“元宇宙与体育的未来” 笔谈
详细信息Academic Conversations on "Metaverse and the Future of Sports"
-
摘要:
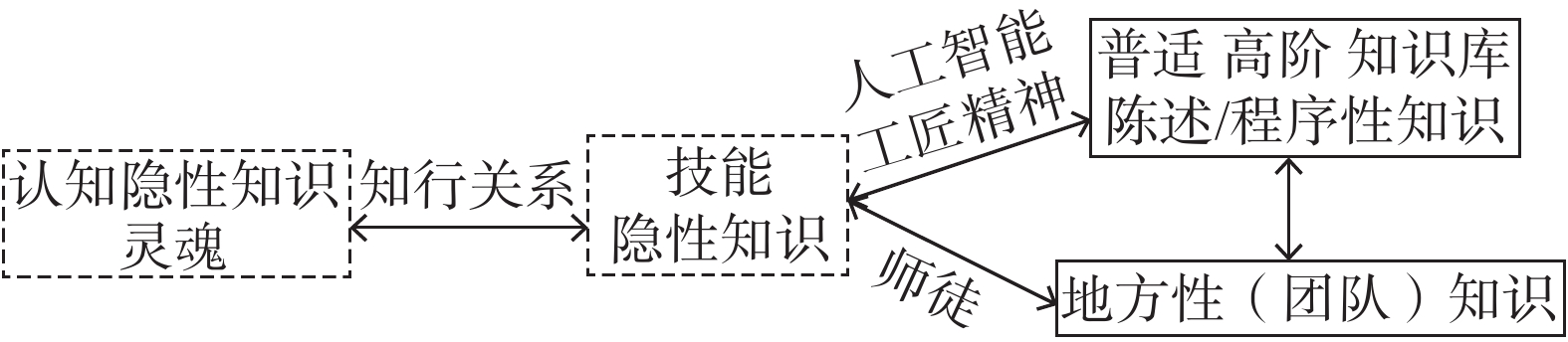
在元宇宙实践与理论探索日渐兴起,新技术不断加持体育发展的现实背景下,需要从多学科视角解构元宇宙与体育发展的关系。为此,本刊邀约不同学科的8名专家聚焦“元宇宙与体育的未来”这一主题展开学术讨论。江苏省体育科学研究所程志理编审认为,从生活世界现实感的存在一旦进入运动场域,人们在游戏状态中获得了乐趣。身体在场的游戏是自在自为的,玩者在行,观者投入。人因游戏而始,文化因游戏而生,体育挣脱了社会建构的价值预设就回到了“情本体”,因此,在游戏创造人的意义上体育的未来指向了元宇宙,体育成了不死的文化场。温州大学易剑东教授认为,人类文明是人的体力和智力综合作用的结果。奥林匹克运动追求身体、精神和意志均衡发展并融为一体,是人类发展的理性逻辑。元宇宙通过人机交互、算力整合等建构新世界,塑造体育新场景,但不能取代人类强化、美化、优化身体能力的文明追求。上海体育学院路云亭教授认为,元宇宙是虚拟实体,具有脑科学、生物进化以及升级版大数据的元素,它是自然科学与契约精神相融合的产物,带有个体体验性和专利制度约束下的创造性。科学具有独立的裁决意义,当今世界并非所有族裔共同体都接纳了科学,人们所理解的科学更多的是科学主义。与体育相比,元宇宙与游戏的关系更为紧密。华东师范大学张震副教授认为,元宇宙产生的脱域(dis-embedding)与离身(dis-embodying)将彻底改变以身体作为本体论的体育。目前体育元宇宙化的路径主要有脑机融合、意识上传和体感模拟,不同的技术路径将可能走向“25号宇宙”“The Play的体育”“后人类身体运动”三种未来。中国社会科学院段伟文教授认为,随着作为下一代数字技术愿景的元宇宙的发展,不仅将为人类主体构建符合主观期待或意愿的世界,还将成为虚拟化身、数字人等泛主体的生成空间。具有“自己生命”的虚拟影响者应运而生,将对运动认知与体育教育带来颠覆性的改变,给体育传播带来全新的机遇和挑战。东南大学吕乃基教授认为,体育运动是一种难以言表的技能隐性知识,既继承于哺乳动物,关系到莫拉维克悖论,也在于后天的训练。大数据有助于提升技能隐性知识并使之显性化,元宇宙提供形形色色的场景,虚拟吃一堑,现实长一智,区块链架起教练员、运动员和技术人员之间的桥梁,贯穿于其间的是体育精神和工匠精神。复旦大学徐英瑾教授认为,体育比赛的公平性主要建立在比赛双方软硬件条件的彼此对等上。元宇宙设备的加入可能会破坏这种对等,因为对于元宇宙设备内在性能的检测很可能会超出传统体育比赛组织方的能力范围,由此造成比赛结果的不公平。浙江大学王俊教授认为,元宇宙的实现有赖于主体沉浸,包括身体感在内的对于主体所处身的生活世界的感受构成了这种主体经验的基础。元宇宙只是生活世界的延伸,如果认为元宇宙可以取代生活世界、脱离身体有限性,最终只会导致主体行动能力退化、交往能力弱化、身体和生命经验边缘化等消极后果。
Abstract:In the context of the rising practice and theoretical exploration of metaverse and the continuous support of new technologies to the development of sports, it is necessary to deconstruct the relationship between metaverse and sports development from a multidisciplinary perspective. To this end, the journal invited 8 experts from different disciplines to focus on the theme of "Metaverse and the Future of Sports" for academic discussion. CHENG Zhili, editor of Jiangsu Research Institute of
Sports Science, believes that once entering the sports field from the existence of the sense of reality of the living world, people get fun in the state of the game. The game in which the body is present is self-contained with the player online and the viewer engaged in. People start from games and culture is born from games while sports break free from the value premise of social construction and return to the "emotion ontology". Therefore, in the sense of games to create people, the future of sports directs into the metaverse, and sports have become an immortal cultural field. Professor YI Jiandong of Wenzhou University believes that human civilization is the result of the comprehensive action of human physical strength and intelligence. The pursuit of balanced development and integration of the body, spirit and will of the Olympic Movement is the rational logic of human development. The metauniverse constructs a new world through human-computer interaction and computing power integration to shape new sports scenes, but it can not replace the civilization pursuit of human beings to strengthen, beautify and optimize physical abilities. Professor LU Yunting of Shanghai University of Sport believes that the metaverse is a virtual entity with elements of brain science, biological evolution and upgraded big data, which is the product of the integration of natural science and the spirit of contract with individual experience and creativity under the constraints of the patent system. Science has independent adjudication significance, and not all ethnic communities in the world today have embraced science, and people understand science more as scientism. Compared to sports, the metaverse is more closely related to games. ZHANG Zhen, an associate professor of East China Normal University, believes that the dis-embedding and dis-embodying produced by the metaverse will completely change the sports that use the body as an ontology. At present, the path of sports metacosmization mainly includes brain-computer fusion, consciousness upload and somatosensory simulation, and different technical paths will likely move towards the three futures of "25th Universe", "The Play's Sports" and "Post-human Body Movement". Professor DUAN Weiwen of Chinese Academy of Social Sciences believes that with the development of metaverse as the vision of the next generation of digital technology, it will not only build a world that meets subjective expectations or wishes for human subjects, but also become the generation space of pan-subjects such as virtual avatars and digital people. Virtual influencers with "their own lives" have come into being, which will bring subversive changes to sports cognition and physical education, and bring new opportunities and challenges to sports communication. Professor LYU Naiji of Southeast University believes that sport is an indescribable skill implicit knowledge, inherited from mammals, related to the Moravik's paradox, also in the acquired training. Big data helps to enhance the implicit knowledge of skills and make it explicit. The metaverse provides a variety of scenes and reality learns from virtual world. Blockchain builds a bridge between coaches, athletes and technicians, running through the spirit of sportsmanship and craftsmanship. Professor XU Yingjin of Fudan University believes that the fairness of sports competitions is mainly established on the reciprocity of the software and hardware conditions of both sides of the competition. The addition of metaverse devices may undermine this equivalence, because the detection of the intrinsic performance of metaverse devices is likely to exceed the capabilities of traditional sports organizers, resulting in unfair results. Professor WANG Jun of Zhejiang University believes that the realization of the metaverse depends on the immersion of the subject, and the feeling of the living world in which the subject is located, including the sense of body, constitutes the basis of this subject experience. The metaverse is only an extension of the living world, and if it is believed that the metaverse can replace the living world and detach it from the finiteness of the body, it will eventually only lead to negative consequences such as the degradation of the subject's ability to act, the weakening of the ability to communicate, and the marginalization of the body and life experience. -
Keywords:
- metaverse /
- game /
- sports /
- scientism /
- sports meta-cosmology /
- virtual influencers /
- Moravik's paradox /
- living world
-
体育研究以人为对象,具有生动的案例场景和鲜活、独特的样本特征。在体育领域采用案例研究往往聚焦于剖析某一体育组织、体育赛事等案例的过程、特征或路径等。然而,体育案例研究应基于中国体育制度、发展阶段、现实条件和改革壁垒等社会性因素,以及体育教学、科学训练和健康促进等生物性因素的具体情境,构建本土化理论体系。中国体育发展之路为构建本土化体育理论提供了坚实的基础。一方面,扎根中国体育现场作为体育案例研究的新视域。在研究过程中,因体育技能教学、体育赛事组织、训练计划制订、体育组织管理和体育技能评价等具有独特的学科特征,研究者应重视观察、参与、访谈、归纳、提炼和总结等实践性过程。依据案例研究“前因状况—事件·活动·选择—结果事件”的过程理论,采用目的性或理论性抽样的原则,遵循“什么人(Who)”“什么事(What)”“在哪里(Where)”“怎么样(How)”“为什么(Why)”的研究思路,以分析现实困境并与理论对话、综述文献并回顾研究现状、呈现案例并突出具体情境、分析理论并提出理论模型为研究框架,进行探索式或解释性案例分析,可探索运动训练、体育教学、体育管理、体育文化等领域所蕴含的理论。另一方面,构建中国体育理论成为体育案例研究的新目标。理论既是实践发展的指引,也是学术研究的目标。以国外体育或相关领域理论解释中国体育现象,通过训练指标检测评价训练质量,以及就体育社会现象进行表浅分析或成为当前我国体育领域研究的常态。体育案例研究应以学科知识为基础,深入体育教学、运动训练、体育竞赛、全民健身、体育管理等现场,按照“突出情景—展示过程—揭示关系”的分析逻辑,从指导科学系统的运动训练实践中提炼具有推广、示范价值的训练规律和方案,从源远流长的民族体育文化中挖掘体育文化传承、传播和传递的本质属性和路径等。显然,体育案例研究不同于自然和社会学科领域的案例研究,研究者身居其中从体育实践中了解那些不可被量化甚至难以察觉但影响重大的训练、教学、政策等社会性、生物性因素,阐释中国体育发展的历史地位和普遍意义,形成对中国本土体育实践发展具有指导性、推广性、复制性价值的成果。
1 ①本文中的体育指人类的一项活动,包括机构(如国际奥委会、国家体育总局、体校等)、制度,以及训练和比赛等全部活动。体育运动单指包括运动员和教练员在内的参与者在训练和参赛时身体的各种运动。 -
[1] 费孝通.乡土中国[M]. 上海: 上海人民出版社, 2007: 245 [2] 程志理.游戏论[M]//胡小明, 虞重干. 体育休闲娱乐理论与实践. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2004: 78 [3] 黑格尔.历史哲学[M]. 北京: 生活·读书·新知三联书店, 1956: 287-288 [4] 林德宏.人与机器: 高科技的本质与人文精神的复兴[M]. 南京: 江苏教育出版社, 1999 [5] 龙天启.体育哲学基础[M]. 北京: 北京体育学院出版社, 1989: 73 [6] 樊熙奇.“人格”与身体之谜: 评埃斯波西托《人与物: 从身体的视点出发》[EB/OL].[2022-01-27].https://www.sohu.com/a/369119755_813358 [7] 余凤高.解剖刀下的风景: 人体探索的背景文化[M]. 济南: 山东画报出版社, 2000: 351 [8] 奥尼尔.身体形态: 现代社会的五种身体[M]. 张旭春, 译. 沈阳: 春风文艺出版社, 1999: 119 [9] 稻见昌彦.超人诞生: 人类增强的新技术[M]. 谢严莉, 译. 杭州: 浙江大学出版社, 2018 [10] 易剑东.中国电子竞技十大问题辨识[J]. 体育学研究,2018,1(4):39 [11] 李玲蔚.夏季奥运会项目设置演变过程与发展趋势[J]. 北京体育大学学报,2008,31(1):37 [12] LEE L H,BRAUD T,ZHOU P,et al. All one needs to know about Metaverse:A complete survey on technological singularity,virtual ecosystem,and research agenda[J]. Journal of Latex Class Files,2021,14(8):1
[13] 蔡曙山.论人类认知的五个层级[J]. 学术界,2015(12):5-20 [14] 鲍捷.脱碳入硅: 不是人类被机器取代, 而是“人类社会”被“社会机器”取代[EB/OL]. [2022-03-26].http://36kr.com/p/5070536.html [15] 列维-布留尔.原始思维[M]. 丁由, 译. 北京: 商务印书馆, 2007 [16] 徐奕春.一部结构主义人类学的名著:列维-斯特劳斯著《野性的思维》[J]. 出版工作,1988(2):55-60 [17] 李幼蒸.列维-斯特劳斯《野性的思维》中译本新版序、跋[EB/OL]. [2022-03-27]http://www.semioticsli.com/li/a/xueshupiping/2011/0119/127.html [18] 经济学人集团.运动能力: 人类对AI的终极优势? [EB/OL]. [2022-03-27].http://weibo.com/ttarticle/p/show?id=2309404242527652819497 [19] 马克思, 恩格斯.马克思恩格斯全集: 第2卷[M]. 北京: 人民出版社, 1973: 163 [20] 吕乃基.论编码知识与隐性知识[J]. 长沙理工大学学报(社会科学版),2021(5):39-46 [21] 吕乃基.论“物质极大丰富”[J]. 科学技术与辩证法,2006(1):3-6 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7062.2006.01.002 [22] 梅洛-庞蒂.眼与心[M]. 杨大春, 译. 北京: 商务印书馆, 2007: 59 [23] 赫拉利.今日简史[M]. 林俊宏, 译. 北京: 中信出版社, 2018: 66 -
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 柳鸣毅,敬艳,孔年欣,尹子康,蔡静洁,彭李奥,郭成根. 体育案例研究的学理基础、基本要素与中国探索. 首都体育学院学报. 2024(01): 12-21 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 刘娟. 大学生体育核心素养数字化评价的内在价值、阻滞因素与应对策略. 吉林体育学院学报. 2024(03): 78-84 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 姬爱冬,焦润艺,董德河,韩松岩,宋雅芳,白东艳. 传统阴阳丹法养生术在鼓励生育背景下的医学伦理重塑及教学策略. 武当. 2023(06): 54-57 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)




 下载:
下载: