Aerodynamic Drag Reduction Effect of Drafting Formation in Race Walking Based on Wind Tunnel Tests
-
摘要:目的 探讨不同编队位置对核心运动员气动阻力的影响以及与单人竞走情况相比的气动减阻效果,并量化评估不同编队策略对竞走成绩的影响。方法 选取由不同国家队竞走运动员人数组成的编队模拟不同竞走场景,通过风洞试验获取不同编队位置核心运动员的气动阻力。风洞试验内容包括核心运动员单人测试、双人编队测试、3人编队测试、4人编队测试。结果 与单人竞走情况相比,双人编队中核心运动员位于辅助运动员的正后方时气动阻力减小最为明显,减阻率可达64.9%,此编队站位为相对最佳双人编队;3人编队中核心运动员位于其他2名辅助运动员沿着运动方向连线的中间时气动阻力减小最为明显,减阻率可达79.9%,此编队站位为相对最佳3人编队;4人编队中核心运动员位于其他3名辅助运动员组成的V型编队的正后方时气动阻力减小最为明显,减阻率可达83.8%,此编队站位为相对最佳4人编队。在50 km竞走比赛中,与单人竞走成绩相比,若采用相对最佳双人编队策略,比赛成绩将至少提升约3.89%;若采用相对最佳3人编队策略,比赛成绩将至少提升约4.79%;若采用相对最佳4人编队策略,比赛成绩将至少提升约5.03%。结论 不同编队位置下竞走项目核心运动员的气动减阻效应存在一定差异,研究不同编队的气动减阻效应能为减小核心运动员气动阻力、优化能量分配、改进团队协作策略、提高运动成绩提供重要的科学指导。Abstract:Objectives To determine the influences of different drafting formations on the core athlete's aerodynamic drag as well as the drag reduction effects compared to individual race walking conditions, and to quantify the effects of different drafting formation strategies on race walking performance.Methods Drafting formations composed of different elite race walkers were used to simulate different race walking scenarios, and the core athlete's aerodynamic drag in different formations positions was obtained by wind tunnel tests, including individual, two-athlete, three-athlete and four-athlete drafting formation tests, respectively.Results Compared to individual race walking situations, when the core athlete was located directly behind the auxiliary athlete, his aerodynamic drag reduced most obviously with the reduction rate of 64.9%, which could be the optimal two-athlete drafting formation. When the core athlete was located in the middle part of the line while the other two auxiliary athletes moved along, his aerodynamic drag reduced most obviously with the reduction rate of 79.9%, the position of which is relatively optimal; While when the core athlete was located directly at the rear of the Type V formation of three other auxiliary athletes, his aerodynamic drag reduced most obviously with the reduction rate of 83.8% as the optimal four-athlete drafting formation. In the 50 km race walking, compared to the individual race walking, the two-athlete's result would be improved approximately by at least 3.89% with the optimal drafting formation strategy; similarly, the result for three-athlete drafting formation would be improved by 4.79%, and the result for four-athlete, 5.03%.Conclusions There exist differences of aerodynamic drag reduction effects for race walking core athletes in different drafting formation positions. Related research can provide important scientific guidance for reducing aerodynamic drag for core athletes, optimizing energy distribution, improving teamwork strategies and athletic performance.
-
Keywords:
- race walking /
- wind tunnel test /
- drafting formation /
- aerodynamic drag /
- drag reduction
-
在有其他运动员参与同场竞速或计时的大多数运动项目中,运动员移动时需全力对抗周围的流体(如水或空气)产生的阻力,该阻力往往具有至关重要的作用。因此,在竞速或计时运动和赛车运动项目中,利用其他运动员或车辆的存在减轻流体阻力,已成为一种常见的竞技策略。如编队利用前面的运动员或车辆的尾流,在尾流中不仅流体速度大大降低,而且有一个产生抽吸力效应的负压系数,这均有利于后面的运动员或车辆获取优异成绩[1-2]。
编队策略广泛应用于自行车[3-9]、公开水域游泳[10]、短道速滑[11-12]、速度滑冰[13-14]、越野滑雪[15-16]和铁人三项[17-19]等运动项目。同样,跑步编队是大多数田径项目(如马拉松)中所采用的一种关键策略,在此类运动过程中,一名运动员在一名或多名领跑运动员后面的适当位置跟跑,既可减少因维持监控配速导致的精神压力[20],又可节约能量消耗,而在编队策略上只要保持适当位置,就可以大大降低气动阻力[18,21-25]。Kyle[21]研究发现,中长跑运动员在队伍后面时能量消耗下降约2%~4%,这也使得他们的跑步速度能够提升约0.1 m/s。Zouhal等[18]以10名精英运动员(elite athlete)作为样本评估了编队对3000 m跑表现的影响,发现位于2名领跑者后面的运动员比领先的运动员快1.59%,相当于获得的平均时间增益为8.85 s。Beaumont等[23]研究了一名国际级水准中长跑运动员(international level middle-distance runner)在次最大跑步运动(速度比项目最快速度低一些的跑步运动)中空气动力学参数与生理反应之间的关系,该运动员在室内跑道上以5.83 m/s的速度单独或以位于2名领跑者后面的编队形式跑1000 m,发现与单独跑步相比,在2名领跑者的空气动力学护罩(aerodynamic shadow)下其正面风阻面积降低33%,从而使得耗氧量下降6%、心率降低1%、能量消耗降低33%。目前,越来越多的研究想要努力减少运动员的气动阻力,特别是试图打破2 h内完成马拉松长跑的难关。Polidori等[24]应用计算流体力学(Computational Fluid Dynamics,CFD)计算了运动员贝克勒在参加柏林马拉松赛和使用协作编队策略比赛时的阻力和能量消耗功率节省情况,发现与单独跑步相比,在距离领跑者1.3 m跑步的理想情况下,可减少高达57.3%的抗气动阻力功率。
截至2021年8月,尚未发现从空气动力学角度来研究竞走运动员编队气动减阻效应的相关报道。本文通过国内首个体育综合训练风洞试验室开展竞走项目编队试验,选取由不同竞走运动员人数组成的编队来模拟在一定的竞走速度和逆风环境下不同的竞走场景,通过风洞测试获取不同编队位置中核心运动员的气动阻力,探讨与核心运动员单独竞走相比不同编队位置对气动阻力的影响,并基于测试结果讨论不同编队策略对竞走成绩的影响,以期为进一步明确竞走项目编队气动减阻效应提供支撑,也为减小核心运动员气动阻力、优化能量分配、改进团队协作策略、提高运动成绩提供科学指导。
1. 研究对象与方法
1.1 研究对象
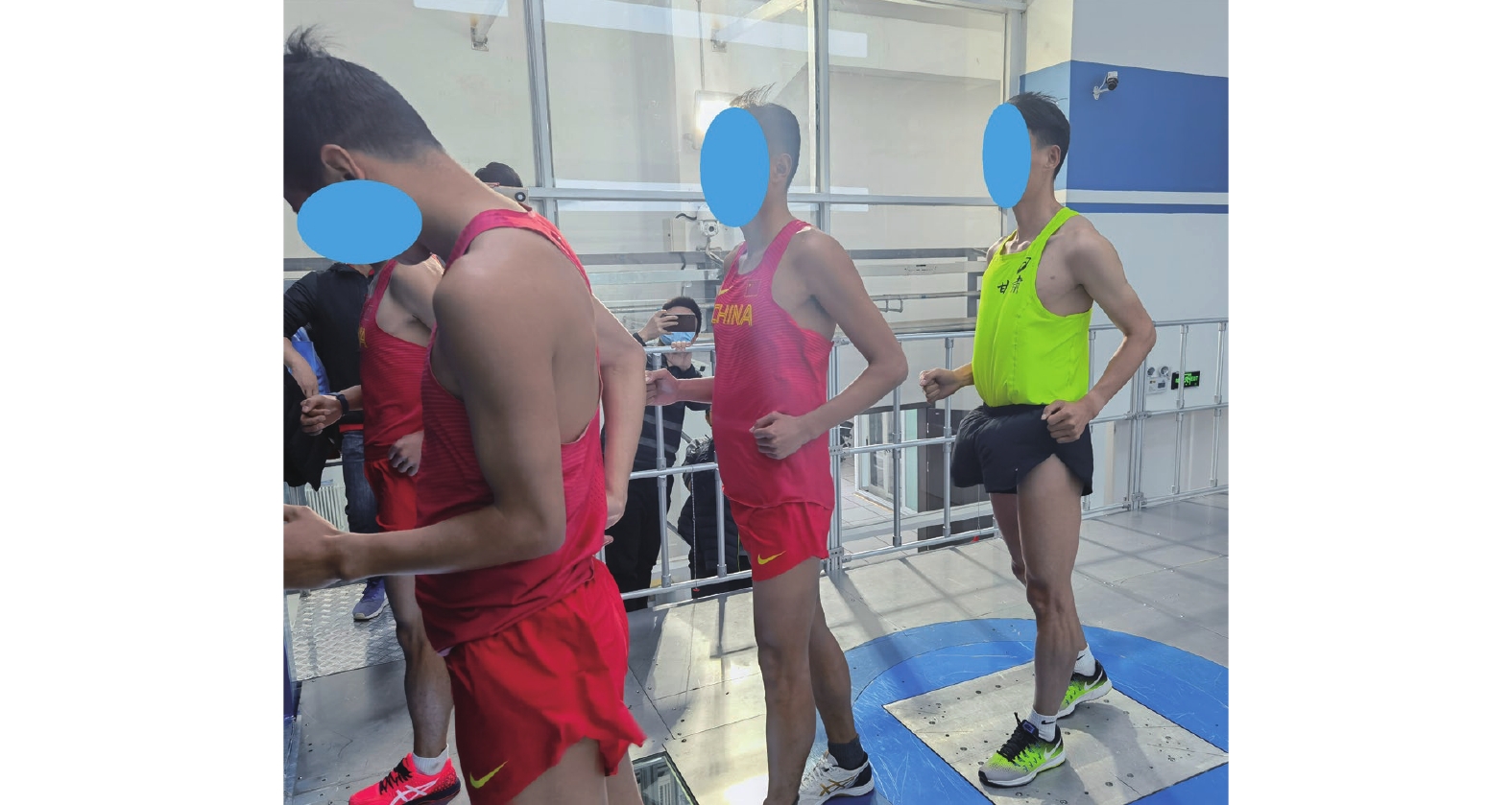
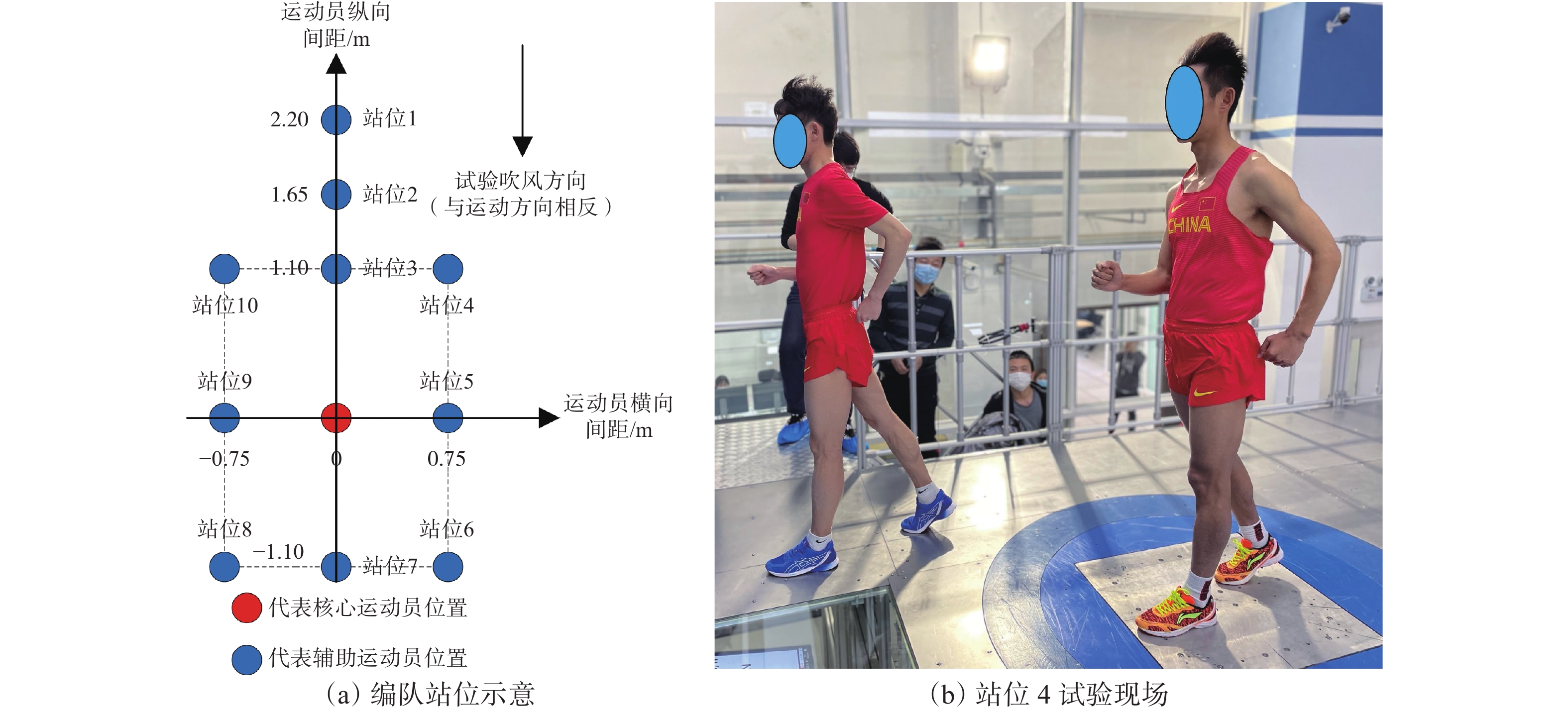
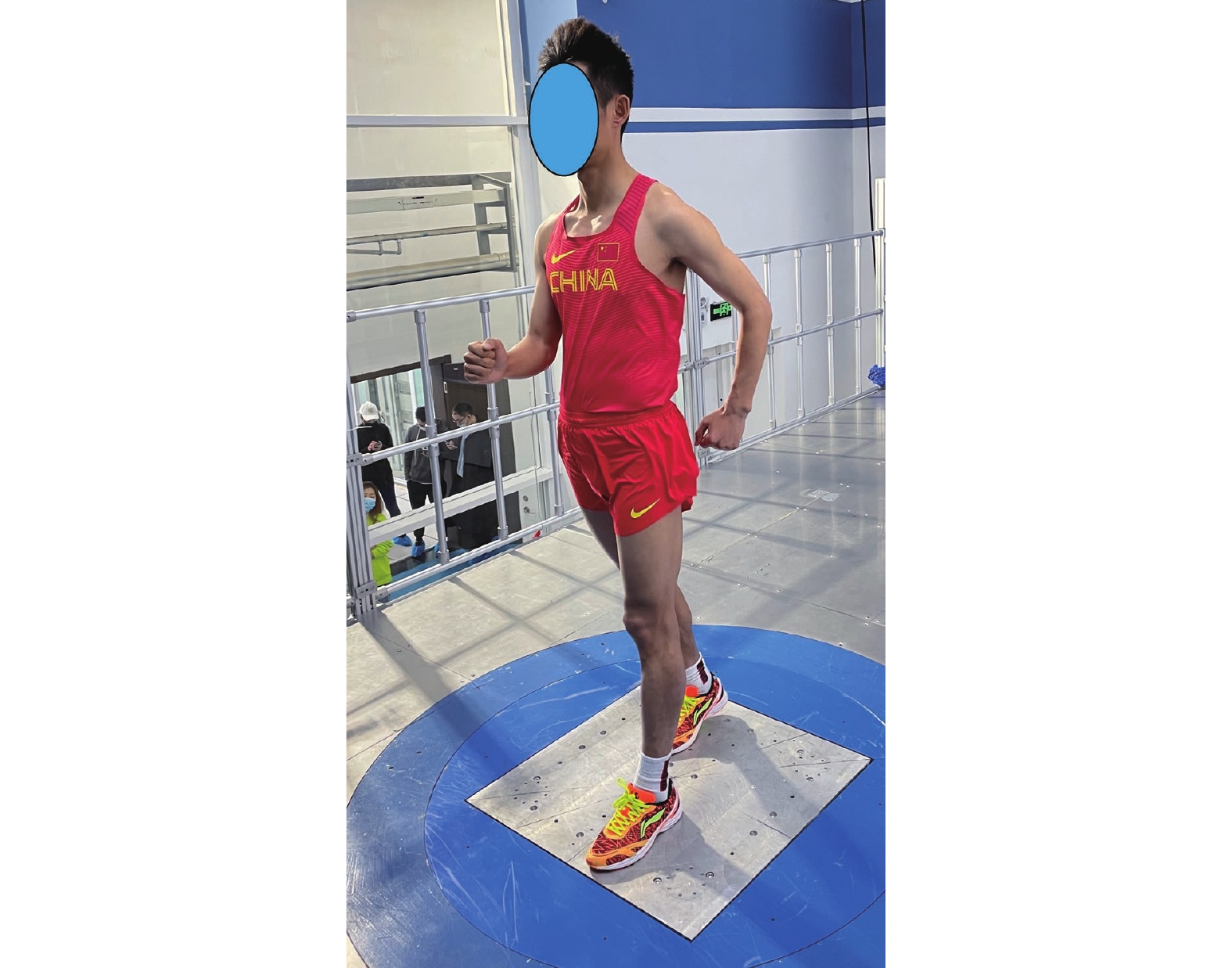
研究对象为国家队竞走运动员:男子50 km竞走项目4名、男子20 km竞走项目4名、女子竞走20 km项目4名,共计12名。测试时运动员须保持静态竞走姿势,如图1所示。
1.2 试验风洞
竞走项目编队风洞试验在二七厂国家冰雪运动训练科研基地综合风洞试验室开展。如图2所示,该风洞是一座开口回流式(带驻室)低速风洞,其试验段在驻室内,试验段长8 m,横截面为2.5 m×3.0 m的长方形,试验风速在0~42 m/s范围内无级连续可调,气流的湍流度低于0.75%,气流偏角小于0.75°。该风洞能够模拟各种真实比赛现场运动风环境,拥有陆地训练难以实现的精准风速、精准调节、精准测量等特性,可用于大量竞速类项目辅助训练、运动员动作姿态与编队位置减阻测试、运动器材与服装减阻优化测试、赛场赛道环境风及其对运动员表现的影响研究等领域。
本次风洞试验使用盒式六分量天平进行测力,并通过HBM数据采集系统对测力天平数据、流场参数等信号进行采集与处理。盒式六分量天平具有较高的分辨率、良好的动态响应、较好的固有频率,为KWB6 L668系列六分量天平,其技术参数如表1所示。HBM数据采集系统具备2000 Hz连续采样能力,能实时采集时变(time-variant)的六分量天平数据[26]。
表 1 盒式六分量天平技术参数(精度0.2%)Table 1. Technical parameters of the box-type six-component balance分量 阻力
(Fx)/N升力
(Fy)/N侧向力
(Fz)/N滚转力矩
(Mx)/(N·m)偏航力矩
(My)/(N·m)俯仰力矩
(Mz)/(N·m)量程 ±400 ±2000 ±400 ±500 ±500 ±500 1.3 试验方法
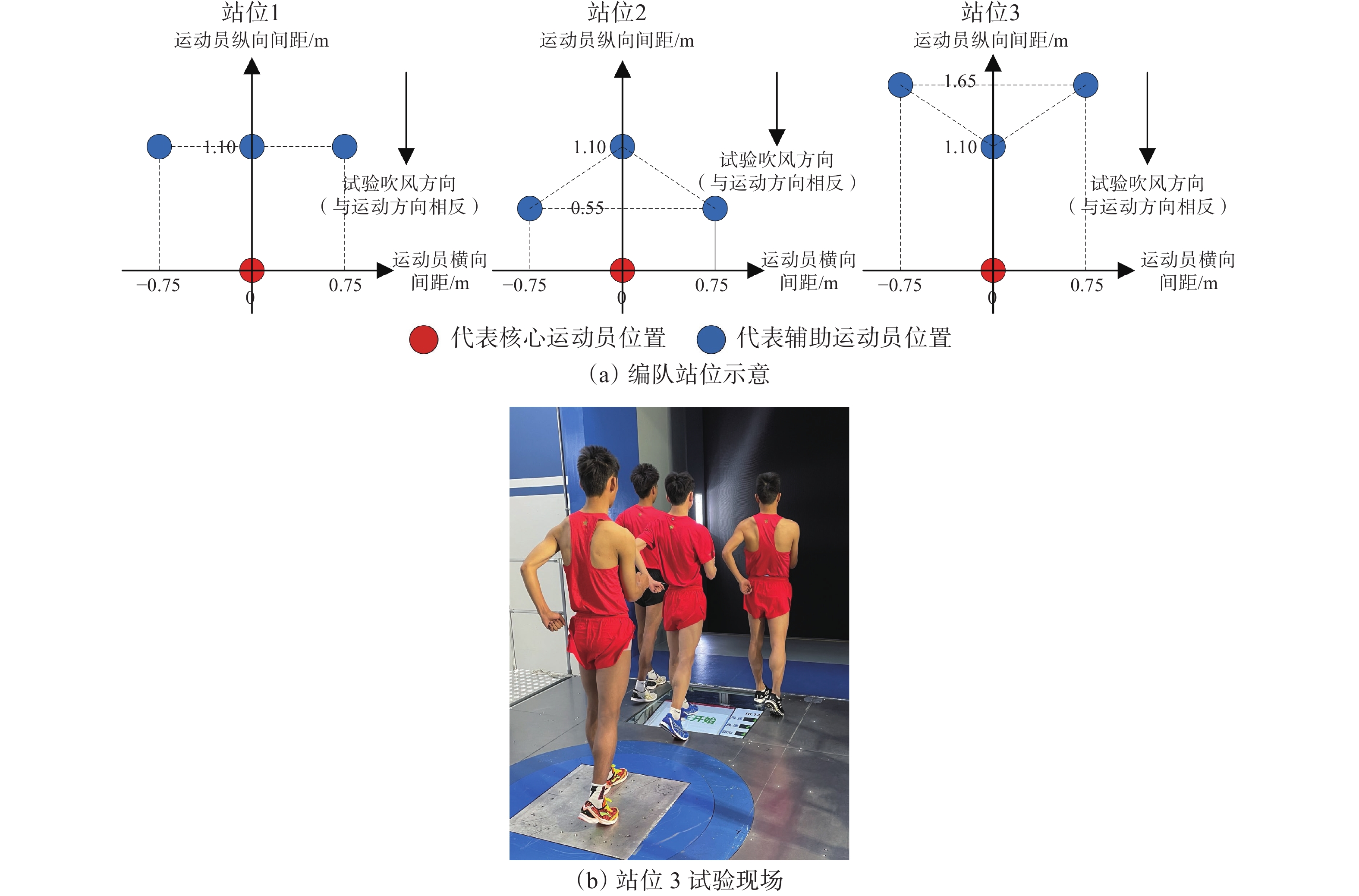
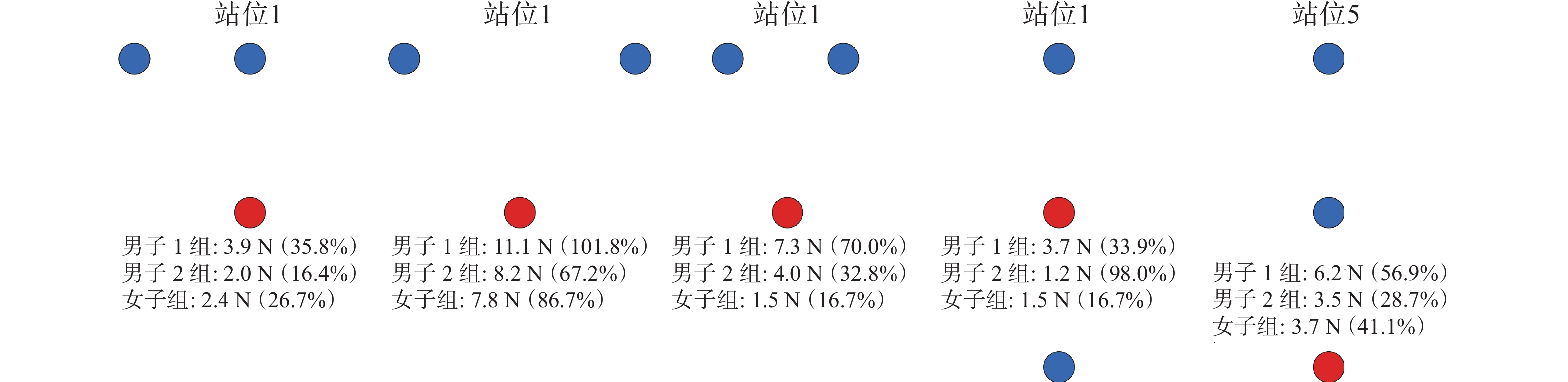
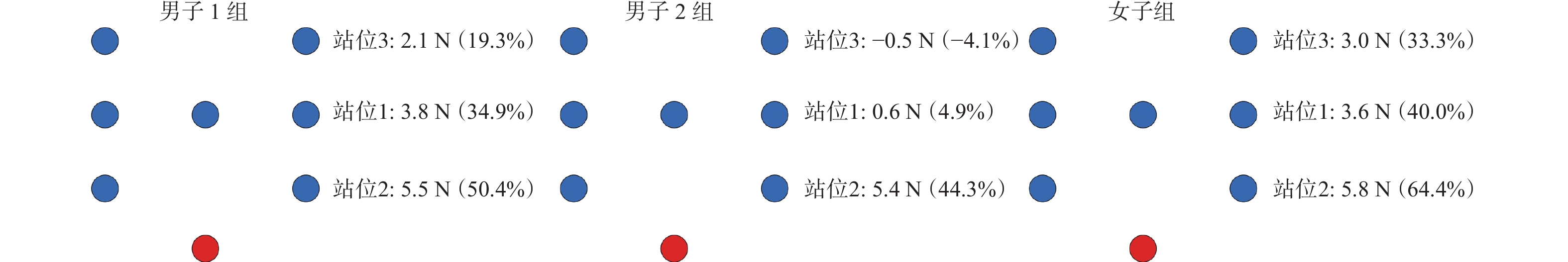
在体育综合训练风洞试验室中通过人工方式产生并控制气流,模拟比赛运动现场运动员所处的流场环境,利用盒式六分量天平通过风洞试验获取不同编队位置核心运动员的气动阻力。选取由不同国家队竞走运动员人数组成的编队来模拟不同竞走场景,包括双人编队、3人编队和4人编队,分别如图3、图4和图5所示。依据参加风洞试验运动员所属运动小项的差异,分成3组,即每种编队类型均包括男子1组、男子2组、女子组。在双人编队测试中,如图3(a)所示,考虑编队站位的对称性,故减少一侧3个站位(站位8、站位9、站位10),每组双人编队测试包括7个站位;如图4(a)所示,每组3人编队测试包括5个站位;如图5(a)所示,每组4人编队测试包括3个站位。测试风速选取竞走项目中的典型速度6 m/s,即无环境风下竞走速度4 m/s与逆风风速2 m/s的叠加,且在每种编队站位测试时,核心运动员以静态竞走姿势站立在盒式六分量天平转接板上,采样频率为2000 Hz,采样时间为15 s,通过天平测力得到核心运动员所受到的风载荷,进而得到不同编队位置中核心运动员的气动阻力。
2. 结 果
核心运动员在单人状态与不同编队站位状态下气动阻力的测试结果如图6~图8所示;核心运动员在不同编队站位状态下气动减阻率结果如图9~图11所示。
2.1 双人编队
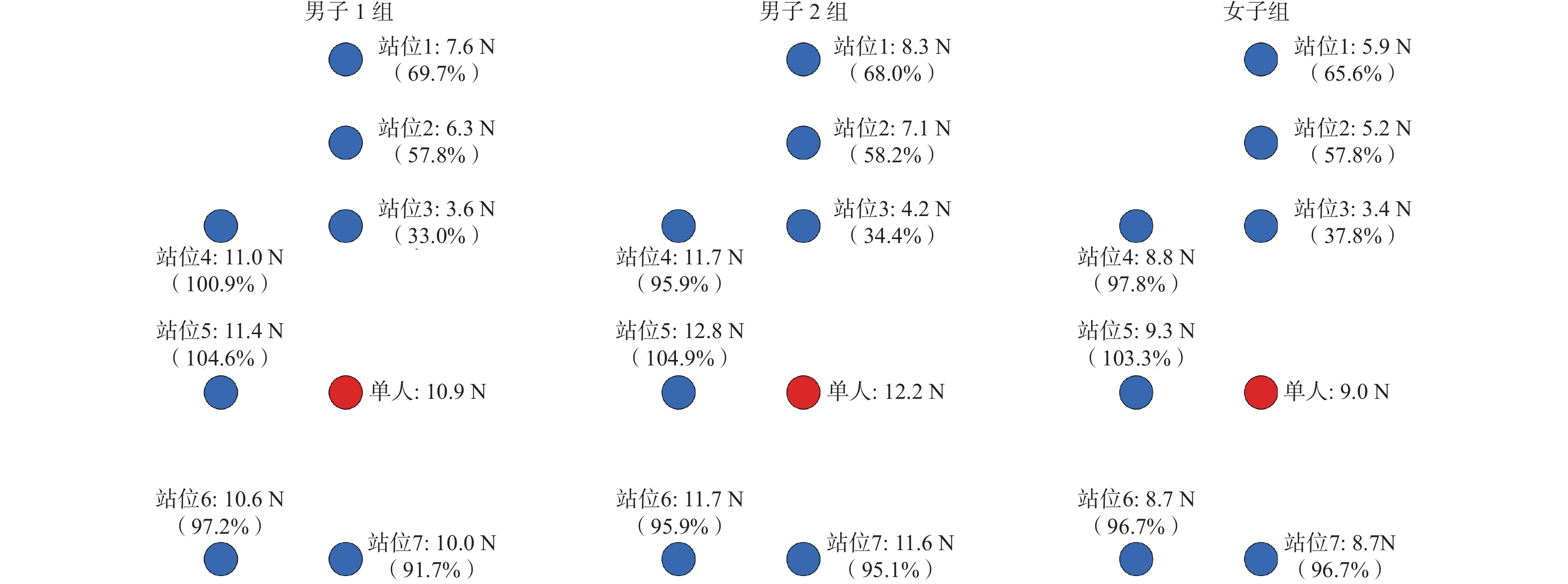
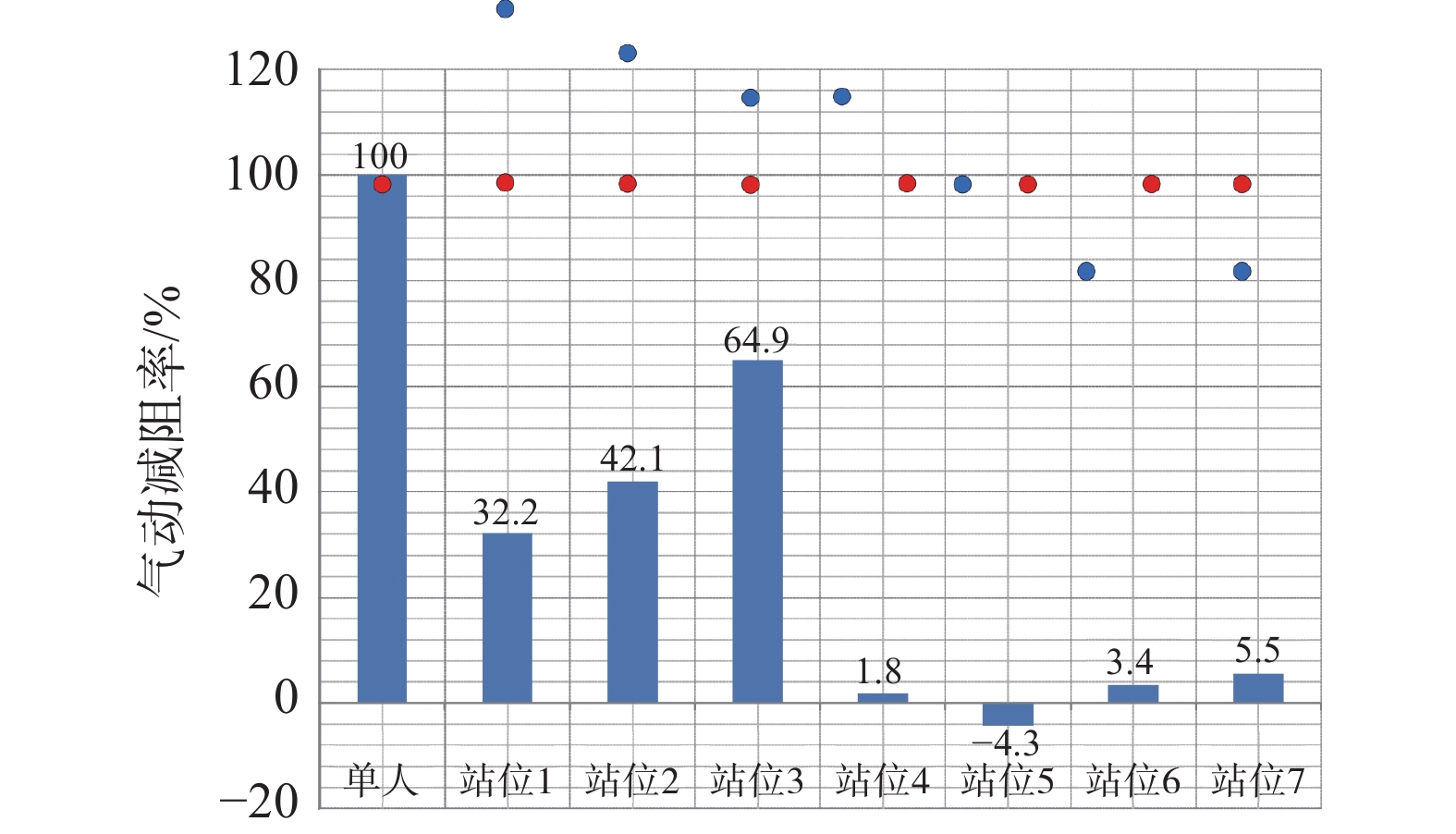
如图6所示,与单人竞走相比,在双人编队中,除辅助运动员与核心运动员并排的编队站位外,不同站位核心运动员的气动阻力均有不同程度的减小。男子组核心运动员的气动阻力普遍高于女子组,但男子组核心运动员在编队站位状态下与单人状态下气动阻力的比值百分比普遍低于女子组。如图9所示,与单人竞走相比,核心运动员位于辅助运动员的正后方且距离最近时气动阻力减小效果最明显,减阻率可达64.9%,但当核心运动员与辅助运动员完全并排时,核心运动员的气动阻力有所增大,增阻率可达4.3%。当辅助运动员位于核心运动员正前方时,辅助运动员距离核心运动员越近,核心运动员的气动阻力越小;但当辅助运动员位于核心运动员侧方时,辅助运动员的遮挡效果明显低于正前方,当辅助运动员与核心运动员完全并排时,核心运动员的气动阻力反而略有增大。此外,当辅助运动员位于核心运动员正后方或侧后方时,核心运动员的气动阻力仍有小幅减小。
2.2 3人编队
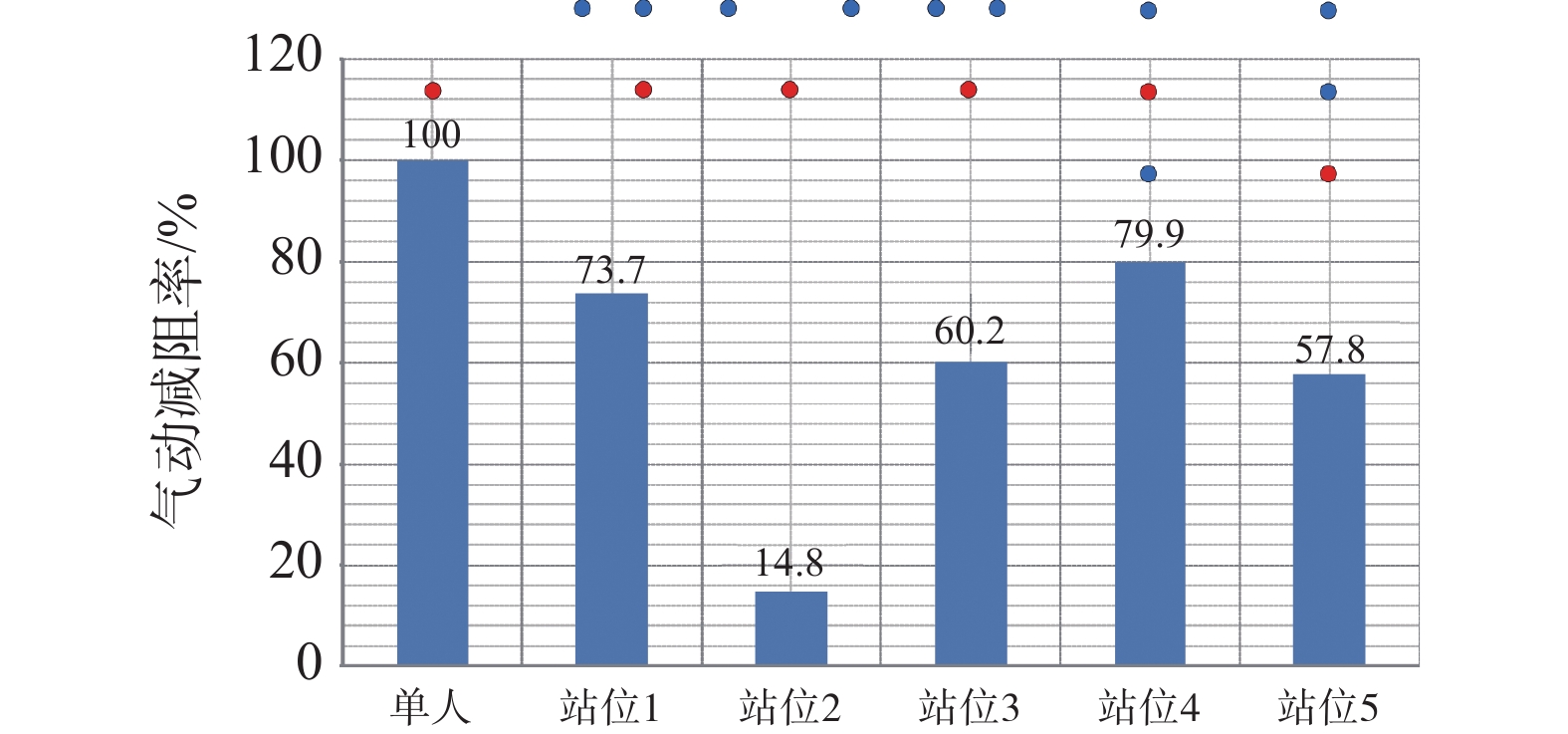
如图7所示,与单人竞走相比,在3人编队中除男子1组站位2外,不同站位核心运动员的气动阻力均有不同程度的减小。男子组中核心运动员的气动阻力普遍高于女子组,且男子2组中核心运动员编队站位状态下与单人状态下气动阻力的比值百分比普遍低于男子1组与女子组。如图10所示,与单人竞走相比,核心运动员位于2名辅助运动员前后连线的中间时气动阻力减小效果最为明显,减阻率可达79.9%,但当核心运动员位于前面2名完全并排辅助运动员的中轴线后方时,核心运动员的气动阻力减小效果有所减弱;且当前面2名辅助运动员并排间距增大时,辅助运动员的遮挡效果明显降低,进而核心运动员的气动阻力减小效果也随之减弱,故在3人编队的站位2中,核心运动员气动阻力的减阻率仅为14.8%。此外,与双人编队的站位3相比,3人编队中站位1(在原有双人编队站位基础上增加1名辅助运动员,且与原有辅助运动员并排)的核心运动员气动减阻率有所增加,从64.9%增加至73.7%,但3人编队中站位5(在原有双人编队站位基础上增加1名辅助运动员,且位于原有辅助运动员正前方)的核心运动员气动减阻率有所减小,从64.9%减小至57.8%。
2.3 4人编队
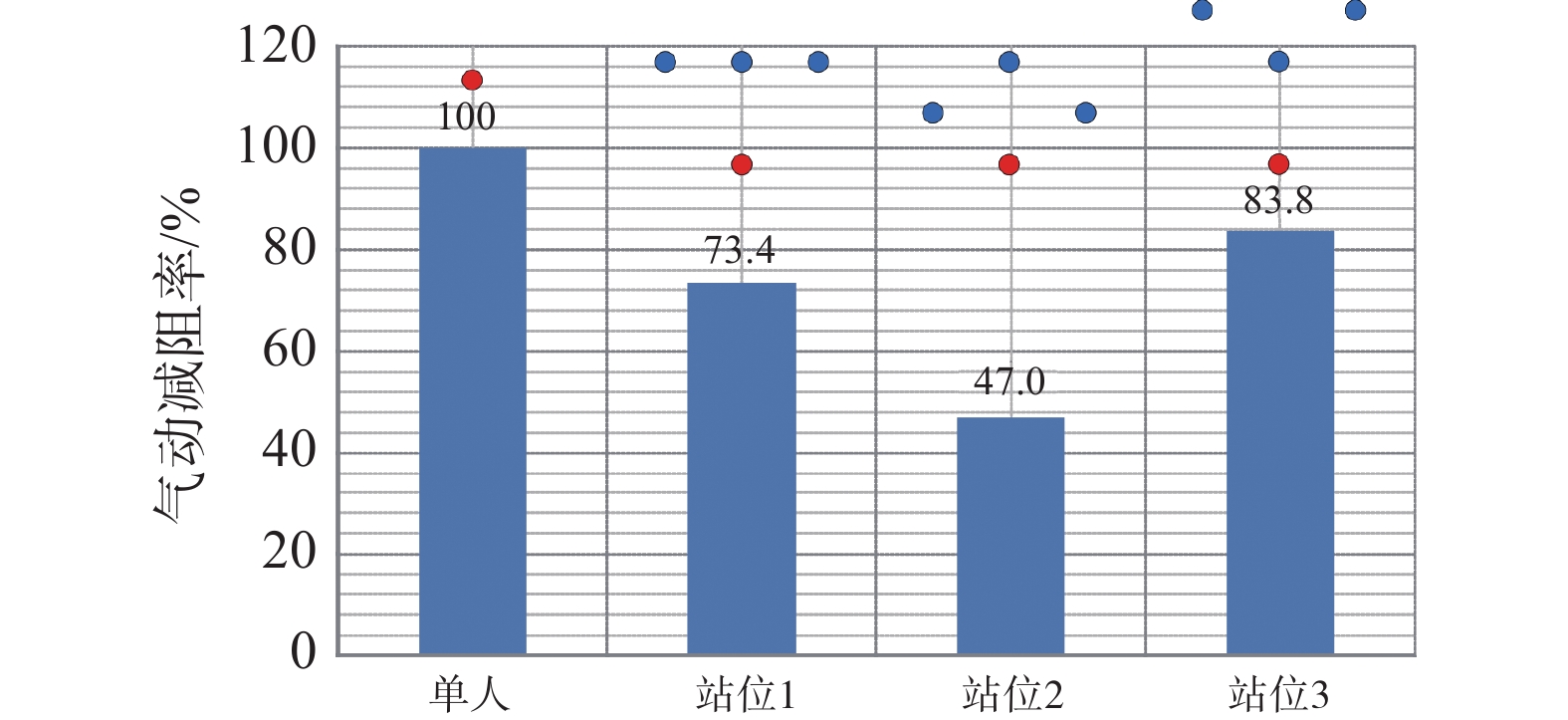
如图8所示,与单人竞走相比,在4人编队中不同站位核心运动员的气动阻力均有不同程度的减小,且男子2组站位3中核心运动员的气动阻力消失并产生向前的推力。男子2组中核心运动员的气动阻力普遍低于男子1组与女子组,且男子2组中核心运动员编队站位状态下与单人状态下气动阻力的比值百分比也普遍低于男子1组与女子组。如图11所示,与单人竞走相比,核心运动员位于3名辅助运动员组成的V型编队的正后方时气动阻力减小效果最为明显,减阻率可达83.8%,但随着位于V型编队两翼的辅助运动员向后移动时,核心运动员的气动阻力减小效果有所减弱,当核心运动员位于3名辅助运动员组成的倒V型编队的正后方时气动阻力减小效果明显降低,减阻率仅为47.0%。此外,与双人编队中站位3相比,4人编队中站位1(在原有双人编队站位3基础上增加2名并排辅助运动员,且与原有辅助运动员完全并排)的核心运动员气动减阻率有所增加,从64.9%增加至73.4%,4人编队中站位3(在原有双人编队站位3基础上增加2名并排辅助运动员,且位于原有辅助运动员前方)的核心运动员气动减阻率增大较为明显,从64.9%增加至83.8%,但4人编队中站位2(在原有双人编队站位基础上增加2名并排辅助运动员,且位于原有辅助运动员与核心运动员之间)的核心运动员气动减阻率减小较为明显,从64.9%减小至47.0%。
3. 讨 论
Schickhofer等[25]针对女子马拉松项目不同编队气动减阻效应进行了数值计算研究,编队中每2名运动员重心的左右横向间距为0.7 m,前后纵向间距为1.2 m,与本文编队站位工况基本一致。Schickhofer等[25]的研究结果表明,3人编队站位4下核心运动员减阻率为75.6%,双人编队站位3下核心运动员减阻率为70.1%,3人编队站位3下核心运动员减阻率为41.3%,4人编队站位2下核心运动员减阻率为33.4%;本文结果表明,3人编队站位4下核心运动员减阻率为79.9%,双人编队站位3下核心运动员减阻率为64.9%,3人编队站位3下核心运动员减阻率为60.2%,4人编队站位2下核心运动员减阻率为47.0%。不难发现,这2项研究结果中核心运动员减阻率随站位变化趋势是一致的,但具体数值不一致,这可能是由运动员身型以及动作姿态的差异造成的。
男子2组核心运动员的编队气动减阻效应相较于男子1组和女子组更为明显(图6~图8),这可能是由运动员身型差异造成的,在编队站位时身型高大的运动员能够为后面运动员提供更多的遮挡,从而更有利于减小气动阻力。经对照运动员的身型特征,男子2组中辅助运动员的身型普遍更为高大一些,这与男子2组核心运动员的编队气动减阻效应结果相符。此外,4人编队站位3中男子2组核心运动员气动阻力消失并受到较小且与风向相反的推力(图8),同时如图12所示,核心运动员所在区域产生向前的气流,运动员服装被往前拽的现象非常明显。此结果与上述Li等[1]和Alam等[2]的数值模拟研究结果一致。Li等[1]和Alam等[2]数值模拟探讨分析了双圆柱周围空气动力学行为及两者之间的相互影响效果,结果表明,2个圆柱体编队方向跟风向一致时气动减阻效果更好,且编队间距在允许范围内,距离越近气动减阻效果越好。同时,当2个圆柱体之间距离比较近时,后面圆柱体位于前面圆柱体尾流负压区,此时后面圆柱体气动阻力消失,并产生一定的气动推力或反向拽力。更进一步分析,可能正是因为男子2组中辅助运动员的身型普遍更为高大一些,所以其他3名辅助运动员组成的V型编队后方的尾流负压区更大一些,核心运动员正好位于或部分位于尾流负压区,从而出现核心运动员的气动阻力为负数的结果。
在制定团队协作编队策略时,可首选双人编队中站位3即核心运动员位于辅助运动员的正后方、3人编队站位4即核心运动员位于其他2名辅助运动员沿着运动方向连线的中间、4人编队中站位3即核心运动员位于其他3名辅助运动员组成的V型编队的正后方这3种相对最佳编队,并且在不影响正常竞走比赛的前提下,前后距离越小,减阻效果越好,越节省能量。总体而言,可多尝试几种典型易控制成形的有利编队策略,同时结合实战,针对不同运动员组成的编队,如高、矮、胖、瘦等不同身型进行训练配合演练。此外,双人编队站位5中核心运动员气动阻力不仅未减小,反而有所增加,这说明当2名运动员并排时对2名运动员都不利,均需消耗更多的能量来抵抗气动阻力。这也为教练团队针对不同竞争对手提供了一种有效的进攻型编队策略。
竞走项目属于田径类长距离运动项目,具有速度低、距离长、运动员身体容易达到生理极限、高水平运动员成绩接近等特点。依据基本运动学方程以及机械功率输出的经验数学模型,可获取运动员抵抗阻力消耗的空气动力功率[21,24-25,27]。对于50 km竞走项目而言,空气动力功率约占能量消耗总功率的6%,即当运动员的气动阻力减小1%时,能量消耗总功率减小0.06%,运动成绩相应地约提升0.06%。与核心运动员单人竞走运动成绩相比:若采用核心运动员位于辅助运动员正后方的相对最佳双人编队,核心运动员的运动成绩将提升约3.89%;若采用核心运动员位于其他2名辅助运动员沿着运动方向连线的中间的相对最佳3人编队,核心运动员的运动成绩将提升约4.79%;若采用核心运动员位于其他3名辅助运动员组成的V型编队正后方的相对最佳4人编队,核心运动员的运动成绩将提升约5.03%。以2019年多哈田径世界锦标赛男子50 km竞走项目比赛结果(表2)为例,前6名运动员成绩相差不到4 min,前10名运动员成绩相差不到10 min。同时,以此次田径世界锦标赛前10名运动员的成绩为基准,分析编队气动减阻效应对运动成绩的影响。从表2可以看出,若排名第4运动员想夺冠,则其编队气动减阻率仅达到8.60%即可,若排名第10运动员想夺冠,则其编队气动减阻率须达到63.01%。
表 2 编队气动减阻效应对运动成绩的影响Table 2. Influence of aerodynamic drag reduction effect of drafting formation on sport performance排名 运动成绩/(h:min:s) 与冠军成绩的差距/(h:min:s) 若夺冠成绩须提升百分比/% 若夺冠编队减阻率应达到值/% 1 4:04:20(14660 s) 0 0 0 2 4:04:59(14699 s) 0:00:39(39 s) 0.27 4.42 3 4:05:02(14703 s) 0:00:42(42 s) 0.29 4.76 4 4:05:36(14736 s) 0:01:16(76 s) 0.52 8.60 5 4:06:49(14809 s) 0:02:29(149 s) 1.01 16.77 6 4:07:46(14866 s) 0:03:26(206 s) 1.39 23.10 7 4:10:22(15022 s) 0:06:02(362 s) 2.41 40.16 8 4:11:28(15088 s) 0:07:08(428 s) 2.84 47.28 9 4:12:28(15148 s) 0:08:08(488 s) 3.22 53.69 10 4:13:56(15236 s) 0:09:36(576 s) 3.78 63.01 4. 结 论
与单人竞走相比,双人编队中核心运动员位于辅助运动员的正后方时、3人编队中核心运动员位于其他2名辅助运动员沿着运动方向连线的中间时、4人编队中核心运动员位于其他3名辅助运动员组成的V型编队的正后方时气动阻力减小最为明显,为相对最佳编队。在50 km竞走比赛中,与单人竞走成绩相比:若采用相对最佳双人编队,比赛成绩将至少提升约3.89%;若采用相对最佳3人编队,比赛成绩将至少提升约4.79%;若采用相对最佳4人编队,比赛成绩将至少提升约5.03%。因此,不同编队站位下竞走核心运动员的气动减阻效应存在一定差异,研究不同编队的气动减阻效应能为减小核心运动员空气阻力、优化能量分配、改进团队协作策略、提高运动成绩提供重要的科学指导。
致谢:感谢中国田径协会、竞走国家队与英陶国际体育赛事管理(北京)有限公司对此次风洞试验的大力支持与积极配合。
胡齐:提出论文主题,设计论文框架,撰写论文;李波:提供技术参考,处理数据;沈梦:核实数据,修改论文;洪平:提出论文主题,指导修改论文。 -
表 1 盒式六分量天平技术参数(精度0.2%)
Table 1 Technical parameters of the box-type six-component balance
分量 阻力
(Fx)/N升力
(Fy)/N侧向力
(Fz)/N滚转力矩
(Mx)/(N·m)偏航力矩
(My)/(N·m)俯仰力矩
(Mz)/(N·m)量程 ±400 ±2000 ±400 ±500 ±500 ±500 表 2 编队气动减阻效应对运动成绩的影响
Table 2 Influence of aerodynamic drag reduction effect of drafting formation on sport performance
排名 运动成绩/(h:min:s) 与冠军成绩的差距/(h:min:s) 若夺冠成绩须提升百分比/% 若夺冠编队减阻率应达到值/% 1 4:04:20(14660 s) 0 0 0 2 4:04:59(14699 s) 0:00:39(39 s) 0.27 4.42 3 4:05:02(14703 s) 0:00:42(42 s) 0.29 4.76 4 4:05:36(14736 s) 0:01:16(76 s) 0.52 8.60 5 4:06:49(14809 s) 0:02:29(149 s) 1.01 16.77 6 4:07:46(14866 s) 0:03:26(206 s) 1.39 23.10 7 4:10:22(15022 s) 0:06:02(362 s) 2.41 40.16 8 4:11:28(15088 s) 0:07:08(428 s) 2.84 47.28 9 4:12:28(15148 s) 0:08:08(488 s) 3.22 53.69 10 4:13:56(15236 s) 0:09:36(576 s) 3.78 63.01 -
[1] LI T,ISHIHARA T. Numerical study on wake galloping of tandem circular cylinders considering the effects of mass and spacing ratios[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,2021,210:104536 doi: 10.1016/j.jweia.2021.104536
[2] ALAM M M, MEYER J P. Fluid dynamics around twin cylinders and interactions[C]. 8th International Conference on Heat Transfer, Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics HEFAT 2011, July 11-13, Pointe Aux Piments, Mauritius. 2011: 635-649
[3] BELLOLI M,GIAPPINO S,ROBUSTELLI F,et al. Drafting effect in cycling:Investigation by wind tunnel tests[J]. Procedia Engineering,2016,147:38-43 doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2016.06.186
[4] EDWARDS A G,BYRNES W C. Aerodynamic characteristics as determinants of the drafting effect in cycling[J]. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise,2007,39(1):170-176 doi: 10.1249/01.mss.0000239400.85955.12
[5] BLOCKEN B,TOPARLAR Y,VAN DRUENEN T,et al. Aerodynamic drag in cycling team time trials[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,2018,182:128-145 doi: 10.1016/j.jweia.2018.09.015
[6] BLOCKEN B,MALIZIA F,DRUENEN T,et al. Aerodynamic benefits for a cyclist by drafting behind a motorcycle[J]. Sports Engineering,2020,23(1):1-11 doi: 10.1007/s12283-019-0315-4
[7] MALIZIA F,BLOCKEN B. Bicycle aerodynamics:History,state-of-the-art and future perspectives[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,2020,200:104134 doi: 10.1016/j.jweia.2020.104134
[8] FITTON B,CADDY O,SYMONS D. The impact of relative athlete characteristics on the drag reductions caused by drafting when cycling in a velodrome[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers,Part P:Journal of Sports Engineering and Technology,2018,232(1):39-49 doi: 10.1177/1754337117692280
[9] BLOCKEN B,DEFRAEYE T,KONINCKX E,et al. CFD simulations of the aerodynamic drag of two drafting cyclists[J]. Computers & Fluids,2013,71:435-445
[10] BASSETT D R,FLOHR J,DUEY W J,et al. Metabolic responses to drafting during front crawl swimming[J]. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise,1991,23(6):744-747
[11] BRISSWALTER J,HAUSSWIRTH C. Consequences of drafting on human locomotion:Benefits on sports performance[J]. International Journal of Sports Physiology and Performance,2008,3(1):3-15 doi: 10.1123/ijspp.3.1.3
[12] VAN INGEN SCHENAU G J. The influence of air friction in speed skating[J]. Journal of Biomechanics,1982,15(6):449-458 doi: 10.1016/0021-9290(82)90081-1
[13] RUNDELL K W. Effects of drafting during short-track speed skating[J]. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise,1996,28(6):765-771 doi: 10.1097/00005768-199606000-00016
[14] MILLET G P,GESLAN R,FERRIER R,et al. Effects of drafting on energy expenditure in in-line skating[J]. The Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness,2003,43(3):285-290
[15] BILODEAU B,ROY B,BOULAY M R. Effect of drafting on heart rate in cross-country skiing[J]. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise,1994,26(5):637-641
[16] BILODEAU B,ROY B,BOULAY M R. Effect of drafting on work intensity in classical cross-country skiing[J]. International Journal of Sports Medicine,1995,16(3):190-195 doi: 10.1055/s-2007-972990
[17] SILVA A J,ROUBOA A,MOREIRA A,et al. Analysis of drafting effects in swimming using computational fluid dynamics[J]. Journal of Sports Science & Medicine,2008,7(1):60-66
[18] ZOUHAL H,BEN ABDERRAHMAN A,PRIOUX J,et al. Drafting's improvement of 3000-m running performance in elite athletes:Is it a placebo effect?[J]. International Journal of Sports Physiology and Performance,2015,10(2):147-152 doi: 10.1123/ijspp.2013-0498
[19] HAUSSWIRTH C,VALLIER J M,LEHENAFF D,et al. Effect of two drafting modalities in cycling on running performance[J]. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise,2001,33(3):485-492 doi: 10.1097/00005768-200103000-00023
[20] RENFREE A,CRIVOI CARMO E,MARTIN L,et al. The influence of collective behavior on pacing in endurance competitions[J]. Frontiers in Physiology,2015,6:373
[21] KYLE C R. Reduction of wind resistance and power output of racing cyclists and runners travelling in groups[J]. Ergonomics,1979,22(4):387-397 doi: 10.1080/00140137908924623
[22] BARRY N,BURTON D,SHERIDAN J,et al. Aerodynamic drag interactions between cyclists in a team pursuit[J]. Sports Engineering,2015,18(2):93-103 doi: 10.1007/s12283-015-0172-8
[23] BEAUMONT F,BOGARD F,MURER S,et al. How does aerodynamics influence physiological responses in middle-distance running drafting?[J]. Mathematical Modelling of Engineering Problems,2019,6(1):129-135 doi: 10.18280/mmep.060117
[24] POLIDORI G,LEGRAND F,BOGARD F,et al. Numerical investigation of the impact of Kenenisa Bekele's cooperative drafting strategy on its running power during the 2019 Berlin marathon[J]. Journal of Biomechanics,2020,107:109854 doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2020.109854
[25] SCHICKHOFER L,HANSON H. Aerodynamic effects and performance improvements of running in drafting formations[J]. Journal of Biomechanics,2021,122:110457 doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2021.110457
[26] 蔺世杰,郑伟涛,马勇.基于风洞试验的奥运会RS:X级帆板摇帆推进特性研究[J]. 体育科学,2021,41(3):74-83 [27] CAVAGNA G A,KANEKO M. Mechanical work and efficiency in level walking and running[J]. Marine Policy,1977,268(2):467-481 doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011866
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 泥凯旋,郑贺. 我国女子20km竞走运动员东京奥运会竞技实力解析. 中国体育教练员. 2023(02): 39-41 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 胡齐,刘宇. 冬季运动项目气动减阻的风洞实验研究进展. 体育科学. 2022(12): 55-67 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载: