.31±0.12 19.94±0.75 21.50±1.45 新手组 6.39±0.25 27.70±1.11 31.16±3.11 表 4 对2种判罚难度的方差分析结果
Table 4 List of ANOVA results for the two penalty difficulties
变异来源 注视时间/s 注视数/次 眼跳数/次 SS df MS F P ηp2 SS df MS F P ηp2 SS df MS F P ηp2 组间 组别 7.612 1 7.612 327.935 <0.001 0.91 369.574 1 369.574 304.212 <0.001 0.91 512.189 1 512.189 242.506 <0.001 0.89 难度 0.632 1 0.632 35.827 <0.001 0.54 34.101 1 34.101 53.599 <0.001 0.63 157.895 1 157.895 157.895 <0.001 0.48 组别×难度 0.151 1 0.151 8.571 0.006 0.22 13.147 1 13.147 20.663 <0.001 0.40 40.189 1 40.189 7.193 0.012 0.19 组内 0.547 29 0.018 19.723 29 0.680 173.199 29 5.972 总变异 8.942 32 436.545 32 883.472 32 表 5 2组被试在有/无干扰条件下执裁时对各AOI注视时间
Table 5 Results of the fixation time of each AOI when the two groups were performing in the presence/absence of interference
s 难度 组别 髋 膝 踝 上肢 干扰物 无干扰 专家组 0.88±0.12 1.74±0.10 1.70±0.09 0.82±0.16 — 新手组 1.37±0.17 1.52±0.19 1.47±0.22 1.41±0.17 — 有干扰 专家组 0.79±0.11 1.70±0.15 1.64±0.14 0.80±0.11 0.37±0.07 新手组 1.32±0.19 1.31±0.09 1.18±0.13 1.23±0.12 1.23±0.12 注:“—”代表无对应指标。 表 6 2组被试各AOI注视时间的方差分析结果
Table 6 List of ANOVA results for the fixation time in AOI for the two groups
类别 变异来源 SS df MS F P ηp2 类别 变异来源 SS df MS F P ηp2 髋 组间 膝 组间 组别 2.751 1 2.751 202.235 <0.001 0.87 组别 2.065 1 2.065 66.799 <0.001 0.68 难度 1.071 1 1.071 2.287 0.141 0.07 难度 0.762 1 0.762 16.537 <0.001 0.35 组别×难度 0.064 1 0.064 0.262 0.613 0.01 组别×难度 0.136 1 0.136 5.962 0.021 0.16 组内 1.395 29 0.048 组内 0.506 29 0.017 总变异 5.281 32 总变异 2.980 32 踝 组间 上肢 组间 组别 1.103 1 1.103 61.358 <0.001 0.66 组别 3.493 1 3.493 191.832 <0.001 0.86 难度 0.621 1 0.621 17.477 <0.001 0.36 难度 0.629 1 0.629 7.367 0.011 0.19 组别×难度 0.135 1 0.135 8.570 0.014 0.18 组别×难度 0.301 1 0.301 5.209 0.029 0.14 组内 0.899 29 0.031 组内 0.620 29 0.021 总变异 2.758 32 总变异 5.043 32 表 7 2组被试在有/无干扰条件下执裁时对各AOI注视次数
Table 7 Results of the number of AOI fixations of the two groups in the presence/absence of interference
难度 组别 髋 膝 踝 上肢 干扰物 无干扰 专家组 3.74±0.22 5.23±0.39 5.03±0.27 3.56±0.32 — 新手组 5.80±0.26 6.24±0.33 6.11±0.26 5.68±0.28 — 有干扰 专家组 3.71±0.19 5.31±0.19 5.16±0.22 3.45±0.21 1.90±0.17 新手组 5.46±0.27 5.84±0.21 5.46±0.33 5.28±0.24 5.10±0.21 注:“—”代表无对应指标。 表 8 2组被试各AOI注视次数的方差分析结果
Table 8 ANOVA results for the fixation count in each AOI for the two groups at different difficulty levels
类别 变异来源 SS df MS F P ηp2 类别 变异来源 SS df MS F P ηp2 髋 组间 膝 组间 组别 28.634 1 28.634 707.769 <0.001 0.96 组别 4.670 1 4.670 113.899 <0.001 0.79 难度 0.529 1 0.529 13.497 <0.001 0.30 难度 0.429 1 0.429 5.125 0.031 0.14 组别×难度 1.216 1 1.216 10.115 0.003 0.25 组别×难度 2.596 1 2.596 11.015 0.002 0.26 组内 1.312 29 0.045 组内 2.645 29 0.091 总变异 31.691 32 总变异 10.340 32 踝 组间 上肢 组间 组别 3.741 1 3.741 96.995 <0.001 0.76 组别 30.730 1 30.730 749.261 <0.001 0.96 难度 1.048 1 1.048 13.556 0.001 0.30 难度 1.000 1 1.000 16.803 <0.001 0.35 组别×难度 2.324 1 2.324 30.061 <0.001 0.49 组别×难度 0.321 1 0.321 5.389 0.027 0.15 组内 2.397 29 0.083 组内 1.844 29 0.063 总变异 9.510 32 总变异 33.985 32 -
[1] 董取胜,柯勇. 运动竞赛中裁判判罚决策的研究述评[J]. 体育学刊,2017,24(6):132-137 [2] 阮浩轩. 不同水平篮球裁判员在执裁过程中的眼动研究[D]. 天津:天津体育学院,2015:1 [3] GHASEMI A,MOMENI M,REZAEE M,et al. The difference in visual skills between expert versus novice soccer referees[J]. Journal of Human Kinetics,2009,22(2009):15-20 doi: 10.2478/v10078-009-0018-1
[4] 刘悦. 伦敦田径世锦赛女子20公里竞走前8名运动员竞技特征分析[J]. 山东体育科技,2018,40(1):44-47 [5] 王万慧敏. 专家—新手网球裁判执裁过程中直觉性决策的ERP研究[D]. 成都:成都体育学院,2018:15 [6] NEVILL A M,BALMER N J,MARK WILLIAMS A. The influence of crowd noise and experience upon refereeing decisions in football[J]. Psychology of Sport and Exercise,2002,3(4):261-272 doi: 10.1016/S1469-0292(01)00033-4
[7] 王天阳,朱从庆. 不同等级篮球裁判员多目标视觉追踪实证研究[J]. 天津体育学院学报,2020,35(6):703-707 [8] WILLIAMS M,DAVIDS K. Declarative knowledge in sport:A by-product of experience or a characteristic of expertise?[J]. Journal of Sport and Exercise Psychology,1995,17(3):259-275 doi: 10.1123/jsep.17.3.259
[9] BABADI AGHAKHANPOUR N,ABDOLI B,FARSI A,et al. Comparison of visual search behavior and decision-making accuracy in expert and novice fencing referees[J]. Optometry and Vision Science,2021,98(7):783-788 doi: 10.1097/OPX.0000000000001726
[10] 王福兴,侯秀娟,段朝辉,等. 中国象棋经验棋手与新手的知觉差异:来自眼动的证据[J]. 心理学报,2016,48(5):457-471 [11] CATTEEUW P,HELSEN W,GILIS B,et al. Visual scan patterns and decision-making skills of expert assistant referees in offside situations[J]. Journal of Sport and Exercise Psychology,2009,31(6):786-797 doi: 10.1123/jsep.31.6.786
[12] WILLIAMS A M,DAVIDS K,BURWITZ L,et al. Visual search strategies in experienced and inexperienced soccer players[J]. Research Quarterly for Exercise and Sport,1994,65(2):127-135 doi: 10.1080/02701367.1994.10607607
[13] 马杰. 我国青少年竞走运动员不同速度区间运动技术标准研究[D]. 北京:北京体育大学,2018:61 [14] PIZZERA A,RAAB M. Perceptual judgments of sports officials are influenced by their motor and visual experience[J]. Journal of Applied Sport Psychology,2012,24(1):59-72 doi: 10.1080/10413200.2011.608412
[15] SPITZ J,PUT K,WAGEMANS J,et al. Visual search behaviors of association football referees during assessment of foul play situations[J]. Cognitive Research:Principles and Implications,2016,1(1):12 doi: 10.1186/s41235-016-0013-8
[16] SCHMIEDEK F,OBERAUER K,WILHELM O,et al. Individual differences in components of reaction time distributions and their relations to working memory and intelligence[J]. Journal of Experimental Psychology:General,2007,136(3):414-429 doi: 10.1037/0096-3445.136.3.414
[17] UNSWORTH N,ROBISON M K. Pupillary correlates of lapses of sustained attention[J]. Cognitive,Affective,& Behavioral Neuroscience,2016,16(4):601-615
[18] 漆昌柱,贺梦阳,王浩宇. 运动专长的记忆痕迹:基于注意竞争优势的脑机制研究[J]. 武汉体育学院学报,2021,55(2):68-75 [19] GIBSON J J,GIBSON E J. Perceptual learning; differentiation or enrichment?[J]. Psychological Review,1955,62(1):32-41 doi: 10.1037/h0048826
[20] 王明辉,李建民,闫苍松. 篮球运动员运动决策准确性和速度差异性的眼动研究[J]. 北京体育大学学报,2007,30(6):774-776 [21] 肖坤鹏,孙建华,张铁民. 发球方式对排球运动员视觉搜索特征影响的研究[J]. 天津体育学院学报,2016,31(4):351-357 [22] 肖坤鹏,孙建华. 排球运动员接发球过程中视觉搜索特征的研究[J]. 体育科学,2012,32(9):67-74 [23] THEEUWES J,KRAMER A,HAHN S,et al. Our eyes do not always go where we want them to go:Capture of the eyes by new objects[J]. Psychological Science,1998,9(5):379-385 doi: 10.1111/1467-9280.00071
[24] RAAB M,JOHNSON J G. Expertise-based differences in search and option-generation strategies[J]. Journal of Experimental Psychology. Applied,2007,13(3):158-170 doi: 10.1037/1076-898X.13.3.158
[25] HAIDER H,FRENSCH P A. Eye movement during skill acquisition:More evidence for the information-reduction hypothesis[J]. Journal of Experimental Psychology:Learning,Memory,and Cognition,1999,25(1):172-190
[26] 孙延林,白学军. 运动情境中运动员的视觉搜索行为[J]. 天津体育学院学报,2009,24(2):111-115 [27] CRESPI S,ROBINO C,SILVA O,et al. Spotting expertise in the eyes:Billiards knowledge as revealed by gaze shifts in a dynamic visual prediction task[J]. Journal of Vision,2012,12(11):30 doi: 10.1167/12.11.30
[28] 解缤,于新彦. 不同水平羽毛球运动员后场球落点判断过程直觉性决策的眼动特征分析[J]. 西安体育学院学报,2014,31(6):735-740 [29] 金鹏,郭洪波,蔺铎,等. 篮球运动员动态视觉注意特征与运动表现的相关性研究[J]. 首都体育学院学报,2020,32(6):555-561




 下载:
下载: