Impact of Physical Exercise on Adolescents' Academic Performance and its Mechanisms: An Empirical Analysis Based on China Education Panel Survey Data
-
摘要:目的 探讨体育锻炼对青少年学业表现的影响及其中介机制。方法 利用中国教育追踪调查2013—2015年的数据,采用面板分层线性模型考察体育锻炼对青少年学业表现的影响,并通过结构方程模型和KHB法检验可能存在的中介机制。结果 青少年每天的体育锻炼投入时间对其学业表现的影响呈倒U型曲线效应,每天体育锻炼时间45.6 min对学生文化课平均成绩的提升作用最大;多重中介效应分析结果显示,体育锻炼可通过降低负面情绪、增强同学间的互动、促进同学的积极行为、增强自信心等4种渠道提升青少年学业表现。结论 结果支持了前人提出的“积极效应说”,并非体育锻炼时间最多或极力压缩体育锻炼时间对学业表现收益最大,每天坚持合适剂量运动对青少年学业表现的促进效应最优。青少年的心理健康因子、同学积极行为、同学关系、对自己未来的信心是体育锻炼影响学业表现的重要中介机制,青少年BMI、每天睡眠时间等生理健康的中介机制效应未得到统计验证。Abstract: In order to explore the impact of physical exercise on adolescents' academic performance and its mechanisms, using the data from 2013 to 2015 China Education Panel Survey, the impact of physical exercise on adolescents' academic performance was examined by means of hierarchical linear model, and the influencing mechanisms between the two variables through structural equation model and KHB.It is found there is an inverted U-Shaped relationship between the time students spend on physical exercise and their academic performance, with its highest point when reaching 45.6 minutes of daily exercise.The result of multiple mediating effects analysis shows that physical exercise can improve students' academic performance through four mechanisms:reducing students' negative emotions, enhancing interactions among classmates, promoting positive behaviors and building self-confidence.Conclusions are drawn that these findings support the previous "positive effect theory"; persistent and appropriate daily exercise has the best effect on the students' academic performance rather than the largest or contracted time spent on daily exercise does.The students' psychological health, positive behaviour, classmate interaction and self-confidence become the important mediating machanism.The medating machanism of the other two variables including adolescents' BMI and daily average sleeping time are yet to be calculated and tested.
-
Keywords:
- adolescent /
- physical exercise /
- academic performance /
- mediating effect /
- education /
- health
-
1. 问题的提出
教育和健康是个体人力资本的重要组成部分[1],青少年时期是人力资本积累的关键阶段。然而,在中国应试教育的长期发展过程中,学校的教学多在围绕升学的“指挥棒”运转。学业表现和体育锻炼处于一种不平衡的矛盾关系之中,文化课在学校教学内容中始终居于主导地位,校方、家长和学生本人往往担心在非文化课上的投入会影响学业表现,因而压缩学生的体育锻炼时间,造成学生身体素质下降等问题。那么,体育锻炼对青少年学业表现有何影响?这些影响存在怎样的中介机制?这是本文探讨的两大问题。
国内外学者对此开展了大量研究,关于两者之间关系的理论解释大致可分为“积极效应说”“消极效应说”“无关说”等。然而,国外研究的社会背景不同于中国快速发展的国情,在当前中国城镇化快速推进的情况下,教育事业的东、中、西部地区差距依然存在,国外学者的理论解释在中国是否适用值得商榷。此外,在分析数据层面,学者们基本以神经医学、脑科学等方面的医疗数据、横向调查数据或实验数据为主,分析数据以小样本为主,因此不具有全国代表性,所得结论仅适用于特定地区。在实证方法层面,多数研究结论建立在体育锻炼与学业表现的相关关系之上,但这并不能证明二者存在因果关系。即使有学者[2]使用短期运动干预进行研究,但仍缺乏通过长期追踪数据所得的因果关系证据。在具体作用机制的探讨方面,多数研究者关于体育锻炼影响学业表现机制的考察比较单一。事实上,体育锻炼影响青少年学业表现的机制十分复杂。例如,国外研究者[3]提出了一个由肥胖等体质因素、睡眠质量等健康因素、自我效能感等心理因素构成的多种可能机制并存的理论模型。蒋莹等[4]首次将认知机制、社会心理机制、神经生理机制等三大机制整合到一个分析框架内,并对体育锻炼影响儿童学业表现的多层作用机制进行解释。但以青少年为研究对象的机制探讨还不充分,体育锻炼影响青少年学业表现的中介机制也需从多个方面进行揭示。
基于此,本文使用中国教育追踪调查(China Education Panel Survey,CEPS)数据,采用面板分层线性模型(Hierarchical Linear Model,HLM)对体育锻炼是否影响青少年不同学科的学业表现进行分析,并探讨可能存在的多种中介机制。与以往研究相比,本文创新之处在于:①以往研究所使用的数据存在样本规模小、代表性不足的问题,且以横向调查数据居多,相比之下,本文所使用的CEPS的2期数据,具有较好的全国代表性,且追踪数据可反映学生及其所在家庭和学校的信息变化,因此,可获得相对更为可靠的结论,进一步补充学界关于中国学生体育锻炼与学业表现关系的研究。②体育锻炼影响青少年学业表现的中介渠道研究相对单一,本文使用结构方程模型(Structural Equation Model,SEM)和KHB法(2012年由Karlson、Holm和Breen提出),首次从生理、心理健康等自然发展属性和同学关系、同伴效应等社会建构属性2个层面检验了体育锻炼影响青少年学业表现的中介路径。这不仅丰富了现有关于体育锻炼与学业表现关系及其影响机制的研究,也为完善体教融合政策、促进青少年健康发展提供了证据支持。
2. 文献综述及研究假设
2.1 体育锻炼与青少年学业表现的关系研究
体育与身体、教育获得的关系是体育人文社会学领域关注的经典议题,研究人员[5]从身体记忆、规训制度、身份互动、角色认同等角度开展了大量研究,且主要遵循社会建构和自然发展这2条分析路径[6]:前者关注身体如何被社会结构规训以及身体如何形塑社会关系;后者着重关注性别等自然属性差异对个体身体行为的影响。在体育锻炼与青少年学业表现的关系问题上,与公众对体育锻炼持有的消极看法不同的是,学界对二者关系以社会建构路径分析为主,但研究结论一直存在争议。国际上该领域的研究始于20世纪50年代,国内则最早始于20世纪80年代,经过半个多世纪的发展,这一领域已取得了丰硕的研究成果。笔者通过梳理相关文献,将对二者关系的研究大体归纳为以下3类:第1类研究对体育锻炼与青少年学业表现之间的关系持“正相关”立场[7],认为学生参加体育锻炼不仅对学业表现有积极效应[8],而且能提升认知能力[9]和记忆能力[10]。这种观点的理论基础是“唤醒理论”[11]和“认知神经科学理论”[12],且得到了来自脑成像等医学影像领域研究的证据支持[13-15]。Howie等[16]通过对2006—2011年发表的125篇论文的收集以及Busch等[17]通过梳理1992年以来关于体育锻炼与青少年学业表现关系的研究,均发现参加体育锻炼可提升青少年学业表现并为其带来其他积极收益。第2类研究对两者之间的关系持“不相关”或“弱相关”立场[18],该类研究并未发现体育锻炼促进青少年学业表现的证据[19]。第3类研究对两者之间的关系持“负相关”立场[20],该类研究发现体育锻炼对学生认知能力、阅读能力等学业表现有消极效应[21]。
总体而言,国内外不同学科的研究者所开展的关于体育锻炼与青少年学业表现的研究结论以第1类研究(“积极效应说”)为主,其内部又围绕体育锻炼时间的长短、不同维度的学业表现这2个问题继续争论。在体育锻炼时间方面,运动剂量对学业表现的影响效应一直存在争论:Siegel[22]的一项针对六年级学生的研究发现,每天20 min体育锻炼会对青少年学业表现产生显著促进作用;Budde等[23]的一项针对13~16岁中学生的研究发现,10 min的体育锻炼可改善学生的注意力水平;Chaddock-Heyman等[24]发现,每天至少60 min的体育锻炼可有效改善9~12岁青少年的抗干扰能力;傅建等[25]认为,1次30 min的短时中等强度体育锻炼对儿童学业表现的积极效应更显著。在学业表现方面,主要围绕不同学科、认知与非认知能力展开。Stevens等[26]认为,参加体育锻炼对学生数学成绩有显著积极影响,对阅读成绩无显著影响。这一结论在后续的研究[17, 27]中也得到了验证。然而,Castelli等[28]、Buck等[29]通过实验数据和调查数据发现,体育锻炼可有效促进青少年阅读能力的提升。
综上所述,运动剂量对青少年学业表现的影响可能存在1个阈值临界点,且该临界点可能会在学科方面有所差异。据此,提出研究假设1:体育锻炼对青少年的学业表现提升存在1个阈值效应,即低于阈值的体育锻炼对青少年学业表现存在促进效应,超出阈值的则存在消极效应。
2.2 体育锻炼影响学业表现的具体机制
关于体育锻炼通过哪些机制影响青少年学业表现的讨论也在不断丰富。早期的研究更关注生理机制这一作用渠道,如有学者[30-31]将肥胖、心肺能力等体质健康因素视为中介机制并进行了实证分析。但目前较多的研究将机制分析的重点聚焦在了心理因素上。项明强等[32]研究了自我实现型动机在体育锻炼和学生文化成绩之间的中介效应。周赞[33]分析了大学生体育锻炼如何通过提升个人自尊促进学业表现的,但上述研究机制均呈现相对单一化的特点。遵循体育科学主要从自然发展和社会建构2条路径考察体育锻炼对个体身心健康影响的分析模式,笔者认为,体育锻炼可能通过影响学生的生理和心理健康等自然发展路径以及同学关系、同伴效应等社会建构路径使学业表现发生变化。
(1)在生理健康方面,适度的体育锻炼作为一种燃脂和身体功能激活方式,可提升青少年身体素质。开展协调性锻炼可激活青少年大脑皮层特定位置,改善青少年的注意力水平[23],而不同强度的体育锻炼能改善青少年的脑激活模式和促进执行功能改变[34]。此外,基于智能可穿戴设备的研究[35]表明,适当的体育锻炼可有效改善青少年的睡眠质量,而睡眠质量与学业表现呈倒U型关系。在对儿童肥胖问题的研究方面:Grieco等[36]发现,学生体育锻炼通过影响学生的BMI,影响其学业表现;杨剑等[37]发现,体育锻炼的阶段变化特点可有效降低小学生的BMI,促进其学业表现。
(2)在心理健康方面,体育锻炼增加了个体与他人之间开展互动的机会和频率,影响了个体的心理健康。随着学习竞争愈发激烈,学业压力严重影响了青少年心理健康。根据应激源的类型和作用时间,学业压力对青少年心理健康的影响可能是轻微的干扰,也可能会诱发心理障碍和导致身体亚健康。体育锻炼作为一种实践过程,往往是群体行为,群体通过责任扩散可帮助学生有效释放学习和心理压力。青少年在体育锻炼中基于自身经验而形成的文化价值观念、学业状态等方面的交流,通过身体及其认知评价实现了对自身情绪的调节,并帮助自我摆脱消极情绪,促进学业表现提升。陈四光等[38]基于228名初中生的情绪调控研究发现,长期处于消极情绪状态会显著削弱青少年的学业表现和学习效能感;而通过体育锻炼形成的运动友谊可促进青少年的心理健康,提升学业表现[39]。
(3)在同学关系方面,青少年在体育锻炼过程中,通过身体和语言互动而获得同辈群体互动,满足了内群体归属需求。青少年积极参与体育锻炼,因与其他同学共享相同的交流象征符号而满足了与同辈群体成员进行互动的归属需求,缩短了与他人的心理距离,降低了疏离感。换言之,青少年通过体育锻炼可搜寻到与自己同质性程度较高的人,这种一致性的匹配有利于良好关系的开展和维持,并促进社会行为的发展。福柯的权力理论认为,规训的权力分散在社会各场域之中,现代生产社会对个体的监督和控制可能并不是通过强力压制的方式实现的,而是通过鼓励、激励等方式实现的[40]。因此,在体育锻炼过程中,青少年之间的信息交换和信息支持是一种具有激励功能的社会互动仪式。此外,参加体育锻炼还扩大了青少年的交友圈层,具有同样兴趣爱好的青少年交流各自所经历的不同生活体验和日常话语,增强了话语内容的交换并建构了良好的人际关系。张光珍等[41]发现,“负人缘关系”会恶化青少年的学业表现,友善的同学关系则会显著提升学业表现。
此外,处于义务教育阶段的青少年获得的社会支持,既有来自教师和家长的关怀支持,也有来自同学群体的社会支持。从社会互动角度看,体育锻炼作为一种互动仪式,具有投资功能,即体育锻炼可能不仅有助于青少年在活动中积累社会资本、调整情绪、促进身心健康,而且也可获得内群体的身份认同,促进学业表现。社会支持反映了个体获得的来自他人的社会资源,是个体社会资本的重要构成。黄谦等[42]发现,体育锻炼频率越高,个体的同学关系相对越好,个体社会资本也相对越高。青少年参加体育锻炼可帮助他们融入同辈群体之中,提升来自个人层面和集体层面的社会资本[43]。另有研究[44]表明,来自同学、朋友的社会支持能降低青少年的孤独感和社交焦虑,改善学业表现。因此,青少年参加体育锻炼可促进积极行为的传播,加强同学之间的交流、学习和相互鼓励,从而巩固学生在课堂上接受的知识并拓展知识获取来源,提升学业表现。根据上述分析,提出机制分析的研究假设2:青少年参加体育锻炼会促进其生理和心理健康、改善同学关系、增加同伴支持等,进而提升青少年的学业表现。
3. 数据、变量和实证模型
3.1 数据来源
本文所用数据为中国人民大学中国调查与数据中心设计并实施的CEPS。CEPS于2012年首次试调查,2013年开始全国范围调查,每年秋季学期和次年春季学期分别调查1次,目前已公布的数据有2013—2014学年和2014—2015学年的数据,该调查旨在揭示家庭、学校及社会结构对个人教育产出的影响。CEPS 2013—2014学年开展的首轮调查基线样本涵盖了全国28个县级单位(县、区、市),抽样框包括3个部分:第1个抽样框是在全国所有县级行政单位中随机抽取15个县的学校作为样本;第2个抽样框从上海市18个县区中随机抽取2个核心样本和1个流动人口县区的补充样本;第3个抽样框是从全国120个流动人口大县中随机抽取10个作为补充样本。在入选的28个抽样单位中随机抽取了112所学校438个班级进行调查,被抽取班级中七年级学生10 279人、九年级学生9 207人,入选学生全部进入调查样本[45]。项目组在2014—2015学年开展实施的第2轮调查以首轮调查为基础,追访了首轮调查的七年级学生(首轮调查九年级的学生为实验性测试样本,并未纳入第2轮调查范围)。第2轮调查成功追访9 449人,流失样本830人,新进样本471人。
在后续的实证分析中,本文使用2轮追踪的平衡面板数据进行实证分析:首先通过匹配2轮调查学生ID、班级ID、学校ID,将第2轮调查中参加首轮调查的学生性别、学校所在地区等数据与首轮调查匹配一致;然后通过剔除未成功追访到学生的数据、新增样本数据和首轮调查的九年级学生样本数据以及第2轮调查中存在的样本缺失值和重复值,构建2轮调查都参加的平衡面板数据,最后符合本文需要的样本为18 702(9 351×2)个。
3.2 变量介绍
因变量为语文成绩、数学成绩、英语成绩和3科平均成绩。CEPS首轮调查对青少年3科文化课成绩均采用了计算标准分的方式,即以70分为平均值、10分为标准差的分数。本文将第2轮调查得到的数据标准化为首轮调查的标准分形式。自变量为青少年体育锻炼时间,CEPS调查了学生每周平时和周末的锻炼小时数和分钟数,本文将其加总为一周锻炼分钟数,再计算每天锻炼的平均值,剔除异常值后,得到学生体育锻炼时间变量。考虑到体育锻炼对青少年学业表现的影响可能是非线性的,构建了体育锻炼时间平方项变量。
本文使用的控制变量涉及青少年个人(家庭)和学校2个层次。控制变量的选择参考了吴愈晓等[46]、杨宝琰等[47]对影响青少年学业表现的控制变量操作方法。个人(家庭)层次变量包括学生年龄、性别、是否本地户口、是否独生子女、教育期望、课业压力、家长自评的家庭经济地位、父母最高受教育年限、家庭藏书量等。学生年龄为连续变量;学生性别,男性=1,女性=0;是否为本地户口(显示了学生和家庭的迁移状态),户口在本县=1,不在本县=0;是否独生子女,是=1,否=0;教育期望是虚拟变量,有高等教育期望=1,无高等教育期望=0;课业压力采用3科学业压力分值加总形式,构成0~9分的连续变量,分值越大表示学生课业压力越大;CEPS同时调查了青少年自评的家庭经济地位和家长自评的家庭经济地位,由于青少年在法律上并非完全民事行为能力人,因此,本文采用家长自评的家庭经济地位作为家庭经济地位的代理变量;父母最高受教育年限是一个取值范围为[0, 22]的连续变量,2个端点值分别代表“文盲”和“博士”;家庭藏书量是家庭文化资本存量的重要指标,CEPS调查提供的答案及赋值方式为,很少=1,比较少=2,一般=3,比较多=4,很多=5。学校层次的变量包括学校性质、学校当地排名、学校设备资源、学校所在地区。学校性质为定序变量,公立学校=1,民办公助学校=2,普通民办学校=3,民办打工子弟学校=4;学校在本地的排名为定序变量,中等及以下=1,中上=2,最好=3。学校基础设施指学校拥有实验室、电脑室、音乐室、游泳池、图书馆、餐厅、心理咨询室、活动室、运动场等10项场馆设施得分,没有=1,有但需要改善=2,设备良好=3,加总后得到10~30分的连续变量;学校所在地区为分类变量,西部=1,中部=2,东部=3。
本文重点关注学生的生理健康、心理健康、同学关系、同伴效应等4个方面的中介机制。①测量生理健康机制的变量包括青少年BMI和每天睡眠时间。BMI的计算公式是:体质量(kg)/身高(m)2,且剔除了特别肥胖和特别瘦等离群值。睡眠变量是学生每天平均睡眠时间,剔除15 h、5 h等离群值。②测量心理健康机制的变量有2个:心理健康因子和对自己未来的信心。心理健康因子运用因子分析从反映青少年心理健康的4个指标(沮丧、抑郁、不快乐、悲伤)中提取的1个综合性指标,取值越高表示学生心理健康程度越低;青少年对自己未来的信心的赋值方式为,根本没信心=1,不太有信心=2,比较有信心=3,很有信心=4。③同学关系变量所对应的题项是“同学对学生本人非常友善”,答案赋值方式为,完全不同意=1,比较不同意=2,比较同意=3,完全同意=4。④使用同学校园行为的积极性程度测量同伴效应。关于同学积极行为变量,CEPS调查了青少年好朋友的积极行为和消极行为,前者包括学业表现良好、学习努力、想上大学等3类行为,后者包括旷课逃学、违纪处分、打架等7类行为,答案赋值方式为,没有这样=1,1到2个这样=2,很多这样=3,本文首先将消极行为进行逆算赋值,然后将10个行为得分加总后得到10~30分的连续变量。变量描述性统计结果如表 1所示。
表 1 青少年体育锻炼与学业表现变量的描述性统计结果Table 1. Descriptive statistics for all variables变量类型 变量名称 均值 标准差 最小值 最大值 自变量 锻炼时间 32.25 31.26 0 120 锻炼时间的平方 2 017.332 3 179.685 0 14 400 因变量 语文成绩 70.94 10.83 13.63 112.8 数学成绩 71.01 12.55 8.42 115.1 英语成绩 71.15 12.36 11.35 115.0 平均成绩 71.05 10.53 20.27 112.8 第1层次
控制变量年龄 14.650 0.999 12 16 性别 0.495 0.500 0 1 是否本地户口 0.815 0.388 0 1 是否独生子女 0.463 0.499 0 1 教育期望 0.683 0.465 0 1 课业压力 4.560 1.953 0 9 家庭经济地位 1.830 0.589 0 4 父母最高受教育年限 11.100 3.057 0 19 家庭藏书量 3.213 1.175 1 5 第2层次
控制变量学校性质 1.126 0.521 1 4 学校当地排名 2.087 0.640 1 3 学校设备资源 21.26 4.175 12 30 学校所在地区 1.668 0.823 1 3 机制变量 BMI 18.470 2.435 12 25 每天睡眠时间/min 483.00 61.450 360 659 心理健康因子 -0.045 0.970 -1.430 3.532 对自己未来的信心 3.220 0.693 1 4 同学关系 3.304 0.770 1 4 同学积极行为 27.520 2.709 10 30 3.3 实证模型
青少年的学业表现不仅受学校因素影响,还受个人和家庭因素影响,这意味着存在分层嵌套效应。虽然家庭不能嵌套于学校内,但本文考察的家庭藏书量、父母最高受教育年限等家庭层次变量最后都可投射到学生个人层次,且参考已有文献[45],本文设定了包含个人和学校2个层次的模型。这表明使用HLM方法对个人和学校层次变量间的关系进行检验是合适的。
本文实证检验采用Stata 16.0统计软件进行分析。在实证模型方面,采用平衡面板数据的两层线性随机截距模型方法,即首先要考虑学生个人特征变量是否导致了学生之间的成绩差异,然后再考虑学校特征变量是否也会影响校内青少年身体特征和心理文化特征与学业表现的关系,并将学校层次的变量均值作为估计结果的模型。使用平衡面板数据可较好地解决遗漏变量等问题导致的内生性问题。
HLM的第1层次为青少年个人层次。个人层次的系数可解释学生特征导致的学业表现差异,即个体效应差异,在学校k学习的学生i的学业表现模型具体形式如式(1)所示:
$$ {Y_{ij}} = {\beta _{0k}} + \mathop \sum \limits_{j = 1}^n {\beta _{jk}} \times {x_{ijk}} + {\varepsilon _{ik}} $$ (1) 其中:Yij为青少年学业表现标准化得分;n表示个体层次的解释变量个数;β0k是学校层次的第k个学校的特征对青少年学业表现的影响;xijk表示第i个青少年在第k个学校第j个个人特征变量上的值;βjk是xijk的估计系数;εik为个体层次的误差项。
HLM的第2层次为学校层次。该层次可解释不同学校层次特征对青少年学业表现造成的影响,也被称为“池塘效应”。实证模型具体形式如式(2)和(3)所示:
$$ {\beta _{0k}} = {\alpha _0} + \mathop \sum \limits_{q = 1}^n {\alpha _{0q}} \times {z_{qk}} + {\mu _{0k}} $$ (2) $$ {\beta _{kj}} = {\alpha _j} $$ (3) 其中:q表示学校层次的解释变量个数;α0为学校层次特征的常数项;zqk表示第k所学校q个变量的值;α0q是zqk的估计系数;μ0k为学校层次的残差,即学校的组效应,假定服从正态分布。
最后,本文将学校层次方程代入个人层次方程,得到HLM的完整组合模型,具体形式如式(4)所示:
$$ {Y_{ij}} = {\alpha _0} + \mathop \sum \limits_{t = 1}^q {\alpha _{0q}} \times {z_{qk}} + \mathop \sum \limits_{j = 1}^n {\alpha _{jk}} \times {x_{ijk}} + {\mu _{0k}} + {\varepsilon _{ik}} $$ (4) 4. 实证分析结果
4.1 基准回归结果
如表 2所示,学生体育锻炼时间对学业表现影响的估计结果,模型1是平衡面板数据HLM的估计结果,模型2~模型4为稳健性检验的估计结果。模型1~模型4的因变量分别是平均成绩、语文成绩、数学成绩及英语成绩。4个模型均将学生成绩的变异总方差分解为学生个体层次和学校层次,并估计2个层次的变量对青少年学业表现的影响,以及层1的变量与被解释变量之间的因果关系是否会随着层2变量特征的变化而变化。
表 2 体育锻炼对学生学业成绩影响效应的HLM估计Table 2. The HLM estimation of physical exercise time on students' academic performance变量类型 变量名称 模型1
平均成绩模型2
语文成绩模型3
数学成绩模型4
英语成绩解释变量 锻炼时间 0.050*** 0.049*** 0.050*** 0.052*** 锻炼时间的平方 -0.001*** -0.001*** -0.001*** -0.001*** 个人(家庭)层次 年龄 0.028 0.126* -0.042 -0.004 性别 -3.050*** -4.413*** -0.165 -4.615*** 是否本地户口 0.203 -0.009 0.153 0.446** 是否独生子女 5.763*** 4.690*** 6.571*** 6.054*** 教育期望 0.045 0.194*** -0.122 0.063 课业压力 1.644*** 1.252*** 1.765*** 1.916*** 家庭经济地位 -0.103 -0.177 -0.111 -0.005 父母最高受教育年限 0.101*** 0.098*** 0.082** 0.113*** 家庭藏书量 0.193 0.033 0.250 0.315* 学校层次 学校性质(参照项:公立学校) 民办公助学校 4.341 4.790 5.732* 2.762 普通民办学校 2.202 3.798 0.632 2.188 民办打工子弟学校 1.073 2.133 1.469 -0.558 学校排名(参照项:中等及以下) 中上 0.238 0.706* 0.607 2.044*** 最好 1.542*** 2.021*** 0.371 3.078*** 学校基础设施 0.101*** 0.074** 0.055 0.173*** 学校所在地区(参照项:西部) 中部 1.217* 2.156** 0.971 0.553 东部 1.897*** 2.101*** 1.310* 2.308*** 常数项 56.53*** 57.78*** 56.16*** 55.81*** 学生样本量 18 660 18 702 18 697 18 690 学校样本量 111 111 111 111 注:*表示P < 0.1,**表示P < 0.05,***表示P < 0.01。 (1)模型1显示,体育锻炼时间在1%水平显著为正,表明体育锻炼有助于提升青少年的学业表现。具体而言,体育锻炼每增加1 min,青少年学业表现可相应提高0.050个单位。然而,体育锻炼时间的平方项对学业表现在1%水平上显著为负,这说明体育锻炼时间对学业表现的影响呈倒U型曲线效应。此外,模型2~模型4的估计结果与模型1中的研究发现是一致的,即体育锻炼对学生单科成绩的影响是“先上升后下降”。具体而言,模型4的估计系数最大,模型2的估计系数最小,说明体育锻炼对英语成绩的积极效应最大,数学成绩次之,而对语文成绩的积极效应最小。上述结论不仅支持了已有文献中的“积极效应说”,且为学业表现的具体内容提供了更为细致的研究证据,假设1得到验证。
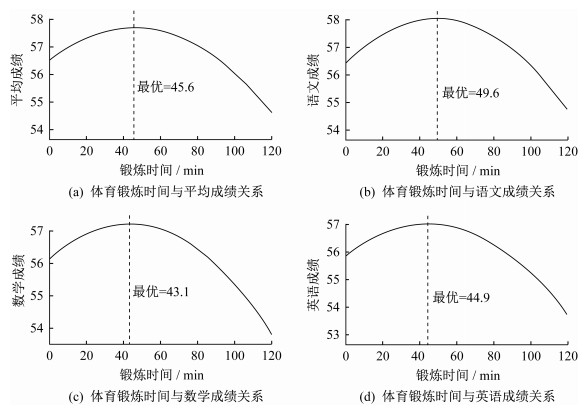
此外,关于体育锻炼最优时间的问题也是学界讨论的焦点[16]。本文分别将平均成绩、语文成绩、数学成绩、英语成绩作为被解释变量,体育锻炼时间及其平方项作为解释变量进行线性拟合分析,结果如图 1所示,体育锻炼时间影响语文成绩、数学成绩、英语成绩的时间顶点分别为49.6 min、43.1 min、44.9 min,影响平均成绩的时间顶点为45.6 min,即每天体育锻炼45.6 min对青少年学业表现的积极影响达到最大。
(2)从个人层次变量看,学生的年龄仅对语文成绩有显著影响,年龄每增加1岁,语文成绩提高0.126个单位。相比于女生,男生的学业表现较低,平均成绩、语文成绩和英语成绩分别低3.050、4.413、4.615个单位,且在1%统计水平上显著;但在数学成绩上,男女生并无显著差异。与非独生子女相比,独生子女的平均成绩和具体文化课学业表现均显著更高,后者的平均成绩比前者高5.763个单位,印证了“资源稀释理论”。与无高等教育期望的学生相比,有高等教育期望学生的语文成绩显著更高,英语和数学成绩无显著差异。家庭藏书量仅在10%统计水平上显著促进了学生的英语成绩,对语文成绩和数学成绩无显著影响。学生的课业压力在1%统计水平上显著提升了学业表现,课业压力每增加1个单位,平均成绩提高1.644个单位。父母最高受教育年限在1%统计水平上显著提升了青少年各科成绩。
(3)从学校层次变量特征看,与就读学校在本地排名中等及以下的学生相比,学校排名越高对学生成绩的促进效应越显著,就读于排名最好学校的学生平均成绩比前者高1.542个单位。在具体科目上,表现为英语和语文成绩更好,两者均在1%统计水平上显著成立。学校的基础设施资源越完善,青少年学业表现越好。与西部学校相比,东部学校的学生在文化课方面均在1%统计水平上影响显著,但中部学校对学生的语文成绩在5%统计水平上影响显著,在数学和英语成绩上与西部学校并无显著差异。综上所述,体育锻炼对青少年学业表现的影响呈倒U型曲线效应,并在45.6 min的位置达到最优状态,本文的分析结果支持了前人提出的“积极效应说”,假设1得到验证。
4.2 多重中介效应分析
体育锻炼对青少年学业表现的促进效应是通过哪些渠道进行的?本文对此进行了探索性分析。学界常用的机制分析方法是中介效应检验,本文首先采用KHB方法进行中介效应检验。KHB方法可较好地估计多个中介变量同时存在的效应,并计算间接效应的解释比例。模型设定的基本思路如下:①简约模型纳入解释变量和控制变量,汇报的是体育锻炼时间对青少年学业表现影响的总效应;②完整模型进一步加入了中介变量(BMI、每天睡眠时间、心理健康因子、对自己未来的信心、同学关系、同学积极行为),报告的是体育锻炼对学业表现影响的直接效应。2个效应的差值是本文主要关注的中介变量效应值。
如表 3所示,与简约模型的估计系数相比,加入中介变量的完整模型所估计的系数均在1%统计水平上显著降低,中介变量对青少年平均成绩的间接效应为0.038,间接效应的贡献率为20.11%,从表 3的Panel-B发现,同学积极行为变量的贡献率最大,为80.89%。总体而言,上述结果意味着本文关注学生的身心健康、同学关系、同伴效应等中介机制在体育锻炼对青少年学业表现影响的因果关系中发挥着重要作用。假设2得到部分验证。
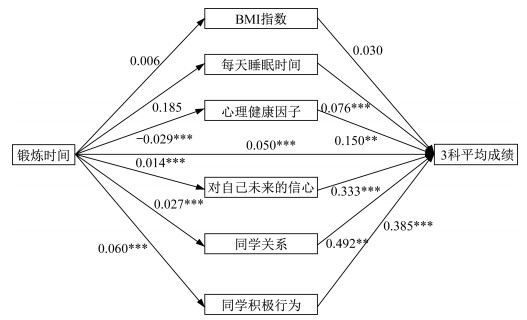
表 3 体育锻炼对学业表现影响效应的KHB中介效应估计Table 3. The KHB analysis of physical exercise on students' academic performancePanel-A 总效应 直接效应 间接效应 间接效应贡献率/% 0.189*** 0.151*** 0.038*** 20.106 Panel-B 中介变量 BMI 每天睡眠时间 心理健康因子 对自己未来的信心 同学关系 同学积极行为 各自的效应(贡献率/%) 0.62 -7.01 -23.12 25.59 23.02 80.89 注:***表示P < 0.01。 在具体的中介变量效应方面,本文进一步使用SEM,以平均成绩为被解释变量对上述可能的中介机制分别进行考察,结果如图 2所示。体育锻炼时间在1%统计水平上显著影响了其中4个中介变量,表明体育锻炼的增加可降低负面情绪、提高其对自己未来的信心、促使同学做出积极行为、使同学关系变得和谐友善。学生睡眠时间、对自己未来的信心、同学积极行为等均在1%统计水平上显著提升了学业表现,同学关系、心理健康因子在5%统计水平上显著提升了学业表现。以同学积极行为这一中介变量为例,总效应为0.050,直接效应为0.060×0.385=0.023,间接效应为0.050-0.023=0.027,间接效应在1%统计水平上显著,表明同学积极行为在学生体育锻炼和平均成绩的因果关系路径中发挥着重要作用。同理,心理健康因子、同学关系、对自己未来的信心等也是重要的中介机制。但学生的BMI和睡眠时间并不存在中介效应。假设2再次得到部分验证。
5. 结论与建议
青少年是国家的未来和民族的希望,而学校教育在青少年成长过程中发挥着不可替代的作用,是影响青少年发展质量的关键因素。本文采用CEPS 2013—2015共2个学年调查构成的平衡面板数据,采用HLM对青少年体育锻炼对学业表现影响的因果关系进行分析,并对其中可能的路径因素进行检验。结果显示:①青少年每天的体育锻炼投入时间对其学业表现的影响呈倒U型曲线效应,每天体育锻炼时间45.6 min对学生文化课平均成绩的提升作用最大,这一结果支持了前人提出的“积极效应说”。换言之,并非体育锻炼时间最多或极力压缩体育锻炼时间对青少年学业表现收益最大,反而是每天坚持合适剂量运动对青少年学业表现的促进效应最优。②心理健康因子、同学积极行为、同学关系、对自己未来的信心是体育锻炼影响青少年文化课成绩的重要中介机制,BMI、每天睡眠时间等生理健康因素的中介机制未得到统计验证。体育锻炼有效扩展了青少年的同学交往,增加了彼此的信息交流与互动,降低了消极情绪,强化了互帮互助利他行为的发生,同时在体育锻炼过程中也培养了青少年学业积极行为,这些机制因素都显著改善了青少年的学业表现。
上述发现对如何提升中国青少年的人力资本和推进体教融合的实施具有重要的政策意义。首先,对于学校层次而言:①学校应优化现有学科时间分配方式,保证学生每天适当的体育运动量,促进学业表现和身体健康共同发展,校方和教师在处理体育锻炼与学习的问题上可将开展学生体育锻炼作为提高青少年学业表现的可行途径,运用各种资源构建“文体并重”的校园文化,激发学生对体育锻炼的兴趣,养成勤于锻炼的习惯,以体促学、体学结合,全面提升青少年的发展质量,为中国青少年人力资本的积累创造坚实的人才基础;②学校应重视同辈亚文化对学生成长的重要影响,加强采取多种教学方式抑制不良行为的发生和蔓延,宣传同学之间的积极行为,创造友爱、互助、和谐的校风和学风,从而提高青少年的同辈支持,缓解青少年因学业压力产生的负面情绪等心理健康问题。其次,对于家庭而言,应让青少年参与合适剂量的运动,既要防止过度体育锻炼,又要杜绝完全压缩锻炼时间,在生活上要保证青少年的睡眠时间,注重对青少年心理健康的关注和自信心的培养,从而提升青少年的学业表现。最后,对青少年而言,在体育锻炼中应注重互帮互助等积极行为的培养,加强自信心,建立友善的同学关系等。
-
表 1 青少年体育锻炼与学业表现变量的描述性统计结果
Table 1 Descriptive statistics for all variables
变量类型 变量名称 均值 标准差 最小值 最大值 自变量 锻炼时间 32.25 31.26 0 120 锻炼时间的平方 2 017.332 3 179.685 0 14 400 因变量 语文成绩 70.94 10.83 13.63 112.8 数学成绩 71.01 12.55 8.42 115.1 英语成绩 71.15 12.36 11.35 115.0 平均成绩 71.05 10.53 20.27 112.8 第1层次
控制变量年龄 14.650 0.999 12 16 性别 0.495 0.500 0 1 是否本地户口 0.815 0.388 0 1 是否独生子女 0.463 0.499 0 1 教育期望 0.683 0.465 0 1 课业压力 4.560 1.953 0 9 家庭经济地位 1.830 0.589 0 4 父母最高受教育年限 11.100 3.057 0 19 家庭藏书量 3.213 1.175 1 5 第2层次
控制变量学校性质 1.126 0.521 1 4 学校当地排名 2.087 0.640 1 3 学校设备资源 21.26 4.175 12 30 学校所在地区 1.668 0.823 1 3 机制变量 BMI 18.470 2.435 12 25 每天睡眠时间/min 483.00 61.450 360 659 心理健康因子 -0.045 0.970 -1.430 3.532 对自己未来的信心 3.220 0.693 1 4 同学关系 3.304 0.770 1 4 同学积极行为 27.520 2.709 10 30 表 2 体育锻炼对学生学业成绩影响效应的HLM估计
Table 2 The HLM estimation of physical exercise time on students' academic performance
变量类型 变量名称 模型1
平均成绩模型2
语文成绩模型3
数学成绩模型4
英语成绩解释变量 锻炼时间 0.050*** 0.049*** 0.050*** 0.052*** 锻炼时间的平方 -0.001*** -0.001*** -0.001*** -0.001*** 个人(家庭)层次 年龄 0.028 0.126* -0.042 -0.004 性别 -3.050*** -4.413*** -0.165 -4.615*** 是否本地户口 0.203 -0.009 0.153 0.446** 是否独生子女 5.763*** 4.690*** 6.571*** 6.054*** 教育期望 0.045 0.194*** -0.122 0.063 课业压力 1.644*** 1.252*** 1.765*** 1.916*** 家庭经济地位 -0.103 -0.177 -0.111 -0.005 父母最高受教育年限 0.101*** 0.098*** 0.082** 0.113*** 家庭藏书量 0.193 0.033 0.250 0.315* 学校层次 学校性质(参照项:公立学校) 民办公助学校 4.341 4.790 5.732* 2.762 普通民办学校 2.202 3.798 0.632 2.188 民办打工子弟学校 1.073 2.133 1.469 -0.558 学校排名(参照项:中等及以下) 中上 0.238 0.706* 0.607 2.044*** 最好 1.542*** 2.021*** 0.371 3.078*** 学校基础设施 0.101*** 0.074** 0.055 0.173*** 学校所在地区(参照项:西部) 中部 1.217* 2.156** 0.971 0.553 东部 1.897*** 2.101*** 1.310* 2.308*** 常数项 56.53*** 57.78*** 56.16*** 55.81*** 学生样本量 18 660 18 702 18 697 18 690 学校样本量 111 111 111 111 注:*表示P < 0.1,**表示P < 0.05,***表示P < 0.01。 表 3 体育锻炼对学业表现影响效应的KHB中介效应估计
Table 3 The KHB analysis of physical exercise on students' academic performance
Panel-A 总效应 直接效应 间接效应 间接效应贡献率/% 0.189*** 0.151*** 0.038*** 20.106 Panel-B 中介变量 BMI 每天睡眠时间 心理健康因子 对自己未来的信心 同学关系 同学积极行为 各自的效应(贡献率/%) 0.62 -7.01 -23.12 25.59 23.02 80.89 注:***表示P < 0.01。 -
[1] BLEAKLEY H. Health, human capital, and development[J]. Annual Review of Economics, 2010, 2(1):283-310 doi: 10.1146/annurev.economics.102308.124436
[2] 殷恒婵, 陈爱国, 马铮, 等.两种运动干预方案对小学生执行功能影响的追踪研究[J].体育科学, 2014, 34(3):24-28 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TYKX201403003.htm [3] TOMPOROWSKI P D, LAMBOURNE K, OKUMURA M S.Physical activity interventions and children's mental function:An introduction and overview[J]. Preventive Medicine, 2011, 521:S3-S9
[4] 蒋莹, 杨玉冰, 邢淑芬.体育运动促进儿童学业成就及其作用机制研究进展述评[J].体育学刊, 2016, 23(5):86-92 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7116.2016.05.015 [5] BILLINGS A C. Routledge handbook of sport and new media[M]. New York:Routledge Press, 2014:374
[6] 高昕.权力规训视域下的健身实践:以健身房为例[J].中国青年研究, 2019(12):30-36 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGQL201912005.htm [7] MESQUITA I, FARIAS C, HASTIE P. The impact of a hybrid sport education-invasion games competence model soccer unit on students' decision making, skill execution and overall game performance[J].European Physical Education Review, 2012, 18(2):205-219 doi: 10.1177/1356336X12440027
[8] DAVIS C L, COOPER S. Fitness, fatness, cognition, behavior, and academic achievement among overweight children:Do cross-sectional associations correspond to exercise trial outcomes?[J]. Preventive Medicine, 2011, 521:S65-S69
[9] 温煦.体育锻炼对青少年认知能力和学业表现的影响:研究的历史、现状与未来[J].体育科学, 2015, 35(3):73-82 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-677X.2015.03.010 [10] MOEIJES J, BUSSCHBACH J TVAN, FORTUIN B, et al.Sports participation and psychosocial health in elementary school children[J].Health Behavior And Policy Review, 2017, 4(6):582-592 doi: 10.14485/HBPR.4.6.8
[11] PESCE C, CROVA C, CEREATTi L, et al.Physical activity and mental performance in preadolescents:Effects of acute exercise on free-recall memory[J]. Mental Health & Physical Activity, 2009, 2(1):16-22
[12] FISCHER K W, DANIEL D B, IMMORDINO-YANG M H, et al.Why mind, brain, and education? Why now?[J]. Mind Brain and Education, 2007, 1(1):1-2 doi: 10.1111/j.1751-228X.2007.00006.x
[13] 鞠恩霞, 李红, 龙长权, 等.基于神经成像技术的青少年大脑发育研究[J].心理科学进展, 2010, 18(6):907-913 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XLXD201006008.htm [14] 魏高峡, 李佑发. 21世纪中国运动心理学的新方向:运动认知神经科学研究[J].体育科学, 2012, 32(1):54-63 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-677X.2012.01.007 [15] KRAFFT C E, SCHWARZ N F, CHI L, et al. An 8-month randomized controlled exercise trial alters brain activation during cognitive tasks in overweight children[J]. Obesity, 2014, 22(1):232-242 doi: 10.1002/oby.20518
[16] HOWIE E K, PATE R R.Physical activity and academic achievement in children:A historical perspective[J]. Journal of Sport and Health Science, 2012, 1(3):160-169 doi: 10.1016/j.jshs.2012.09.003
[17] BUSCH V, LOYEN A, LODDER M, et al. The effects of adolescent health-related behavior on academic performance:A systematic review of the longitudinal evidence[J]. Review of Educational Research, 2014, 84(2):245-274 doi: 10.3102/0034654313518441
[18] DWYER T, COONAN W E, LEITCH D R, et al. An investigation of the effects of daily physical-activity on the health of primary-school students in south-Australia[J]. International Journal of Epidemiology, 1983, 12(3):308-313 doi: 10.1093/ije/12.3.308
[19] TOMPOROWSKI P D, DAVIS C L, MILLER P H, et al. Exercise and children's intelligence, cognition, and academic achievement[J].Educational Psychology Review, 2008, 20(2):111-131 doi: 10.1007/s10648-007-9057-0
[20] TREMBLAY M S, INMAN J W, WILLMS J D.The relationship between physical activity, self-esteem, and academic achievement in 12-year-old children[J]. Pediatric Exercise Science, 2000, 12(3):12-323
[21] CARLSON S A, FULTON J E, LEE S M, et al. Physical education and academic achievement in elementary school:Data from the early childhood longitudinal study[J].American Journal of Public Health, 2008, 98(4):721-727 doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2007.117176
[22] SIEGEL E D.Relating physical education and activity levels to academic achievement in children[J]. Journal of Physical Education Recreation & Dance, 2007, 78(1):10
[23] BUDDE H, VOELCKER-REHAGE C, PIETRASSYK-KENDZIORRA S, et al.Acute coordinative exercise improves attentional performance in adolescents[J]. Neuroscience Letters, 2008, 441(2):219-223 doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2008.06.024
[24] CHADDOCK-HEYMAN L, HILLMAN C H, COHEN N J, et al.The importance of physical activity and aerobic fitness for cognitive control and memory in children[J]. Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development, 2014, 79(4):25-50 doi: 10.1111/mono.12129
[25] 傅建, 刘思良.不同时间中-大强度体育锻炼对初中生学习自控力及学业成绩影响的实验研究[J].体育与科学, 2018, 39(1):114-120 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TYYK201801017.htm [26] STEVENS T A, TO Y, STEVENSON S J, et al.The importance of physical activity and physical education in the prediction of academic achievement[J].Journal of Sport Behavior, 2008, 4(31):368-388
[27] LAMBOURNE K, HANSEN D M, SZABO A N, et al. Indirect and direct relations between aerobic fitness, physical activity, and academic achievement in elementary school students[J].Mental Health and Physical Activity, 2013, 6(3SI):165-171
[28] CASTELLI D M, HILLMAN C H, BUCK S M, et al. Physical fitness and academic achievement in third- and fifth-grade students[J].Journal of Sport & Exercise Psychology, 2007, 29(2):239-252
[29] BUCK S M, HILLMAN C H, CASTELLI D M.The relation of aerobic fitness to stroop task performance in preadolescent children[J].Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise, 2008, 40(1):166-172
[30] LI Y, DAI Q, JACKSON J C, et al.Overweight is associated with decreased cognitive functioning among school-age children and adolescents[J].Obesity, 2008, 16(8):1809-1815 doi: 10.1038/oby.2008.296
[31] YU Z B, HAN S P, CAO X G, et al.Intelligence in relation to obesity:A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Obesity Reviews, 2010, 11(9):656-670 doi: 10.1111/j.1467-789X.2009.00656.x
[32] 项明强, 胡敏.青少年体育锻炼与心理幸福感的关系:实现型动机的调节作用[J].广州体育学院学报, 2016, 36(3):12-16 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-323X.2016.03.004 [33] 周赞.体育锻炼与大学生学业成就的关系:自尊的中介效应[J].浙江体育科学, 2018, 40(3):84-89 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3624.2018.03.019 [34] 陈爱国, 席嘉辰, 殷恒婵, 等.功能磁共振成像技术及其在运动心理学研究中的应用[J].中国运动医学杂志, 2011, 30(5):486-490 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YDYX201105021.htm [35] 刘娜, 沈亚茹.睡眠时间视角下我国初中生学业表现的城乡差异研究:基于CEPS面板数据的实证[J].中国人民大学教育学刊, 2019(1):160-180 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RDXK201901014.htm [36] GRIECO L A, JOWERS E M, BARTHOLOMEW J B. Physically active academic lessons and time on task:The moderating effect of body mass index[J].Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 2009, 41(10):1921-1926 doi: 10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181a61495
[37] 杨剑, 季浏, 杨文礼, 等.基于体育锻炼的阶段变化模型干预对肥胖小学生自我效能、自尊及体重影响的研究[J].天津体育学院学报, 2014, 29(3):185-189 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0000.2014.03.001 [38] 陈四光, 余仙平, 朱荣, 等.初中学生情绪调控策略与学业自我效能感、学习成绩关系的研究[J].教育学术月刊, 2015(10):53-57 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANG201510009.htm [39] 杨剑, 王韶君, 季浏, 等.中学生运动友谊质量、体育锻炼行为与心理健康关系模型构建[J].沈阳体育学院学报, 2013, 32(4):9-13 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0560.2013.04.003 [40] 唐军, 谢子龙.移动互联时代的规训与区分:对健身实践的社会学考察[J].社会学研究, 2019, 34(1):29-56 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHXJ201901002.htm [41] 张光珍, 梁宗保, 邓慧华, 等.学校氛围与青少年学校适应:一项追踪研究[J].心理发展与教育, 2014, 30(4):371-379 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XLFZ201404005.htm [42] 黄谦, 张晓丽, 葛小雨.体育参与促进社会资本生成的路径和方式:基于2014年《中国家庭追踪调查》数据的实证分析[J].中国体育科技, 2019, 55(7):63-70 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTY201907008.htm [43] 张晓丽, 雷鸣, 黄谦.体育锻炼能提升社会资本吗?:基于2014 JSNET调查数据的实证分析[J].上海体育学院学报, 2019, 43(3):76-84 http://www.styb.cbpt.cnki.net/WKE/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=8126d642-87d0-45d0-a905-033e1fdc2439 [44] 王晖, 熊昱可, 刘霞.亲子关系和朋友支持对流动儿童情绪和行为适应的保护作用[J].心理发展与教育, 2018, 34(5):614-624 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XLFZ201805012.htm [45] 张云亮.亲子互动、学校资源与学生教育期望:基于"中国教育追踪调查"的异质性分析[J].青年研究, 2018(2):46-56 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QNYJ201802005.htm [46] 吴愈晓, 黄超.基础教育中的学校阶层分割与学生教育期望[J].中国社会科学, 2016(4):111-134 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSHK201604007.htm [47] 杨宝琰, 万明钢.父亲受教育程度和经济资本如何影响学业成绩:基于中介效应和调节效应的分析[J].北京大学教育评论, 2015, 13(2):127-145 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJPL201502012.htm -
期刊类型引用(19)
1. 彭冲,钟辉勇. 消费的生产性与中国经济增长的新动能. 学术月刊. 2025(02): 56-66 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 卢琦. 初中生体育锻炼与学习成绩的关系及非认知能力的中介作用. 冰雪体育创新研究. 2024(07): 89-91 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 田浩然,崔盛. “双减”政策背景下学校体育的促学效应及其公平性探讨. 中国人民大学教育学刊. 2024(04): 166-180 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 冯沁雪,王严淞,马莉萍. 高三学生体育锻炼特点及其与高考成绩关系的实证研究. 教育学报. 2024(03): 167-181 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 陆宇榕,张伊弛,周伟楠. 网络欺凌对高中生负面情绪及学业倦怠的影响:体育锻炼投入的调节中介效应. 现代基础教育研究. 2024(03): 54-62 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 吴进,李利强,杨宇航. 家校合作对初中生体育锻炼的影响——基于CEPS数据的实证研究. 吉林体育学院学报. 2023(01): 15-23 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 张心悦,韩西丽,孙贵博,张运崇. 儿童放学后户外活动场地偏好及中高强度体力活动的影响因素. 现代城市研究. 2023(05): 14-21 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 杨中亚,刘龙飞,张龙,王继,彭杰. 体育锻炼对亚高原地区初中生心理健康影响实证研究——以贵州省六盘水市为例. 六盘水师范学院学报. 2023(04): 76-86 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 章文,张浩帆,张卫平,孙波,陈晓雷,王玉秀. 高三、大一学生生活方式因素与心理健康关系的研究. 浙江体育科学. 2023(06): 64-70 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 丁小燕,洪平. 后疫情时期:学校体育对农村中小学生体育锻炼行为的影响研究. 安徽体育科技. 2023(05): 93-98 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 钟泽. 体育锻炼对青少年心理健康水平影响及其中介机制的实证分析. 吉林体育学院学报. 2022(01): 77-84 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 马超,石振国,王先亮,田玉戈. 体育活动与幸福感的互促互进:基于大学生同伴关系与自我认知的中介效应. 中国健康心理学杂志. 2022(06): 893-899 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 程韵枫. 我国大学生锻炼心理需求满足感的测量与特征研究. 广州体育学院学报. 2022(02): 87-97 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 孟祥波,刘红建. 我国青少年体质健康促进的现实困境与突破. 南京体育学院学报. 2022(07): 15-20 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 乔玉成. 体育何以能够提升学业成绩——脑神经科学解释框架. 沈阳体育学院学报. 2022(04): 43-49 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 成刚,陈瑾,张田书. 青少年体重影响因素研究——基于中国教育追踪调查的实证分析. 教育学术月刊. 2022(07): 74-83 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. 胡德刚,张吾龙. 课外体育锻炼对初中生学业表现的影响——基于CEPS调查数据的实证分析. 福建体育科技. 2022(05): 71-76 .  百度学术
百度学术
18. 黄璐,刘波. 体育锻炼作为教育惩戒手段的合理性与实施策略研究. 河北体育学院学报. 2022(06): 57-66 .  百度学术
百度学术
19. 陈萱,朱从庆. 社区体育环境对青少年余暇体育锻炼的影响:邻里关系、内部动机的多重中介效应. 中国体育科技. 2022(12): 57-64 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(26)




 下载:
下载: