Influence of Proprioceptive Training on the Balance Ability, Lower Limb Strength and Map Reading Skills of Orienteers
-
摘要:目的
探讨本体感觉训练对定向运动员平衡能力、下肢肌肉力量以及识图能力的影响程度,为后期的专项训练实践提供科学依据。
方法将45名男子定向运动员随机分为实验组和对照组,实验组进行12周本体感觉训练和专项体能训练,对照组进行12周专项体能训练和基础耐力训练。利用表面肌电仪器采集运动员模拟上、下坡专项训练的下肢主要肌肉贡献率特征;采用平衡测试仪、等速肌力测试分析系统、秒表等进行平衡能力、肌力和现场识别地图能力的测试,对训练前后不同识图能力进行比较,分析运动员在视觉、认知、本体感觉等多因素干扰下的静态和动态平衡能力、下肢力量和专项识图能力。
结果12周干预后:①在静态平衡条件下,2组运动员在压力中心(COP)的X轴(左右方向)与Y轴(前后方向)的移动距离、移动速度上,实验组均显著优于对照组(P<0.05);②在动态平衡条件下,2组运动员在动作完成时间、X轴与Y轴的移动距离上,实验组均显著低于对照组(P<0.05);③2组运动员的最大力量、维持最大值的时间、平均力量、最大功率和平均功率均有不同程度的提高,实验组显著高于对照组(P<0.05);④实验组的动态识图能力指标显著高于对照组(P<0.05)。
结论12周的本体感觉训练可有效提升定向运动员的静态和动态平衡能力,增加下肢屈伸肌群肌力,改善运动员的姿势控制能力,提高定向运动员在复杂环境中的专项技术能力,本体感觉训练和专项识图技术训练方法切实可行。
Abstract:ObjectiveTo explore the influence of proprioceptive training on the balance ability, lower limb strength and map reading skills of orienteering athletes, providing a scientific basis for future training practice.
Methods45 male orienteers were randomly divided into experimental group and control group. The experimental group received 12 weeks of proprioceptive training and special physical training, and the control group received 12 weeks of special physical training and basic endurance training. Surface electromyography instrument was used to collect the contribution rate characteristics of the main muscles of the athletes' lower limbs in simulated uphill and downhill special training. Balance tester, isokinetic muscle strength test and analysis system, stopwatch, etc, were used to test athletes' balance ability, muscle strength and field map recognition ability. Different map reading abilities before and after training were compared, and static and dynamic balance ability, lower limb strength and special map reading ability under the interference of multiple factors such as vision, cognition and proprioception were analyzed.
ResultsAfter 12 weeks of intervention: ① Under static equilibrium condition, the movement distance and speed of COP in the experimental group were significantly better than those in the control group (P<0.05); ② Under the dynamic balance condition, the movement completion time and the movement distance of X-axis and Y-axis in the experimental group were significantly lower than those in the control group (P<0.05); ③ The maximum strength, maximum maintenance time, average strength, maximum power and average power of the two groups were increased in different degrees, and the experimental group was significantly higher than the control group (P<0.05); ④ The index of dynamic map reading ability in the experimental group was significantly higher than that in the control group (P<0.05).
Conclusion12-week proprioceptive training can effectively improve the static and dynamic balance ability of orienteers, increase their muscle strength of lower limb flexor and extensor, and improve their postural control ability and specialized technical ability in complex environments. Proprioceptive training and specialized image recognition technology training methods seem feasible.
-
Keywords:
- proprioception /
- orienteering /
- special skill /
- balance ability /
- muscle strength
-
定向运动活动场地以野外山地、森林公园、城市公园以及校园为主,适合多种年龄人群参与,是一项真正让人们走向户外、人人皆可参与的运动[1]。其项目开展已有100多年历史,在我国也有近50年发展史。定向运动并不是单一的跑步运动,还融合了体力竞技与智力博弈,需要参与者在奔跑中动脑、在探索中思考、在思考中前行。定向运动在我国展现出广阔的发展前景,其独特的魅力横跨群众性体育与专业性竞技两大领域,不仅吸引了广泛的参与者群体,还成为2025年第十五届全国运动会、2025年成都世界运动会及世界军人运动会等国内外顶尖综合性体育赛事的参赛项目。随着定向运动竞赛的激烈程度不断增加,对运动员的专项技术及综合运动能力提出了更为严格的要求,促进了该运动领域的专业化与高水平化发展。其中,动态环境下的快速准确读图、识图、获取关键地形特征物、路线选择与保持正确行进方向技术,以及野外山地精确辨向、快速执行路线与快速奔跑能力是定向运动的核心技能。这些技能不仅要求运动员空间方位辨析和精确导航能力强[2],而且对运动员的肢体感觉、平衡能力以及下肢力量有特殊要求,尤其是山地野外环境下的动态平衡能力和下肢力量是确保运动员快速识图、奔跑的关键。在备战2025年全国运动会的重要时刻,结合运动训练实践,围绕定向运动员动态平衡能力、下肢肌肉力量及动态识图专项技能提升积极开展研究,提升运动员整体专项技术水平,提高比赛竞争力是亟待解决的关键问题。
近年来,本体感觉被应用于不同人群的研究[3−5]并引起广泛关注。在运动实践中,本体感觉系统的主要目的是维持姿势平衡和控制肢体肌肉协调运动[6−7],人体本体感觉训练注重身体稳定和不稳定之间的灵活转换,感受器需要根据人体外在变化及时进行反馈调节,从而维持人体自身的姿势稳定性和方向性。本体感觉训练可有效提升运动员的平衡控制能力和下肢肌肉力量,在冰雪项目中已有应用并取得了良好效果[3,8]。李旭鸿等[9]的研究表明,长期太极拳锻炼可降低老年人群下肢骨骼肌力量流失,并进一步指出不稳定的支撑面训练可显著提升老年人的肌肉力量和平衡能力。胡潇月[10]通过对老年人的8周复合足部机械感受器刺激训练发现,本体感觉训练不仅可提升老年人抵抗外界干扰的能力,还可促进踝关节肌肉力量的提升,最终可有效改善老年人的姿势控制能力。Gidu等 [11]通过对青少年足球运动员进行12周的干预研究发现,本体感觉训练可有效提升运动员的平衡、力量、反应能力和运球技术。Grushko等[12]针对上肢肱桡肌的本体感觉反馈与肌肉活动关系提出了人体神经肌肉的控制方法理论,并深入探讨本体感觉训练对改善肌肉力量的内在关系。然而,目前针对定向运动项目在复杂环境下的本体感觉训练、动态识图能力及平衡能力等方面的研究相对较少,其专项训练方法与效果评估仍处于探索阶段。因此,围绕不同环境、状态下的肢体感觉和身体平衡能力训练,探索本体感觉训练的方法与手段,对提升运动员在快速奔跑状态下的精准识图、读图能力和效率具有重要意义。
综上所述,本文通过对定向运动员施以本体感觉训练,探讨本体感觉训练对运动员的平衡能力与下肢肌肉力量的影响程度,分析运动员在多因素干扰下本体感觉训练与专项技能的关系,为进行科学的定向运动训练提供参考依据,持续提升定向运动的竞技水平。
1. 研究对象和方法
1.1 研究对象
选取河南省省级、校级定向男子运动队运动员为受试者,随机分为实验组和对照组。实验前均向受试者介绍实验方案、要求和流程,并征得受试者同意。实验期间对受试者进行集中训练,训练环境、训练负荷一致,运动员饮食、休息基本一致。受试者在训练和测试期间无运动损伤,整体竞技状态良好。受试者基本情况如表1所示。
表 1 受试者基本情况Table 1. Basic information of subjects类别 年龄/岁 身高/cm 体重/kg 训练年限/年 实验组(n=23) 20.39±2.27 177.02±6.11 68.31±3.37 3.07±1.87 对照组(n=22) 20.11±2.53 177.39±6.62 68.15±5.86 3.11±1.61 注:训练年限以第1次参与定向活动为时间节点进行统计。 1.2 研究方法
1.2.1 下肢表面肌电测试
根据研究目的开展双侧下肢主要肌肉表面肌电测试,采样频率为
1000 Hz。两电极贴附于目标肌肉的肌腹处,方向与肌纤维的走向平行,电极间的距离为2 cm。贴电极前用砂纸轻轻打磨皮肤,去掉角质皮和体毛,再用酒精棉球清除油脂,以减小电极间阻抗。运动员使用滑板车模拟上坡和下坡2个动作,采集蹬伸过程中左、右侧股四头肌内侧头、股二头肌长头、腓肠肌内侧头、胫骨前肌共八块肌肉的表面肌电数据[13];同时,在BOSU半圆平衡球上进行平衡能力评估。数据处理采用Megwin 2.5软件,分别进行全波整流、提取包络,采集运动员身体前倾和后仰2个模仿动作的积分肌电(IEMG),提取动作开始前100 ms和结束后100 ms。平衡能力评估采取主观评价,观察运动员跳上BOSU半圆平衡球的稳定性,并采取针对性训练。
肌肉贡献率是指每块肌肉的积分肌电值占所有肌肉的比例,该数值越高表明该肌肉对完成动作的影响越大。选取动作阶段从运动员的膝关节和髋关节处于屈曲角度最小(T1时刻)开始,到双下肢直立,髋关节和膝关节处于完全伸展状态(T2时刻)结束。
1.2.2 本体感觉的训练方法
依据运动员下肢主要肌肉积分肌电贡献率结果,采用BOSU半圆平衡球对运动员进行各种训练,其目的是通过增强机体功能和恢复正常的神经肌肉反馈环路改善本体感觉控制能力[14]。Wester等[15]的研究指出,平衡训练可以提高人体下肢肌力和整体协调性,并减少踝关节复发性扭伤的发生。支撑面不稳会导致感觉信息只能依靠视觉和前庭的输入,从而导致人体稳定性下降。研究[16]进一步指出,本体感觉对姿势控制的影响大于视觉和前庭,且本体感觉训练对运动员的平衡、力量、灵敏有较大影响。因此,本文采用BOSU半圆平衡球进行长期干扰本体感觉训练,增强运动员的抵抗干扰能力,提升其平衡能力。
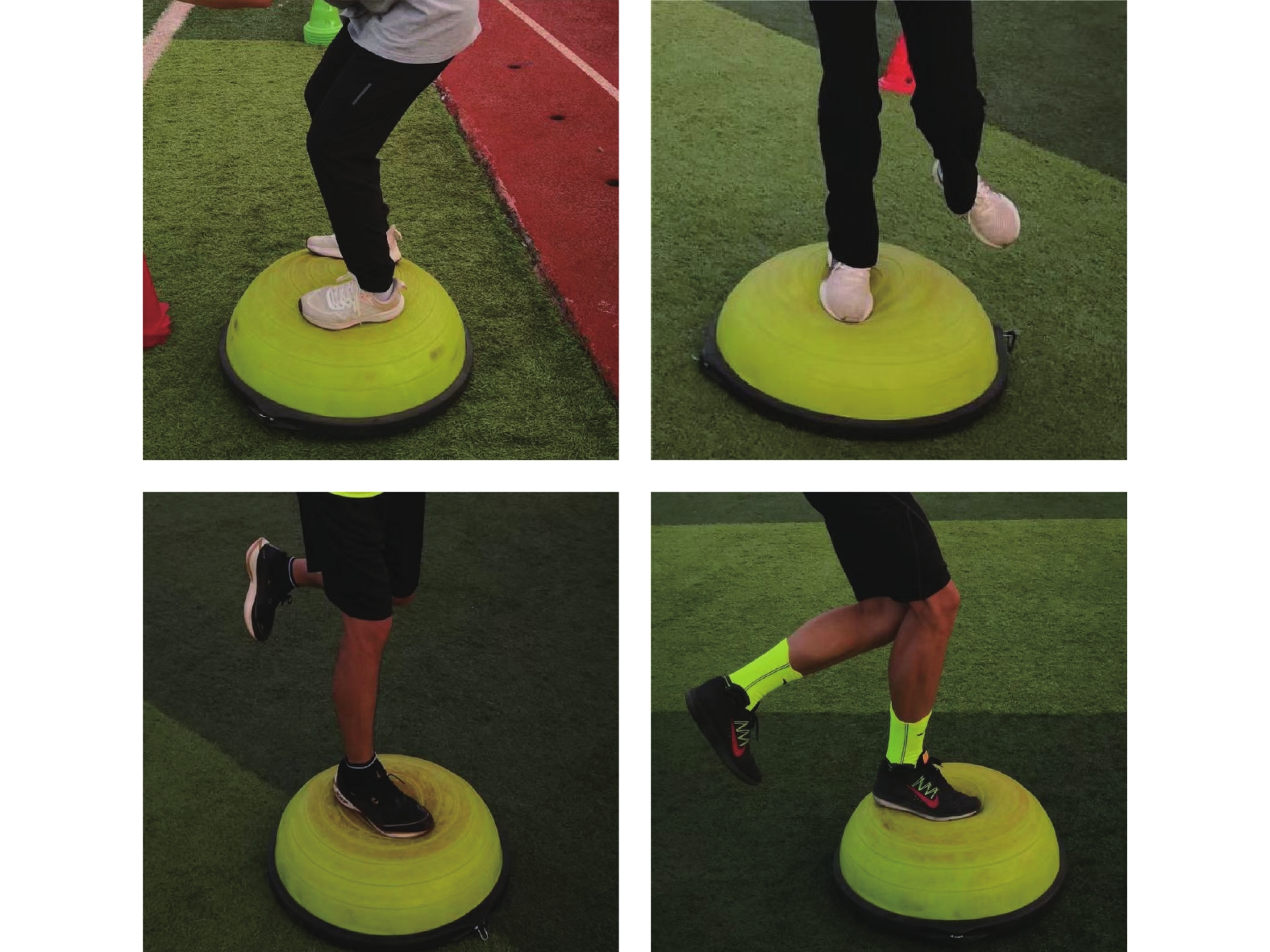
采取分组训练模式,实验组进行本体感觉训练,对照组进行一般耐力训练。实验组运动员在BOSU半圆平衡球上进行前倾和后仰的技术动作模仿练习后,对运动员进行本体感觉训练(图1),具体训练内容包括:①运动员双脚平行/单脚依次交替站在BOSU半圆平衡球一侧上,身体保持上坡姿势,沿着球面移动,在练习过程中,脚不能接触地面,如接触地面或从球面掉下,则需重复前面的练习。②运动员双脚平行/单脚依次交替站在BOSU半圆平衡球一侧上,身体保持下坡姿势,沿着球面移动,在练习过程中,脚不能接触地面。③运动员双脚平行/单脚依次交替站在BOSU半圆平衡球一侧上,身体保持稳定姿势,沿着球面移动,在练习过程中,脚不能接触地面。④股前、股后肌群训练:运动员双脚/单脚依次交替站在BOSU半圆平衡球上,双脚分开与肩同宽,背部挺直,在深吸气的同时慢慢屈膝下蹲,蹲至大腿与地面平行(单脚时蹲至膝关节呈120°即可)时保持1~2 s,后蹬腿伸膝至还原站立。⑤胫前肌训练:运动员双脚/单脚依次交替站在BOSU半圆平衡球上,双脚稍分开,背部挺直,在深吸气的同时双腿慢慢做反向提踵练习,单脚练习要求同上。上述内容共训练12周,每周训练3次,共60 min;每次训练①~⑤项内容循环练习,每个练习内容控制在1 min左右,每个练习之间休息1~2 min,每完成1个循环为1组,共6组;①~③项内容在保持稳定的前提下逐步提高移动速度。
专项体能训练主要包括下肢和躯干的肌肉力量以及核心稳定性训练。具体内容包括:①直立提腿。笔直单腿站立,作用腿向上屈膝提腿,作用腿小腿放松,大腿发力,每组训练30个,以左右腿依次分别完成为1组,每组用时1 min。②平板支撑。运动员俯卧,双肘支撑在地面上,肩膀和肘关节垂直于地面,双脚踩地,每组训练1~2 min。③单腿半蹲。单脚站立,站立脚立脚踝,上半身保持笔直,作用腿屈膝下蹲,运动员能感觉到小腿肌肉与膝关节上部肌肉在发力,每组训练20个,左右腿依次分别完成为1组,每组用时1 min。④深蹲练习。运动员身体直立,两眼平视前方,两脚与肩同宽,要求运动员慢慢屈膝下蹲至大腿平行于地面或稍低于膝,静止1~2 s后蹬腿伸膝至还原状态,每组训练15~20个。⑤收腹跳。双脚起跳,双腿屈膝收至腹部,轻落地,身体不要摇摆,连续起跳,每组20个。上述内容共训练12周,每周训练3次,每次60 min;每个练习内容控制在要求时间内完成,每完成1个循环为1组,每组之间休息1~2 min,共6组。
1.2.3 平衡能力测试
为更好地验证BOSU半圆平衡球本体感觉训练效果,运用芬兰产Good Balance平衡测试系统,平衡测试包括静态平衡测试和动态平衡测试。在训练前及训练12周后测定运动员左右腿单脚站立30 s的静态平衡能力[3],以及双腿的动态平衡能力。
静态平衡测试要求受试者站立于平衡仪上并保持稳定姿势,测定其在睁眼、闭眼及外界视动光刺激时人体压力中心(center of pressure,COP)的稳定状态。通过分析 COP 移动路径的总长度、面积、左右向和前后向的重心位移平均速度等参数,全面评估运动员的静态平衡能力[9]。
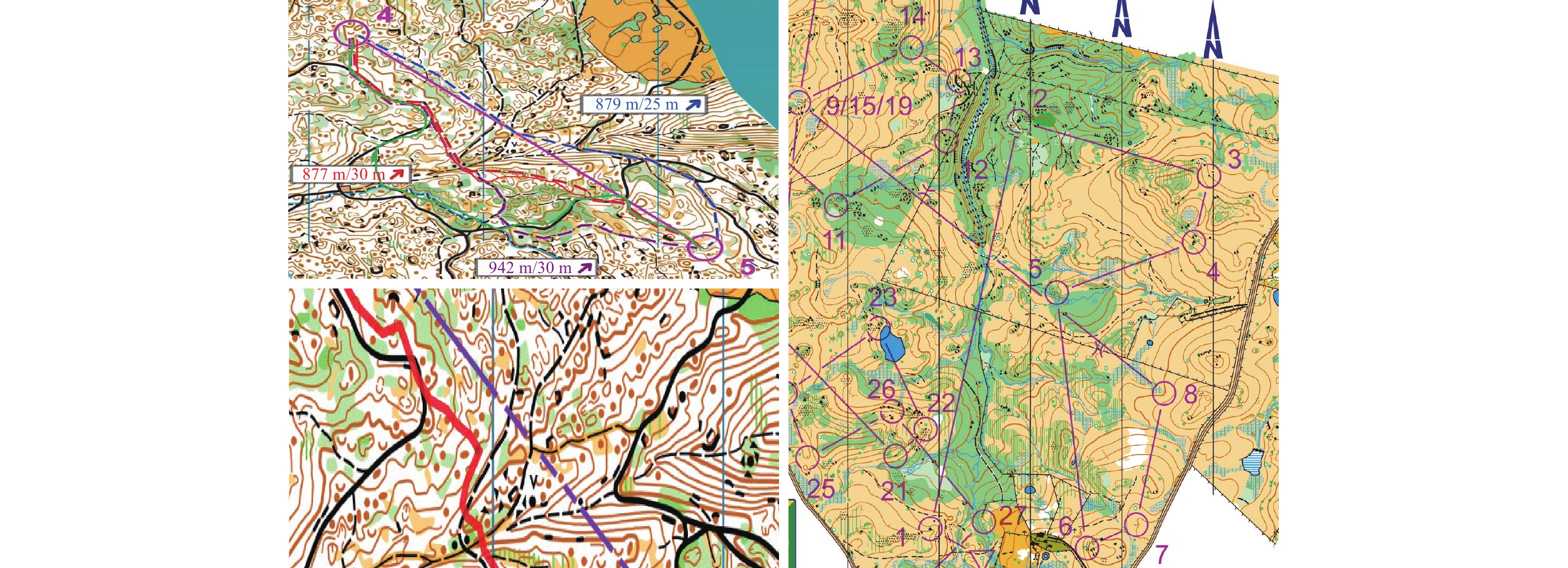
动态平衡测试要求受试者以躯体运动反应跟踪出现在显示器上的视觉目标,在受试者无意识状态下,或显示器及其支架突然摇动时,在支撑面移动,按照前、后、左、右、左前、右前、左后、右后8个点位移动[3],测试上述情况下受试者在规定时间内控制人体重心的完成情况,即最短的有效距离(图2),以了解机体感觉和运动器官对外界环境变化的反应能力及大脑感知觉的综合能力等。
静态平衡测试指标包括:①X轴方向移动距离。分析时间段内测试者COP在X方向移动的总距离(左右方向移动距离)。②Y轴方向移动距离。分析时间段内测试者COP在Y方向移动的总距离(前后方向移动距离)。③X轴方向平均速度。分析时间段内测试者COP在X方向的移动速度(左右方向移动速度)。④Y轴方向平均速度。分析时间段内测试者COP在Y方向的移动速度(前后方向移动速度)。⑤区域半径。分析时间段内测试者COP在不同方向移动区域的平均半径[17]。
动态平衡测试指标包括:①平衡时间。各种姿势方向间在转换运动时能重新获得稳定状态的时间。②X轴方向移动距离。分析时间段内测试者COP在X方向移动的总距离(左右方向移动距离)。③Y轴方向移动距离。分析时间段内测试者COP在Y方向移动的总距离(前后方向移动距离)[16]。
1.2.4 下肢联动肌肉力量特征测试
运用美国产Ariel等速肌力测试动力学分析系统,在实验前后对2组运动员的肩部施加载荷,让运动员在屈膝位(自我感觉最适宜发力的位置)开始蹬伸,对运动员蹬伸过程中下肢肌肉整体所表现出的力量及做功情况进行评测,并对发力过程中下肢整体肌肉的最大力量、维持最大值的时间、平均力量、最大功率、平均功率进行记录,对运动员蹬伸过程中下肢肌肉联动蹬伸效果进行合理性评价[18]。
下肢蹬伸能力测试指标包括:①最大力量。在静力或退让性工作中,最大随意收缩抵抗阻力所表现的最高力值[19]。②维持最大值的时间。将力量值维持在90%最大力量的时间。③平均力量。在完成蹬伸时最大力量与所用时间的比值。④最大功率。单位时间内做功的最大变化量。⑤平均功率。单位时间内的功率。
1.2.5 专项技术的训练方法
定向运动专项技术训练主要围绕运动员在不同环境下的识图技术能力进行,对运动员分别在平地、BOSU半圆平衡球以及跑步机上进行识图、读图以及路线选择与规划技术的训练,实验包括静态/走动/跑动状态+识图信息提取与记忆+地图路线规划,实验任务揭示了不同水平运动员在定向地图专项识图、读图能力上的差异及在不同环境下的差异,识图记忆任务和读图路线规划任务是为了进一步了解运动员对地图符号信息熟识与识别的基本能力[20],尤其是在动态下的信息获取与识别能力,从而探究制约定向运动员专项识图、读图能力的因素。
具体训练内容包括:①运动员在平地进行10 m折返跑,边跑边读图,在练习过程中,原则上不允许静止读图;②在运行的跑步机上跑步,边跑边读图,在练习过程中,原则上双手不触碰跑步机;③运动员站在BOSU半圆平衡球上,沿着球面移动,边移动边读图,在练习过程中,脚不能接触地面。上述内容共训练12次,每次训练1张地图,其中:折返跑每组训练1~2 min,组间休息2~3 min;在跑步机上跑步时逐步提高速度;每次原地识图训练为最后练习,每次统计完成读图、识图以及路线选择的时间。
同时,从2个组各选取5名运动员进行跟踪分析,在训练前及第4次、第8次、第12次训练后进行对比分析。静态识图、动态识图、静态线路规划使用图3训练,动态线路规划使用图4训练,其中,训练前和第8次训练后用图为同一类型地图,第4次和第12次训练后用图为同一类型地图。实验训练地图主要有2类:一是郊区田园、公园场景地图,比例尺为 1∶
7500 ,地图信息多为建筑物、路、绿地、田地等地物特征;二是野外、山地场景地图,比例尺为 1∶10000 ,地图信息多为山体等地貌特征[21]。训练对比对象为实验组和对照组运动员选择的线路,并辅以运动员实际GPS运动轨迹进行对比,分析线路规划的科学性和合理性。1.2.6 数理统计法
应用SPSS 17.0软件进行数据分析,根据研究需要,使用 Shapiro-Wilk 检验验证数据的正态分布情况。若变量呈现正态分布,则组间采用独立样本t检验,组内采用配对样本t检验,不同时间点采用单因素重复测量方差分析(one-way repeated measures ANOVA)。若重复测量方差分析或 Friedman 检验有显著结果,则使用 Bonferroni事后两两比较或配对样本 t 检验进行事后两两比较。效应量以η2表示,其数值越大,效应量越高,根据Cohen效应量标准,η2为>0.4、>0.25、>0.1时,分别对应高、中和低效应。设定检验水准为α=0.05,P<0.05为有显著性差异,所有结果以
$ \overline{X} $ ±SD表示。2. 研究结果
2.1 下肢主要肌肉贡献率特征
由表2可知:在上坡阶段,下肢主要肌群股四头肌和腓肠肌贡献率较大;在下坡阶段,胫骨前肌和股二头肌贡献率较大。在上坡阶段,股四头肌内侧头显著大于股二头肌长头,腓肠肌内侧头显著大于胫骨前肌;在下坡阶段,胫骨前肌贡献率达(43.35±4.87)%,并显著大于腓肠肌。下坡阶段胫骨前肌的贡献率显著高于上坡阶段,上坡阶段腓肠肌贡献率显著高于下坡阶段,股四头肌贡献率上坡阶段显著高于下坡阶段。
表 2 下肢蹬伸阶段的各肌肉贡献率结果Table 2. The contribution rate of each muscle in the lower extremity push and stretch stage% 动作名称 股四头肌内侧头 股二头肌长头 腓肠肌内侧头 胫骨前肌 上坡 31.73±3.02 25.86±2.45**## 30.25±2.28 12.15±1.26**## 下坡 10.15±1.10## 25.44±2.36** 20.86±2.56## 43.35±4.87**## 注:**表示膝、踝关节屈伸肌肉贡献率相比,P<0.01;##表示上下坡肌肉贡献率相比,P<0.01。 2.2 运动员平衡能力特征
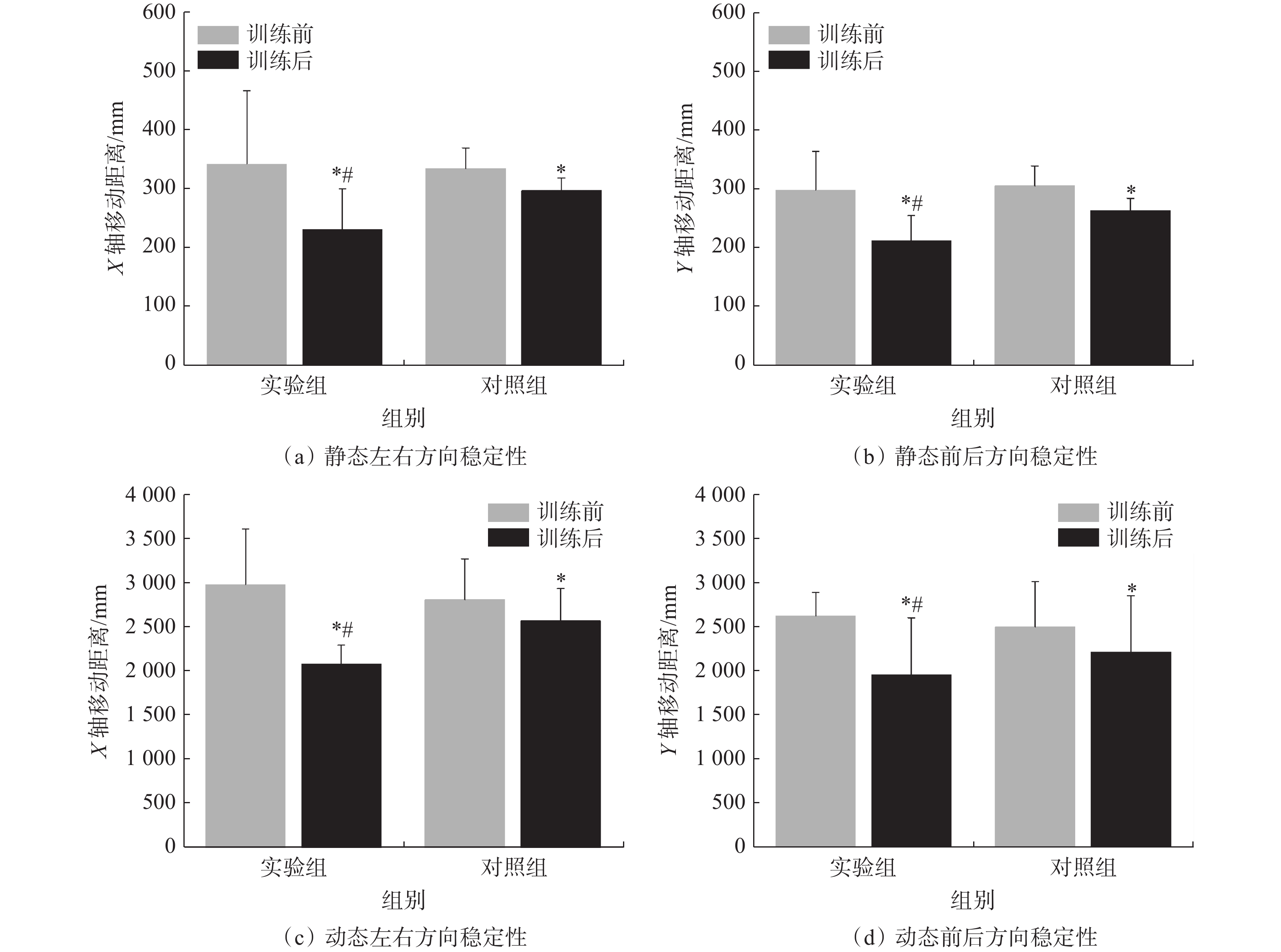
运动员进行12周本体感觉训练后,左右腿平衡能力在前后、左右方向均有不同程度的显著提高,前后方向移动距离也显著减小;在移动速度上,左右和前后方向均显著减小,前后方向移动速度具有非常显著的差异。训练前2组运动员的X轴与Y轴的移动距离、X轴与Y轴的平均速度及区域半径的差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。经12周训练后,2组运动员的X轴与Y轴的移动距离、X轴与Y轴的平均速度、区域半径、稳定时间均有不同程度的提高,且实验组显著高于对照组(P<0.05),表明在进行本体感觉训练后,运动员的静态、动态平衡能力在前后、左右方向均有不同程度的提高,结果见表3、表4和图5。同时,从实验现场观察和表4数据统计看,实验组运动员平衡能力提升更为明显。
表 3 训练前后静态平衡能力测试结果Table 3. Test results of static balance ability before and after training评估指标 实验组 对照组 训练前 训练后 训练前 训练后 X轴移动距离/mm 332.41±134.15 243.32±56.65*# 328.39±36.32 292.52±21.36* Y轴移动距离/mm 289.74±45.56 213.24±46.31*# 310.34±33.52 265.12±21.85* X轴平均速度/(mm·s−1) 11.75±6.31 8.36±1.66* 9.05±2.19 6.36±1.59* Y轴平均速度/(mm·s−1) 10.57±3.35 7.78±1.93* 7.88±1.87 6.23±1.67* 区域半径/mm 16.23±4.26 12.17±2.64* 15.82±5.46 11.25±2.38* 注:表3中数据为左右腿平均数据;*表示与训练前比较,P<0.05;#表示与对照组比较,P<0.05。 表 4 训练前后动态平衡能力测试结果Table 4. Test results of dynamic balance ability before and after training评估指标 实验组 对照组 训练前 训练后 训练前 训练后 稳定时间/s 58.56±8.31 35.12±7.58*# 54.22±4.32 44.26±5.16* X轴移动距离/mm 3086.65 ±682.122183.32 ±213.71*#2832.56 ±425.362552.52 ±316.25*Y轴移动距离/mm 2826.56 ±745.212061.58 ±863.25*#2521.58 ±501.712289.37 ±621.12*注:*表示与训练前比较,P<0.05;#表示与对照组比较,P<0.05。 2.3 下肢联动肌肉力量特征
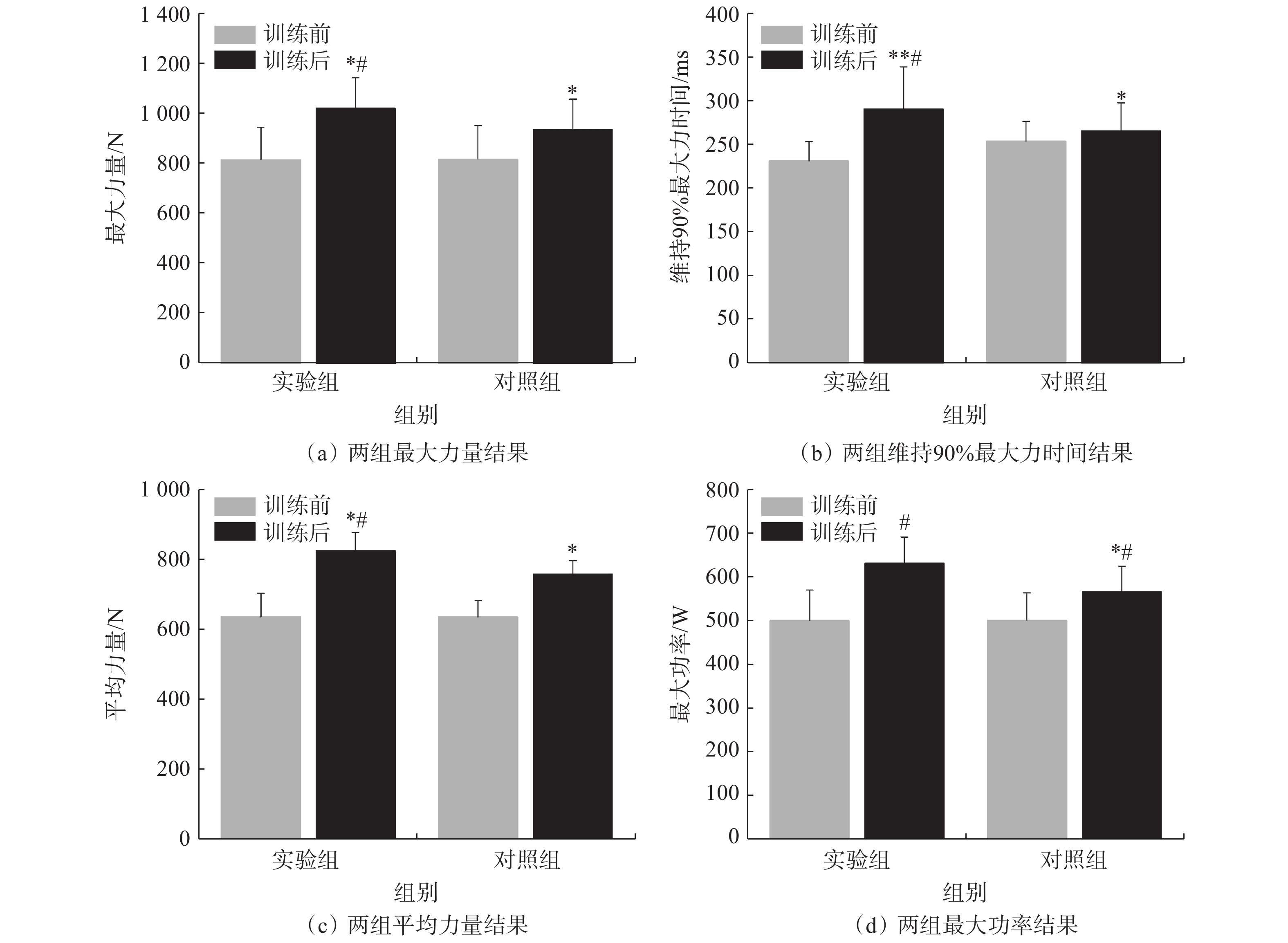
训练前2组运动员的最大力量、维持90%最大力的时间、平均力量、最大功率和平均功率的差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05),经12周训练后,2组运动员各项指标均有不同程度的提高,且实验组显著高于对照组(P<0.05),表明使用平衡训练器训练后,运动员对下肢各块肌肉协调用力的能力明显提高,髋膝踝联动蹬伸力量保持能力明显提高,具体结果见表5和图6。
表 5 训练前后下肢蹬伸效果测试结果Table 5. Test results of lower limb extension before and after training评估指标 实验组 对照组 训练前 训练后 训练前 训练后 最大力量/N 786.58±331.27 1020.56 ±128.62*#812.71±132.23 938.62±221.23* 维持90%最大力的时间/ms 256.26±27.32 296.62±36.56**# 251.16±21.56 268.36±32.37* 平均力量/N 633.38±65.66 828.84±51.26*# 626.79±87.85 766.89±38.83* 最大功率/W 502.82±68.38 629.85±87.68# 503.52±56.14 578.46±53.52* 平均功率/W 329.85±91.87 450.36±85.16*# 336.19±79.15 387.19±76.81* 注:*表示与训练前比较,P<0.05,**表示与训练前比较,P<0.01;#表示与对照组比较,P<0.05。 2.4 定向运动专项技术特征
重复测量方差分析显示时间的主效应显著,进行Bonferroni事后两两比较,具体结果见表6。被试人员经过训练前及第4次、第8次、第12次训练后共4轮次对比分析,训练前2组运动员的读图用时、完成任务时间均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。经第4次、第8次、第12次训练后,2组运动员的各项指标均有不同程度的提高,且实验组显著高于对照组(P<0.05);不同组别运动员在测试中差异较大,第4次和第12次训练后实验组与对照组差异明显,这是由于每次训练对比分析的地图不一样,训练前和第4次训练后为同一类型地图,第8次训练和第12次训练后为同一类型地图。这表明使用平衡训练器训练后,运动员维持平衡的能力显著提升。
表 6 训练前后专项技术训练结果Table 6. Results of special technical training before and after training评估指标 实验组 对照组 静态 动态 静态 动态 训练前 18.8±1.82 22.4±3.24 18.7±2.87 23.1±5.51 第4次训练后 13.2±1.61 15.9±5.36*# 12.9±5.56 17.9±5.26* 第8次训练后 23.7±6.31 27.6±3.56# 22.8±5.43 33.8±6.04 第12次训练后 17.8±2.37 20.3±2.63*# 18.2±9.08 30.1±7.12* 注:时间单位为s;*表示与训练前比较,P<0.05;#表示与对照组比较,P<0.05。 3. 讨 论
3.1 本体感觉训练对运动员下肢肌肉活动特征的影响
本体感觉是指本体感受器受到刺激对躯体的空间位置、姿势、运动状态和运动方向的感觉[22]。本体感觉能力是感觉关节位置和关节运动的能力[23]。本体感觉系统的主要目的是维持姿势平衡和控制肢体肌肉协调运动[6],肌肉发力的稳定性反映同一肌群在完成某一动作过程中与其他肌群的协调关系[24],如某肌群对整个动作的贡献率变化过大,导致技术动作的不稳定[25],而运动水平对后天的姿势控制和平衡能力的改变尤为重要[26]。
本文发现,定向运动员上坡阶段下肢主要肌群贡献率由高到低依次为股四头肌、腓肠肌、股二头肌和胫骨前肌,其中股四头肌和腓肠肌为主要发力肌群,这与前期研究[25]结果一致。运动员在蹬地时踝关节充分跖屈导致腓肠肌需充分发力,因此应在训练实践中增加大量腓肠肌专项训练[27]。下坡阶段主要肌肉贡献率由高到低依次为胫骨前肌、股二头肌、腓肠肌。在定向运动中,股四头肌、胫骨前肌和腓肠肌为主要发力肌肉,跑步动作中腓肠肌虽参与踝关节跖屈运动,但其主要作用不仅是直接产生推动力,还作为稳定器和辅助肌肉与胫骨前肌协同工作,以维持足部稳定性和姿势。因此,胫骨前肌力量不足可导致运动员在跑动过程中足部稳定性和姿势控制能力的下降,从而影响其整体运动表现。此外,因定向运动场地地面高低起伏大且运动员处于高速奔跑状态,为维持支撑侧踝关节的稳定[27],胫骨前肌需要剧烈收缩,若关节不稳将导致肌肉力量输出能力下降。因此,在本体感觉训练中,需重视胫骨前肌力量的发展,即加强非平衡状态下踝关节的稳定性练习,以及胫骨前肌力量和关节平衡能力训练。在定向运动中,为减少跑动过程中的植被干扰或路况条件影响,运动员需不断调整身体姿势,这要求髋关节在蹬伸过程中保持必要的伸展幅度,不断调动髋部肌群的收缩能力。股二头肌作为伸髋屈膝的双关节肌,对维持膝关节的稳定性具有重要作用。为此,本文在本体感觉训练方案的设计上,充分考虑股骨前后肌群的共激活现象,针对性训练股后肌群力量,并模拟不同地形上下坡动作,以提高在不平坦路面行走的稳定性,使身体在陡坡上保持稳定[28]。
本文所设计的本体感觉训练方案遵循从易到难、从单平面运动到多平面运动、从静态训练到动态训练的原则,制定多样化的本体感觉训练方案。第一阶段要求运动员在训练器上进行前后方向和左右方向的摆动练习,以重心转移、关节角度回归等练习为主,目的是让运动员在不稳定平面下感受训练过程中的位置反馈。第二阶段要求运动员在多个BOSU半圆平衡球上依次有次序地进行跑动练习,以平衡练习和闭链练习为主,通过平衡练习的反复刺激训练和闭链运动多关节联动,增强本体感受器的敏感性,改善神经肌肉控制。平衡练习有助于恢复运动员下肢关节稳定性,尤其以膝、踝关节为主;闭链运动有助于神经肌肉控制系统的恢复以及肌力的提升[29]。第三阶段进行更高水平的本体感觉训练,并配合主要发力的股四头肌和胫骨前肌的肌力练习,以增加难度并进一步刺激关节周围本体感受器,使胫骨前肌在训练中得到更大的强化,增强运动员下肢肌肉力量[8]。
3.2 本体感觉训练对运动员平衡能力的影响
平衡能力又称稳定性,是调控人体的支撑面和人体质心关系的一种能力[8]。人体平衡分为静态维持固定姿势和动态调整维持姿势,其中动态平衡又分为自动态平衡(无外力作用下进行各种自主运动重新获得稳定状态的能力)和他动态平衡(受到外力干扰时恢复稳定状态的能力)[30]。良好的平衡能力不仅有利于提高运动能力,还可预防运动损伤的发生[8]。在运动过程中,本体感觉训练通过引入不稳定支撑面、增加肌肉负荷、改变运动速度等方式,直接刺激肌肉、肌腱和关节内的本体感受器[12,31],促使感受器更敏感地感知身体的位置、运动状态和外界负荷。随着训练的深入,本体感受器对微小变化的感知能力逐渐增强,感知阈值降低[32]。这意味着运动员能够更准确地感知到身体姿态的微小变化,从而及时调整,保持平衡。除增强感知能力外,本体感觉训练还可提高中枢神经系统对本体感受器传递信息的处理能力,反复训练可增强突触可塑性和神经元连接,使中枢神经系统更有效整合处理信息[33],这不仅能增强肌梭、高尔基腱器官等内感受器的信号传递效率,还能使中枢神经系统更快地解析运动信息,并做出正确的决策,从而更精确地控制肌肉的收缩与放松,确保运动员在不同运动状态下都能保持稳定的姿态。
本文通过12周的本体感觉训练发现,实验组运动员的静态、动态平衡能力在前后、左右方向均有不同程度的提高,尤其是动态平衡能力提升更明显。分析原因可能是定向运动项目运动员本体感觉训练多在不稳定状态下进行,训练动作可能比常规练习更能刺激前庭系统,增强内耳的平衡能力,从而增强内耳的椭圆囊和球囊上听斑的功能以及半规管壶腹嵴功能,进而改善平衡能力。此外,本体感觉训练增强了本体感受器的敏感性和抗干扰能力,提高了该项目运动员的神经肌肉控制能力,改善大小肌群的协调能力,从而增强中枢神经系统对核心肌群的支配能力,调节和支配神经纤维产生肌肉紧张性动作和收缩活动[34],维持机体稳定,最终提高了运动员从身体失衡恢复到平衡状态的能力。由于训练动作涉及不同解剖面的练习,比如在训练器上屈膝半蹲练习是双脚在球状面上固定运动,而左右方向的摇摆练习是单足在球面上来回运动,不同环境、状态的训练刺激能够最大化地激活人体中枢神经系统的兴奋性,募集更多肌纤维,动员各个神经肌肉骨骼系统协同配合[35]。这与前人[36]研究结果一致,持续的运动和多变的动作转换促使人体肌纤维变粗、增多,表现为肌肉的力量增大;同时还使神经系统兴奋性增加,参与收缩的肌纤维增多;又可增强本体感觉和前庭的敏感性,从而起到提高平衡能力的作用。因此,本体感觉训练在提高定向运动员平衡能力方面,是通过前庭功能、肌梭腱梭以及肌肉力量使中枢神经系统的整合调节效率提高,从而使运动员在前后、左右各个方向的平衡能力得到提升。
3.3 本体感觉训练对运动员下肢肌力的影响
肌肉力量也是决定运动成绩的重要因素[37]。在定向运动中,运动员需具备野外复杂地形长时间奔跑和高强度爬坡能力,不仅要有极强的下肢肌肉力量,还要具备维持力量最大值时间的能力,更需要具备维持平衡状态下的持续能力和为维持平衡实时调整的能力,这也是定向运动专项力量训练的核心部分。通过适当协调肌肉和运动模式来维持姿势控制[38],需要精确监控下肢和全身运动,因为下肢肌肉或任何本体感觉能力的下降都有可能降低运动员整体的动作质量。有研究 [39] 指出,当人体体位控制能力和躯干本体感觉能力下降时,所表现出的运动能力降低,可能会增加下肢或下背部的受伤风险。下肢关节扭伤是定向运动赛事中的大概率伤病事件[40]。在跑步过程中,与静态的站立稳定性不同,人体质心在步态周期约80%的时间内处于支撑面积之外[41],这使得步态期间的稳定性成为一个动态且复杂的挑战。在这一动态过程中,对髋、膝、踝关节的功能需求较高,尤其是迈步腿的位置和支撑腿的髋关节扭矩等机制对于维持步态稳定性至关重要。这些机制不仅涉及肌肉力量的协调,还涉及本体感觉对步态信息的精确处理。增强本体感觉有助于传递机体运动的各种信息,激活神经肌肉,从而确保个体能够根据周围环境做出适当的姿势反应[42]。因此,在定向运动员的训练中,在增强平衡能力的同时,还应关注强肌肉力量的训练和提升,以确保在复杂动态环境中提升运动员的运动控制能力和运动表现。
本文发现,在12周本体感觉训练后,下肢整体肌肉的最大力量、维持最大值的时间、平均力量、最大功率、平均功率都有显著的提高。分析原因可能是本体感觉训练本质上是一种针对神经肌肉系统的特殊训练方式,运动员通过本体感觉训练刺激了骨骼肌主要的本体感受器(高尔基腱器官和肌肉纺锤体)[43],其中高尔基腱器官主要感受肌肉收缩和关节伸展的程度,肌肉纺锤体主要感受肌肉被牵拉的程度[38]。此外,在非稳定状态下,为了维持身体的平衡和稳定,机体需要不断调整各个肌群之间的协作关系,通过不断尝试和修正,强化下肢各肌群的做功能力,以提高神经肌肉控制效率[44]。当骨骼肌的肌肉纺锤体受到外界训练刺激后,其敏感性和兴奋性增加,进而使感受器募集到更多数量的运动单位,最终提高运动员的下肢肌肉力量[44]。在本体感觉训练中,通过控制肌肉的收缩强度和时间,可以适度刺激高尔基腱器官,使其发挥保护作用。同时,由于高尔基腱器官与α运动神经元之间的抑制性连接,适当的刺激可以促进肌肉在收缩过程中的协调性,使肌肉在收缩和放松之间达到更好的平衡[45]。本体感觉训练还能强化神经肌肉系统的信息交互与整合能力,精确捕捉肌肉张力、关节位置等感觉信息,经神经系统高效处理后,可精准调控肌肉力量与动作轨迹[38],优化运动效率与表现。因此,在本体感觉训练后运动员在蹬伸过程中下肢整体肌肉的运动能力及肌肉力量、耐力水平得以提高。
3.4 本体感觉训练对运动员识图专项技能的影响
地图是定向运动项目最重要的工具,识图技术包括标定地图、确定站立点、确定前进方向、选择路线及保持正确行进方向,为定向运动重要的专项技术。定向运动赛事要求运动员在不同类型植被覆盖的野外山地或有一定起伏的地形中,在大脑高度紧张状态下或体力处于极限挑战的状态下,具备快速[46]、准确完成读图、路线选择[47]以及保持正确行进方向的识图专项技能。比赛过程中存在原地识图、走动中识图、慢跑中识图及快速奔跑中识图几种情况,通过各级锦标赛事运动轨迹、视频影像分析可知,优秀运动员的路线选择技术水平已非常接近,但在读图与路线选择的时间上和效率上差距明显[40],读图与路线选择时间的差异直接决定运动成绩。同时,在跑动过程中还需要维持姿势平衡和控制肢体肌肉协调,尤其是在山地行进时更需要保持身体姿势平衡,防止摔倒,减少伤病发生。娄彦涛等[3]对滑雪运动员平衡能力训练的结果表明,躯体感觉和视觉干扰均会降低运动员的平衡控制能力,其中躯体感觉干扰更为严重,该结果对定向运动员动态平衡训练具有一定的借鉴意义。
本文通过12周的本体感觉训练和专项识图训练发现,定向运动员在复杂环境中的专项识图技术能力得到有效提升。本文中的本体感觉训练主要是在不稳定状态下进行的,运动员在各个方向的平衡能力得到提升,实现了身体不稳定和稳定之间的快速转换,并具备保持长时间身体稳定平衡状态的能力,其维持保障平衡能力明显提升;下肢整体肌肉的运动能力得以提高,运动员在复杂野外地形中肢体感觉和身体平衡能力得到有效提升。在定向运动比赛中,运动员在保持高速奔跑的状态下,需要快速识别地图符号,从复杂的地图符号中快速搜索与路线选择相关的信息,对二维平面的定向地图进行认知加工,在大脑中形成相应的三维地形,并与现实场景中的地物信息相匹配[20],保持正确行进方向。该过程是运动员对地图信息的记忆储存和提取,为运动员识图专项技能的体现,稳定的身体姿势控制能力和下肢运动能力是运动员识图专项技术实现的关键。
4. 结论、局限与展望
12周的本体感觉训练可有效提升定向运动员的静态和动态平衡能力,也可有效增加运动员下肢主要屈伸肌群的肌肉力量,达到提升该项目运动员姿势控制能力的目的。另外,本体感觉训练还可提升运动员在复杂环境中的专项识图技术能力。本体感觉训练和专项识图技术训练方法和手段在定向运动项目中切实可行,为该项目运动员制定训练方案提供了新的方法和手段。
本文还存在一定的局限性。首先,运动员样本量相对较少,可能影响研究的可推广性。其次,因受试者技术水平存在一定差异,在一定程度上削弱了样本在特定领域内的代表性。未来研究可针对运动员训练模式(短期集训和自主训练)的特点,围绕动态识图专项技术构建本体感觉科学训练方法的实时监控体系。
作者贡献声明:任卫华:提出论文选题,设计论文框架,检索、筛选文献,开展实验测试,撰写、修改论文;作者贡献声明:高天:协助开展实验测试,协助检索、筛选文献,修改论文;作者贡献声明:刘珂:协助收集、整理部分外文文献,统计、整理数据;作者贡献声明:李艳辉:核实数据,修改论文;作者贡献声明:娄彦涛:提出论文选题,设计论文框架,指导修改论文。 -
表 1 受试者基本情况
Table 1 Basic information of subjects
类别 年龄/岁 身高/cm 体重/kg 训练年限/年 实验组(n=23) 20.39±2.27 177.02±6.11 68.31±3.37 3.07±1.87 对照组(n=22) 20.11±2.53 177.39±6.62 68.15±5.86 3.11±1.61 注:训练年限以第1次参与定向活动为时间节点进行统计。 表 2 下肢蹬伸阶段的各肌肉贡献率结果
Table 2 The contribution rate of each muscle in the lower extremity push and stretch stage
% 动作名称 股四头肌内侧头 股二头肌长头 腓肠肌内侧头 胫骨前肌 上坡 31.73±3.02 25.86±2.45**## 30.25±2.28 12.15±1.26**## 下坡 10.15±1.10## 25.44±2.36** 20.86±2.56## 43.35±4.87**## 注:**表示膝、踝关节屈伸肌肉贡献率相比,P<0.01;##表示上下坡肌肉贡献率相比,P<0.01。 表 3 训练前后静态平衡能力测试结果
Table 3 Test results of static balance ability before and after training
评估指标 实验组 对照组 训练前 训练后 训练前 训练后 X轴移动距离/mm 332.41±134.15 243.32±56.65*# 328.39±36.32 292.52±21.36* Y轴移动距离/mm 289.74±45.56 213.24±46.31*# 310.34±33.52 265.12±21.85* X轴平均速度/(mm·s−1) 11.75±6.31 8.36±1.66* 9.05±2.19 6.36±1.59* Y轴平均速度/(mm·s−1) 10.57±3.35 7.78±1.93* 7.88±1.87 6.23±1.67* 区域半径/mm 16.23±4.26 12.17±2.64* 15.82±5.46 11.25±2.38* 注:表3中数据为左右腿平均数据;*表示与训练前比较,P<0.05;#表示与对照组比较,P<0.05。 表 4 训练前后动态平衡能力测试结果
Table 4 Test results of dynamic balance ability before and after training
评估指标 实验组 对照组 训练前 训练后 训练前 训练后 稳定时间/s 58.56±8.31 35.12±7.58*# 54.22±4.32 44.26±5.16* X轴移动距离/mm 3086.65 ±682.122183.32 ±213.71*#2832.56 ±425.362552.52 ±316.25*Y轴移动距离/mm 2826.56 ±745.212061.58 ±863.25*#2521.58 ±501.712289.37 ±621.12*注:*表示与训练前比较,P<0.05;#表示与对照组比较,P<0.05。 表 5 训练前后下肢蹬伸效果测试结果
Table 5 Test results of lower limb extension before and after training
评估指标 实验组 对照组 训练前 训练后 训练前 训练后 最大力量/N 786.58±331.27 1020.56 ±128.62*#812.71±132.23 938.62±221.23* 维持90%最大力的时间/ms 256.26±27.32 296.62±36.56**# 251.16±21.56 268.36±32.37* 平均力量/N 633.38±65.66 828.84±51.26*# 626.79±87.85 766.89±38.83* 最大功率/W 502.82±68.38 629.85±87.68# 503.52±56.14 578.46±53.52* 平均功率/W 329.85±91.87 450.36±85.16*# 336.19±79.15 387.19±76.81* 注:*表示与训练前比较,P<0.05,**表示与训练前比较,P<0.01;#表示与对照组比较,P<0.05。 表 6 训练前后专项技术训练结果
Table 6 Results of special technical training before and after training
评估指标 实验组 对照组 静态 动态 静态 动态 训练前 18.8±1.82 22.4±3.24 18.7±2.87 23.1±5.51 第4次训练后 13.2±1.61 15.9±5.36*# 12.9±5.56 17.9±5.26* 第8次训练后 23.7±6.31 27.6±3.56# 22.8±5.43 33.8±6.04 第12次训练后 17.8±2.37 20.3±2.63*# 18.2±9.08 30.1±7.12* 注:时间单位为s;*表示与训练前比较,P<0.05;#表示与对照组比较,P<0.05。 -
[1] 任卫华. 基于品牌视域下城市坐标定向赛发展模式与路径创新研究[J]. 河南教育学院学报(自然科学版),2022,31(4):65-71 [2] 郭程,丁道群,郑澜,等. 具身认知视角下定向运动专家-新手心理旋转能力的研究[J]. 北京体育大学学报,2023,46(9):106-117 [3] 娄彦涛,李艳辉,郝卫亚,等. 不同感觉条件干扰对自由式滑雪空中技巧运动员平衡控制能力的影响[J]. 上海体育学院学报,2020,44(12):43-52 [4] 彭春政,李红琴. 多模态功能训练对女大学生功能性踝关节不稳患者下肢肌力、本体感觉和动态平衡能力的影响[J]. 山东体育学院学报,2020,36(1):66-72 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2076.2020.01.011 [5] DOMÍNGUEZ-NAVARRO F,IGUAL-CAMACHO C,SILVESTRE-MUÑOZ A,et al. Effects of balance and proprioceptive training on total hip and knee replacement rehabilitation:A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Gait & Posture,2018,62:68-74
[6] 吴加弘,袁陆军,袁空军. FIFA 11+练习对高校足球运动员膝踝关节肌力、本体感觉和动态平衡的研究[J]. 天津体育学院学报,2019,34(4):344-349 [7] 张弛,王惠芳. 膝关节本体感觉康复研究的进展[J]. 中华物理医学与康复杂志,2000,22(6):52-54 [8] 欧晓涛,娄彦涛,王家伟. 自由式滑雪空中技巧运动员姿势控制训练及效果评价研究[J]. 体育科研,2020,41(1):49-55 doi: 10.12064/ssr.20200106 [9] 李旭鸿,范年春,许鑫华,等. 长期太极拳和广场舞锻炼老年女性骨骼肌含量、骨骼肌力量以及平衡能力的研究[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2016,35(9):844-848 [10] 胡潇月. 足踝感觉的年龄差异及感觉训练对老年人姿势控制的影响[D]. 上海:上海体育学院,2022:5 [11] GIDU D V,BADAU D,STOICA M,et al. The effects of proprioceptive training on balance,strength,agility and ribbling in adolescent male soccer players[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health,2022,19(4):2028 doi: 10.3390/ijerph19042028
[12] GRUSHKO S,SPURNÝ T,ČERNÝ M. Control methods for transradial prostheses based on remnant muscle activity and its relationship with proprioceptive feedback[J]. Sensors,2020,20(17):4883 doi: 10.3390/s20174883
[13] STINGEL J P,HICKS J L,UHLRICH S D,et al. Simulating muscle-level energetic cost savings when humans run with a passive assistive device[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters,2023,8(10):6267-6274 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2023.3303094
[14] WINSER S,PANG M Y C,RAUSZEN J S,et al. Does integrated cognitive and balance (dual-task) training improve balance and reduce falls risk in individuals with cerebellar ataxia?[J]. Medical Hypotheses,2019,126:149-153 doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2019.03.001
[15] WESTER J U,JESPERSEN S M,NIELSEN K D,et al. Wobble board training after partial sprains of the lateral ligaments of the ankle:A prospective randomized study[J]. The Journal of Orthopaedic and Sports Physical Therapy,1996,23(5):332-336 doi: 10.2519/jospt.1996.23.5.332
[16] 段林茹,郑洁皎. 脑卒中患者姿势控制的感觉系统特征[J]. 医用生物力学,2023,38(4):770-776 [17] 范超群. 评价中老年动、静态平衡能力测试方法的比较研究[D]. 北京:北京体育大学,2011:25 [18] 来章琦. 基于足部核心系统探究足部肌肉功能训练对老年人姿势控制的影响[D]. 上海:上海体育学院,2022:34-35 [19] 蔡书荣. 游泳专项力量测试系统建立和评价方法研究[J]. 山东体育学院学报,2014,30(4):87-92 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2076.2014.04.018 [20] 刘阳,何劲鹏. 不同任务情境下定向运动员视觉记忆特征及加工策略[J]. 体育学刊,2017,24(1):64-70 [21] 易妍,刘静如,张言,等. 不同认知负荷条件下定向运动员心理旋转能力的行为绩效及脑加工特征[J]. 体育学刊,2022,29(2):136-144 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7116.2022.2.tyxk202202020 [22] AHMAD I,NOOHU M M,VERMA S,et al. Effect of sensorimotor training on balance measures and proprioception among middle and older age adults with diabetic peripheral neuropathy[J]. Gait & Posture,2019,74:114-120
[23] OH H T,HWANGBO G. The effects of proprioception exercise with and without visual feedback on the pain and balance in patients after total knee arthroplasty[J]. Journal of Physical Therapy Science,2018,30(1):124-126 doi: 10.1589/jpts.30.124
[24] 黄达武. 优秀女子500 m速度滑冰运动员速度节奏及专项力量肌肉用力特征研究[D]. 上海:上海体育学院,2013:76 [25] DE BRITTO M A,CARPES F P,KOUTRAS G,et al. Quadriceps and hamstrings prelanding myoelectric activity during landing from different heights among male and female athletes[J]. Journal of Electromyography and Kinesiology,2014,24(4):508-512 doi: 10.1016/j.jelekin.2014.04.009
[26] 刘晓晨,崔芳,董煜琳,等. 年龄和性别对腰椎本体感觉的影响[J]. 中国康复理论与实践,2018,24(12):1446-1450 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9771.2018.12.017 [27] 李芙蓉,陈月亮,吴新炎. 我国优秀短距离速滑运动员直道滑冰腿部肌肉肌电特征研究[J]. 天津体育学院学报,2014,29(1):14-18 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0000.2014.01.004 [28] BARNES K R,KILDING A E. Running economy:Measurement,norms,and determining factors[J]. Sports Medicine-Open,2015,1(1):8 doi: 10.1186/s40798-015-0007-y
[29] POWELL D W,WILLIAMS D S B 3rd. Athletes trained using stable compared to unstable surfaces exhibit distinct postural control profiles when assessed by traditional and nonlinear measures[J]. Human Movement Science,2015,44:73-80 doi: 10.1016/j.humov.2015.08.013
[30] 娄彦涛,郝卫亚,王振. 自由式滑雪空中技巧运动员平衡控制能力研究[J]. 中国体育科技,2016,52(4):113-126 [31] LEE G. Whole-body vibration in horizontal direction for stroke rehabilitation:A randomized controlled trial[J]. Medical Science Monitor,2019,25:1621-1628 doi: 10.12659/MSM.912589
[32] WANG J W,LIU W,FU H T. Effects of traditional Chinese herb hot compress combined with therapeutic exercise on pain,proprioception,and functional performance among older adults with knee osteoarthritis:A randomized controlled trial[J]. Frontiers in Physiology,2022,13:1070754 doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.1070754
[33] CONCHA-CISTERNAS Y,CASTRO-PIÑERO J,LEIVA-ORDÓÑEZ A M,et al. Effects of neuromuscular training on physical performance in older people:A systematic review[J]. Life,2023,13(4):869 doi: 10.3390/life13040869
[34] 翟宏伟,孙洁,巩尊科,等. 本体感觉训练对踝关节功能障碍恢复的影响[J]. 中华物理医学与康复杂志,2016,38(2):147-149 doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-1424.2016.02.017 [35] 卢岩岩,许学猛,刘文刚,等. 本体感觉和平衡训练对全膝关节置换后膝关节功能恢复影响的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2019,23(16):2601-2607 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1217 [36] PERRIN P P,GAUCHARD G C,PERROT C,et al. Effects of physical and sporting activities on balance control in elderly people[J]. British Journal of Sports Medicine,1999,33(2):121-126 doi: 10.1136/bjsm.33.2.121
[37] ROBERSON A R,STARKWEATHER A,GROSSMAN C,et al. Influence of muscle strength on early mobility in critically ill adult patients:Systematic literature review[J]. Heart & Lung,2018,47(1):1-9
[38] FRYER C,ITHURBURN M P,MCNALLY M P,et al. The relationship between frontal plane trunk control during landing and lower extremity muscle strength in young athletes after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction[J]. Clinical Biomechanics,2019,62:58-65 doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2018.11.012
[39] WALSH G S. Effect of static and dynamic muscle stretching as part of warm up procedures on knee joint proprioception and strength[J]. Human Movement Science,2017,55:189-195 doi: 10.1016/j.humov.2017.08.014
[40] 任卫华. 河南省定向越野短距离项目竞技状况调查与分析[J]. 河南师范大学学报(自然科学版),2016,44(2):183-188 [41] SHARBAFI M A,SEYFARTH A. FMCH:A new model for human-like postural control in walking[C]//2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). September 28-October 2,2015,Hamburg,Germany. IEEE,2015:5742-5747
[42] DELAFONTAINE A,HANSEN C,MAROLLEAU I,et al. Effect of a concurrent cognitive task,with stabilizing visual information and withdrawal,on body sway adaptation of parkinsonian's patients in an off-medication state:A controlled study[J]. Sensors,2020,20(18):5059 doi: 10.3390/s20185059
[43] De VASCONCELOS G,张长杰. 本体感觉训练与踝关节扭伤[J]. 中国康复,2019,34(5):273 [44] HAN J,WADDINGTON G,ANSON J,et al. Level of competitive success achieved by elite athletes and multi-joint proprioceptive ability[J]. Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport,2015,18(1):77-81 doi: 10.1016/j.jsams.2013.11.013
[45] LI F Y,GUO C G,LI H S,et al. A systematic review and net meta-analysis of the effects of different warm-up methods on the acute effects of lower limb explosive strength[J]. BMC Sports Science,Medicine & Rehabilitation,2023,15(1):106
[46] 刘阳. 定向运动选手识图的认知加工特征与技能训练研究[D]. 长春:东北师范大学,2017:11 [47] 郭丽敏,杨万兰,刘阳. 定向运动员现实场景图景识别的视觉搜索特征研究[J]. 中国体育科技,2023,59(11):24-31 -
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 薛鑫宇. 2024年欧洲足球锦标赛冠军西班牙队进球特征. 中国体育教练员. 2025(01): 49-51+58 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: