Precision Intervention of Targeted Neuropsychiatric Disorders Treatment: The Tapping, Application and Transformation of Exerkins
-
摘要:
运动因子(Exerkines)作为由骨骼肌及其他组织分泌的生物活性物质,在调节神经系统功能、改善神经炎症、促进神经修复等方面具有重要作用。系统探讨运动因子的来源、转运机制及其在神经精神疾病中的作用,详细阐述运动因子的神经生物功能,并探讨其在神经精神疾病精准干预中的潜力。运动因子可分为骨骼肌源性因子、心源性因子、肝源性因子、脂肪源性因子和神经源性因子等,其神经生物学功能包括神经修复与再生、神经炎症调节、神经发育等。在运动的诱导下,这些因子通过血液循环或囊泡转运等方式传递信息,并在靶组织中发挥作用。在神经精神疾病的精准干预中,可通过运动因子进行个性化评估、精准诊断和治疗监测。通过整合生物组学、神经影像学及数据分析技术,可以更全面地了解运动因子的功能机制,并为疾病的精准干预提供科学依据。
Abstract:Exerkines, which serves as bioactive substances secreted by skeletal muscles and other tissues, play a crucial role in regulating nervous system function, improving neuroinflammation and promoting neurorepair. This study systematically explores the sources, transport mechanisms and the roles of exerkines in neuropsychiatric disorders, elaborates their neurobiological functions and the potential in precise interventions for neuropsychiatric disease treatment. Exerkines can be categorized into myokines, cardiokines, hepatokines, adipokines and neurokines. Their neurobiological functions include neural repair and regeneration, regulation of neuroinflammation and neurodevelopment. The factors induced by exercises transmit messages through blood circulation or vesicular transport, and exert effects on target tissues. In the precise intervention of neuropsychiatric disorders, exerkines can be utilized for personalized assessment, precise diagnosis and treatment monitoring. By integrating omics, neuroimaging and data analysis technologies, a more comprehensive understanding of the functional mechanisms of exerkines can be obtained, providing scientific evidence for precise intervention in diseases.
-
Keywords:
- exerkines /
- precision intervention /
- neuropsychiatric disorder /
- neurobiology
-
神经精神疾病(Neuropsychiatric Disorder)是全球疾病负担十大原因之一[1],具体包括抑郁症、焦虑症、阿尔茨海默病(Alzheimer's Disease,AD)、帕金森综合征(Parkinson's Disease,PD)、精神分裂症、成瘾、自闭症谱系障碍(Autism Spectrum Disorder,ASD)、强迫症、注意缺陷多动障碍(Attention-Deficit/Hyper-activity Disorder,ADHD)等[2]。目前,越来越多的研究聚焦于运动干预在神经精神疾病治疗中的潜力[3−4],运动的低风险、低成本和高收益等特性有望使其成为神经精神疾病辅助治疗的有效策略。在机制层面,越来越多的研究[5−7]发现,运动产生的一系列分子变化可能介导了运动对神经精神疾病的改善作用,这些运动诱导的分子可引起下游广泛的信号通路活动变化,最终产生生理心理效应,这些分子被称为运动因子(Exerkine)[5]。运动诱导骨骼肌等组织器官释放的、在其他组织中发挥中介作用的、参与调控机体对运动的反应与适应的各类生物活性物质(如蛋白质、多肽、核酸等)被统称为运动因子[8−9]。运动因子通过内分泌、旁分泌和自分泌等方式作用于相应靶点,参与机体对急性和长期运动的反应与适应过程[5]。根据运动因子的来源,可将运动因子分为骨骼肌源性运动因子(肌因子,Myokines)、心源性运动因子(心因子,Cardiokines)、肝脏源性运动因子(肝因子,Hepatokines)、脂肪源性运动因子(脂肪因子,Adipokines)以及由神经源性运动因子(神经因子,Neurokines)[5]。运动也可刺激肠道、性腺中部分物质的大量分泌并作用于其他器官,但此类物质并非传统的运动因子[4−10]。
本文将各器官组织来源的、受运动直接影响并参与机体对运动的反应和适应的多个分子纳入运动因子范畴。近年来,运动因子的发现和应用为神经精神疾病的精准干预策略提供了新的理论和方法。运动因子主要通过传统生物学检测手段、多组学技术和新兴组学技术(如单细胞测序分析)进行筛选、鉴别和应用。在将运动因子应用于神经精神疾病干预的过程中,个性化干预和剂量效应的优化是关键。运动强度、个体差异和干预方案的动态调整都可能显著影响运动因子的效应。此外,运动因子还显示出在情绪障碍(如抑郁症、焦虑症)和神经退行性疾病(如AD)中的特异性干预潜力。通过利用新兴检测技术和更高精度的分析手段,运动因子的筛选与应用有望在神经精神疾病的精准干预中发挥更大作用。
1. 运动因子的神经生物学基础
1.1 运动因子的来源
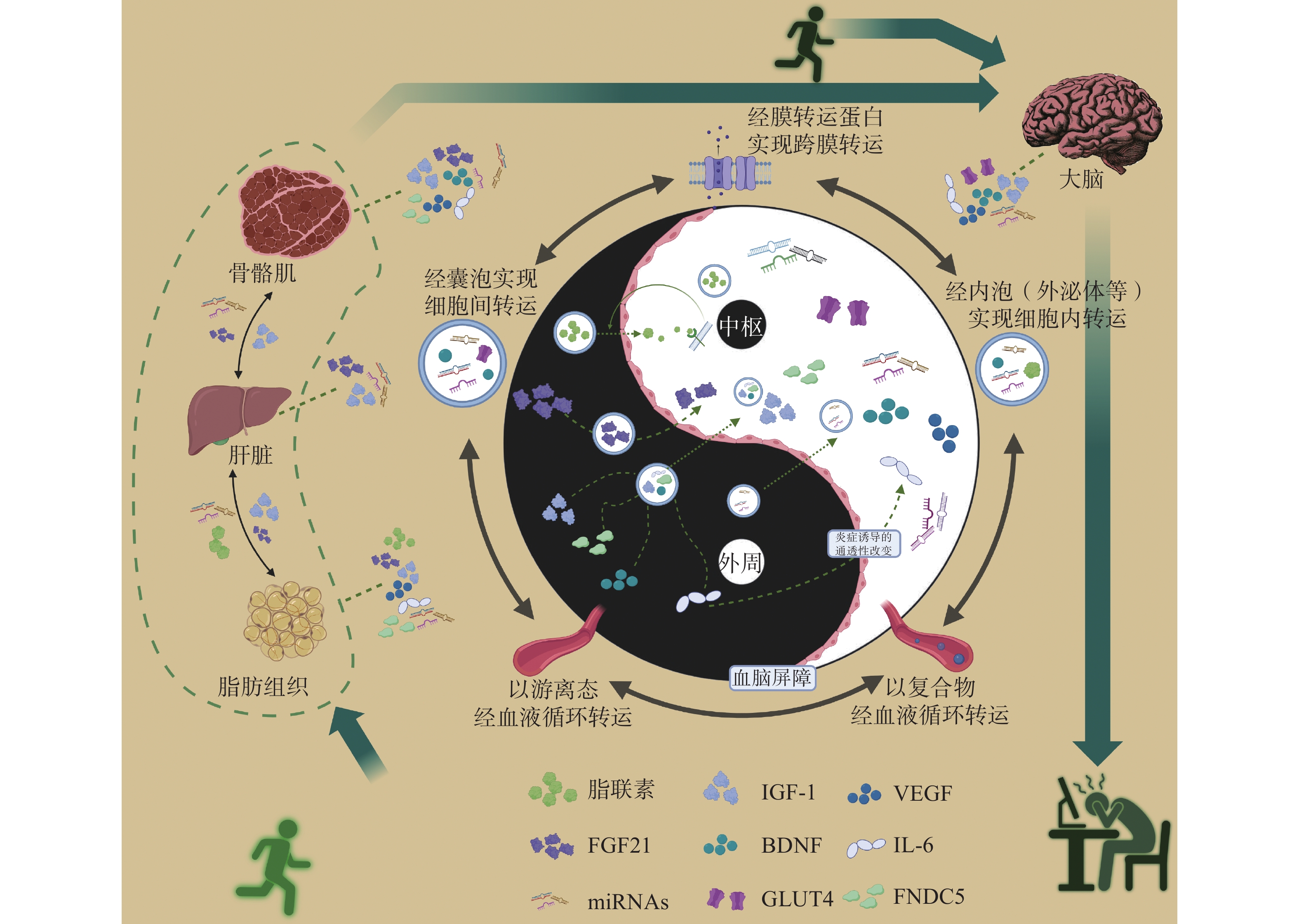
骨骼肌是运动因子产生和分泌的主要器官。2003年的研究[11]发现,运动时肌肉会分泌大量白介素-6(Interleukin-6,IL-6),并将其命名为肌因子。IL-6通过骨骼肌与大脑之间的串扰作用以维持情绪与认知功能[12]。组织蛋白酶B(Cathepsin B,CTSB)也是肌因子的一种:跑步训练后小鼠腓肠肌和血浆中的CTSB水平增加,CTSB进入大脑后可调节海马祖细胞中脑源性神经营养因子(Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor,BDNF)和双皮质素(Doublecortin,DCX)的表达[13]。运动过程中肌肉还会分泌大量乳酸到血液中,血乳酸进入大脑后会影响小鼠脑中的表观遗传修饰并对神经系统产生有益影响[14]。此外,骨骼肌中的转录因子EB(Transcription Factor EB,TFEB)、葡萄糖转运体4(Glucose Transporter Type 4,GLUT4)、BDNF与核因子κB(Nuclear Factor kappa B,NF-κB)等均是可调节机体活动的肌因子[15-16]。其中,骨骼肌并非BDNF的主要表达部位,BDNF在哺乳动物大脑中表达最为广泛[17]。运动可提升小鼠海马CA1脑区中BDNF的表达以改善PD相关症状[18]。γ-氨基丁酸(γ Aminobutyric Acid,GABA)在运动改善神经系统功能中也发挥着作用,一次性力竭运动即可观察到小鼠下丘脑中GABA含量显著升高[19]。FNDC5、大麻素受体1(Cannabinoid Receptor Type 1,CB1R)、血管内皮生长因子(Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor,VEGF)和胰岛素样生长因子1(Insulin-like Growth Factor,IGF-1)等均是在神经系统中合成与分泌的运动因子[20−22]。此外,运动可引起雌激素表达的变化,肌肉活动也能直接刺激其受体活性并由此产生神经保护作用,这提示雌激素及其受体也可能是潜在运动因子[4]。总之,运动因子可在机体多个组织器官中合成与分泌,并在远距离器官和组织中发挥神经生物学作用(表1)。
表 1 主要运动因子的来源、转运及靶向组织Table 1. Sources, transport, and target tissues of major exerkines运动因子 主要来源/表达组织 转运方式/信号转导方式 神经生物学功能 脂联素 骨骼肌[16]、脑[18]、
脂肪[23]由囊泡运输至胞外[23],经血液循环运送[24],与靶细胞上的特异性受体结合进行信号转导[25] 抗氧化、抗凋亡[25]
增强突触可塑性[26]
改善神经炎症[27]
促进神经发生[28]GLUT4 心肌[29]、骨骼肌[15]、
脂肪[30]囊泡转运到细胞膜上[23] 参与神经元葡萄糖代谢[31]
改善中枢胰岛素敏感性[32]成纤维生长因子21(Fibroblast Growth Factor 21, FGF 21) 肝脏[33]、脂肪[34]、
肌肉[35]以游离态通过血液循环转运[36] 改善神经炎症[37]
应对应激,调节代谢[38]
调节摄食行为[39]
促进中枢神经系统髓鞘再生[40]
促进神经元发育[41]IGF-1 肝脏[42]、骨骼肌[43] 与IGFBP结合形成复合物在血液中运输[44],与靶细胞膜上的特异性受体结合进行信号转导[45] 促进早期大脑功能及发育[46]
参与神经保护,塑造大脑结构[47]
促进神经可塑性,有助于学习与记忆[48]
改善脑血管功能[49]BDNF 脑[19]、骨骼肌[50] 以游离态经过血液循环转运[51]
由囊泡运输[52]减少神经元凋亡,缓解认知障碍[53]
恢复突触可塑性,改善神经发生,减少神经炎症[54]VEGF 成纤维细胞[55]、平滑肌细胞[56]、小胶质细胞[57] 以游离态在血液循环中转运[58]
与结合蛋白形成复合物在血液中转运[59]刺激神经发生[60]
改善神经炎症[61]
促进脑血管生成[62]FNDC5 肌肉[63]、肝脏[64]、
脂肪[65]在骨骼肌细胞中,FNDC5先剪切、修饰后生成鸢尾素,鸢尾素再分泌至血液中,经血液循环运送至靶向部位发挥作用[20] 提高突触可塑性[66]
促进神经营养因子表达[66]
改善神经炎症[66]乳酸 肌肉、肝脏、脑[67] 经过乳酸转运蛋白转运[68]
经血液循环运输促进胶质细胞与神经元之间的能量传递[69]
维持正常的突触功能[70]
改善神经炎症,缓解认知功能障碍[14]MicroRNA miR-382-3p
miR-186
miR-146a
miR-133a/b
miR-532-5p几乎所有器官和组织 囊泡运输、胞吐、脂质体运输 改善认知障碍[71]
改善神经元凋亡[72]
减少大脑炎症[73]
提高胰岛素敏感性[74]
改善认知功能[75]1.2 运动因子的转运
运动因子转运形式多样,包括囊泡转运、通过血液循环转运、与受体结合形成复合物转运等(图1)。研究[76]发现,运动康复训练能有效改善慢性精神分裂症患者的认知功能,这一过程伴随着血清BDNF水平的提升。神经源性细胞外囊泡(Neurogenic Derived Extracellular Vesicles,NDEV)可以转运BDNF,长期运动者血液中NDEV内含的BDNF水平提升,可使AD患者对身体活动的神经保护作用更加敏感,提示BDNF经由NDEV的转运途径可能是运动干预神经精神疾病的重要靶点[52]。此外,过表达小细胞外囊泡(Small Extracellular Vesicles,sEV)中的BDNF也已被初步应用于小鼠脑缺血损伤模型的治疗[54]。sEV在鼻内给药后具有较好的脑组织区域靶向性,搭载的BDNF到达梗死区域后也能有效改善神经炎症、促进神经修复[54]。运动因子经不同转运途径到达目标组织或细胞后,可通过跨膜转运的方式进入细胞内发挥作用,或直接通过与特异性膜蛋白结合进行信息传递,其转运方式差异可能与物质结构有关(表1)。
1.3 运动因子的神经生物功能
在正常生理状态下,运动因子参与神经系统的代谢调节、神经修复与再生、神经炎症调节、神经发育等多个神经生物学过程;在运动刺激后,运动因子的表达受运动影响而出现显著变化(增加或减少),从而影响其调控的诸多神经生物学过程,这是运动因子在神经精神疾病的运动干预中发挥作用的基础。
脂联素是由脂肪组织分泌的一种蛋白质。运动时脂联素主要由骨骼肌分泌并作用于大脑[24]。在小鼠皮层中,脂联素通过BDNF/TrkB信号通路改善神经炎症并由此产生抗抑郁作用[27]。脂联素与脂联素受体(AdiopR1) 结合后通过激活AMP依赖的蛋白激酶[Adenosine 5'-Monophosphate (AMP)-activated Protein Kinase,AMPK]/转录辅激活子过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体-γ(PPARγ)-辅激活子1α(Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator-1α,PGC1α)通路促进线粒体中脱乙酰酶3(Sirtin 3,SIRT3)表达,维持小鼠正常的线粒体功能并防止氧化损伤[25]。GLUT4是一种膜蛋白,与GLUT3共同维持神经元的葡萄糖代谢,海马等脑区中GLUT4的缺失与认知障碍等脑部疾病有关[31-32]。VEGF、BDNF等运动因子在血管修复、维持血脑屏障完整性、促进神经发生等过程中起到重要作用[27, 57, 77]。骨骼肌、肝脏等外周器官分泌FGF21后,经血液循环运送到中枢神经系统,可改变个体的酒精摄入等摄食行为[35, 39]。FGF21还能参与中枢神经系统中的髓鞘再生、神经发育等过程,并能有效延缓神经炎症,从而起到神经保护作用[37, 40]。乳酸是脑中的能源物质,主要由星形胶质细胞产生[69]。运动诱导的乳酸水平提升可作为表观遗传修饰底物,改变小胶质细胞中的组蛋白乳酸化修饰以改善神经炎症,最终延缓AD大鼠的认知功能障碍[14]。
microRNA(miR)通过脂质体、外泌体囊泡等方式由胞内分泌至胞外并转运到靶向部位,不同的microRNA具有不同功能。在相关疾病的运动干预中,外泌体microRNA是运动改善神经系统功能的运动因子:运动可增加大鼠血浆外泌体中miR-146a向脑组织的递送以减轻大脑炎症,促进脑卒中后大脑功能的修复[78]。在AD大鼠模型中,长期运动能诱导大脑中外泌体miR-532-5p的显著变化,以改善血脑屏障功能障碍最终改善认知功能[75]。上述研究表明,microRNA在抑郁症、PD、AD等神经精神疾病相关的神经生物学变化中发挥着重要作用,是疾病的潜在生物标记物。
2. 运动因子与神经精神疾病的精准干预
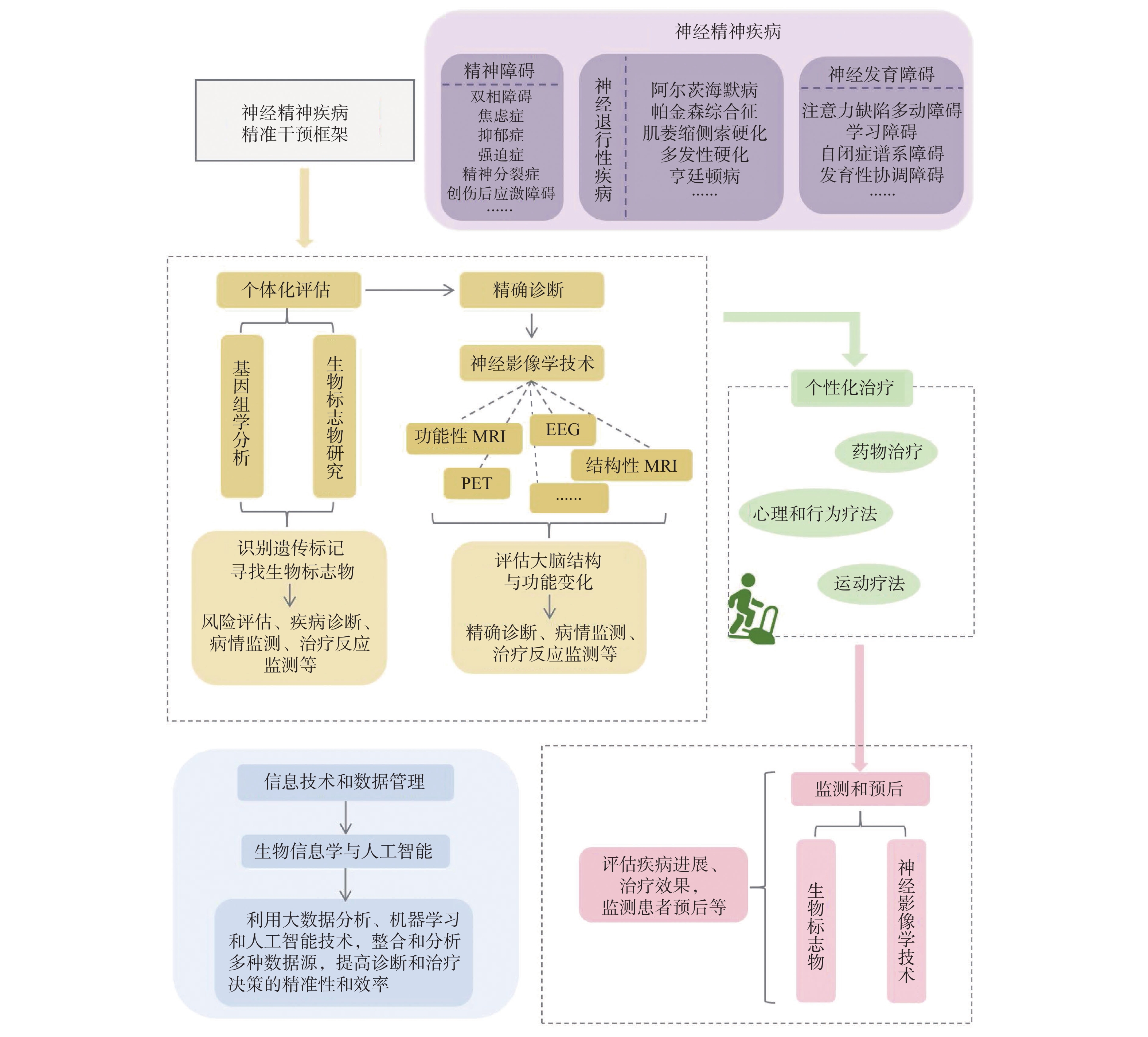
精准医疗(Precision Medicine)是一种基于个体病理生理特征、遗传变异、环境因素和生活方式等个体化信息的医疗模式。在神经精神疾病的精准干预框架中,利用现有基因组学技术、影像学和分子生物学技术、数据分析技术等深入了解每位患者的患病机制,通过上述技术找到具有高度辨别性的诊断、治疗及监测靶点,并将其应用至实践中。具体框架如图2所示。
血清中的炎症因子IL-6是抑郁症诊断中的重要生物标志物,同时该分子也是较早被发现的运动因子之一[79]。因此,在抑郁症的运动干预中IL-6可作为抑郁症诊断的生物标志物,同时具有监测和评估运动疗效的潜力。BDNF是调节突触可塑性和神经发生等过程的运动因子,与多种精神障碍密切相关[54]。研究[80]显示,精神分裂症患者血清BDNF水平与认知功能之间存在时间效应、组别效应及交互效应,这提示BDNF是监测和评估精神障碍的潜在生物标志物。笔者前期的研究[22]认为,BDNF作为运动抗抑郁研究中较为成熟的生物标志物,建立BDNF与抑郁程度之间的量化关系,可用于监测运动干预抑郁症的效果,但相关领域至今仍有待进一步探索。血清BDNF、IGF-1水平已被用于焦虑症药物治疗的疗效评估,老年中风后焦虑患者药物治疗后血清BDNF水平升高、IGF-1水平降低被认为是焦虑症状改善的标志[81]。在神经退行性疾病AD的运动干预中,炎症因子IL-6表达水平的变化与认知功能呈负相关[82]。PD患者血清miR-124、IGF-1含量则可用于反映疾病的治疗效果[83-84]。个体对运动的反应因性别、年龄、训练水平等诸多因素的差异而表现出个性化特点,上述证据则支持在精准医疗背景下使用血清中的运动因子含量及变化以诊断、评估和监测个体精神健康及其运动干预效果。
在精确诊断方面,神经成像技术(如fMRI)可以直接呈现特定脑区的神经元活动,这可能间接反映出BDNF等与神经元活动密切相关的生物标志物的活动。抑郁症患者的fMRI结果显示,特定脑区ALFF值与外周炎症因子生物标记物等有关[85]。此外,磁共振波谱技术(Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy,MRS)已被用于定位并检测AD患者脑中的葡萄糖及其代谢物浓度[86]。目前,关于运动因子应用于神经精神疾病的精准干预研究有限。通过对AD患者脑脊液进行蛋白质组学测序发现,AD存在5种亚型,其中3种亚型是以脑脊液Tau蛋白水平升高为病理标志[87]。在对运动因子鸢尾素(Irisin)干预AD的临床研究[88]中发现,女性AD患者脑脊液的Irisin水平显著较低,而在血浆中Irisin水平与Tau蛋白磷酸化水平呈负相关。这提示在对AD患者的精准干预中,脑脊液和血浆中的Irisin水平具有AD的亚型区分以及性别特异性诊断治疗的潜力,同时这也为其他类型运动因子精准干预神经精神疾病提供了思路。
3. 神经精神疾病精准干预中运动因子的发掘
3.1 运动因子的微观筛选:基于传统生物学手段的检测
传统生物学检测手段在发掘运动因子的研究中扮演着关键角色,通过多种技术手段揭示并验证运动产生的各类因子。在AD患者和模型小鼠中,脑脊液和血浆中的Irisin水平显著下降,并且在运动后产生显著性变化[20]。在对抑郁症患者的运动干预研究中,急性运动会显著增加血液中的BDNF水平[89]。笔者在前期研究[90]中检测到海马表达的运动因子FGF9受运动和抗抑郁药调控并且介导了小鼠抑郁行为的改善。目前关于运动因子的检测均离不开传统的生物学检测技术,这些手段多角度、多层次地揭示了运动因子的产生、分泌及其在神经系统中的作用,为运动干预神经精神疾病研究提供了重要的科学依据。
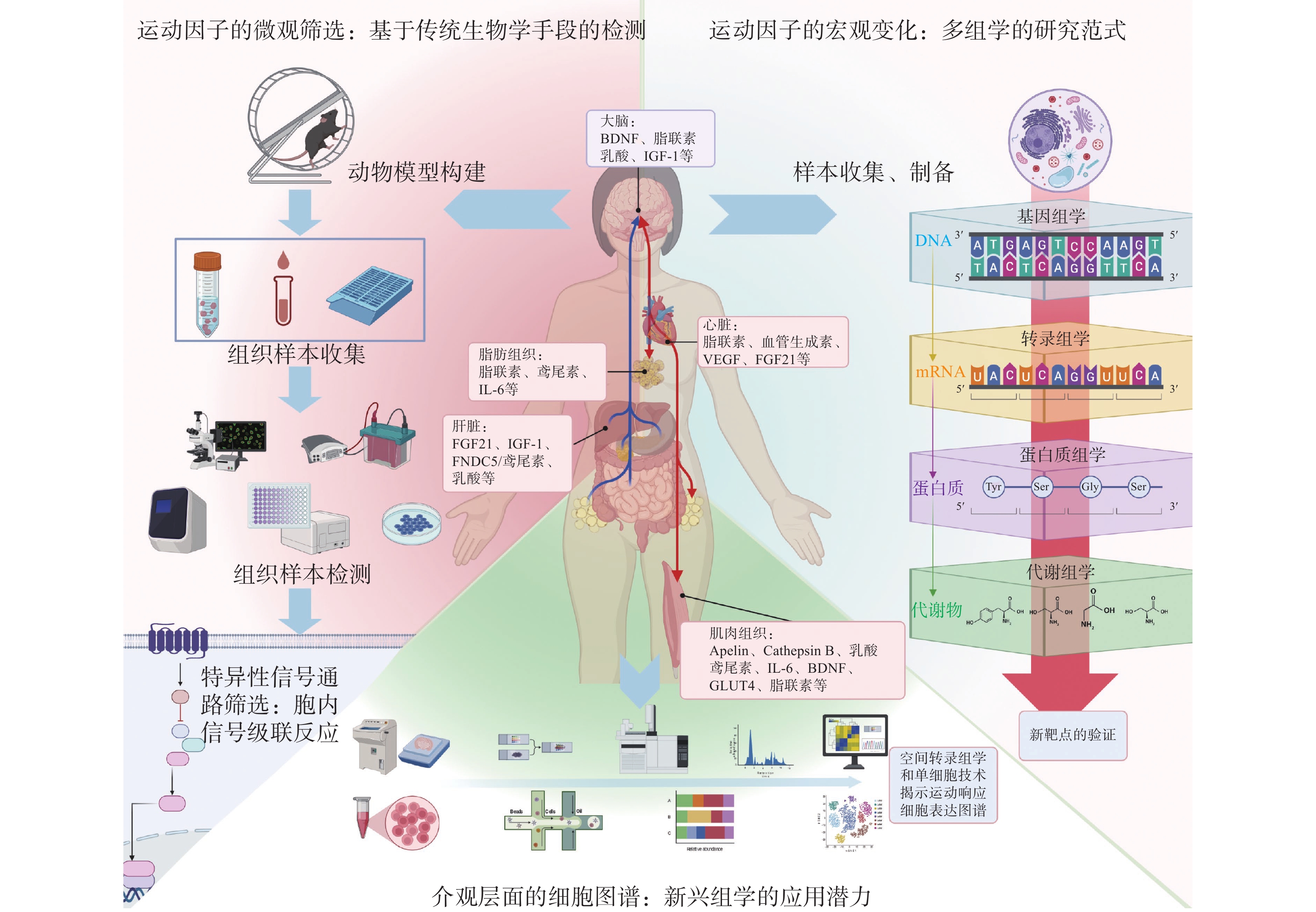
传统检测手段虽然能够提供一定的细胞和分子信息,但在时间和空间分辨率上有限,难以实时、动态地监测运动因子的快速变化,无法全面捕捉运动因子的复杂动态变化和多层次生物效应。有研究[91]提出在复杂生物动态演化或疾病发生发展过程中,存在一个可观测的“动态网络标志物”(Dynamic Network Biomarker,DNB),它在临界期形成一个分子之间具有强相关并强震荡的奇异分子网络,并具备早期干预和诊断的潜力。此外,传统的研究方法往往只能提供某一特定时间点的静态数据,无法反映运动因子在不同运动强度、类型和持续时间下的动态波动。有研究[92]曾发现人体在运动中、运动后会诱导产生高通量的分子变化。因此,在研究运动因子对神经精神疾病的影响时,传统检测手段难以揭示其复杂的调控机制和时空特性(图3)。
3.2 运动因子的宏观变化:多组学的研究范式
运动诱发的生理变化是多样复杂的,如何筛选出更多的运动因子、揭示运动诱发的分子变化图谱是靶向神经精神疾病精准干预的前提。体育活动分子传感器联盟(The Molecular Tranducers of Physical Activity Consortium,MoTrPAC)便在此背景下产生。近年来,该联盟利用多组学技术全面揭示了运动训练引起的分子适应性动态变化和性别差异性机制[93−94]。
多组学技术如基因组学、转录组学、蛋白质组学和代谢组学等,能够提供系统性的生物学数据,通过整合不同层次的分子信息,揭示运动对生物系统的全面影响。基因组学研究主要通过全基因组关联分析(Genome-Wide Association Studies,GWAS)识别与运动反应相关的遗传变异,从而找到潜在的运动关联基因。2022年的一项GWAS研究[95]发现,肌肉中ACTN3基因的rs2229456突变个体会更偏向于进行中高强度运动,其原因是该位点突变会降低由于运动导致的肌肉酸痛和损伤的敏感性。转录组学分析通过检测运动前后基因表达的变化,能够揭示哪些基因在转录水平上被运动激活或抑制。有研究[96]利用转录组学分析发现慢性有氧运动通过促进肝脏中氨基酸代谢,分泌特定的甲基化供体SAM(S-腺苷-甲硫氨酸,S-adenosyl methionine)进入大脑,在前额叶皮质区域介导兴奋突触相关转录本的RNA甲基化,改善皮层神经网络,增强小鼠对慢性束缚环境压力的抵抗,防止焦虑样行为的发生。有研究[97]利用转录组学技术揭示了运动小鼠血液移植诱导的海马转录水平变化,发现接受运动血液移植的小鼠对神经炎症诱发的表达有拮抗作用。该研究[97]还进一步利用蛋白质组学筛选引起这些变化的目标蛋白,发现大脑神经炎症水平的改善与参与补体和凝血途径的簇蛋白(clusterin)相关。笔者在前期研究[98−99]中利用蛋白质组学和靶向代谢组学发现了运动干预N-乙酰基-5-羟色胺-甲基转移酶(N-acetylserotonin O-methyltransferase,ASMT)基因敲除诱导抑郁行为改变的蛋白靶点和靶向代谢物。通过综合多组学数据,可以构建出运动对机体的多层次影响网络,筛选出那些在多个层次上显著变化的分子作为潜在运动因子(图3)。
3.3 介观层面的细胞图谱:新兴组学的应用潜力
介观层面(mesoscopic level)指的是介于分子和整体组织或器官之间的一个层次。在细胞图谱中,介观层面关注的是细胞群体、细胞之间的相互作用以及它们在特定区域内的组织结构和连接[100]。有研究[101]利用基因标记的胆碱能神经元进行成像以绘制介观水平上全脑胆碱能神经元的投射和分布。
单细胞转录组测序可以测定单个细胞的基因表达图谱,同时可以在同一疾病条件下比较细胞亚群变化及各亚群内转录组水平的改变,从而有力推动神经精神疾病发病机制的探索、疾病亚型分类、治疗新靶点的发现[102]。Cathomas等[103]利用单细胞测序发现应激会增加循环和大脑中的单核细胞数量,并诱导应激易感小鼠单核细胞的促炎转录特征。在重度抑郁患者大脑中,利用单细胞测序发现前额皮质少突胶质细胞前体细胞和兴奋性神经元的基因表达变化[104]。目前利用单细胞测序技术探究运动诱导的分子变化图谱的研究仍有限。有研究[105]揭示了运动能在多种细胞类型(包括心肌细胞和血管内皮细胞)中逆转节律转录因子(Brain and muscle arnt-like protein 1,BMAL1)随衰老出现的表达沉默。在组织器官层面,空间转录组学将成像技术和单细胞测序技术结合,能构建器官时间转录图谱。近期有研究[106]利用空间转录组学技术揭示了全脑转录组细胞类型图谱和不同细胞类型的衰老分子特征。通过与单细胞测序技术的联用,构建每个大脑结构的细胞类型综合图谱,对于理解哺乳动物大脑的功能和神经细胞类型的分子特征具有重要意义[107]。目前有研究[108]将此技术应用于神经康复和运动能力恢复领域以绘制出瘫痪恢复的神经分子图谱。在运动科学领域,空间转录组学技术的应用仍有限,如何利用该技术实现运动因子的筛查及神经精神疾病精准干预的潜力是未来值得探索的方向(图3)。
4. 神经精神疾病精准干预中运动因子的应用
4.1 运动因子的剂量效应优化
运动因子剂量效应优化的生物学基础是运动强度、个体差异和干预方案的动态调整会对运动因子的合成和分泌产生影响。
首先,运动强度和运动方式在运动因子的调控中可能存在特异性,表现为运动因子的响应程度差异。有研究[109]对比了不同运动周期对运动因子Irisin水平的影响,发现6周振荡训练不能提高成年女性循环Irisin的基线水平,但急性振荡训练会显著提高这一指标。与耐力运动和耐力联合抗阻运动相比,单纯的抗阻运动能更显著地提高成年男性循环Irisin的水平[110]。在关于高强度间歇训练(HIIT)和中等强度持续运动(MICE)对中老年人神经认知功能和分子标志物的急性影响研究[111]中,HIIT和MICE都能显著改善反应时间(RT)和事件相关电位(ERP)振幅,并提高血清中BDNF水平,但Irisin变化仅出现在HIIT后。这提示运动方式差异性诱导的运动因子响应模式可能会影响大脑功能的改善,进而影响神经精神疾病的干预效果。此外,血浆BDNF水平以强度依赖的方式增加,力竭冲刺运动会立即诱导出最高的BDNF浓度[112]。在AD的干预中,适度运动可显著提高BDNF和Irisin的水平,从而改善神经功能和情绪状态[113]。中等强度的有氧运动,如慢跑和游泳,能显著提高BDNF水平,增强神经元的存活率和突触可塑性[114]。过高强度的运动可能引发过度应激反应,从而抑制BDNF的生成并可能加大神经精神疾病的发生风险[115]。因此,运动强度和方式在调控运动因子的过程中可能具有特异性,不同类型的运动对运动因子的响应程度存在显著差异,从而影响神经精神疾病的干预效果。
其次,个体差异也决定了运动因子精准干预神经精神疾病的靶向作用。Morris等[116]利用多模态神经影响特征和模型预测发现,运动坚持性个体存在脑结构和脑功能的差异,这可能为精准和个性化干预方案的制定提供依据。基因型的差异也会影响个体对运动的反应,通过基因检测和个体评估可以更精准地制定运动处方。有研究[117]对青年女性的BDNF val66met多态性分型与抑郁症状关系进行分析,发现对携带BDNF Met等位基因的群体而言,运动具有抑郁症状的保护作用,但对于携带Val/Val多态性的群体而言,运动并无保护作用。在未经受过童年创伤的抑郁患者中,Met携带者的血清成熟BDNF水平更高,并且决定了运动干预的治疗反应[118]。在经历创伤应激的人群中,进行运动锻炼的Met等位基因携带者的创伤后应激障碍(Posttraumatic Stress Disorder,PTSD)和认知功能障碍症状显著低于那些不锻炼的携带者[119−121]。个体差异在运动因子精准干预神经精神疾病中的作用不可忽视,包括年龄、性别、基因多态性等因素都可能影响运动干预的效果。这提示在设计运动干预方案时,考虑个体差异并利用基因检测能够更有效地优化干预效果。
运动因子精准干预神经精神疾病可能存在动态调节效应。长期运动干预需要不断监测和调整以维持疗效和避免副作用。使用生物标志物和神经影像技术可以实时监测患者对运动干预的反应,从而及时调整运动剂量。目前有研究[122]将血浆BDNF作为敏感的神经标志物衡量急性耐力运动和恢复期的反应。另一研究[123]发现,主观用力感觉评分(RPE)、多维情绪状态问卷(Multidimensional Mood Questionnaire,MDMQ)、血液生物标志物在耐力运动后不同时期的变化具有显著性,提示这些指标对于量化运动负荷和恢复管理以监测训练过程具有重要意义。患者的反馈和症状变化也应纳入考量,通过综合评估,动态调整运动剂量,以实现最佳治疗效果。目前,此方面的研究仍处于探索阶段,对于运动过程中运动因子的实时监测未来可能需要结合新兴的检测传感器材料以无创的方式进行[124]。
4.2 神经精神疾病的病理特异性
4.2.1 情绪障碍
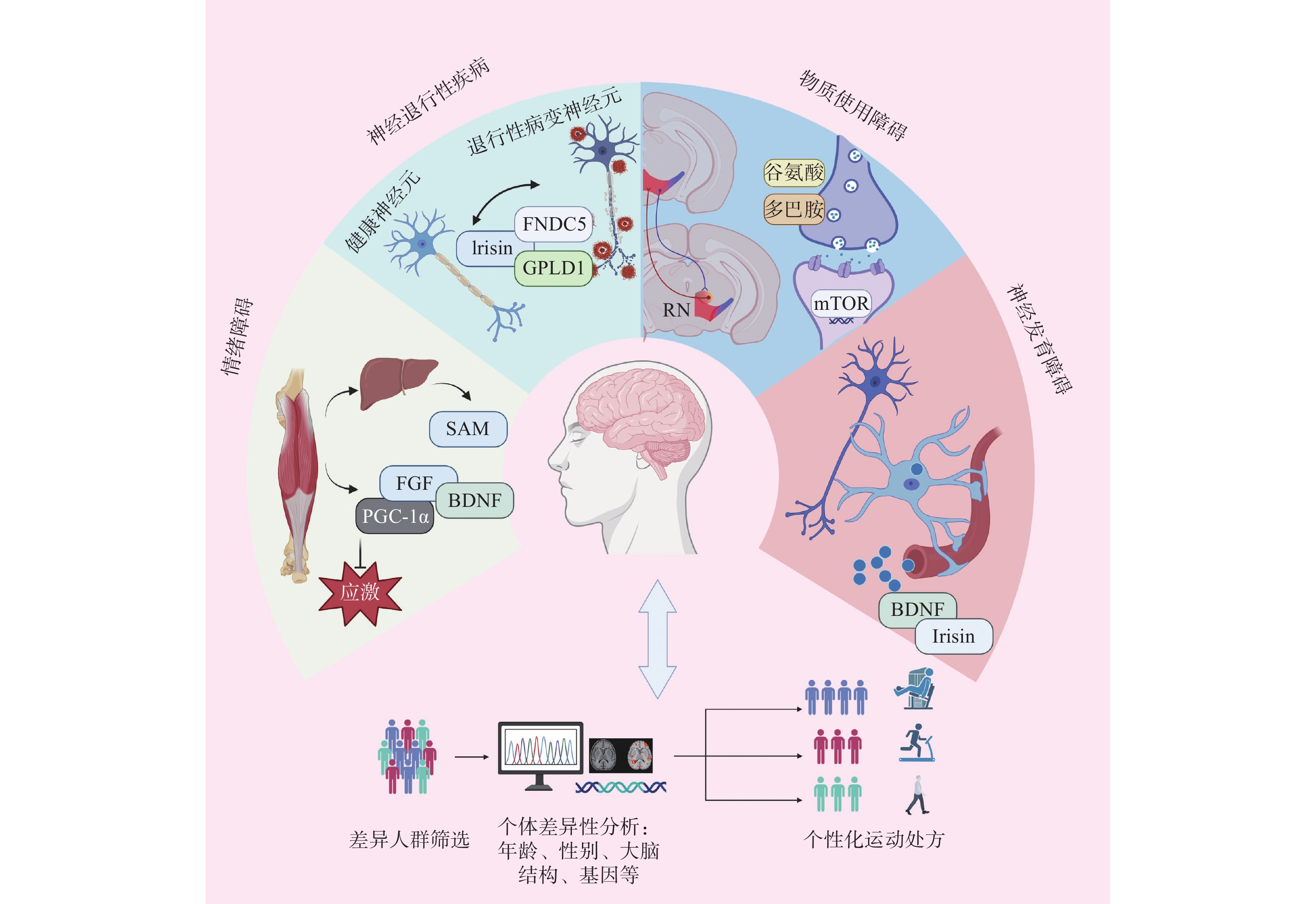
情绪障碍是指主要以情绪状态的异常为特征的精神疾病。情绪障碍包括抑郁症、焦虑障碍等,表现为情绪的长期低落或异常高涨,并可能伴有其他心理和生理症状[125]。运动在干预抑郁症中扮演关键角色,尤其是运动因子在其中的介导作用。一直以来,PGC-1α作为一个运动干预情绪障碍的“明星分子”备受关注。在神经元水平上,跑步运动通过PGC-1α调控海马CA3区GABA能神经元亚型PV中间神经元的活动,进而使小鼠产生抗抑郁行为表型[126]。在药物联合运动抗抑郁的研究[90]中发现,成纤维生长因子(fibroblast growth factor,FGF)家族信号通路介导了氟西汀和运动的抗抑郁效益。在抑郁症与糖尿病的共病机制研究[127]中,胰高血糖素样肽1(Glucagon-like peptide-1, GLP-1)介导了糖尿病靶向药二甲双胍联合运动的抗抑郁效益。这种共病机制的运动改善效益还可能经由瘦素受体 LepRb磷酸化通路介导[128]。运动的抗抑郁作用还会通过褪黑素(Melatonin,MT)的分泌产生调节作用,表现为生物节律和海马神经发生基因表达同步,还可调节BDNF节律水平及改善炎症和氧化应激[129]。
反复环境应激会诱发机体焦虑症状,运动因子在其中的分子机制鲜有系统性阐述。长期有氧运动促进前额皮质区域兴奋突触相关转录本的RNA甲基化(m6A),改善大脑皮层神经网络,增强小鼠对慢性束缚环境压力的抵抗,减少焦虑样行为的发生[96]。短期跑步运动改变了小鼠海马区神经元一氧化氮合酶(nitric oxide synthase,NOS)和BDNF基因的DNA甲基化模式,减少了焦虑样行为[130]。
4.2.2 神经退行性疾病
运动因子作为信号分子触发的级联反应被认为是运动改善神经功能、认知情绪的重要途径。运动产生的Irisin是改善认知的重要调节因子,是治疗包括AD在内的认知障碍的一种非常有前景的药物。研究[6]通过构建AD模型小鼠发现,空间学习和记忆能力都出现显著下降,而外周的Irisin递送会改善其认知功能。Irisin可能通过αVβ5整合素受体复合物抑制星形胶质细胞和小胶质细胞活化,从而改善AD小鼠的认知功能[6]。此外,运动后肝脏会产生糖基磷脂酰肌醇特异性水解酶磷脂酶D1(Gpld1),可促进成体神经元再生,改善老龄化小鼠的认知障碍[131]。运动对AD的干预效益还表现在小胶质细胞的代谢水平上,跑步运动通过维持小胶质细胞的激活因子TREM2蛋白水平(Triggering Receptor Expressed on Myeloid cells 2,TREM2),进而提高AD小鼠海马糖代谢水平、小胶质细胞糖代谢水平和小胶质细胞的形态可塑性,改善AD小鼠的学习记忆功能,延缓海马体积的萎缩及Aβ蛋白斑块的沉积[132]。在认知衰退的病理进程中,长期跑步运动可增强蛋白磷酸酶2A活性,缓解海马体Tau蛋白过度磷酸化,进而改善认知功能障碍[133]。
此外,运动也通过调控释放大脑内神经递质,对PD发挥干预作用。自主跑轮运动可促进小鼠大脑纹状体的多巴胺释放,其释放是以大脑BDNF释放为必要条件的[130]。有研究[134]认为,运动可通过调节谷氨酸受体的表达进而减少谷氨酸过度释放。该过程涉及运动皮层-纹状体谷氨酸能神经功能连接可塑性和传递效能[135−136]。
4.2.3 药物成瘾
药物成瘾作为一种典型的物质使用障碍,是一种慢性、复发性脑疾病。近年来,运动戒毒成为我国司法机构戒毒的有效手段,已形成规模化实践应用,成为戒毒康复的重要策略。尽管运动本身是具有成瘾性的行为,但其分子效应不会对机体产生毒性,并且具有药物成瘾的可替代性。有研究[137]发现,利用可卡因慢性暴露的小鼠模型,运动的药物成瘾戒断效益是靶向于皮层突触重塑机制的。持续的可卡因暴露会引起小鼠初级运动皮层(M1)的L5层锥体神经元局部兴奋-抑制稳态(E/I balance)的失衡,这一生理现象与运动激活皮层神经元内mTOR通路、调控突触活动、增加新生树突棘有关[137]。长期运动使红核(Red Nucleus,RN)的激活程度比其他脑区更为强烈;运动激活RN谷氨酸神经元,该神经元投射到腹侧被盖区(VTA)多巴胺神经元;运动可减少动物模型的可卡因自我给药和戒断期可卡因渴求行为[138]。此外,耐力运动通过调节纹状体谷氨酸信号通路,阻断GSK-3β的激活,从而抑制冰毒诱导的神经元高兴奋性[139]。近期也有研究[140]发现,跑台运动使成瘾小鼠脑内伏隔核多巴胺2型受体的中棘神经元的低兴奋性正常化,且同时增加多巴胺2型受体的中棘神经元向腹侧苍白球的GABA传递,加强环路功能。目前关于运动对药物成瘾依赖行为的干预研究集中于探究运动的奖赏效益替代性,神经元活动的兴奋抑制性平衡等方面,其分子生物学靶点不明显。基于此,后续研究可从运动因子靶向神经功能细胞、神经环路、神经递质等层面对运动的奖赏效益进行更多探索。
4.2.4 神经发育障碍
ASD和ADHD是2种主要的神经发育障碍,通常在儿童期显现,并伴随终生。运动能在一定程度上改善儿童青少年的ASD症状,包括认知能力、动作技能学习、执行功能等[141]。在ADHD的干预中,运动作为补充干预措施在注意力、多动、冲动、行为问题、执行功能和情绪问题上展现出积极作用[142−144]。
运动因子在神经发育障碍中的作用主要体现在其对神经营养因子和神经功能的调控上。对于ASD的儿童患者,为期12周的水上运动可有效提高BDNF水平,这可能会促进神经元的生长和突触可塑性,进而改善认知功能和社会行为[145]。在ASD小鼠中,运动可使妊娠期丙戊酸暴露诱导子代的ASD小鼠海马BDNF水平提高,改善了认知功能灵活性和海马脑区的异常发育[146−147]。此外,VEGF可能介导了运动对ASD小鼠学习缺陷的影响[148]。同样,在临床研究[149]中,运动可增加哌醋甲酯对ADHD临床症状的疗效。但这种效益的增加是否由运动因子介导目前仍未明晰。在ADHD基础研究中,研究人员常采用自发性高血压大鼠作为ADHD模型大鼠,研究[150−151]发现,BDNF和Irisin会介导运动对ADHD小鼠的大脑神经可塑性、学习能力及认知功能的改善,同时促进多巴胺的合成。这些发现提示,运动因子可能会成为未来个性化治疗ASD和ADHD的重要干预靶点。结合个体化的运动干预策略,运动因子有望在未来的治疗方案中发挥更加重要的作用,为神经发育障碍的患者带来更多的改善机会(图4)。
5. 运动因子的医学转化及应用潜力
5.1 从基础研究到临床应用的转化路径
基础研究提供了对运动因子作用于神经元和行为的基本理解,但这些发现往往是在动物模型中获得的,直接应用于人类治疗时,面临生物差异和实验环境差异的挑战[152]。基于动物模型的发现需要通过早期的临床试验在小规模人群中进行验证,这些试验通常关注运动因子的安全性、生物利用度及初步的治疗效果。此外,大规模的随机对照试验(RCTs)对验证运动因子在更大、更多样化的患者群体中的疗效至关重要[153]。由于神经精神疾病的异质性(如抑郁症的表现形式在个体间差异巨大),试验设计需要充分考虑个体差异和共病因素[154]。运动因子的临床应用不仅局限于疗效评估,还需要长期随访以观察其对疾病进展的影响。例如,AD患者的脑部退行性变化可能需要15~25年才能显现[155]。目前随着神经影像学技术和单细胞技术的发展,通过构建大规模脑影像常模,结合回顾性和前瞻性设计,建立多样化的多中心数据集,使得运动因子对神经精神疾病的个性化诊断及精准干预具有极大的潜力[156]。
5.2 运动因子药物开发前景
运动因子作为药物靶点的开发仍处于临床前研究和早期临床试验阶段。当前,针对运动因子的药物开发面临的挑战主要集中在药物递送和靶向性上。由于脑部血脑屏障的存在,许多直接增加运动因子水平的药物难以有效到达大脑[157]。药物从血液循环到大脑主要基于合成制剂通过大脑内皮胞吞作用、生物载体递送、暂时破坏血脑屏障实现[158]。目前,研究者[159−160]正尝试通过基因疗法、纳米技术和小分子激动剂等途径,开发能够提高药物特异性表达或模仿其功能的药物。研究人员通过设计弓形虫的内分泌系统以模拟其在人体内强大的穿越能力,能有效将大分子的治疗蛋白质递送到神经元[161]。此外,针对运动因子及其靶向信号通路的“运动模拟”药物开发也是一种新兴治疗方式,侧重于增强或模拟体育锻炼的有益效果[162]。比如,研究[163]发现,AMPK激动剂AICAR作为最常见的运动模拟药物可增加大脑海马神经元数量和提高BDNF表达。此外,PGC-1α的共激活因子PPARδ的激动剂GW0742和GW501516也会促进海马神经发生、增强学习记忆能力[164]。一项临床二期研究[165]测试了新合成的PPAR激动剂T3D-959在轻中度AD患者中的作用,这提示靶向运动因子的药物模拟在临床神经精神疾病干预中具有较大应用前景。
6. 结论与展望
本文系统地探讨了运动因子的来源、转运机制及其在神经精神疾病中的作用。运动因子作为由骨骼肌及其他组织分泌的生物活性物质,在调节神经系统功能、改善神经炎症、促进神经修复等方面具有重要作用。本文详细阐述了运动因子的神经生物功能,并探讨了其在神经精神疾病精准干预中的潜力。随着精准医疗和生物技术的发展,运动因子有望在神经精神疾病的个性化评估、诊断、治疗及预后管理中发挥更大作用。通过整合生物学、神经影像学及数据分析技术,我们可以更全面地了解运动因子的作用机制,并为疾病的精准干预提供科学依据。未来需要进一步探索运动因子的分子机制及其在不同疾病中的具体作用,以实现更为精准和有效的治疗。
作者贡献声明:刘微娜:提出论文主题,设计论文框架,撰写、修改论文;作者贡献声明:章森、何文柯:协助检索、筛选、梳理文献,协助修改论文;作者贡献声明:漆正堂:提出论文主题,设计论文框架,审核、指导修改 论文。 -
表 1 主要运动因子的来源、转运及靶向组织
Table 1 Sources, transport, and target tissues of major exerkines
运动因子 主要来源/表达组织 转运方式/信号转导方式 神经生物学功能 脂联素 骨骼肌[16]、脑[18]、
脂肪[23]由囊泡运输至胞外[23],经血液循环运送[24],与靶细胞上的特异性受体结合进行信号转导[25] 抗氧化、抗凋亡[25]
增强突触可塑性[26]
改善神经炎症[27]
促进神经发生[28]GLUT4 心肌[29]、骨骼肌[15]、
脂肪[30]囊泡转运到细胞膜上[23] 参与神经元葡萄糖代谢[31]
改善中枢胰岛素敏感性[32]成纤维生长因子21(Fibroblast Growth Factor 21, FGF 21) 肝脏[33]、脂肪[34]、
肌肉[35]以游离态通过血液循环转运[36] 改善神经炎症[37]
应对应激,调节代谢[38]
调节摄食行为[39]
促进中枢神经系统髓鞘再生[40]
促进神经元发育[41]IGF-1 肝脏[42]、骨骼肌[43] 与IGFBP结合形成复合物在血液中运输[44],与靶细胞膜上的特异性受体结合进行信号转导[45] 促进早期大脑功能及发育[46]
参与神经保护,塑造大脑结构[47]
促进神经可塑性,有助于学习与记忆[48]
改善脑血管功能[49]BDNF 脑[19]、骨骼肌[50] 以游离态经过血液循环转运[51]
由囊泡运输[52]减少神经元凋亡,缓解认知障碍[53]
恢复突触可塑性,改善神经发生,减少神经炎症[54]VEGF 成纤维细胞[55]、平滑肌细胞[56]、小胶质细胞[57] 以游离态在血液循环中转运[58]
与结合蛋白形成复合物在血液中转运[59]刺激神经发生[60]
改善神经炎症[61]
促进脑血管生成[62]FNDC5 肌肉[63]、肝脏[64]、
脂肪[65]在骨骼肌细胞中,FNDC5先剪切、修饰后生成鸢尾素,鸢尾素再分泌至血液中,经血液循环运送至靶向部位发挥作用[20] 提高突触可塑性[66]
促进神经营养因子表达[66]
改善神经炎症[66]乳酸 肌肉、肝脏、脑[67] 经过乳酸转运蛋白转运[68]
经血液循环运输促进胶质细胞与神经元之间的能量传递[69]
维持正常的突触功能[70]
改善神经炎症,缓解认知功能障碍[14]MicroRNA miR-382-3p
miR-186
miR-146a
miR-133a/b
miR-532-5p几乎所有器官和组织 囊泡运输、胞吐、脂质体运输 改善认知障碍[71]
改善神经元凋亡[72]
减少大脑炎症[73]
提高胰岛素敏感性[74]
改善认知功能[75] -
[1] GBD 2019 Mental Disorders Collaborations. Global,regional,and national burden of 12 mental disorders in 204 countries and territories,1990-2019:A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019[J]. The Lancet Psychiatry,2022,9(2):137-150 doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(21)00395-3
[2] FERNANDO A P,ROBBINS T W. Animal models of neuropsychiatric disorders[J]. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology,2011,7:39-61 doi: 10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-032210-104454
[3] SWENSON S,BLUM K,MCLAUGHLIN T,et al. The therapeutic potential of exercise for neuropsychiatric diseases:A review[J]. Journal of the Neurological Sciences,2020,412:116763 doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2020.116763
[4] HE W K,ZHANG S,QI Z T,et al. Unveiling the potential of estrogen:Exploring its role in neuropsychiatric disorders and exercise intervention[J]. Pharmacological Research,2024,204:107201 doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2024.107201
[5] CHOW L S,GERSZTEN R E,TAYLOR J M,et al. Exerkines in health,resilience and disease[J]. Nature Reviews. Endocrinology,2022,18(5):273-289 doi: 10.1038/s41574-022-00641-2
[6] ISLAM M R,VALARIS S,YOUNG M F,et al. Exercise hormone irisin is a critical regulator of cognitive function[J]. Nature Metabolism,2021,3(8):1058-1070 doi: 10.1038/s42255-021-00438-z
[7] EL HAYEK L,KHALIFEH M,ZIBARA V,et al. Lactate mediates the effects of exercise on learning and memory through SIRT1-dependent activation of hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)[J]. The Journal of Neuroscience,2019,39(13):2369-2382
[8] PEDERSEN B K,FISCHER C P. Beneficial health effects of exercise:The role of IL-6 as a myokine[J]. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences,2007,28(4):152-156 doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2007.02.002
[9] 饶志坚,张建红,赵杰修. 运动因子调控网络分析[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2023,42(12):987-1000 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6710.2023.12.011 [10] 张若琳,漆正堂,刘微娜. 微生物-肠-脑轴视角下色氨酸代谢介导的运动抗抑郁机制研究进展[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2023,42(3):227-235 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6710.2023.03.008 [11] PEDERSEN B K,STEENSBERG A,FISCHER C,et al. Searching for the exercise factor:Is IL-6 a candidate?[J]. Journal of Muscle Research and Cell Motility,2003,24(2-3):113-119
[12] PEDERSEN B K,FEBBRAIO M. Muscle-derived interleukin-6:A possible link between skeletal muscle,adipose tissue,liver,and brain[J]. Brain,Behavior,and Immunity,2005,19(5):371-376
[13] MOON H Y,BECKE A,BERRON D,et al. Running-induced systemic cathepsin B secretion is associated with memory function[J]. Cell Metabolism,2016,24(2):332-340 doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.05.025
[14] HAN H,ZHAO Y W,DU J D,et al. Exercise improves cognitive dysfunction and neuroinflammation in mice through Histone H3 lactylation in microglia[J]. Immunity & Ageing,2023,20(1):63
[15] 王平,李佳欣,陈小龙,等. 转录因子EB在有氧运动改善高脂饮食诱导小鼠骨骼肌胰岛素抵抗中的作用[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2024,43(3):193-204 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6710.2024.03.007 [16] 税晓平,李春莹,李顺昌,等. 有氧和抗阻运动干预2型糖尿病大鼠骨骼肌脑源性神经营养因子、核因子κB及炎症指标的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022,26(5):669-675 doi: 10.12307/2022.109 [17] PARK H,POO M M. Neurotrophin regulation of neural circuit development and function[J]. Nature Reviews. Neuroscience,2013,14(1):7-23 doi: 10.1038/nrn3379
[18] 张康,张业廷,付燕. 跑台运动对帕金森病模型小鼠不同脑区DAT、BDNF和TrkB表达的影响[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2022,41(9):704-713 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6710.2022.09.006 [19] 陆小香,张蕴琨,江年. 力竭运动后大鼠海马CA1区自由基、下丘脑GABA及HPA轴的动态变化[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2007,26(5):563-567 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6710.2007.05.010 [20] LOURENCO M V,FROZZA R L,DE FREITAS G B,et al. Exercise-linked FNDC5/irisin rescues synaptic plasticity and memory defects in Alzheimer's models[J]. Nature Medicine,2019,25(1):165-175 doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0275-4
[21] WANG D C,LIN H T,LEE Y J,et al. Recovery of BDNF and CB1R in the prefrontal cortex underlying improvement of working memory in prenatal DEHP-exposed male rats after aerobic exercise[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2020,21(11):3867 doi: 10.3390/ijms21113867
[22] 刘文彬,刘微娜,漆正堂. 神经营养因子介导运动的抗抑郁作用[J]. 体育科学,2018,38(10):54-66 [23] 崔菊,庞静,宫环,等. GLUT4和脂联素在3T3-L1脂肪细胞中共享囊泡转运机制[J]. 医学研究杂志,2017,46(3):18-21 doi: 10.11969/j.issn.1673-548X.2017.03.006 [24] 王少堃,王世强,王一杰,等. 骨骼肌介导的运动神经保护效应:作用途径和分子机制[J]. 中国体育科技,2023,59(4):58-66 [25] ZHANG S H,WU X,WANG J,et al. Adiponectin/AdiopR1 signaling prevents mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative injury after traumatic brain injury in a SIRT3 dependent manner[J]. Redox Biology,2022,54:102390 doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2022.102390
[26] 田清华,刘霞,邓鹏辉,等. 有氧运动对糖尿病大鼠学习记忆功能、海马突触可塑性及脂联素信号通路的影响[J]. 中华老年医学杂志,2024,43(3):348-353 doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-9026.2024.03.014 [27] LI W F,ALI T,ZHENG C Y,et al. Anti-depressive-like behaviors of APN KO mice involve Trkb/BDNF signaling related neuroinflammatory changes[J]. Molecular Psychiatry,2022,27(2):1047-1058 doi: 10.1038/s41380-021-01327-3
[28] LEE T H,CHRISTIE B R,VAN PRAAG H,et al. AdipoRon treatment induces a dose-dependent response in adult hippocampal neurogenesis[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2021,22(4):2068 doi: 10.3390/ijms22042068
[29] 李欣,余福林,高延. 跑台运动调节线粒体ATP释放改善高脂饮食大鼠的心肌损伤[J]. 心脏杂志,2024,36(3):256-261 doi: 10.12125/j.chj.202304119 [30] 吴彪,范冬霞,张佳,等. PM2.5和热/冷暴露对小鼠骨骼肌和白色脂肪组织AKT/GLUT4通路的影响[J]. 环境与职业医学. 2024,41(4):356-361 [31] PENG W X,TAN C H,MO L J,et al. Glucose transporter 3 in neuronal glucose metabolism:Health and diseases[J]. Metabolism,2021,123:154869 doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2021.154869
[32] YONAMINE C Y,MICHALANI M L E,MOREIRA R J,et al. Glucose transport and utilization in the hippocampus:From neurophysiology to diabetes-related development of dementia[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2023,24(22):16480 doi: 10.3390/ijms242216480
[33] 张媛,盛蕾,刘小玮,等. 不同运动方式对肥胖大鼠肝脏脂质沉积及FGF21分泌的影响[J]. 中国应用生理学杂志,2022,38(1):47-52 [34] GENG L L,LIAO B Y,JIN L G,et al. Exercise alleviates obesity-induced metabolic dysfunction via enhancing FGF21 sensitivity in adipose tissues[J]. Cell Reports,2019,26(10):2738-2752
[35] GAO Y,ZHANG W,ZENG L Q,et al. Exercise and dietary intervention ameliorate high-fat diet-induced NAFLD and liver aging by inducing lipophagy[J]. Redox Biology,2020,36:101635 doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2020.101635
[36] 李良,徐建方,冯连世,等. 有氧运动和抗阻运动训练对肥胖大鼠肝脏FGF21信号通路的影响[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2018,37(10):847-856 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6710.2018.10.007 [37] WANG D X,LIU F,ZHU L Y,et al. FGF21 alleviates neuroinflammation following ischemic stroke by modulating the temporal and spatial dynamics of microglia/macrophages[J]. Journal of Neuroinflammation,2020,17(1):257 doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-01921-2
[38] GENG L L,LAM K S L,XU A M. The therapeutic potential of FGF21 in metabolic diseases:From bench to clinic[J]. Nature Reviews. Endocrinology,2020,16(11):654-667 doi: 10.1038/s41574-020-0386-0
[39] FLIPPO K H,TRAMMELL S A J,GILLUM M P,et al. FGF21 suppresses alcohol consumption through an amygdalo-striatal circuit[J]. Cell Metabolism,2022,34(2):317-328
[40] KURODA M,MURAMATSU R,MAEDERA N,et al. Peripherally derived FGF21 promotes remyelination in the central nervous system[J]. The Journal of Clinical Investigation,2017,127(9):3496-3509 doi: 10.1172/JCI94337
[41] 李晶晶,孙晓彤,柳婷婷,等. 成纤维细胞生长因子21与妊娠期代谢性疾病的研究进展[J]. 国际妇产科学杂志,2023,50(4):400-404 doi: 10.12280/gjfckx.20230156 [42] 黄嵩,王巍,牛燕媚,等. 有氧运动干预父系C57BL/6小鼠对雄性子代IGF-1表达及其甲基化的影响[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2020,39(4):288-294 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6710.2020.04.006 [43] 刘延莹,杨海平,冯庆鲲,等. 弱激光预照射联合有氧运动对增龄大鼠骨骼肌SIRTs/PGC-1α轴及IGF-1蛋白表达的影响[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2019,38(7):577-584 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6710.2019.07.006 [44] HUANG R R,SHI J Y,WEI R H,et al. Challenges of insulin-like growth factor-1 testing[J]. Critical Reviews in Clinical Laboratory Sciences,2024,61(5):388-403 doi: 10.1080/10408363.2024.2306804
[45] 程慧芳,李会会,王庆志,等. 迷走神经刺激对老龄小鼠术后认知功能障碍的影响及海马IGF-1信号通路在其中的作用[J]. 中华麻醉学杂志,2022(9):1048-1053 doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn131073.20220617.00906 [46] RUSIN D,VAHL BECIROVIC L,LYSZCZARZ G,et al. Microglia-derived insulin-like growth factor 1 is critical for neurodevelopment[J]. Cells,2024,13(2):184 doi: 10.3390/cells13020184
[47] NUÑEZ A,ZEGARRA-VALDIVIA J,FERNANDEZ DE SEVILLA D,et al. The neurobiology of insulin-like growth factor I:From neuroprotection to modulation of brain states[J]. Molecular Psychiatry,2023,28(8):3220-3230 doi: 10.1038/s41380-023-02136-6
[48] MAGLIO L E,NORIEGA-PRIETO J A,MAROTO I B,et al. IGF-1 facilitates extinction of conditioned fear[J]. eLife,2021,10:e67267 doi: 10.7554/eLife.67267
[49] ZHANG J Y,LIU M Q,HUANG M H,et al. Ginsenoside F1 promotes angiogenesis by activating the IGF-1/IGF1R pathway[J]. Pharmacological Research,2019,144:292-305 doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2019.04.021
[50] CAVALERI D,MORETTI F,BARTOCCETTI A,et al. The role of BDNF in major depressive disorder,related clinical features,and antidepressant treatment:Insight from meta-analyses[J]. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews,2023,149:105159
[51] REED J L,TERADA T,COTIE L M,et al. The effects of high-intensity interval training,Nordic walking and moderate-to-vigorous intensity continuous training on functional capacity,depression and quality of life in patients with coronary artery disease enrolled in cardiac rehabilitation:A randomized controlled trial (CRX study)[J]. Progress in Cardiovascular Diseases,2022,70:73-83 doi: 10.1016/j.pcad.2021.07.002
[52] DELGADO-PERAZA F,NOGUERAS-ORTIZ C,SIMONSEN A H,et al. Neuron-derived extracellular vesicles in blood reveal effects of exercise in Alzheimer's disease[J]. Alzheimer's Research & Therapy,2023,15(1):156
[53] WANG J,NIU Y L,TAO H Y,et al. Knockdown of lncRNA TUG1 inhibits hippocampal neuronal apoptosis and participates in aerobic exercise-alleviated vascular cognitive impairment[J]. Biological Research,2020,53(1):53 doi: 10.1186/s40659-020-00320-4
[54] ZHOU X,DENG X H,LIU M F,et al. Intranasal delivery of BDNF-loaded small extracellular vesicles for cerebral ischemia therapy[J]. Journal of Controlled Release,2023,357:1-19 doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.03.033
[55] CADAMURO M,BRIVIO S,MERTENS J,et al. Platelet-derived growth factor-D enables liver myofibroblasts to promote tumor lymphangiogenesis in cholangiocarcinoma[J]. Journal of Hepatology,2019,70(4):700-709 doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.12.004
[56] GIELEN S,SANDRI M,ERBS S,et al. Exercise-induced modulation of endothelial nitric oxide production[J]. Current Pharmaceutical Biotechnology,2011,12(9):1375-1384 doi: 10.2174/138920111798281063
[57] CHOI B R,JOHNSON K R,MARIC D,et al. Monocyte-derived IL-6 programs microglia to rebuild damaged brain vasculature[J]. Nature Immunology,2023,24(7):1110-1123 doi: 10.1038/s41590-023-01521-1
[58] MORLAND C,ANDERSSON K A,HAUGEN Ø P,et al. Exercise induces cerebral VEGF and angiogenesis via the lactate receptor HCAR1[J]. Nature Communications,2017,8:15557 doi: 10.1038/ncomms15557
[59] GOEL S,DUDA D,XU L,et al. Normalization of the vasculature for treatment of cancer and other diseases[J]. Physiological Reviews,2011,91(3):1071-1121 doi: 10.1152/physrev.00038.2010
[60] DU PREEZ A,ONORATO D,EIBEN I,et al. Chronic stress followed by social isolation promotes depressive-like behaviour,alters microglial and astrocyte biology and reduces hippocampal neurogenesis in male mice[J]. Brain,Behavior,and Immunity,2021,91:24-47
[61] BOISSERAND L S B,GERALDO L H,BOUCHART J,et al. VEGF-C prophylaxis favors lymphatic drainage and modulates neuroinflammation in a stroke model[J]. The Journal of Experimental Medicine,2024,221(4):e20221983 doi: 10.1084/jem.20221983
[62] ZONG X M,LI Y Y,LIU C,et al. Theta-burst transcranial magnetic stimulation promotes stroke recovery by vascular protection and neovascularization[J]. Theranostics,2020,10(26):12090-12110 doi: 10.7150/thno.51573
[63] KIM H,WRANN C D,JEDRYCHOWSKI M,et al. Irisin mediates effects on bone and fat via αV integrin receptors[J]. Cell,2018,175(7):1756-1768
[64] LI D J,SUN S J,FU J T,et al. NAD+-boosting therapy alleviates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via stimulating a novel exerkine Fndc5/irisin[J]. Theranostics,2021,11(9):4381-4402 doi: 10.7150/thno.53652
[65] HE X Y,HUA Y,LI Q,et al. FNDC5/irisin facilitates muscle−adipose−bone connectivity through ubiquitination-dependent activation of runt-related transcriptional factors RUNX1/2[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry,2022,298(3):101679 doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101679
[66] 章森,邹勇,漆正堂,等. 鸢尾素介导运动干预神经精神疾病的潜在机制[J]. 上海体育学院学报,2023,47(4):39-50 [67] MAGISTRETTI P J,ALLAMAN I. Lactate in the brain:From metabolic end-product to signalling molecule[J]. Nature Reviews. Neuroscience,2018,19(4):235-249 doi: 10.1038/nrn.2018.19
[68] WANG N,JIANG X,ZHANG S,et al. Structural basis of human monocarboxylate transporter 1 inhibition by anti-cancer drug candidates[J]. Cell,2021,184(2):370-383
[69] LIU L,MACKENZIE K R,PUTLURI N,et al. The glia-neuron lactate shuttle and elevated ROS promote lipid synthesis in neurons and lipid droplet accumulation in glia via APOE/D[J]. Cell Metabolism,2017,26(5):719-737
[70] MONSORNO K,GINGGEN K,IVANOV A,et al. Loss of microglial MCT4 leads to defective synaptic pruning and anxiety-like behavior in mice[J]. Nature Communications,2023,14(1):5749 doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-41502-4
[71] WANG M Z,XIE K L,ZHAO S N,et al. Aerobic exercise improves cognitive impairment in mice with type 2 diabetes by regulating the MALAT1/miR-382-3p/BDNF signaling pathway in serum-exosomes[J]. Molecular Medicine,2023,29(1):130 doi: 10.1186/s10020-023-00727-1
[72] NIU Y L,WAN C X,ZHANG J,et al. Aerobic exercise improves VCI through circRIMS2/miR-186/BDNF-mediated neuronal apoptosis[J]. Molecular Medicine,2021,27(1):4 doi: 10.1186/s10020-020-00258-z
[73] ZHANG Z F,ZOU X X,ZHANG R,et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-146a-5p reduces microglial-mediated neuroinflammation via suppression of the IRAK1/TRAF6 signaling pathway after ischemic stroke[J]. Aging,2021,13(2):3060-3079 doi: 10.18632/aging.202466
[74] CASTAÑO C,MIRASIERRA M,VALLEJO M,et al. Delivery of muscle-derived exosomal miRNAs induced by HIIT improves insulin sensitivity through down-regulation of hepatic FoxO1 in mice[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2020,117(48):30335-30343
[75] LIANG X Y,FA W X,WANG N,et al. Exosomal miR-532-5p induced by long-term exercise rescues blood–brain barrier function in 5XFAD mice via downregulation of EPHA4[J]. Aging Cell,2023,22(1):e13748 doi: 10.1111/acel.13748
[76] KIM H J,SONG B K,SO B,et al. Increase of circulating BDNF levels and its relation to improvement of physical fitness following 12 weeks of combined exercise in chronic patients with schizophrenia:A pilot study[J]. Psychiatry Research,2014,220(3):792-796 doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2014.09.020
[77] ZHANG J Q,RONG P J,ZHANG L J,et al. IL4-driven microglia modulate stress resilience through BDNF-dependent neurogenesis[J]. Science Advances,2021,7(12):eabb9888 doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abb9888
[78] 王璐,闫冬,夏瑞洁,等. 运动预处理通过外泌体介导miR-146a对大鼠缺血性脑卒中炎症反应的影响[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2023,42(11):889-898 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6710.2023.11.007 [79] DEL GIUDICE M,GANGESTAD S W. Rethinking IL-6 and CRP:Why they are more than inflammatory biomarkers,and why it matters[J]. Brain,Behavior,and Immunity,2018,70:61-75
[80] XU H,WANG J S,ZHOU Y J,et al. BDNF affects the mediating effect of negative symptoms on the relationship between age of onset and cognition in patients with chronic schizophrenia[J]. Psychoneuroendocrinology,2021,125:105121 doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2020.105121
[81] 王丽. 天麻素片联合盐酸帕罗西汀对老年脑卒中后焦虑抑郁患者血清BDNF、IGF-1浓度的影响[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2017,37(21):5403-5405 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2017.21.083 [82] CHEN Y S,CHEN X F,LUO Z W,et al. Exercise-induced reduction of IGF1R sumoylation attenuates neuroinflammation in APP/PS1 transgenic mice[J]. Journal of Advanced Research,2024,3:25
[83] ESTEVES M,ABREU R,FERNANDES H,et al. MicroRNA-124-3p-enriched small extracellular vesicles as a therapeutic approach for Parkinson's disease[J]. Molecular Therapy,2022,30(10):3176-3192 doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2022.06.003
[84] CAO Z,MIN J H,TAN Q L,et al. Circulating insulin-like growth factor-1 and brain health:Evidence from 369,711 participants in the UK Biobank[J]. Alzheimer's Research & Therapy,2023,15(1):140
[85] PINTO-SANCHEZ M I,HALL G B,GHAJAR K,et al. Probiotic bifidobacterium longum NCC3001 reduces depression scores and alters brain activity:A pilot study in patients with irritable bowel syndrome[J]. Gastroenterology,2017,153(2):448-459
[86] KHAN A S,PETERSON K A,VITTAY O I,et al. Deuterium metabolic imaging of Alzheimer disease at 3-T magnetic field strength:A pilot case-control study[J]. Radiology,2024,312(1):e232407 doi: 10.1148/radiol.232407
[87] TIJMS B M,VROMEN E M,MJAAVATTEN O,et al. Cerebrospinal fluid proteomics in patients with Alzheimer's disease reveals five molecular subtypes with distinct genetic risk profiles[J]. Nature Aging,2024,4(1):33-47 doi: 10.1038/s43587-023-00550-7
[88] PHD M D,MSC P P,MSC C Z,et al. Irisin levels in cerebrospinal fluid correlate with biomarkers and clinical dementia scores in Alzheimer disease[J]. Annals of Neurology,2024,96(1):61-73 doi: 10.1002/ana.26946
[89] SZUHANY K L,OTTO M W. Assessing BDNF as a mediator of the effects of exercise on depression[J]. Journal of Psychiatric Research,2020,123:114-118 doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2020.02.003
[90] XIA J,XUE X L,LIU W B,et al. The role of Fgf9 in the antidepressant effects of exercise and fluoxetine in chronic unpredictable mild stress mice[J]. Psychosomatic Medicine,2021,83(7):795-804 doi: 10.1097/PSY.0000000000000953
[91] LIU R,WANG X D,AIHARA K,et al. Early diagnosis of complex diseases by molecular biomarkers,network biomarkers,and dynamical network biomarkers[J]. Medicinal Research Reviews,2014,34(3):455-478 doi: 10.1002/med.21293
[92] CONTREPOIS K,WU S,MONEGHETTI K J,et al. Molecular choreography of acute exercise[J]. Cell,2020,181(5):1112-1130
[93] VETR N G,GAY N R,GROUP M S,et al. The impact of exercise on gene regulation in association with complex trait genetics[J]. Nature Communications,2024,15(1):3346 doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-45966-w
[94] MANY G M,SANFORD J A,SAGENDORF T J,et al. Sexual dimorphism and the multi-omic response to exercise training in rat subcutaneous white adipose tissue[J]. Nature Metabolism,2024,6:963-979 doi: 10.1038/s42255-023-00959-9
[95] WANG Z,EMMERICH A,PILLON N J,et al. Genome-wide association analyses of physical activity and sedentary behavior provide insights into underlying mechanisms and roles in disease prevention[J]. Nature Genetics,2022,54(9):1332-1344 doi: 10.1038/s41588-022-01165-1
[96] YAN L,WEI J,YANG F Z,et al. Physical exercise prevented stress-induced anxiety via improving brain RNA methylation (adv. sci. 24/2022)[J]. Advanced Science,2022,9(24):2270148 doi: 10.1002/advs.202270148
[97] DE MIGUEL Z,KHOURY N,BETLEY M J,et al. Exercise plasma boosts memory and dampens brain inflammation via clusterin[J]. Nature,2021,600(7889):494-499 doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04183-x
[98] LIU W N,HUANG Z C,ZHANG Y,et al. ASMT determines gut microbiota and increases neurobehavioral adaptability to exercise in female mice[J]. Communications Biology,2023,6(1):1126 doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-05520-8
[99] 章森,刘文彬,夏杰,等. 运动改善ASMT基因敲除小鼠抑郁行为的海马蛋白质组学机制[J]. 上海体育大学学报,2024,48(3):36-48 [100] KALAY Z. Fundamental and functional aspects of mesoscopic architectures with examples in physics,cell biology,and chemistry[J]. Critical Reviews in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,2011,46(4):310-326 doi: 10.3109/10409238.2011.582081
[101] LI X N,YU B,SUN Q T,et al. Generation of a whole-brain atlas for the cholinergic system and mesoscopic projectome analysis of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2018,115(2):415-420
[102] WALTER T J,SUTER R K,AYAD N G. An overview of human single-cell RNA sequencing studies in neurobiological disease[J]. Neurobiology of Disease,2023,184:106201 doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2023.106201
[103] CATHOMAS F,LIN H Y,CHAN K L,et al. Circulating myeloid-derived MMP8 in stress susceptibility and depression[J]. Nature,2024,626(8001):1108-1115 doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-07015-2
[104] NAGY C,MAITRA M,TANTI A,et al. Single-nucleus transcriptomics of the prefrontal cortex in major depressive disorder implicates oligodendrocyte precursor cells and excitatory neurons[J]. Nature Neuroscience,2020,23(6):771-781 doi: 10.1038/s41593-020-0621-y
[105] SUN S H,MA S,CAI Y S,et al. A single-cell transcriptomic atlas of exercise-induced anti-inflammatory and geroprotective effects across the body[J]. The Innovation,2023,4(1):100380 doi: 10.1016/j.xinn.2023.100380
[106] JIN K,YAO Z Z,VAN VELTHOVEN C T J,et al. Cell-type specific molecular signatures of aging revealed in a brain-wide transcriptomic cell-type atlas[J]. bioRxiv,2023:2023.07. 26.550355
[107] LANGLIEB J,SACHDEV N S,BALDERRAMA K S,et al. The cell type composition of the adult mouse brain revealed by single cell and spatial genomics[J]. bioRxiv,2023:2023.03. 06.531307
[108] KATHE C,SKINNIDER M A,HUTSON T H,et al. The neurons that restore walking after paralysis[J]. Nature,2022,611(7936):540-547 doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05385-7
[109] HUH J Y,MOUGIOS V,SKRAPARLIS A,et al. Irisin in response to acute and chronic whole-body vibration exercise in humans[J]. Metabolism,2014,63(7):918-921 doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2014.04.001
[110] TSUCHIYA Y,ANDO D,TAKAMATSU K,et al. Resistance exercise induces a greater irisin response than endurance exercise[J]. Metabolism,2015,64(9):1042-1050 doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2015.05.010
[111] TSAI C L,PAN C Y,TSENG Y T,et al. Acute effects of high-intensity interval training and moderate-intensity continuous exercise on BDNF and irisin levels and neurocognitive performance in late middle-aged and older adults[J]. Behavioural Brain Research,2021,413:113472 doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2021.113472
[112] REYCRAFT J T,ISLAM H,TOWNSEND L K,et al. Exercise intensity and recovery on circulating brain-derived neurotrophic factor[J]. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise,2020,52(5):1210-1217 doi: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000002242
[113] PAHLAVANI H A. Exercise therapy to prevent and treat Alzheimer's disease[J]. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience,2023,15:1243869 doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1243869
[114] DORA K,TSUKAMOTO H,SUGA T,et al. Essential amino acid supplements ingestion has a positive effect on executive function after moderate-intensity aerobic exercise[J]. Scientific Reports,2023,13(1):22644 doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-49781-z
[115] SUZUKI G,TOKUNO S,NIBUYA M,et al. Decreased plasma brain-derived neurotrophic factor and vascular endothelial growth factor concentrations during military training[J]. PLoS One,2014,9(2):e89455 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089455
[116] MORRIS T P,BURZYNSKA A,VOSS M,et al. Brain structure and function predict adherence to an exercise intervention in older adults[J]. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise,2022,54(9):1483-1492 doi: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000002949
[117] MATA J,THOMPSON R J,GOTLIB I H. BDNF genotype moderates the relation between physical activity and depressive symptoms[J]. Health Psychology,2010,29(2):130-133 doi: 10.1037/a0017261
[118] RAHMAN M S,MILLISCHER V,ZEEBARI Z,et al. BDNF Val66Met and childhood adversity on response to physical exercise and Internet-based cognitive behavioural therapy in depressed Swedish adults[J]. Journal of Psychiatric Research,2017,93:50-58 doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2017.05.007
[119] PITTS B L,WHEALIN J M,HARPAZ-ROTEM I,et al. BDNF Val66Met polymorphism and posttraumatic stress symptoms in U. S. military veterans:Protective effect of physical exercise[J]. Psychoneuroendocrinology,2019,100:198-202 doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2018.10.011
[120] BRYANT R A,DAWSON K S,AZEVEDO S,et al. A pilot study of the role of the BDNF Val66Met polymorphism in response to exercise-augmented exposure therapy for posttraumatic stress disorder[J]. Psychoneuroendocrinology,2024,167:107106 doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2024.107106
[121] PITTS B L,WEN V,WHEALIN J M,et al. Depression and cognitive dysfunction in older U. S. military veterans:Moderating effects of BDNF Val66Met polymorphism and physical exercise[J]. The American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry,2020,28(9):959-967 doi: 10.1016/j.jagp.2020.02.001
[122] REICHEL T,HACKER S,PALMOWSKI J,et al. Neurophysiological markers for monitoring exercise and recovery cycles in endurance sports[J]. Journal of Sports Science & Medicine,2022,21(3):446-457
[123] REICHEL T,BOßLAU T K,PALMOWSKI J,et al. Reliability and suitability of physiological exercise response and recovery markers[J]. Scientific Reports,2020,10(1):11924 doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-69280-9
[124] LEE S,NOURAEIN S,KWON J J,et al. Engineered serum markers for non-invasive monitoring of gene expression in the brain[J]. Nature Biotechnology,2024,42(11):1717-1725 doi: 10.1038/s41587-023-02087-x
[125] KONING E,VORSTMAN J,MCINTYRE R S,et al. Characterizing eating behavioral phenotypes in mood disorders:A narrative review[J]. Psychological Medicine,2022,52(14):2885-2898 doi: 10.1017/S0033291722002446
[126] WANG J,TANG J,LIANG X,et al. Hippocampal PGC-1α-mediated positive effects on parvalbumin interneurons are required for the antidepressant effects of running exercise[J]. Translational Psychiatry,2021,11(1):222 doi: 10.1038/s41398-021-01339-1
[127] LIU W N,LIU J T,HUANG Z C,et al. Possible role of GLP-1 in antidepressant effects of metformin and exercise in CUMS mice[J]. Journal of Affective Disorders,2019,246:486-497 doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2018.12.112
[128] LIU W N,LIU J T,XIA J,et al. Leptin receptor knockout-induced depression-like behaviors and attenuated antidepressant effects of exercise are associated with STAT3/SOCS3 signaling[J]. Brain,Behavior,and Immunity,2017,61:297-305
[129] 黄卓淳,漆正堂,刘微娜. 运动与褪黑素抗抑郁的作用、机制以及联合策略研究进展[J]. 中国体育科技,2020,56(2):3-14 [130] BASTIOLI G,ARNOLD J C,MANCINI M,et al. Voluntary exercise boosts striatal dopamine release:Evidence for the necessary and sufficient role of BDNF[J]. The Journal of Neuroscience,2022,42(23):4725-4736 doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2273-21.2022
[131] HOROWITZ A M,FAN X L,BIERI G,et al. Blood factors transfer beneficial effects of exercise on neurogenesis and cognition to the aged brain[J]. Science,2020,369(6500):167-173 doi: 10.1126/science.aaw2622
[132] CHEN K,ZHENG Y H,WEI J,et al. Exercise training improves motor skill learning via selective activation of mTOR[J]. Science Advances,2019,5(7):eaaw1888 doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aaw1888
[133] ZHANG W J,OU H N,ZHANG B R,et al. Treadmill exercise relieves chronic restraint stress-induced cognitive impairments in mice via activating protein phosphatase 2A[J]. Neuroscience Bulletin,2021,37(10):1487-1492 doi: 10.1007/s12264-021-00766-w
[134] 陈平,李刚强,周文辉. 谷氨酸受体在帕金森病中的作用及其介导的帕金森病运动防治研究进展[J]. 体育科学,2022,42(9):72-81 [135] 陈巍,魏翔,刘晓莉,等. 运动对PD模型大鼠皮层-纹状体Glu能神经传递的影响[J]. 北京体育大学学报,2015,38(2):61-66 [136] 时凯旋,刘晓莉,乔德才. 运动通过调节皮层-纹状体通路功能连接可塑性改善PD模型大鼠行为[J]. 体育科学,2020,40(6):49-58 [137] CHENG T,HUANG X D,HU X F,et al. Physical exercise rescues cocaine-evoked synaptic deficits in motor cortex[J]. Molecular Psychiatry,2021,26(11):6187-6197 doi: 10.1038/s41380-021-01336-2
[138] HE Y,MADEO G,LIANG Y,et al. A red nucleus-VTA glutamate pathway underlies exercise reward and the therapeutic effect of exercise on cocaine use[J]. Science Advances,2022,8(35):eabo1440 doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abo1440
[139] JUNG S,KIM Y,KIM M,et al. Exercise pills for drug addiction:Forced moderate endurance exercise inhibits methamphetamine-induced hyperactivity through the striatal glutamatergic signaling pathway in male sprague dawley rats[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2021,22(15):8203 doi: 10.3390/ijms22158203
[140] DONG Y G,GAN Y X,FU Y M,et al. Treadmill exercise training inhibits morphine CPP by reversing morphine effects on GABA neurotransmission in D2-MSNs of the accumbens-pallidal pathway in male mice[J]. Neuropsychopharmacology,2024,49(11):1700-1710 doi: 10.1038/s41386-024-01869-4
[141] LIANG X,LI R,WONG S H S,et al. The effects of exercise interventions on executive functions in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder:A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Sports Medicine,2022,52(1):75-88 doi: 10.1007/s40279-021-01545-3
[142] 朱笑彤,毕小羽,朱飞龙,等. ADHD学龄儿童动作协调能力与其核心症状的关系:基于执行功能的多重中介效应分析[J]. 体育科学,2023,43(7):65-73 [143] 杨孟超,金鹏,王德新,等. 运动改善注意缺陷多动障碍儿童执行功能和注意力的研究进展[J]. 体育科学,2022,42(5):77-87 [144] 苏余,张韧仁,何毅. 中等强度运动积极影响注意缺陷多动障碍儿童的问题行为及心率变异性研究[J]. 中国体育科技,2023,59(5):43-51 [145] ZHAO P T,CHEN K,ZHU G H,et al. Effects of aquatic exercise intervention on executive function and brain-derived neurotrophic factor of children with autism spectrum disorder[J]. Research in Developmental Disabilities,2024,150:104759 doi: 10.1016/j.ridd.2024.104759
[146] KING C,ROGERS L G,JANSEN J,et al. Adolescent treadmill exercise enhances hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) expression and improves cognition in autism-modeled rats[J]. Physiology & Behavior,2024,284:114638
[147] SIVAYOKAN B,KING C,MALI I,et al. Aerobic exercise improves cognitive flexibility and modulates regional volume changes in a rat model of autism[J]. Behavioural Brain Research,2024,471:115136 doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2024.115136
[148] RAHIMI R,AKHAVAN M M,KAMYAB K,et al. Maternal voluntary exercise ameliorates learning deficit in rat pups exposed,in utero,to valproic acid; role of BDNF and VEGF and their receptors[J]. Neuropeptides,2018,71:43-53 doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2018.06.006
[149] CHOI J W,HAN D H,KANG K D,et al. Aerobic exercise and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder:Brain research[J]. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise,2015,47(1):33-39 doi: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000000373
[150] TOSTA A,FONSECA A S,MESSEDER D,et al. Effects of gestational exercise on nociception,BDNF,and irisin levels in an animal model of ADHD[J]. Neuroscience,2024,543:37-48 doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2024.02.008
[151] JEONG H I,JI E S,KIM S H,et al. Treadmill exercise improves spatial learning ability by enhancing brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in the attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder rats[J]. Journal of Exercise Rehabilitation,2014,10(3):162-167 doi: 10.12965/jer.140111
[152] WAKEFIELD L,AGARWAL S,TANNER K. Preclinical models for drug discovery for metastatic disease[J]. Cell,2023,186(8):1792-1813 doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.02.026
[153] COLEY N,GIULIOLI C,AISEN P S,et al. Randomised controlled trials for the prevention of cognitive decline or dementia:A systematic review[J]. Ageing Research Reviews,2022,82:101777 doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2022.101777
[154] SALMERON B J. Heterogeneity exists in healthy populations as well as in neuropsychiatric disorders[J]. Biological Psychiatry. Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging,2021,6(5):501-502 doi: 10.1016/j.bpsc.2021.03.002
[155] SCHELTENS P,DE STROOPER B,KIVIPELTO M,et al. Alzheimer's disease[J]. Lancet,2021,397(10284):1577-1590 doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32205-4
[156] LU B,CHEN X,XAVIER CASTELLANOS F,et al. The power of many brains:Catalyzing neuropsychiatric discovery through open neuroimaging data and large-scale collaboration[J]. Science Bulletin,2024,69(10):1536-1555 doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2024.03.006
[157] MULAY A R,HWANG J,KIM D H. Microphysiological blood-brain barrier systems for disease modeling and drug development[J]. Advanced Healthcare Materials,2024,13(21):2303180 doi: 10.1002/adhm.202303180
[158] NANCE E,PUN S H,SAIGAL R,et al. Drug delivery to the central nervous system[J]. Nature Reviews. Materials,2022,7(4):314-331
[159] JUTHANI R,MADAJEWSKI B,YOO B,et al. Ultrasmall core-shell silica nanoparticles for precision drug delivery in a high-grade malignant brain tumor model[J]. Clinical Cancer Research,2020,26(1):147-158 doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-1834
[160] KAPLAN A L,CONFAIR D N,KIM K,et al. Bespoke library docking for 5-HT2A receptor agonists with antidepressant activity[J]. Nature,2022,610(7932):582-591 doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05258-z
[161] BRACHA S,JOHNSON H J,PRANCKEVICIUS N A,et al. Engineering Toxoplasma gondii secretion systems for intracellular delivery of multiple large therapeutic proteins to neurons[J]. Nature Microbiology,2024,9(8):2051-2072 doi: 10.1038/s41564-024-01750-6
[162] FAN W W,EVANS R M. Exercise mimetics:Impact on health and performance[J]. Cell Metabolism,2017,25(2):242-247 doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.10.022
[163] WRANN C D,WHITE J P,SALOGIANNNIS J,et al. Exercise induces hippocampal BDNF through a PGC-1α/FNDC5 pathway[J]. Cell Metabolism,2013,18(5):649-659 doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2013.09.008
[164] KOBILO T,YUAN C Y,VAN PRAAG H. Endurance factors improve hippocampal neurogenesis and spatial memory in mice[J]. Learning & Memory,2011,18(2):103-107
[165] CHAMBERLAIN S,GABRIEL H,STRITTMATTER W,et al. An exploratory phase Ⅱa study of the PPAR delta/gamma agonist T3D-959 assessing metabolic and cognitive function in subjects with mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease[J]. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease,2020,73(3):1085-1103 doi: 10.3233/JAD-190864




 下载:
下载: